Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
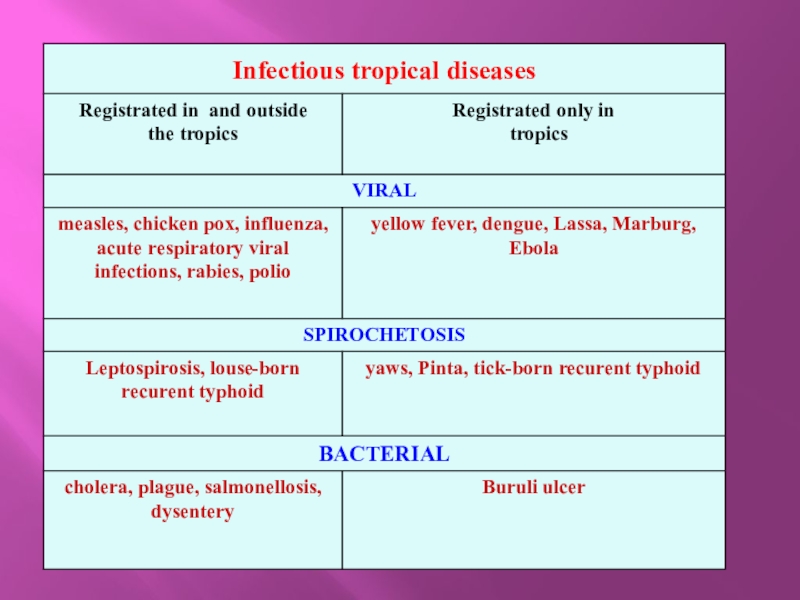
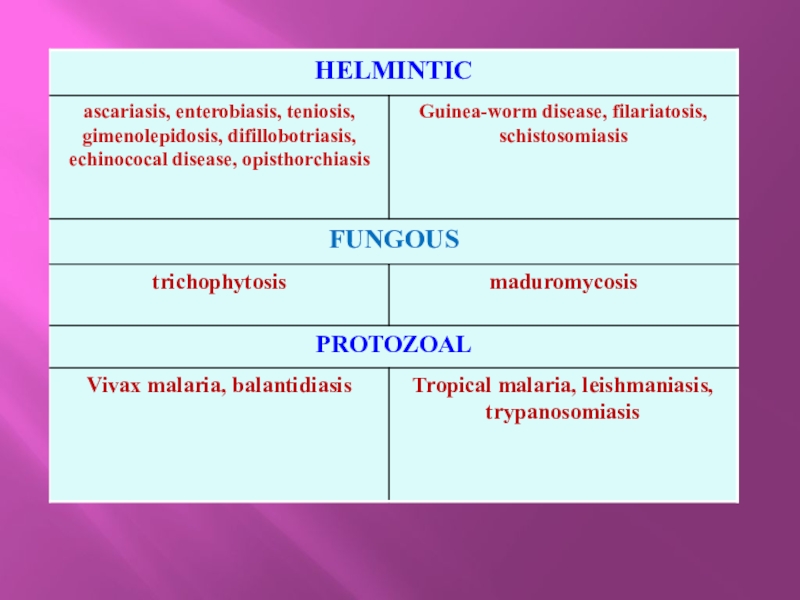
Features of pathology of the tropics. Classification of tropical
Содержание
- 1. Features of pathology of the tropics. Classification of tropical
- 2. TROPICAL MEDICINE - part of medical science,
- 3. TROPICS -part of the earth's surface, located
- 4. EQUATORIAL AREA: constantly high temperature (24
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. SUBEQUATORIAL ZONE:constant high air temperature (22 -
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. TROPICAL AREA: temperature in winter not below
- 9. SUBTROPICAL AREA: alternation of moderate (in winter)
- 10. FEATURES OF TROPICAL CLIMATE:- High sums of
- 11. The FEATURES of tropical pathology depend on environment conditions and social factors
- 12. FACTORS OF THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT: TEMPERATUREDIRECT INFLUENCE:Violation
- 13. INDIRECT INFLUENCE: 1. Wide distribution of numerous kinds of insects (including bloodsucking)SimuliumPhlebotomusAnopheles
- 14. 2. A hot climate assists the height of different types of plants and animals
- 15. 3. Favourable conditions for existence of heat-loving
- 16. WaterReproduction of causative agents and preservation of
- 17. The role of water increases on next
- 18. SOILSource of developing helmints - primary cause
- 19. SOCIAL - ECONOMIC FACTORSLow level of sanitary
- 20. 5. Occupation of the population Leptospirosis and
- 21. 6. Lifestyle, dietary habits, superstitions and customs
- 22. There are ubiquitous and proper tropical (millions
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Peculiarity of the course of the tropical
- 26. 7. Severe course of the disease (meningococcal
- 27. Features the work of doctor in the
- 28. The most important diseases of the tropics(according to WHO)malariafilariatosisleishmaniasisleprosy schistosomiasis trypanosomiasis
- 29. MEASURES OF HEALTH PROTECTION IN THE TROPICSBefore
- 30. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2TROPICAL MEDICINE -
part of medical science, studying the questions
of theory and practice of
health protection in tropical countries
PROBLEMS:
1. Development
of studies about tropical illness2. Questions of hygiene of tropics
3. Оrganization of health саre in the tropics
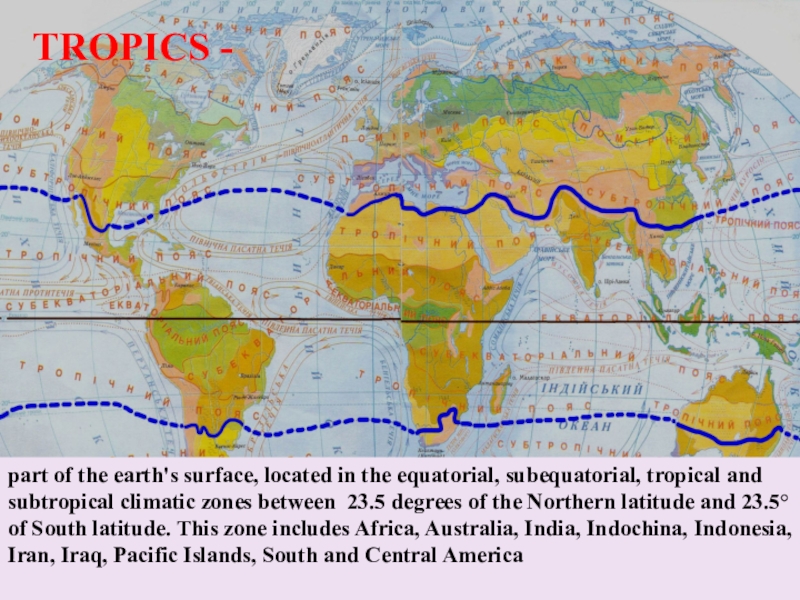
Слайд 3TROPICS -
part of the earth's surface, located in the equatorial,
subequatorial, tropical and subtropical climatic zones between 23.5 degrees of
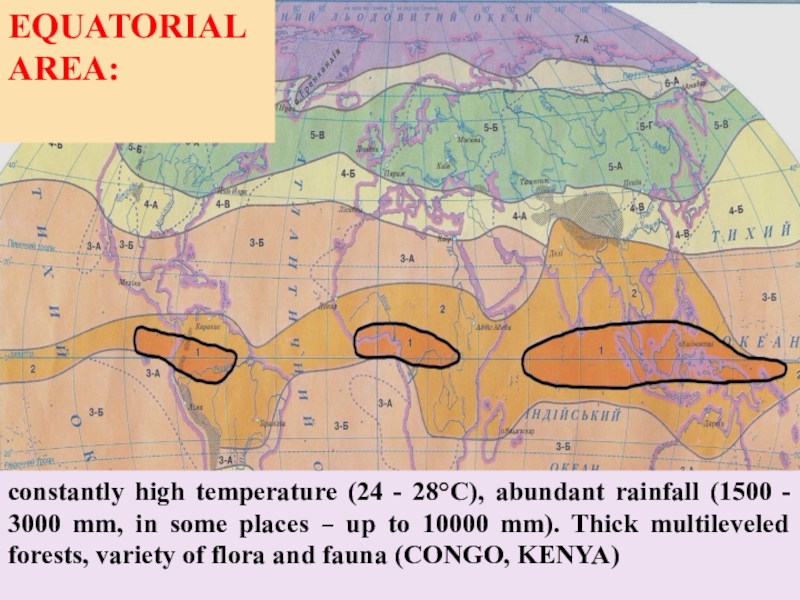
the Northern latitude and 23.5° of South latitude. This zone includes Africa, Australia, India, Indochina, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Pacific Islands, South and Central AmericaСлайд 4EQUATORIAL AREA:
constantly high temperature (24 - 28°С), abundant rainfall
(1500 - 3000 mm, in some places – up to
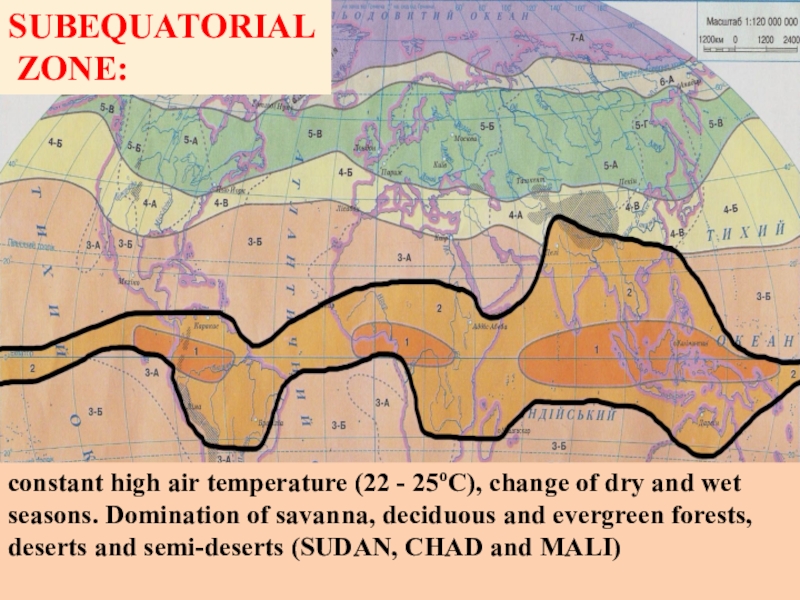
10000 mm). Thick multileveled forests, variety of flora and fauna (CONGO, KENYA)Слайд 6SUBEQUATORIAL
ZONE:
constant high air temperature (22 - 25oC), change of
dry and wet seasons. Domination of savanna, deciduous and evergreen
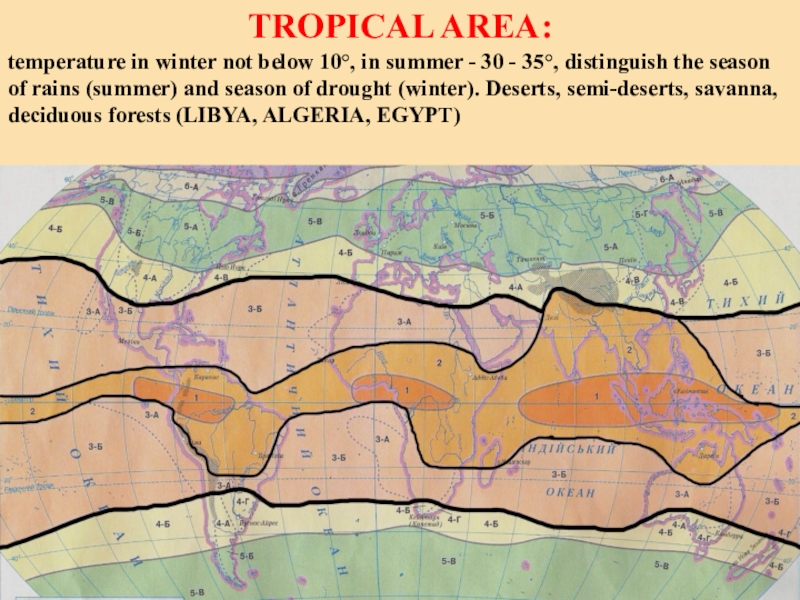
forests, deserts and semi-deserts (SUDAN, CHAD and MALI)Слайд 8TROPICAL AREA:
temperature in winter not below 10°, in summer
- 30 - 35°, distinguish the season of rains (summer)
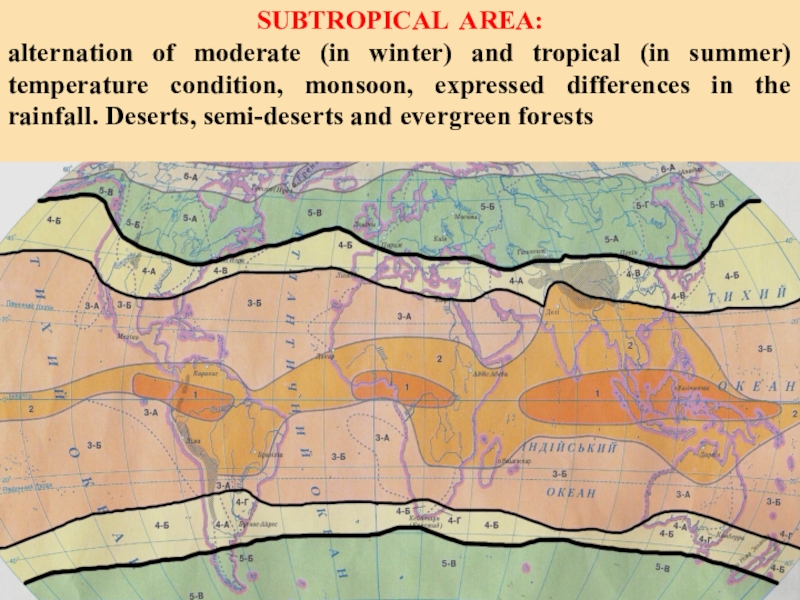
and season of drought (winter). Deserts, semi-deserts, savanna, deciduous forests (LIBYA, ALGERIA, EGYPT)Слайд 9SUBTROPICAL AREA:
alternation of moderate (in winter) and tropical (in
summer) temperature condition, monsoon, expressed differences in the rainfall. Deserts,
semi-deserts and evergreen forestsСлайд 10FEATURES OF TROPICAL CLIMATE:
- High sums of annual heat,
Oscillation of
fallouts in the tropical forests within
3000 - 5000
mm\ year, in deserts - up to 200 mm\ year, - Fluctuation of temperature about 50° in a day,
- There are large temperature drop and freezing in mountains
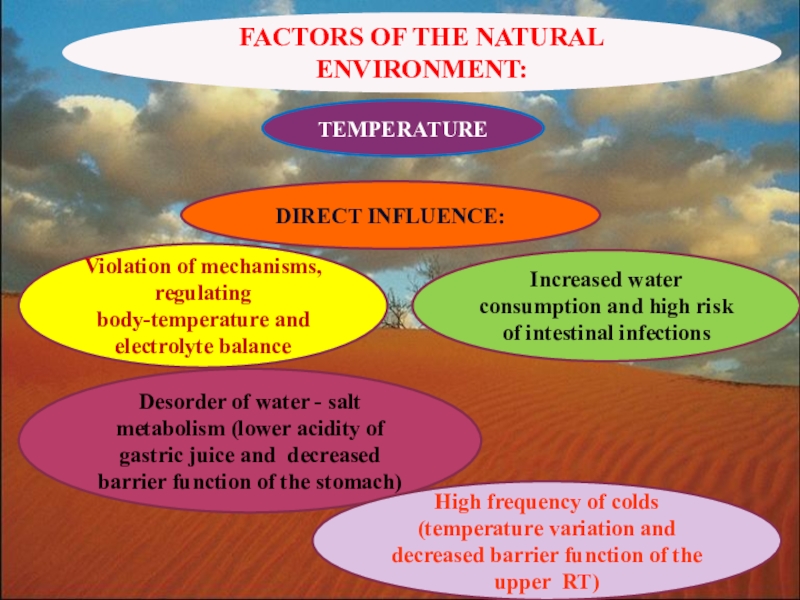
Слайд 12FACTORS OF THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT:
TEMPERATURE
DIRECT INFLUENCE:
Violation of mechanisms, regulating
body-temperature and electrolyte balance
Increased water consumption and high risk of
intestinal infectionsDesorder of water - salt metabolism (lower acidity of gastric juice and decreased barrier function of the stomach)
High frequency of colds (temperature variation and decreased barrier function of the upper RT)
Слайд 13INDIRECT INFLUENCE:
1. Wide distribution of numerous kinds of insects
(including bloodsucking)
Simulium
Phlebotomus
Anopheles
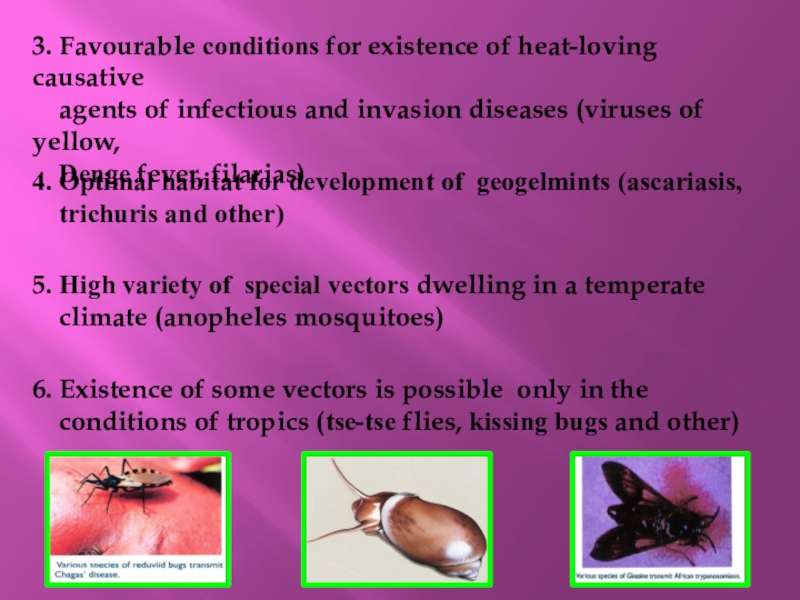
Слайд 153. Favourable conditions for existence of heat-loving causative
agents
of infectious and invasion diseases (viruses of yellow,
Denge
fever, filarias)4. Optimal habitat for development of geogelmints (ascariasis,
trichuris and other)
5. High variety of special vectors dwelling in a temperate
climate (anopheles mosquitoes)
6. Existence of some vectors is possible only in the
conditions of tropics (tse-tse flies, kissing bugs and other)
Слайд 16Water
Reproduction of causative agents and preservation of them in the
water (cholera, typhoid, dysentery, amebiasis, leptospirosis) , shellfishes (schistosomiasis), crawfish
cyclopses (dracunculosis), fishes (opisthorchiasis)2. Development of special vectors - mosquitoes (malaria, filariasis, yellow
and denge fever), midges and other
Слайд 17The role of water increases on next reasons:
Swimming in
opened reservoirs.
Using of reservoirs with a technical
purpose.
3.
Drinking of unboiled water bymajority of population.
4. Use in food of raw water plants (mint,
chestnut, nut, lotus), fish, crustaceas,
shellfishes.
5. Contamination of the rivers, ponds,
wells, soils by microbes and eggs of
helmints in the rain period.
6. Increase of concentration of the
contagious material in reservoirs in
the period of drought.
Слайд 18SOIL
Source of developing helmints - primary cause of disease
agricultural workers
2. Reservoir for multiplication of insects transmitting
infectious illnessesSOLAR RADIATION
1. High frequency of sunburn and skin cancer
2. A radiation assists the sanation of environment
Слайд 19
SOCIAL - ECONOMIC FACTORS
Low level of sanitary culture and illiteracy
of
population (taking of unboiled water is a
reason of 50% of infectious diseases, absence of the sewage system, dirty hands, bad housing terms)High death rate especially among children
High birth-rate - 4-5% in a year.
Insufficient nourishment (is albuminous
starvation, hypovitaminosis and pellagra)
Слайд 20 5. Occupation of the population
Leptospirosis and geohelminthiases more often
registered among the peasants, brucellosis, anthrax, echinococal disease - among
nomads. Loggers and hunters, as a rule, suffer from yellow fever and cutaneous leishmaniasis, plantation workers – from larva migrans.Слайд 216. Lifestyle, dietary habits, superstitions and customs
(presence
of blood in the boys urine in
schistosomiasis is
regarded as evidence of sexualmaturity)
7. Underdeveloped medicine, centralization
of hospitals in cities and their absence in the
villages, the remoteness of villages from each other
impede the provision of medical assistance
(10 000 - 60 000 persons per 1 physician in rural
area)
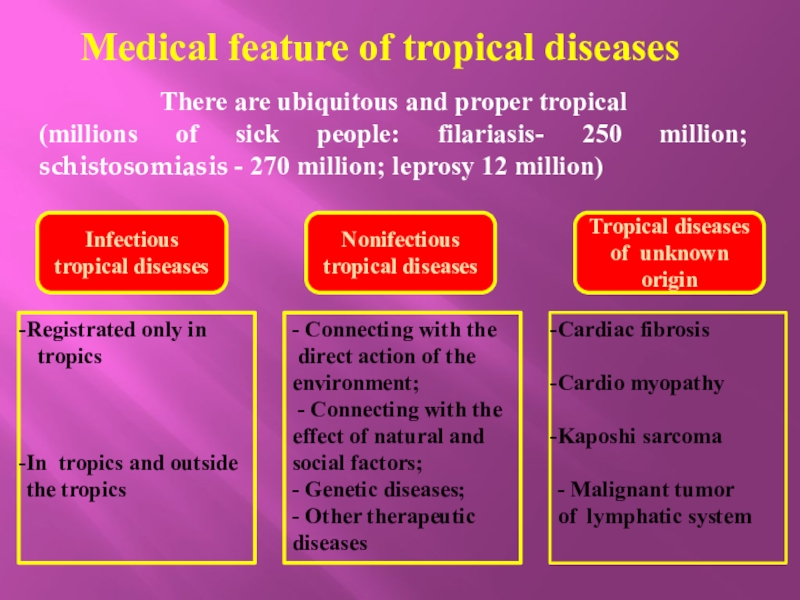
Слайд 22There are ubiquitous and proper tropical
(millions of sick people:
filariasis- 250 million; schistosomiasis - 270 million; leprosy 12 million)
Medical
feature of tropical diseasesInfectious tropical diseases
Nonifectious tropical diseases
Tropical diseases of unknown origin
- Connecting with the
direct action of the environment;
- Connecting with the effect of natural and social factors;
- Genetic diseases;
- Other therapeutic diseases
Cardiac fibrosis
Cardio myopathy
Kaposhi sarcoma
- Malignant tumor
of lymphatic system
Registrated only in
tropics
In tropics and outside
the tropics
Слайд 25Peculiarity of the course of the tropical disease: 1. Unfavorable background
(the deficit of power, hypovitaminosis
and
others).2. Massiveness of the infection. 3. Early age of primary infection. 4. The direct influence of the original
conditions of the environment.
5. Possibility to get several species of
parasites – polyparasitism
(2, 3 and more worms or worm
infections with bacterial infection).
6. Subclinical or obliterated course of
many diseases in the population of
endemic foci due to constant contacts
with pathogenic microorganism
and the development of immunity.
Слайд 267. Severe course of the disease (meningococcal infection, measles, tuberculosis
and other).
8. Chronization of many diseases.
9. Unusual course of some
infections(skin diphtheria –often,
pharyngeal diphtheria - rarely ).
10. Presence of some diseases
prevents contamination of other
diseases (anemia S and C
prevents malaria infection).
11. Combination of some infections
provokes development of tumors
(EBV+malaria provokes Berkit’s
lymphoma).
Слайд 27Features the work of doctor in the tropics
1. In all
cases of unclear fever appoint
antimalarial drugs.
2. In the
treatment of all infectiousdiseases simultaneously appoint
antimalarial drugs.
3. Before a surgical operation appoint antimalarial drugs.
4. Before the surgical operation examine the patient at
helminthiasis and treat him.
5. After reviling a single parasite continue to search of
other pathogens
Слайд 28The most important diseases of the tropics
(according to WHO)
malaria
filariatosis
leishmaniasis
leprosy
schistosomiasis
trypanosomiasis
Слайд 29MEASURES OF HEALTH PROTECTION IN THE TROPICS
Before traveling to tropical
countries is necessary total medical examination
2.Vaccination against typhoid, paratyphoids, tetanus,
polio,yellow fever, cholera, hepatitis A.
3. Follow measures of food hygiene (boiling, chlorination and
filtration of water, thermal processing of vegetables and
fruits).
4. Chemical prophylaxis of malaria and sleeping sickness
(West and Central Africa).
5. Protection from the bites of insects (mechanical
protection, canopies impregnated mosquito
repellents, measures of chemical protection –
the use of insecticides and repellents).