Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
General Characteristics of Old English Grammar
Содержание
- 1. General Characteristics of Old English Grammar
- 2. There were the following parts
- 3. the verbthe adverbthe prepositionthe conjunctionthe interjection
- 4. There were 5 nominal grammatical
- 5. Verbal grammatical categories were not
- 6. The OE Noun OE noun has
- 7. Abstract nouns with suffix –þu
- 8. Nouns with suffix –ere were
- 9. OE wif (wife) was of
- 10. The category of number consisted of
- 11. The category of case had 4 members: Nominative, Genetive, Dative and Accusative.
- 12. System of Declension OE system
- 13. The stem-suffixes could consist of
- 14. The examples of declensional paradigms
- 15. The traces of a-stem declension
- 16. 2. –s (plural of nouns) goes
- 17. The OE Pronoun There were the
- 18. The grammatic categories were either
- 19. The Personal Pronouns The Personal
- 20. Слайд 20
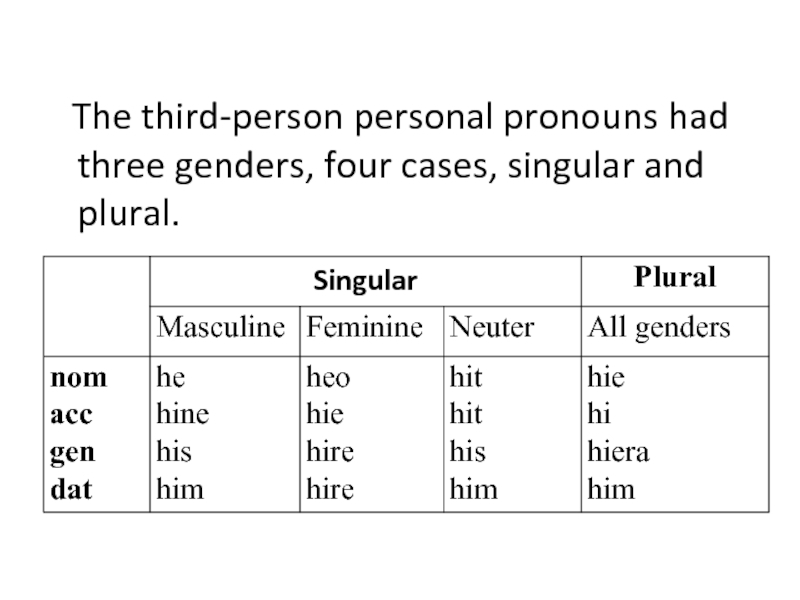
- 21. The third-person personal pronouns had three genders, four cases, singular and plural.
- 22. The oblique cases of personal pronouns + adjective –self could serve as reflexive pronouns.
- 23. Demonstrative Pronouns There were
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Interrogative Pronouns hwā (who)
- 26. Indefinite pronouns Indefinite pronouns were many.ān
- 27. The OE Adjective OE adjectives
- 28. The category of case in
- 29. OE adjectives declined in two
- 30. Some endings in the strong
- 31. The weak declension used the
- 32. Most adjectives could be declined
- 33. The adjective had a strong
- 34. The weak form was employed
- 35. Слайд 35
- 36. But some adjectives were always
- 37. Weak declension had adjectives in the superlative and comparative degrees and the adjective ilca (same)
- 38. There existed also semantic difference
- 39. The weak forms had the
- 40. Degrees of Comparison OE adjectives had
- 41. Suffixes -ra and -est/-ost were
- 42. Sometimes suffixation was accompanied by
- 43. There were suppletive forms:Zod – bettra –
- 44. The OE Adverb OE adverbs were formed
- 45. 2) with the help of suffix –lice
- 46. 3) by adding suffix –es to the
- 47. Adverbs formed from the adjectives
- 48. The OE Verb The OE
- 49. The weak verbs were a
- 50. The number of strong verbs inherited
- 51. The Category of Tense All
- 52. The Category of Mood
- 53. The usage of the Subjunctive
- 54. Subjunctive was used not only
- 55. The Category of Person The Category of
- 56. The Category of Number The predicate agreed with the subject in number and person.
- 57. The Category of Voice
- 58. These verbs were mostly anomalous
- 59. The form hatte (Past, Singular), infinitive
- 60. e.g. þa bōc þe is
- 61. The Strong Verbs
- 62. I. ī
- 63. IV. ea > x
- 64. This group shows different patterns
- 65. The Weak Verbs
- 66. I. cepan cepte cepted (to keep)II. endian endode endod (to end)III. habban hxfde hxfd (to have)
- 67. The weak verbs are subdivided into
- 68. Class I Infinitive –an (seldom –ian)Past forms –de/-ede/-tParticiple II –d/-ed/-t
- 69. Subdivision:double consonants in the infinitive:temman – temede
- 70. Class II: Infinitive – ianPast – odeParticiple II – od
- 71. Class III: Infinitive – anNo vowel before dental suffixPast – deParticiple II –d
- 72. Preterite – Presents Verbs (past -
- 73. 7. witan (to know)8. þurfan (потребувати)9. Ze-nah (досить)10. duZan (годитися)11. munan (пам’ятати)12. unnan (ставитися прихильно)
- 74. Originally they belonged to the
- 75. But in the course of
- 76. They showed attitude to an action
- 77. Anomalous Verbs These verbs have
- 78. wish to rejoIt indicated an
- 79. Eventually willan became a modal verb.
- 80. Some verbs combined the features
- 81. Two OE verbs were suppletive: they
- 82. The Past tense was built from the root wesWesan – wxs – wxron - weren
- 83. Old English Verbals (Non-finite Forms of
- 84. The Infinitive It had
- 85. The form tō drifanne indicated
- 86. Uninflected Infinitive was used in
- 87. The Participle It had both verbal and nominal characteristics.
- 88. Participle I was opposed to Participle
- 89. Participle II has passive meaning
- 90. Participle I is formed from
- 91. Participle II has its own
- 92. Participles were used predicatively and
- 93. Ic nāt hwænne mine daZas
- 94. Скачать презентанцию
There were the following parts of speech in OE: the nounthe adjectivethe pronoun nominal parts of speechthe numeral
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2 There were the following parts of speech in
OE:
the noun
the adjective
the pronoun nominal parts of
speechthe numeral
Слайд 4 There were 5 nominal grammatical categories:
number
case
gender
degrees of comparison
categories of definiteness/indefiniteness
Слайд 5 Verbal grammatical categories were not many:
tense
mood
number verbal categories proper
person
Слайд 6The OE Noun
OE noun has 2 grammatical categories:
number and case.
Nouns also distinguished three forms
of gender: masculine, feminine and neuter.Слайд 9 OE wif (wife) was of neuter gender
mxgden (maiden) was of neuter gender
OE wifman (woman) – masculine genderСлайд 10 The category of number consisted of two members: singular
and plural.
singular, masculine sunu, lural – suna
singular, feminine hand,
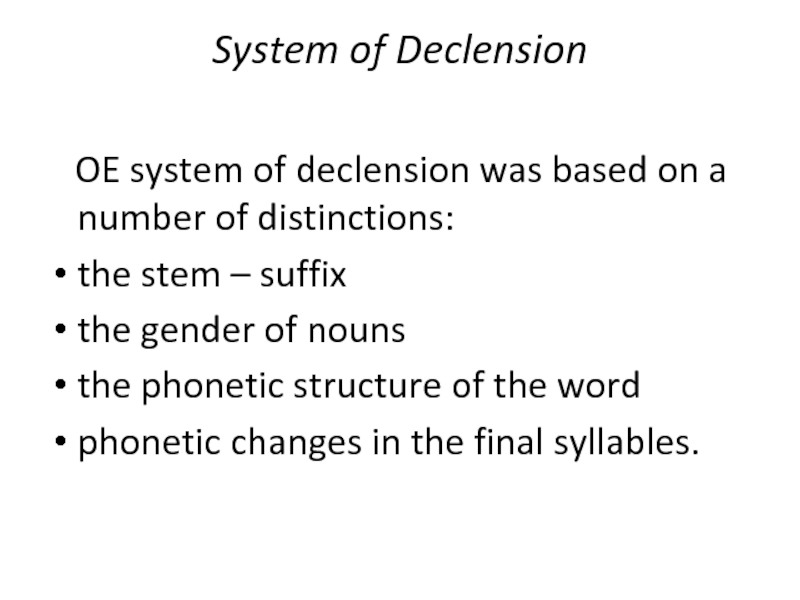
plural – handaСлайд 12System of Declension
OE system of declension was based
on a number of distinctions:
the stem – suffix
the gender of
nounsthe phonetic structure of the word
phonetic changes in the final syllables.
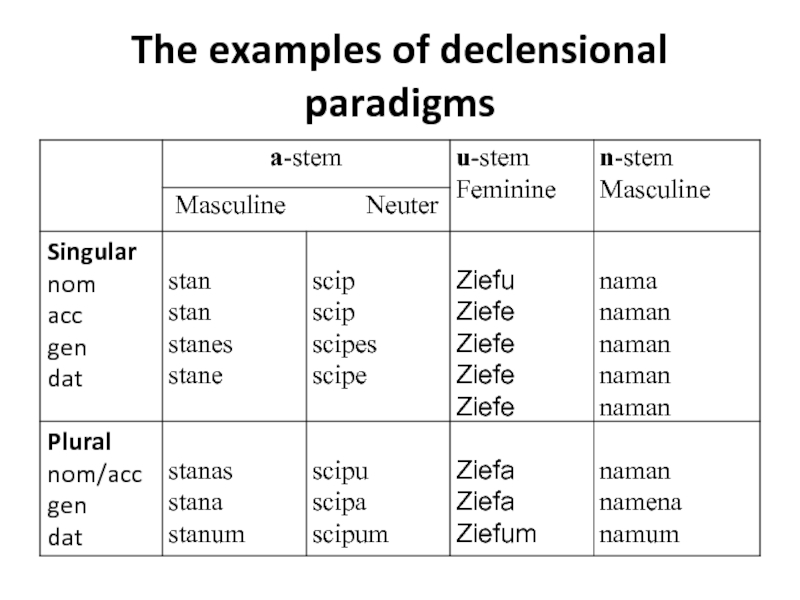
Слайд 13 The stem-suffixes could consist of vowels (a-stems i-stems),
of consonants (n-stems), of sound sequences (-ja-stems, -nd-stems). Some groups
of nouns had no stem-forming suffix. They were called root-stems.Слайд 15 The traces of a-stem declension in Modern English:
’s
(possessive case) goes back to the genitive case singular of
masculine and neuter gender;Слайд 162. –s (plural of nouns) goes back to nominative
and accusative case plural of masculine gender nouns;
3. Uninflected
forms of plural in Modern E (like “sheep”, “deer”) come from the nouns of neuter gender of the long syllabus type.Слайд 17The OE Pronoun
There were the following classes of
pronouns in OE:
personal
demonstrative
interrogative
indefiniteСлайд 18 The grammatic categories were either similar to the
categories of the nouns (in pronouns-nouns) or to the adjectives
(adjective pronouns)Relative, possessive and reflexive were not yet fully developed in OE.
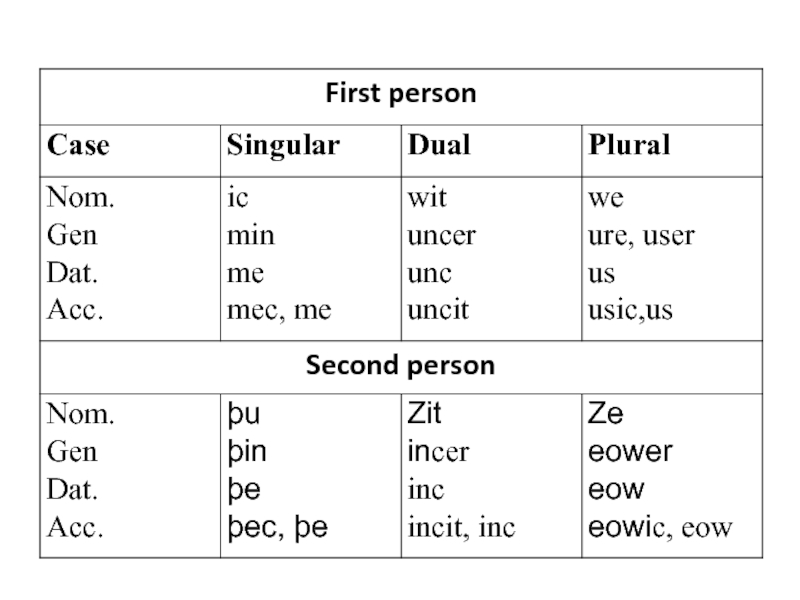
Слайд 19The Personal Pronouns
The Personal Pronouns had three persons,
three numbers, three genders in the third person.
The
first and the second-person personal pronouns declined through the four case system in singular and plural.Слайд 22 The oblique cases of personal pronouns + adjective
–self could serve as reflexive pronouns.
Слайд 23
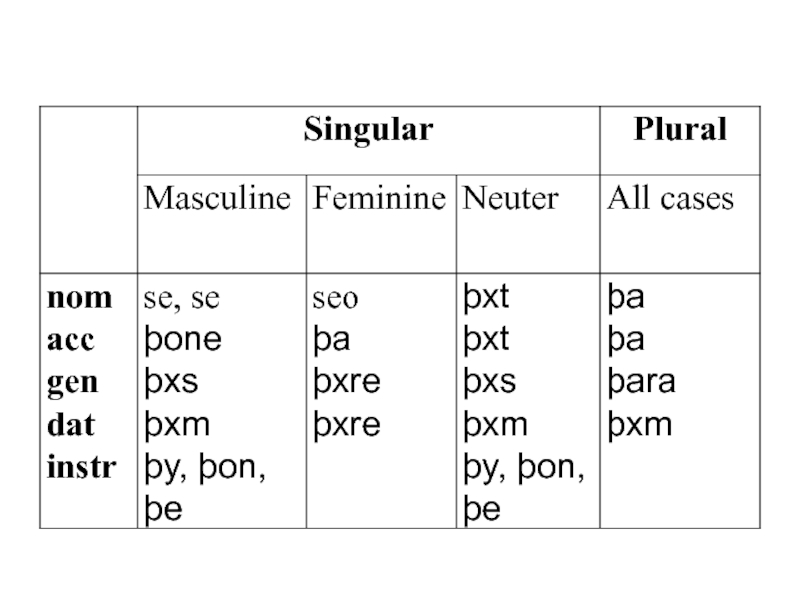
Demonstrative Pronouns
There were the following demonstrative pronouns:
se (masculine) mou
þxt (neuter) me
seo (feminine) maPlural þa
Слайд 25
Interrogative Pronouns
hwā (who) (masculine and feminine)
hwæt
(what) (neuter)
They had four-case paradigm. The instrumental case
of hwæt was used as a separate interrogative word hwy (why). Such interrogative pronouns as hwelc, hwæþer (which) were used as adjective pronouns.Слайд 26
Indefinite pronouns
Indefinite pronouns were many.
ān and its derivative æniZ (one,
any)
nān (none)
nānþinZ (nothing)
nawiht / nowiht / nōht (not)
hwæt – hwuZu
(something)Слайд 27The OE Adjective
OE adjectives had the
categories of numbers, gender and case, degrees of comparison and
definite/indefiniteСлайд 28 The category of case in adjectives differed from
that of nouns. They had one more case – Instrumental.
It was used when the adjective was an attribute to a noun in the Dative case expressing an instrumental meaning:lytle werede – with (the help of) a small troop
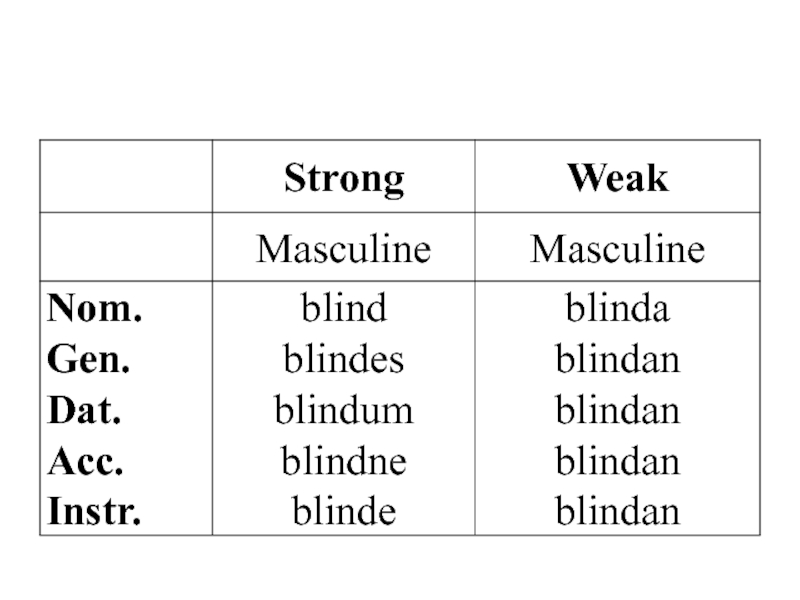
Слайд 29 OE adjectives declined in two ways: according to
the weak and according to the strong declension. The endings
of strong declension coincided with the endings of a-stems of nouns for adjectives in masculine and neuter and of o-stems in the feminine.Слайд 30 Some endings in the strong declension of adjectives
have no parallels in the noun paradigm; they are similar
to the endings of pronouns. The strong declension is called sometimes pronominal.Слайд 31 The weak declension used the same ending as
n-stem nouns except in the Gen. Case, plural it was
-ra (but not -ena)Слайд 32 Most adjectives could be declined in both ways:
strong and weak. It was determined by:
the syntactical function of
the adjectivethe degrees of comparison
the presence of noun determiners
Слайд 33 The adjective had a strong form when used
predicatively and when used attributively without any determiners:
Þa menn sindon
Zode – the men are goodmid hnescre beddinZe – with soft bedding
Слайд 34 The weak form was employed when the adjective
was preceded by a demonstrative pronoun or the Genetive case
of personal pronouns.Слайд 37 Weak declension had adjectives in the superlative and comparative
degrees and the adjective ilca (same)
Слайд 38 There existed also semantic difference between strong and
weak forms of declension. The strong forms were associated with
the meaning of indefiniteness – corresponded to the meaning of a/an.Слайд 39 The weak forms had the meaning of definiteness
(“the”). Weak forms were regularly used together with demonstrative pronouns.
This opposition of weak and strong forms gave the ground for A. Smirnitsky to single out the category of definiteness/ indefiniteness.Слайд 40Degrees of Comparison
OE adjectives had three degrees of
comparison:
positive
comparative
superlative
Слайд 41 Suffixes -ra and -est/-ost were used to form
the comparative and the superlative degrees.
soft – softra
– softest (soft)weriZ – weriZra – weriZost (weary)
Слайд 42 Sometimes suffixation was accompanied by the interchange of
the root + vowel:
Zlxd – Zlxdra – Zladost
(glad)lonZ – lenZra – lenZest (lay)
Слайд 43There were suppletive forms:
Zod – bettra – bet(e)st (good)
lytel –
lxssa – lxst (little)
micel – mara – mxst (much)
yfel –
wiersa – wierest (evil)Слайд 44The OE Adverb
OE adverbs were formed in the following
ways:
1) by adding suffix -e to the adjectives
Adj+e wīd (широкий) – wīde (широко)
sweotul (ясний) – sweotule (яснo)
heard (твердий) – hearde (твердo)
Слайд 452) with the help of suffix –lice
(Modern
–ly) which was added to the nouns
N+licefrēond (друг) – frēondlice (дружньо)
Слайд 463) by adding suffix –es to the nouns. (Historically it
is the ending of the Genitive Case of the masculine
gender a-stem nouns)N+es
dæZ – dæZes (вдень)
nyd (необхідність) – nydes (за необхідністю)
willa (воля) – willes (охотно)
Слайд 47 Adverbs formed from the adjectives had the degrees
of comparison. The degrees-forming suffixes were: -or (for comparative) and
–ost (for superlative)Слайд 48The OE Verb
The OE verbs were
divided into two major categories, the so-called weak and strong
verbs.Слайд 49 The weak verbs were a feature of Germanic
and were formed by adding an inflectional ending that included
a dental or alveolar consonant. The strong verbs were formed by changing the stem vowel.Слайд 50 The number of strong verbs inherited from Germanic probably
amounted to 300-400 and their number was constantly decreasing.
Слайд 51The Category of Tense
All verbs had two tenses:
present and preterite. Other tenses were expressed through adverbs or
were understood from the context. The Future Tense may be expressed by the verbs willan/scullan + infinitive.E.g. Wille ic asecZan.
Слайд 52
The Category of Mood
The verb had an infinitive,
the present and past participle. In addition to the indicative
mood and imperative mood, there was the subjunctive for both tenses.Слайд 53 The usage of the Subjunctive Mood was different
from its usage in later periods. The subjunctive forms denoted
unreal acts or supposition but in a very general way.Слайд 54 Subjunctive was used not only in the conditional
sentences, but in the clauses of time, clauses of result
and in reported speech. In indirect speech indicative mood forms could occur side by side with subjunctive.Слайд 55The Category of Person
The Category of Person consisted of
three forms: the first, the second and the third person
(singular and plural)Слайд 57
The Category of Voice
There was no passive. The
verbs that were to become auxiliary verbs were mostly notional
verbs in the earliest period, though traces of their development towards auxiliaries may be found, particularly in texts translated from or based on Latin.Слайд 58 These verbs were mostly anomalous in structure because,
as so-called preterite-present verbs, they had formed new present tense
forms from old preterits and had formed new preterits. They did not have the forms that were found in other verbs.Слайд 59 The form hatte (Past, Singular), infinitive hattan (call) had
the passive meaning. Passive meaning was usually expressed by the
words bēon, wesan (to be), weorþan (become) and the Past Participle.Слайд 60 e.g. þa bōc þe is enemned on læden
Pastoralis – the book which is called
Latin “Pastoralis”þet hūs wearð þaforbunden – That house was (got) then burned down.
During the OE period such construction gradually turned into analytical Passive Voice forms.
Слайд 61
The Strong Verbs
The strong verbs fall into
seven distinct patterns. The patterns are usually indicated through the
forms of the infinitive, preterite singular (third person), preterite plural and past participle.Слайд 62I. ī
ā i
iwritan wrat writon written
II. ēō/ū ēā u o
beodan bead budon boden
III. e x u o
drincan dranc druncon druncen
Слайд 63IV. ea > x
e x
x oberan bxr bxron boren
V. e x x e
tredan trxd trxdon treden
VI. a ō ō a
faran fōr fōron faren
Слайд 64 This group shows different patterns because it originally
consisted of reduplicating verbs. But the vowel or diphthong of
the infinitive was repeated in the participle and both forms of the preterite had either e or ēō.hātan hēt hēton hāten (to be called)
Слайд 65
The Weak Verbs
There are three categories of
weak verbs. Since the weak verbs form their preterite by
adding an inflection which contains d or t in OE, there is no need to distinguish the preterite singular from its plural, because they differ only in the ending indicating number.Слайд 66
I. cepan cepte cepted (to keep)
II. endian endode endod (to
end)
III. habban hxfde hxfd (to have)
Слайд 67 The weak verbs are subdivided into three classes on
the bases of:
the Infinitive ending
the sonority of the
suffixthe sounds preceding the suffix.
Слайд 69Subdivision:
double consonants in the infinitive:
temman – temede – temed (totame)
vovel
interchange in the root:
telan – tealde – teald
Слайд 72
Preterite – Presents Verbs
(past - present)
They were 12
of them. Six of them survived in ModE.
1. aZ (ought)
2.
cunnan cann (can)3. dear (r) (dear)
4. sculan, sceal (shall)
5. maZan, mxZ (may)
6. mot (must)
Слайд 737. witan (to know)
8. þurfan (потребувати)
9. Ze-nah (досить)
10. duZan (годитися)
11.
munan (пам’ятати)
12. unnan (ставитися прихильно)
Слайд 74 Originally they belonged to the strong verbs and
formed the Past tense form by the change of the
root vowel:witan – wāt – wiste.
Слайд 75 But in the course of time the Past
tense form acquired the meaning of the Present : wāt
– знаю.Слайд 76 They showed attitude to an action denoted by another
verb, the infinitive which followed the preterite – present. Eventually
they developed into modern modal verbs.Слайд 77
Anomalous Verbs
These verbs have irregular forms.
E.g. willan, dōn,
Zān, beon, wesan
resembled the preterite – presents
in meaning and function.Слайд 78 wish to rejoIt indicated an attitude to an
action and was often followed by the infinitive.
Þa
De willaD mines forsiDes fxZnian – those who ice in my deathСлайд 80 Some verbs combined the features of weak Past
tense with a vowel interchange and the Participle in –
n:don – dyde – Zedon (to do)
Слайд 81 Two OE verbs were suppletive: they are beon and
wesan
OE Zan – eode – Ze-Zan (to go)
Beon
(be) 1st p. sing eom, beo2nd p. eart, bist
Слайд 83
Old English Verbals
(Non-finite Forms of the Verb)
There were two
non-finite forms: the Infinitive and the Participle.
Слайд 84
The Infinitive
It had no verbal categories but had
some nominal. As a verbal noun by origin, the infinitive
had two case system: the Nominative and the Dative case:drifan (to drive) (Uninflected Nominative)
tō drifanne (Inflected Dative)
Слайд 86 Uninflected Infinitive was used in the phrases with
the verbs that turned into modal or anomalous verbs:
þū meaht
sinZan – you may singþa ouZon hē sōna sinZan – then began he soon to sing
Слайд 88 Participle I was opposed to Participle II through voice
and tense distinctions: Participle I is active and expresses present
or simultaneous process.Слайд 89 Participle II has passive meaning and denotes the
state/quality resulting from past action.
Participle II of intransitive
verbs has active meaning.Слайд 90 Participle I is formed from the Infinitive with
the help of suffix -ende
Participle I: drīfende (driving)
(infinitive drīfan)Слайд 91 Participle II has its own stem. If it
was a strong verb there was a vowel interchange and
suffix -en. From weak verbs Participle II had -d/-t. As a rule Participle II had the prefix -Ze.Participle II (Ze) – drifen (driven)