They can originate spontaneously in nature or as a result
of various induction techniques.Spontaneous development of haploid plants has been known since 1922, when Blakeslee first described this phenomenon in Datura stramonium.
The potential of haploidy for plant breeding arose in 1964 with the achievement of haploid embryo formation from in vitro culture of Datura anthers, which was followed by successful in vitro haploid production in tobacco.
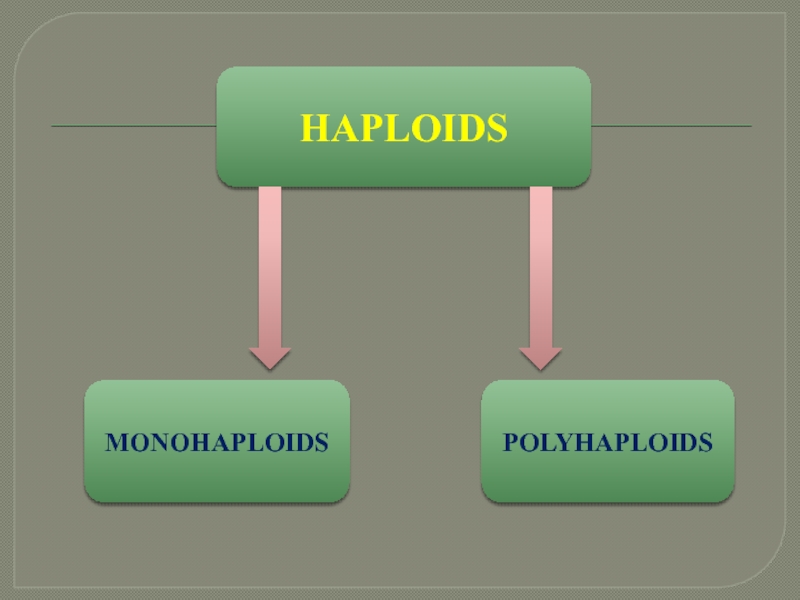
Гаплоїдні рослини ті, які містять гаметне хромосомне число (n).
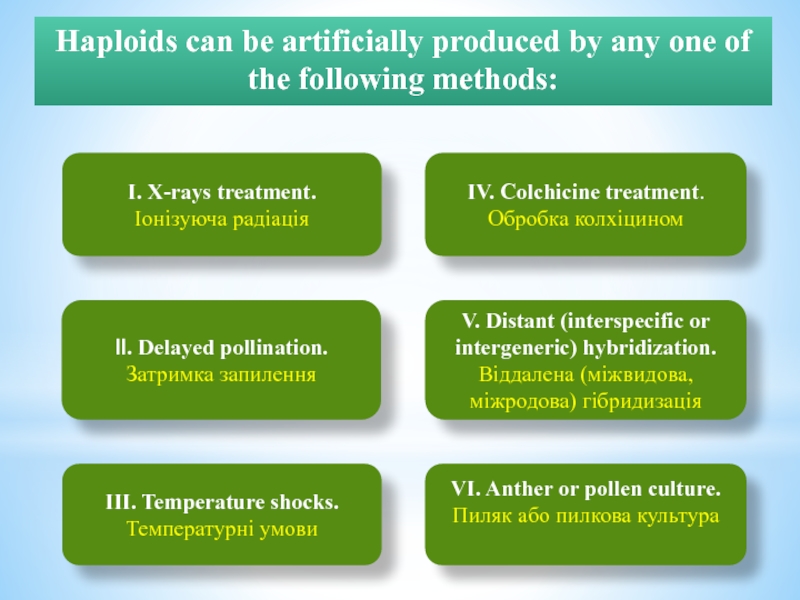
Вони можуть виникати спонтанно в природі або, в результаті різних методів індукції.
Спонтанний розвиток гаплоїдних рослин відомий з 1922 року, коли Блейкеслі вперше описав це явище в Дурману.
Потенціал гаплоїдії для селекції рослин виник в 1964 році з досягненням ембріоноутворення гаплоїда з культури ін вітро пиляків Дурману, який послідував за успішним формуванням гаплоїда у культурі ін вітро в тютюну.