Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
IATA CRM Course Threat and Error Management Captain Zhou Yizhi
Содержание
- 1. IATA CRM Course Threat and Error Management Captain Zhou Yizhi
- 2. IntroductionsNameAirlinePositionFlying experiencePrevious CRM experience
- 3. Course Schedule0900 - Start 1030-1045 Break (approximate)1200 - Lunch1330 – Return1515-1530 Break (approximate)1700 - Finish
- 4. Course OutlineDAY 1 IntroductionIntroduction to Threat and
- 5. Objectives of the courseTo understand the concept
- 6. Module 1Overview History of CRM
- 7. Our Job is to fly from point “A” to point “B” safely and efficiently.
- 8. To accomplish this we must deal with threats and errors from the real world…
- 9. … and the mistakes we make as pilots ...
- 10. ...while maintaining productivity.
- 11. How are Pilots made safe?ProficiencyTechnical knowledgePhysical and mental well beingCRM
- 12. Crew Resource Management
- 13. Evolution of CRMNASA research inspired this response
- 14. First Generation CRMDerived from corporate management development
- 15. Second Generation CRMMore team basedUse of team
- 16. Third Generation CRMSystems approachFocus on specific skills/behavioursIntegration
- 17. Fourth Generation CRMPerformance data guide trainingIntegration of
- 18. Problems with past CRMAdaptation of business models
- 19. …Reduce Human Error
- 20. Error
- 21. NTSB StudyConclusions - When flying the aircraft,
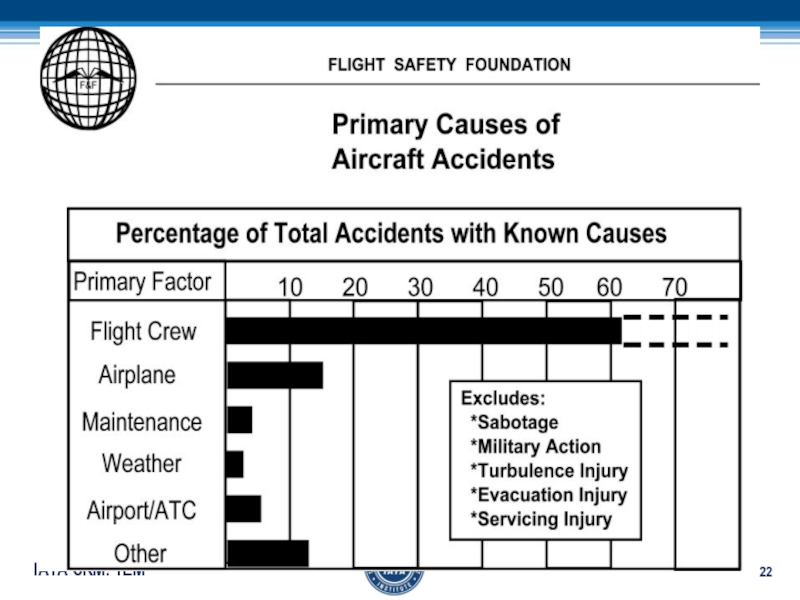
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Error environmentsIncreasing workloadUndo time pressureFatigueProcedural non-compliancePoor crew coordinationInterruptions/distractions
- 24. ErrorActions or inactions by the crew that
- 25. Fifth Generation CRMCannot totally eliminate errorAvoid errors being madeManage errors by trapping or mitigating their consequences“Error Management”
- 26. Threat
- 27. The Real World What is a normal
- 28. ThreatsAre situations external to the flight deck,
- 29. Types of Threat Weather Distractions Missed Approaches Flight Diversions Heavy Traffic Similar
- 30. Types of Threat Weather Distractions Missed Approaches Flight Diversions Heavy Traffic Similar
- 31. What groups are responsible for the safety of a flight?
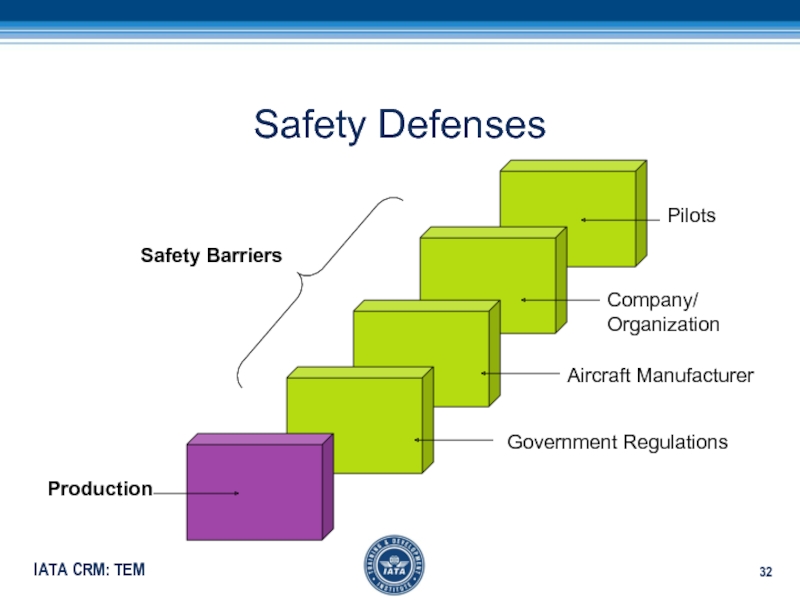
- 32. Safety DefensesAircraft ManufacturerGovernment RegulationsCompany/OrganizationPilotsProduction Safety Barriers
- 33. Safety Defenses - ErrorsAircraft ManufacturerGovernment RegulationsCompany/OrganizationPilotsProduction Safety BarriersErrors
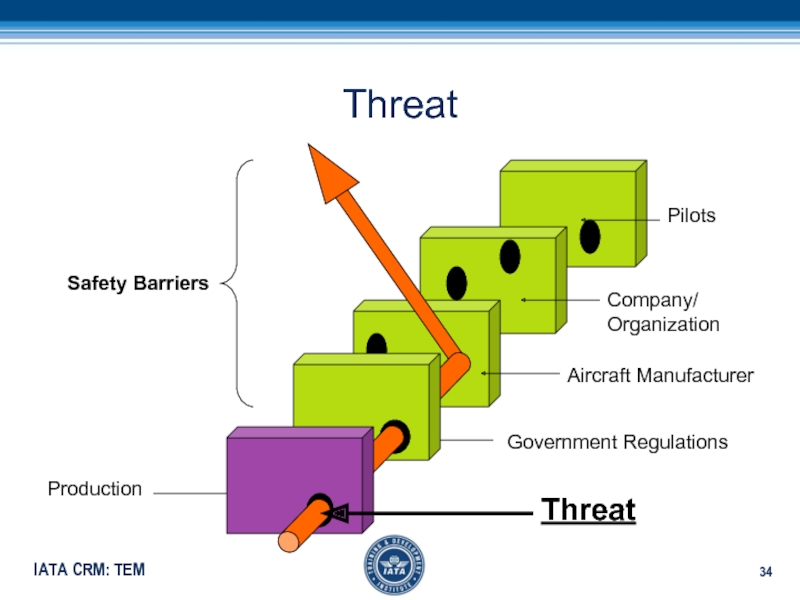
- 34. Threat Aircraft ManufacturerGovernment RegulationsCompany/OrganizationPilotsProduction Safety BarriersThreat
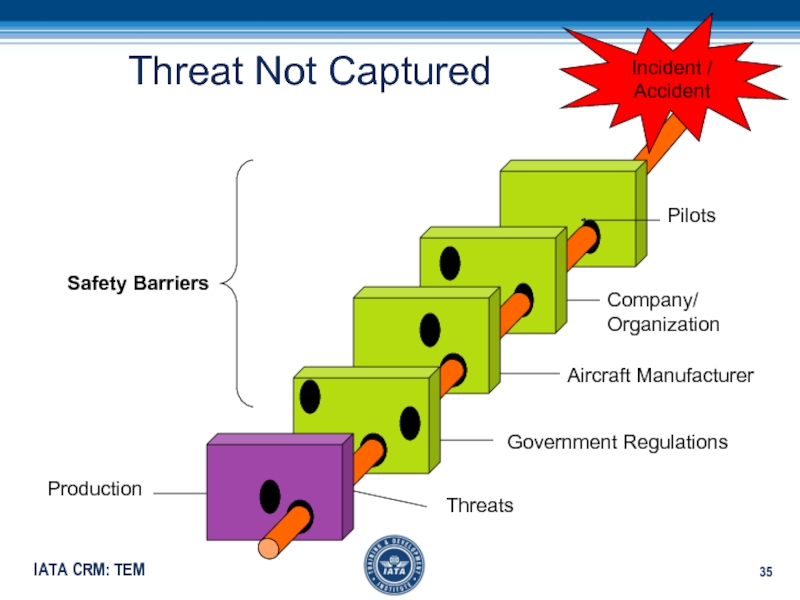
- 35. Incident / AccidentThreat Not CapturedAircraft ManufacturerGovernment RegulationsCompany/OrganizationPilotsProduction Safety BarriersThreats
- 36. Pilots are the last line of defense!
- 37. What do Pilots have to do to
- 38. Crew InvulnerabilityPerceptionPilots perceive themselves as unbreakable under
- 39. Sixth Generation of CRMFocuses on CRM as
- 40. Countermeasures to Threat and ErrorAvoid committing errorsManage
- 41. Our GoalNeed to refocus CRM towards error
- 42. Module 2 CountermeasuresSkill Groups to be used as Countermeasures to Threat and Error
- 43. CRM Skill Groups Four groupings of CRM
- 44. Team Climate CountermeasuresCRM Skill
- 45. In a large number of incidents,
- 46. Team ClimateHow do you create an atmosphere
- 47. Communication EnvironmentCommunication channels established and maintainedBe assertive,
- 48. Some Communication SkillsInquiry – asking questionsActive listening
- 49. What qualities make a good leader?-In command-Decisive -Encourages participation-?
- 50. Leadership Skills Purpose -Explain reason for task -Do what
- 51. “ The Captain demonstrates responsibility
- 52. Conflict ManagementHow do you deal with conflict in the flightdeck?
- 53. Planning CountermeasuresCRM Skill
- 54. PlanningPreparation in dealing with threat and avoiding
- 55. BriefingsWhat is a briefing?Why is it important to give good briefings?How do we accomplish this?
- 56. Briefing PointsMust be short, less than 10
- 57. Plans StatedDevelop plan - Solicit input from
- 58. Workload AssignmentEvaluate -Determine work to be completed -Calculate resources
- 59. Workload AssignmentOne pilot is always monitoring during
- 60. Contingency ManagementContingency Planning - Anticipate
- 61. Back-up plan – to reduce stress in busy timeWhat is your policy? Missed Approach Policy
- 62. Planning for Known ThreatsHow do you plan
- 63. Execution CountermeasuresCRM Skill
- 64. ExecutionApplication of countermeasures to threat and error
- 65. One way of assessing your current monitoring
- 66. Monitor/CrosscheckCrosschecking of systems and actions such as; -
- 67. Monitoring for ErrorPilots must actively monitor the
- 68. Monitor / CrosscheckThis means mentally flying the
- 69. BARRIERS to Effective M/C -
- 70. FatigueLess reliable memory – items missedReduced attention-
- 71. Workload ManagementAbility to manage required tasks. Know
- 72. WM CountermeasuresSpeak up when overloadedChange level of automationAsk for more time - hold, delay vectors
- 73. BARRIERS to Effective W/M -
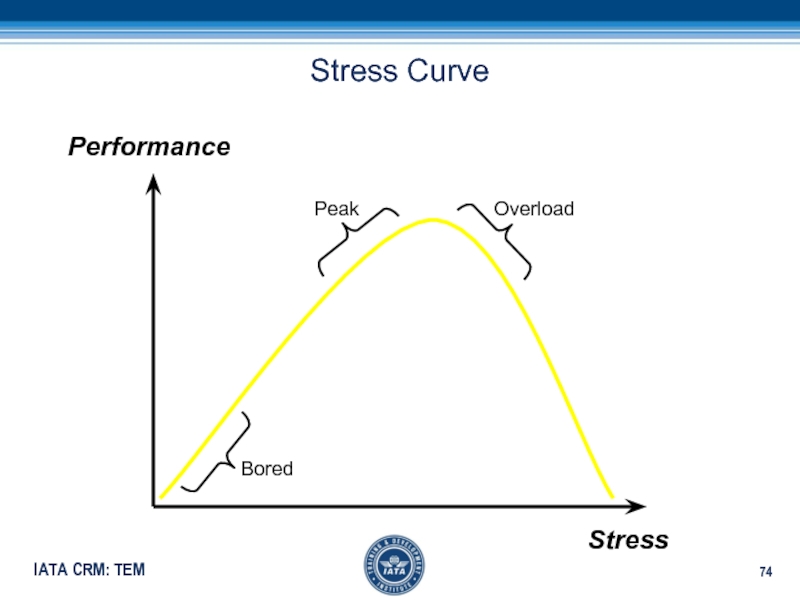
- 74. Stress CurveStressPerformanceOverloadPeakBored
- 75. In stressful situations, the captain will be
- 76. DistractionsInterruptions can form holes in defensesWhat can be done to prevent distractions?Sterile cockpitLocked cockpit door
- 77. DistractionsIdentify the interruptionAsk what was I doing
- 78. Work as a CREWOne pilot is always
- 79. VigilanceIs being alert to the situation, not
- 80. Vigilance - Situational AwarenessIs being alert and
- 81. SWA 1455
- 82. Automation ManagementBalance of automation and workloadDuring high
- 83. Review / Modify CountermeasuresCRM Skill
- 84. Review/Modify CountermeasuresUse against unexpected threat or when
- 85. Evaluation of plansReview and modify plans when
- 86. InquiryAsk questions to clarify – nothing taken
- 87. AssertivenessMaking sure your viewpoint is understoodState critical
- 88. Specific Phrases to Use Are you ready
- 89. Decision Making for an Unexpected ThreatPerceive situation
- 90. Error Avoidance Module 3
- 91. Preventing ErrorMaintaining your healthHigh levels of training
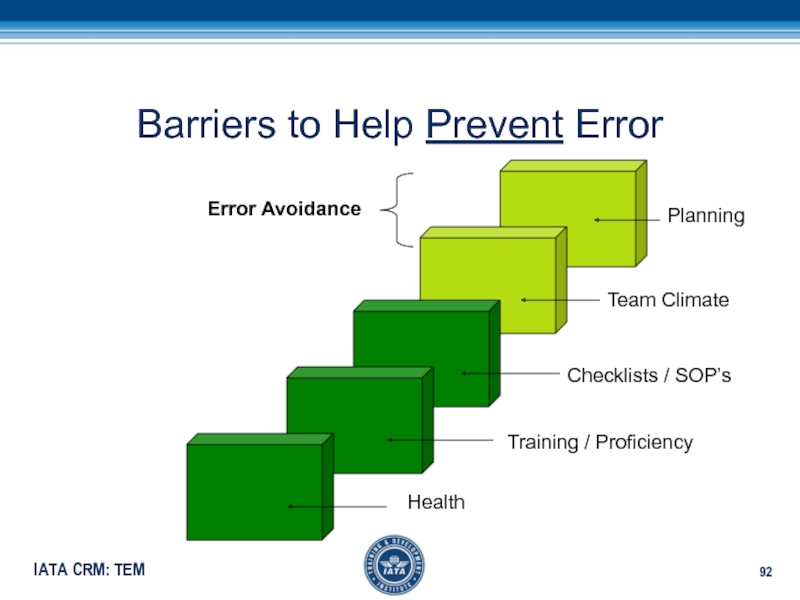
- 92. Barriers to Help Prevent ErrorChecklists / SOP’sTraining / ProficiencyTeam ClimatePlanningHealthError Avoidance
- 93. HealthYour health affects everything you do.Thorough awareness
- 94. Technological ProficiencyAn expert pilot must constantly train.
- 95. Standard Operating ProceduresEstablish a repeatable sequence or
- 96. Accident Cause Factors Flying pilot non-adherence to
- 97. Accident Cause Factors Flying pilot non-adherence to
- 98. How SOP’s relate to errordata show that
- 99. ChecklistsProper checklist usage is... ...a basic strategy
- 100. ChecklistsHelps prioritize itemsFrees up brainpower for other
- 101. What is Checklist abuse?- Memorizing - Self-initiating
- 102. Checklist ErrorsFatigue and stress – increase chance
- 103. Error AvoidanceUsing CRM skills as countermeasures
- 104. Things you can do to help avoid errorCreate a positive team climateDevelop planning strategies
- 105. Team ClimateHow do you create an atmosphere
- 106. Error Avoidance - PlanningWhat/why is planning? How accomplishedBriefingsPlans statedWorkload assignment – distractionsContingency management?
- 107. Module 4 Threat Management
- 108. What was a threat on a recent flight?
- 109. What is threat?
- 110. Threats which originate outside the cockpit.expected or
- 111. Threats which originate outside the cockpit.expected or
- 112. Threats Adverse weather TerrainAirport conditionsAircraft malfunctionsAutomation eventsCommunication
- 113. Threats by Phase of Flight
- 114. Factors that affect our ability to operate
- 115. Latent ThreatsATC practicesScheduling practices that result in fatigueOrganizational, national, professional cultureAircraft characteristicsQualification standardsRegulatory practices
- 116. Locked Cockpit DoorAmbiguous regulations – governmentUntested aircraft systems – manufacturerFlawed procedures – SOP’s-Inadequate training – company
- 117. Runway incursionsBoth pilots have taxi charts availableBoth
- 118. Singapore Airlines SQ006
- 119. Threat Management
- 120. Barriers to Manage ThreatExternal Alerting SystemsAircraft Warning SystemsTeam ClimateReview / Modify(Unexpected Threat)Threat ManagementPlanning(Expected Threat)Training / Proficiency
- 121. What are countermeasures for Expected Threat? Unexpected Threat?
- 122. Team ClimateWhy is communication and leadership important
- 123. PlanningUsed for expected threatBrief, state plans, assign work and contingency strategies
- 124. LOSA DataIn complex or high threat conditions,
- 125. Review/ModifyUnexpected threatEvaluation of plans – reviewed and
- 126. Module 5 Error Management
- 127. Why do we make errors?Lack of experienceRushedDistractionsStressCrews
- 128. DistractionsHow do you manage distractions?PrioritizeTell intruder to be quietSterile cockpitLook in books
- 129. Professional culturePilots have a strong professional culture
- 130. Personal InvulnerabilityThe majority of pilots agree thatTheir
- 131. Areas of VulnerabilityTaxi-out10,000 ftTransition Alt.Within 1,000 ft of level offCruise / DescenttransitionDescent, approachand landingTaxi-in
- 132. Flight Safety FoundationMany of the accidents raise
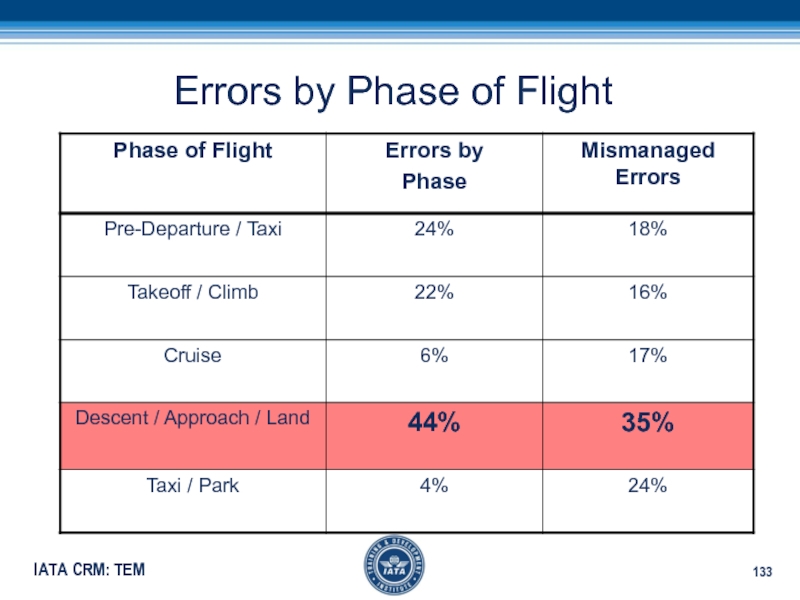
- 133. Errors by Phase of Flight
- 134. Highlighting CRM in the Blue BoxBriefTOD18000ft10000ftSlow andConfigureFAF/OMStabilizedApproachBottom LineFlare / Touchdown
- 135. Blue BoxMost crew errors (LOSA)Most consequential crew
- 136. Types of ErrorIntentional Noncompliance – violations
- 137. Barriers to Manage ErrorExternal Alerting SystemsAircraft Warning SystemsTeam ClimateExecutionError Management
- 138. Managing ErrorsOnce an error is committed, it
- 139. Managing Error TopicsPilot invulnerability?Culture?Team Climate is important alsoDistractions?ExecutionMonitor crosscheckWorkload managementVigilanceAutomation management
- 140. - Timely -
- 141. SummaryWhat error management isWhy we need itHow
- 142. NWA 1482
- 143. Module 5A Undesired Aircraft State Management
- 144. Undesired Aircraft State ManagementUAS - Aircraft deviations
- 145. Barriers to Manage Aircraft DeviationsAircraft Systems(Stick pusher
- 146. CountermeasuresTeam ClimateReview/Modify
- 147. Threat and Error ManagementModule 6 TEM
- 148. “The Tip of the Iceberg...”
- 149. ...is a small part of what lies beneath”
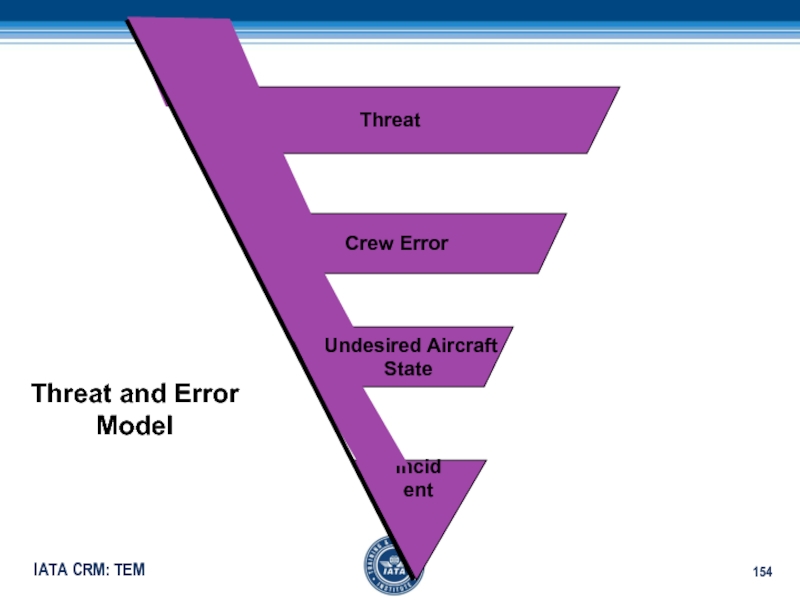
- 150. ThreatLatent Threats – National Culture,
- 151. Crew ErrorCrew mismanages threatError Types - Communication
- 152. Undesired Aircraft StateAircraft is not where it
- 153. Incident (Accident)Crew ErrorThreat Undesired Aircraft
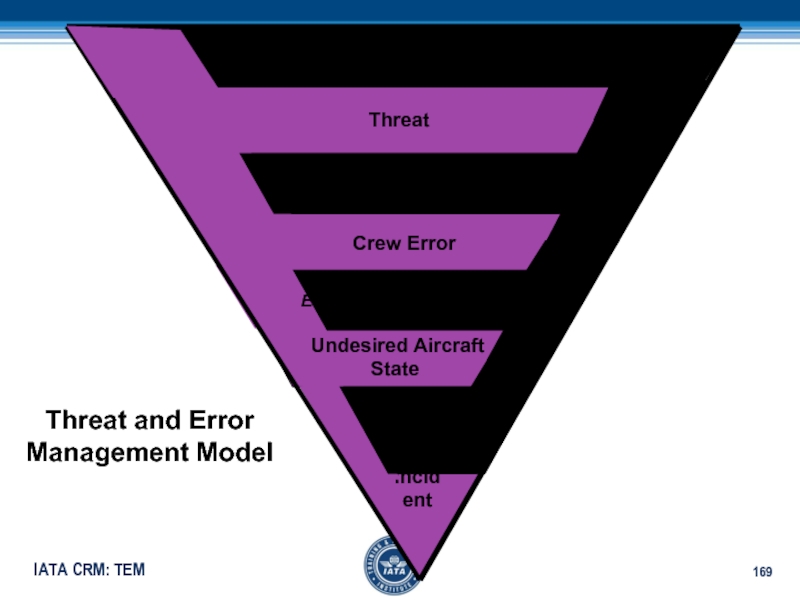
- 154. ThreatCrew Error Undesired Aircraft StateIncidentThreat and ErrorModel
- 155. ApplicationApply the TEM model to SQ006
- 156. ApplicationApply the TEM model to SQ006
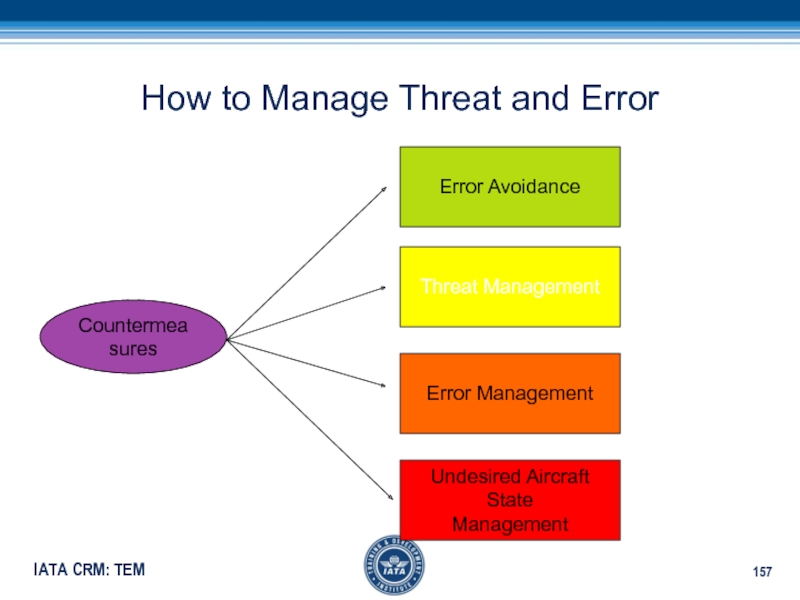
- 157. How to Manage Threat and ErrorCountermeasuresError AvoidanceThreat ManagementError ManagementUndesired Aircraft State Management
- 158. Countermeasure SkillsTeam ClimatePlanningTask ExecutionReview and Modify
- 159. How do we apply these skills?
- 160. Error AvoidanceProactive strategies to avoid committing errorsPlanningFollowing
- 161. Error AvoidanceHuman limitations lead to errorLimited memory
- 162. ThreatCrew Error Undesired Aircraft StateIncidentError AvoidanceTeam ClimatePlanning
- 163. Threat ManagementManage operational complexity, which translates into
- 164. ThreatCrew Error Undesired Aircraft StateIncidentError
- 165. Error ManagementManage crew errors.Error is an inevitable
- 166. ThreatCrew Error Undesired Aircraft StateIncidentError
- 167. Undesired Aircraft State ManagementManage aircraft deviations, wrong
- 168. ThreatCrew ErrorIncidentError Avoidance
- 169. Слайд 169
- 170. Слайд 170
- 171. AA 1420
- 172. Safety Management SystemsModule 7
- 173. Our Job is to fly from point “A” to point “B” safely and efficiently.
- 174. ProductivityErrors cost moneyFind out where mistakes are being made and adjust resourcesBetter use of training
- 175. Expose Yourself!!!How can management better understand
- 176. Management’s Role establish trust, which includes
- 177. FeedbackNeed a process to identify and feedback
- 178. Слайд 178
- 179. How does TEM fit into a Safety
- 180. TEM at the Organizational levelRecognize dangers of
- 181. Data CollectionCompany, industry and regulating authorities get
- 182. More Realistic Training Focus on Threat
- 183. Tools to Improve SafetySOP’s and Checklists
- 184. Line Orientated Safety Audit LOSASafety data acquisition
- 185. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4Course Outline
DAY 1
Introduction
Introduction to Threat and Error Management -
TEM
Countermeasure (CRM) Skills
DAY 2
Review
Error Avoidance
Threat Management
Error
ManagementUndesired Aircraft State Management
DAY 3
Review
Threat and Error Management Model
Safety Management Systems
Test
Слайд 5Objectives of the course
To understand the concept of threats.
To understand
that operational errors are normal, expected and a consequence of
mismanaged threats.To develop strategies to:
Recognize and manage threats
Identify and manage errors
Minimize the consequences of errors
To recognise that the safety system can be improved by the application of the TEM model to events.
At the end of this course students will be able to apply the TEM process to their area of operation.
Слайд 13Evolution of CRM
NASA research inspired this response to non-mechanical accidents
Goal
to reduce Human Error
Слайд 14First Generation CRM
Derived from corporate management development training
Focus on individual
management style/interpersonal skills
Insure captain accept input from F/O
Addressed lack of
assertiveness by F/O “Cockpit Resource Management”
Слайд 15Second Generation CRM
More team based
Use of team building exercises
Focus on
concepts
Situational Awareness
Stress Management
Modular
Teach the error chain
Train individual decision making, briefing
strategies, team building“Crew Resource Management”
Слайд 16Third Generation CRM
Systems approach
Focus on specific skills/behaviours
Integration with technical performance
Emphasis
on evaluating human factors
Special training for Instructor/Check pilots
Broadened perspective
Flight attendants,
dispatchers, maintenance “Advanced CRM”
Слайд 17Fourth Generation CRM
Performance data guide training
Integration of CRM into technical
Training
Proceduralization of CRM
Checklists include CRM issues
Specialized curriculum topics
Automation, etc.
Reinforcement of
human factors in full mission simulation (LOFT) “Integrated CRM”
Слайд 18Problems with past CRM
Adaptation of business models
Confusing
Industry has evolved
and matured
Diluted
Separation of technical and CRM training
Forgot the primary objective
of CRM…Слайд 21NTSB Study
Conclusions
- When flying the aircraft, captains appear to
have difficulty in monitoring their own performance
- Many new
on the line crewmembers have difficulty in voicing concerns about the captain’s decision making, particularly if they have not flown together before.Слайд 23Error environments
Increasing workload
Undo time pressure
Fatigue
Procedural non-compliance
Poor crew coordination
Interruptions/distractions
Слайд 24Error
Actions or inactions by the crew that lead to deviations
from organizational or flight crew intentions or expectations.
Errors in
the operational context tend to reduce the margin of safety and increase the probability of incidents or accidents.Слайд 25Fifth Generation CRM
Cannot totally eliminate error
Avoid errors being made
Manage errors
by trapping or mitigating
their consequences
“Error Management”
Слайд 27The Real World
What is a normal flight?
What hazards do
pilots have to deal with on the line?
Слайд 28Threats
Are situations external to the flight deck, that must be
managed by the cockpit crew during normal, everyday flights.
Such
events increase the operational complexity of flight and pose a safety risk to the flight at some level. Слайд 29Types of Threat
Weather Distractions
Missed Approaches
Flight Diversions
Heavy Traffic
Similar call signs
Passenger Events
Cabin
Crew error
Ground Crew error
Maintenance error
System Malfunctions
Time Pressures
Automation Events
ATC error
Unfamiliar Airport Слайд 30Types of Threat
Weather Distractions
Missed Approaches
Flight Diversions
Heavy Traffic
Similar call signs
Passenger Events
Cabin
Crew error
Ground Crew error
Maintenance error
System Malfunctions
Time Pressures
Automation Events
ATC error
Unfamiliar Airport Слайд 32Safety Defenses
Aircraft Manufacturer
Government Regulations
Company/
Organization
Pilots
Production
Safety Barriers
Слайд 33Safety Defenses - Errors
Aircraft Manufacturer
Government Regulations
Company/
Organization
Pilots
Production
Safety Barriers
Errors
Слайд 34Threat
Aircraft Manufacturer
Government Regulations
Company/
Organization
Pilots
Production
Safety Barriers
Threat
Слайд 35Incident / Accident
Threat Not Captured
Aircraft Manufacturer
Government Regulations
Company/
Organization
Pilots
Production
Safety Barriers
Threats
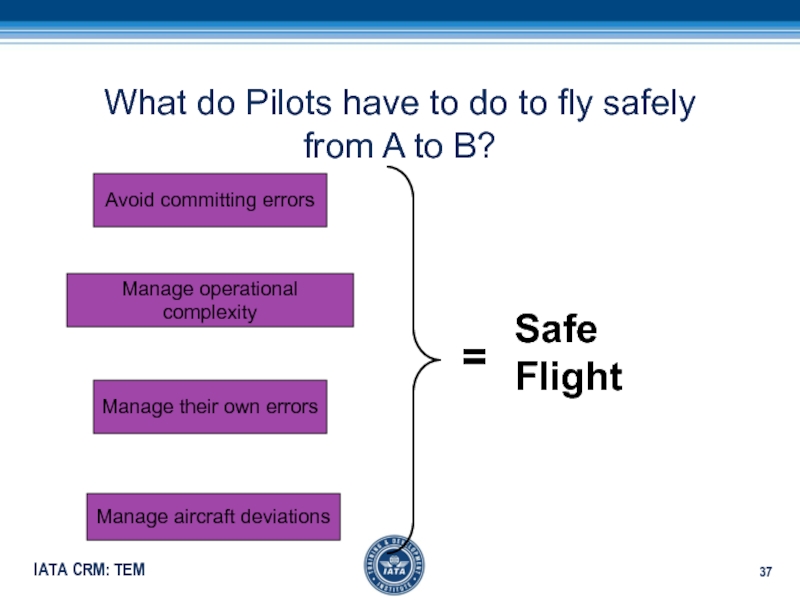
Слайд 37What do Pilots have to do to fly safely from
A to B?
Avoid committing errors
Manage operational complexity
Manage their own errors
Manage
aircraft deviationsSafe
Flight
=
Слайд 38Crew Invulnerability
Perception
Pilots perceive themselves as unbreakable under pressure, that they
can handle all problems
Reality
Pilots are affected by various factors which
influence their ability to perform, their personal limitationsСлайд 39Sixth Generation of CRM
Focuses on CRM as set of countermeasures
against threat and error
Error avoidance
Threat and error management
Undesired aircraft state
management“Threat and Error Management”
TEM
Слайд 40Countermeasures to Threat and Error
Avoid committing errors
Manage operational complexity
Manage their
own errors
Manage aircraft deviations
Error Avoidance
Undesired Aircraft State
Management
Error Management
Threat
ManagementСлайд 41Our Goal
Need to refocus CRM towards error reduction and threat
recognition
Adaptation of existing skills towards countermeasures in the real world
Слайд 43CRM Skill Groups
Four groupings of CRM skills are
threat
and error countermeasures
Team building and climate
Planning
Execution
Review / modify
Слайд 45In a large number of incidents, one
person knew something was wrong and did not speak up!
Least
errors made by crews who communicated the most!Слайд 46Team Climate
How do you create an atmosphere for constructive TEM?
develop
and maintain a good communication environment
effective leadership
Important in all aspects
of safety ( CRM/TEM)Слайд 47Communication Environment
Communication channels established and maintained
Be assertive, yet respectful
Ask for
information and advice
Create climate for critique – give and take
Слайд 48Some Communication Skills
Inquiry – asking questions
Active listening - acknowledge message
Clarity - clear communication
Appropriate assertiveness – proper level for
situationСлайд 50Leadership Skills
Purpose -Explain reason for task
-Do what is right for
the group
Direction -Define crewmembers responsibilities
-Good influence
Motivate -Build the team
-Give and receive
feedback-Maintain focus on objective
Слайд 51“ The Captain demonstrates responsibility
for the operation
of the flight,
is the final authority and
decision maker”Слайд 54Planning
Preparation in dealing with threat and avoiding error by using;
-
Good Briefings- Stating Plans
- Workload assignment
- Contingency management
Слайд 55Briefings
What is a briefing?
Why is it important to give good
briefings?
How do we accomplish this?
Слайд 56Briefing Points
Must be short, less than 10 ideas to be
fully understood
Better to split the briefing into two parts if
longerIndividually prepared for each flight, automatic briefings used as routine activate none of the memory and are ineffective
Must be understood by all crew members, better to have a simple well understood plan than a brilliant misunderstood one!
Слайд 57Plans Stated
Develop plan - Solicit input from other sources
- Responsibility of all crewmembers to
contribute to the decision making process
State plan - Make plan known to crew, company and
others as appropriate
- Communicating decisions clearly reduces confusion and misunderstandings
Shared Mental Model - constructing and maintaining a common image of the situation
- synchronization of ideas
Слайд 58Workload Assignment
Evaluate
-Determine work to be completed
-Calculate resources and time required
Prioritize
-Match
abilities with available time
-Avoid distractions
Assign Work
-Assign actions based on
crewmember experience and workload
-Issue clear and concise instructions or guidance
Слайд 59Workload Assignment
One pilot is always monitoring during
low workload and
both pilots are monitoring
as much as possible during high
workloadStrategically plan workload to maximize
monitoring during those areas of vulnerability
i.e. stowing charts, approach briefing, PA’s
Слайд 60Contingency Management
Contingency Planning
- Anticipate potential outcomes
- Alternate plan is initiated when limits
are exceededEstablish Limits
- Assess time available
- Assess capability to complete task
- Set limits
Слайд 62Planning for Known Threats
How do you plan for known threats?
Diagnose-
identify, knowledge, memory, problem solving skills
Generate solutions – find alternatives,
hard to do under stressAssess risks – predict consequences and success rate
Слайд 64Execution
Application of countermeasures to threat and error
- Monitor / Crosscheck
- Workload Management - Vigilance
- Automation Management
Слайд 65One way of assessing your current monitoring ability is to
ask:
“How often have I missed making the 1,000’ before
altitude callout?” Слайд 66Monitor/Crosscheck
Crosschecking of systems and actions such as;
- aircraft trajectory
- automation
systems and mode status
- Aircraft systems and/or components
Inadequate flight crew
monitoring has been cited by a number of sources as a problem for aviation safetyСлайд 67Monitoring for Error
Pilots must actively monitor the aircraft.
Consider changing title
of “Pilot-Not-Flying” (PNF) to “Pilot Monitoring” (PM)
Describes what the pilot
should be doing, (monitoring), versus what he/she is not doing, (not flying)Слайд 68Monitor / Crosscheck
This means mentally flying the aircraft, even though
the autopilot or other pilot is flying.
- monitor the flight
instruments as when hand flying- if the aircraft or Pilot Flying is not doing what it is supposed to do, the take appropriate actions to rectify
Слайд 70Fatigue
Less reliable memory – items missed
Reduced attention- tunnel vision, reduced
Withdrawn mood - more accepting of own
errors
Rough motor skills – poor timing
Слайд 71Workload Management
Ability to manage required tasks.
Know the capabilities and
reliability of crew
Detect work overload
Initiate assistance when required
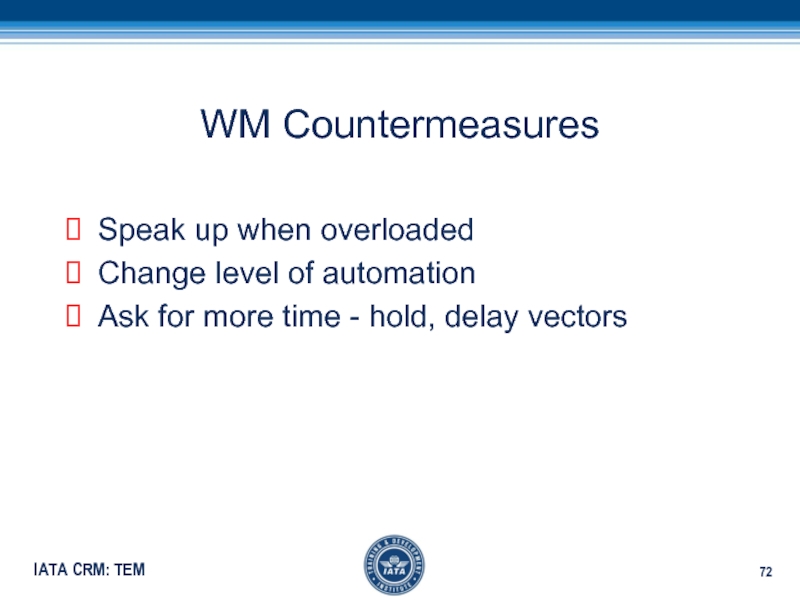
Слайд 72WM Countermeasures
Speak up when overloaded
Change level of automation
Ask for more
time - hold, delay vectors
Слайд 75In stressful situations, the captain will be better able to
manage the problem when not flying the aircraft!
Слайд 76Distractions
Interruptions can form holes in defenses
What can be done to
prevent distractions?
Sterile cockpit
Locked cockpit door
Слайд 77Distractions
Identify the interruption
Ask what was I doing before...
being interrupted
Decide what action to take to get back on track
Слайд 78Work as a CREW
One pilot is always monitoring during low
workload and both pilots are monitoring as much as possible
during high workloadPerform non-essential duties/activities during
lowest workload periods such as cruise
Strategically plan workload to maximize monitoring during those areas of vulnerability
i.e. stowing charts, approach briefing, PA’s
Слайд 79Vigilance
Is being alert to the situation, not only what is
happening, but what may happen
Anticipate problems
Gives you the ability to
think about options without being under the stress of an emergencyCannot be expected to be 100% vigilant during low workloads ie long haul flights, take turns monitoring
Particular attention must be devoted to altitude and course changes
Слайд 80Vigilance - Situational Awareness
Is being alert and applying knowledge of
what is normal
Anticipating what will happen
Prepare for problems that may
ariseWhat skills are used to maintain SA?
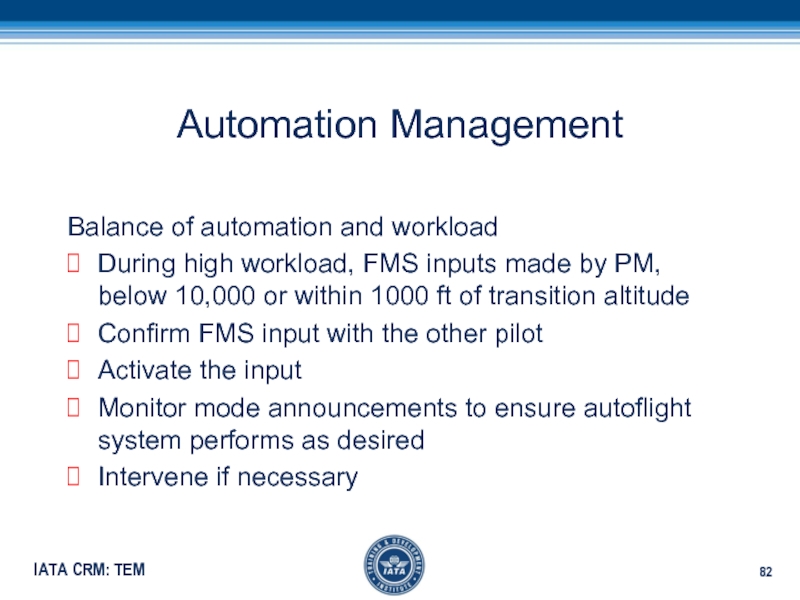
Слайд 82Automation Management
Balance of automation and workload
During high workload, FMS inputs
made by PM, below 10,000 or within 1000 ft of
transition altitudeConfirm FMS input with the other pilot
Activate the input
Monitor mode announcements to ensure autoflight system performs as desired
Intervene if necessary
Слайд 84Review/Modify Countermeasures
Use against unexpected threat or when aircraft is in
an undesired state.
Evaluation of plans – review and modify
plans when necessary
Inquiry – ask questions to clarify
Assertiveness – state critical information
with persistence
Слайд 85Evaluation of plans
Review and modify plans when necessary
- Review plan
to asses if course of action appropriate to the conditions
-
Consider alternativesConsider time available
Establish options
Слайд 86Inquiry
Ask questions to clarify – nothing taken for granted
- Actively
seek information
- Question ambiguous or difficult situations until
there
is understandingBetter to have questioned information before,
than to have to ask for help later!
Слайд 87Assertiveness
Making sure your viewpoint is understood
State critical information with persistence
Make
position known when safety is in question
Sense persons concern
Слайд 88Specific Phrases to Use
Are you ready for…?
What heading did he
give us?
I'm uncomfortable.
We are off our heading/altitude.
I thought he gave
us….Слайд 89Decision Making
for an Unexpected Threat
Perceive situation
- gather
and process information
- vigilant – alert to situation
- knowledge- variation from the normWhat is the risk?
Is it time critical?
Select a course of action
Слайд 91Preventing Error
Maintaining your health
High levels of training and proficiency
Following SOP’s
Proper
use of Checklists
Minimizing distractions
Planning ahead
Open two-way communication
Maintaining situational awareness
Слайд 92Barriers to Help Prevent Error
Checklists / SOP’s
Training / Proficiency
Team Climate
Planning
Health
Error
Avoidance
Слайд 93Health
Your health affects everything you do.
Thorough awareness of one’s own
limitations is a vital prerequisite for adapting to our flying
environment.the following affects our ability to perform
Noise
Medication
Diet
Stress
Fatigue - greatest workload is at the end of the flight, when one is most fatigued - be aware
Слайд 94Technological Proficiency
An expert pilot must constantly train. No expertise without
training and expertise is lost if training is not maintained,
need to practiceTechnical proficiency is important to TEM / CRM
Слайд 95Standard Operating Procedures
Establish a repeatable sequence or rhythm, so that
all items can be covered in a logical manner, easy
to pick up where it was left off if interruptedStandard use of phraseology – standard calls
Increased margin of safety – confirming actions by other pilot
Workload management is improved by specifying and prioritizing the duties each person is responsible for
Sets limits
Teamwork is standardized - can work with any crew
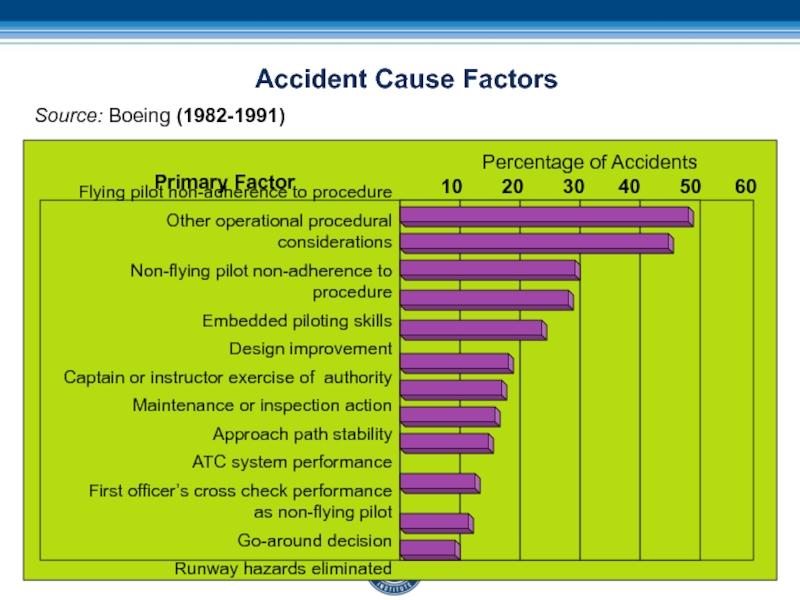
Слайд 96Accident Cause Factors
Flying pilot non-adherence to procedure
Other operational procedural
considerations
Non-flying pilot non-adherence to procedure
Embedded piloting skills
Design improvement
Captain or instructor
exercise of authorityMaintenance or inspection action
Approach path stability
ATC system performance
First officer’s cross check performance
as non-flying pilot
Go-around decision
Runway hazards eliminated
Percentage of Accidents
10 20 30 40 50 60
Primary Factor
Source: Boeing (1982-1991)
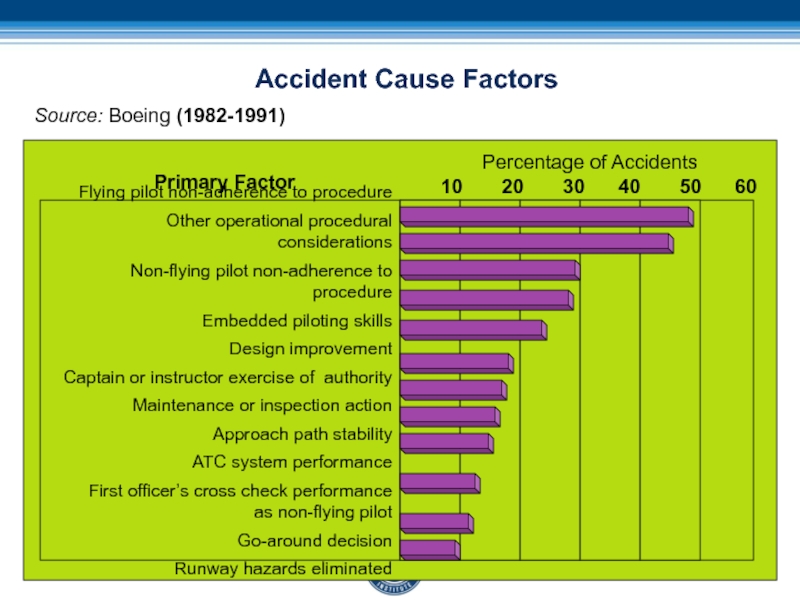
Слайд 97Accident Cause Factors
Flying pilot non-adherence to procedure
Other operational procedural
considerations
Non-flying pilot non-adherence to procedure
Embedded piloting skills
Design improvement
Captain or instructor
exercise of authorityMaintenance or inspection action
Approach path stability
ATC system performance
First officer’s cross check performance
as non-flying pilot
Go-around decision
Runway hazards eliminated
Percentage of Accidents
10 20 30 40 50 60
Primary Factor
Source: Boeing (1982-1991)
Слайд 98How SOP’s relate to error
data show that crews who intentionally
erred by not following SOP’s were 1.8 times more likely
to commit another error with consequential resultsIntentional crew non-compliance was a factor in 39.5% of accidents
Слайд 99Checklists
Proper checklist usage is...
...a basic strategy for error avoidance.
...essential
for safe flight operation of complex equipment.
...a countermeasure to mistakes
.Слайд 100Checklists
Helps prioritize items
Frees up brainpower for other tasks
Reminds us of
items when under pressure
Good reminder when we are fatigued
Standardization
Слайд 101What is Checklist abuse?
- Memorizing
- Self-initiating
- Ignoring, not
completing
- Not getting any responses
- Accepting incorrect response
-
Crew failed to verify settings visuallyHow do you handle the pilot who abuses checklists?
Слайд 102Checklist Errors
Fatigue and stress – increase chance of overlooking or
missing item when fatigued we prioritize tasks in order of
perceived importanceInterruptions – lose place
Do not put checklist down in its normal spot during interruption
Слайд 104Things you can do to help avoid error
Create a positive
team climate
Develop planning strategies
Слайд 105Team Climate
How do you create an atmosphere for constructive TEM?
by
developing and maintaining a good communication environment
effective leadership
Important in all
aspects of safety ( CRM/TEM)Слайд 106Error Avoidance - Planning
What/why is planning?
How accomplished
Briefings
Plans stated
Workload assignment
– distractions
Contingency management?
Слайд 109What is threat?
Are situations
external to the flight deck, that must be managed by
the cockpit crew during normal, everyday flights.Why is it a problem?
Such events increase the operational complexity of flight and pose a safety risk to the flight at some level – increase error potential
How do we respond to threat?
Countermeasures
Слайд 110Threats which originate outside the cockpit.
expected or unexpected things like
mechanical failures, adverse weather conditions, and ill passengers.
errors made by
the people we deal with during our flight, ground crew, air traffic control, maintenanceoversight in decisions made by those responsible for our working environment (latent).
Слайд 111Threats which originate outside the cockpit.
expected or unexpected things like
mechanical failures, adverse weather conditions, and ill passengers.
errors made by
the people we deal with during our flight, ground crew, air traffic control, maintenanceoversight in decisions made by those responsible for our working environment (latent).
Слайд 112Threats
Adverse weather Terrain
Airport conditions
Aircraft malfunctions
Automation events
Communication events
Operational time pressures
Non-normal
operations
ATC command events/errors
Cabin events/errors
Maintenance events/errors
Dispatch events/errors
Ground crew events/errors
Слайд 114Factors that affect our ability to operate safely without our
prior knowledge of their consequences.
People unwillingly create conditions for
crews to commit error by negligence in; - design
- manufacture
- regulations
- procedures
Latent Threats
Слайд 115Latent Threats
ATC practices
Scheduling practices that result in fatigue
Organizational, national, professional
culture
Aircraft characteristics
Qualification standards
Regulatory practices
Слайд 116Locked Cockpit Door
Ambiguous regulations – government
Untested aircraft systems – manufacturer
Flawed
procedures – SOP’s
-
Inadequate training – company
Слайд 117Runway incursions
Both pilots have taxi charts available
Both pilots monitor taxi
clearance
Captain will verbalize any hold short instructions, FO to request
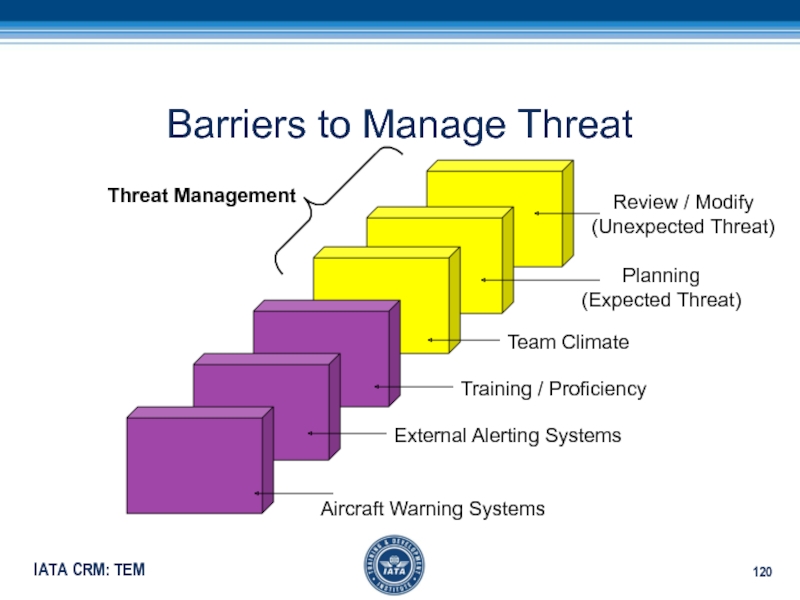
confirmation from Captain if not receivedСлайд 120Barriers to Manage Threat
External Alerting Systems
Aircraft Warning Systems
Team Climate
Review /
Modify
(Unexpected Threat)
Threat Management
Planning
(Expected Threat)
Training / Proficiency
Слайд 122Team Climate
Why is communication and leadership important to threat management?
Review
skills relevant to threat management with examples
Слайд 124LOSA Data
In complex or high threat conditions, performance is better
when First Officer is pilot fling
Captain can manage situation
Use automation
to decrease workloadСлайд 125Review/Modify
Unexpected threat
Evaluation of plans – reviewed and modified plans when
necessary
Inquiry – asked questions to clarify
Assertiveness – stated critical information
with persistenceСлайд 127Why do we make errors?
Lack of experience
Rushed
Distractions
Stress
Crews make mistakes several
times during each flight, most of which are unimportant
However it
can be beneficial to recognize and learn from errors, since it will help manage your resources better during the next flightСлайд 128Distractions
How do you manage distractions?
Prioritize
Tell intruder to be quiet
Sterile cockpit
Look
in books
Слайд 129Professional culture
Pilots have a strong professional culture with positive and
negative aspects
Positive
Strong motivation to do well
Pride in profession
Negative
Training that stresses
the need for perfectionSense of personal invulnerability
Слайд 130Personal Invulnerability
The majority of pilots agree that
Their decision-making is as
good in emergencies as in normal situations
Their performance is not
affected by personal problemsThey do not make errors under high stress
True professional can leave behind personal problems
ALL FALSE
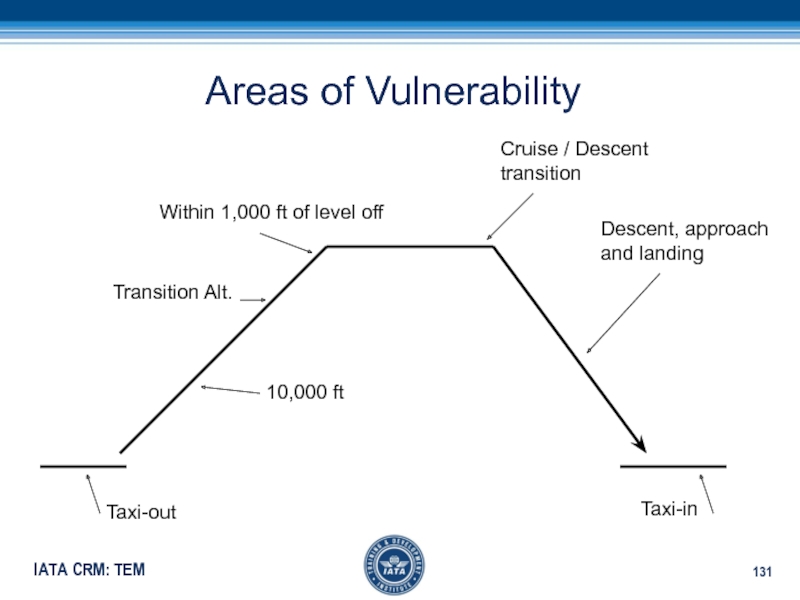
Слайд 131Areas of Vulnerability
Taxi-out
10,000 ft
Transition Alt.
Within 1,000 ft of level off
Cruise
/ Descent
transition
Descent, approach
and landing
Taxi-in
Слайд 132Flight Safety Foundation
Many of the accidents raise questions about pilot
training
Most accidents occur during the approach & landing phase
The approach
is only 11% of the flight timeThe landing is only 4% of the flight time
55% of all commercial aviation deaths are caused by controlled flight into terrain
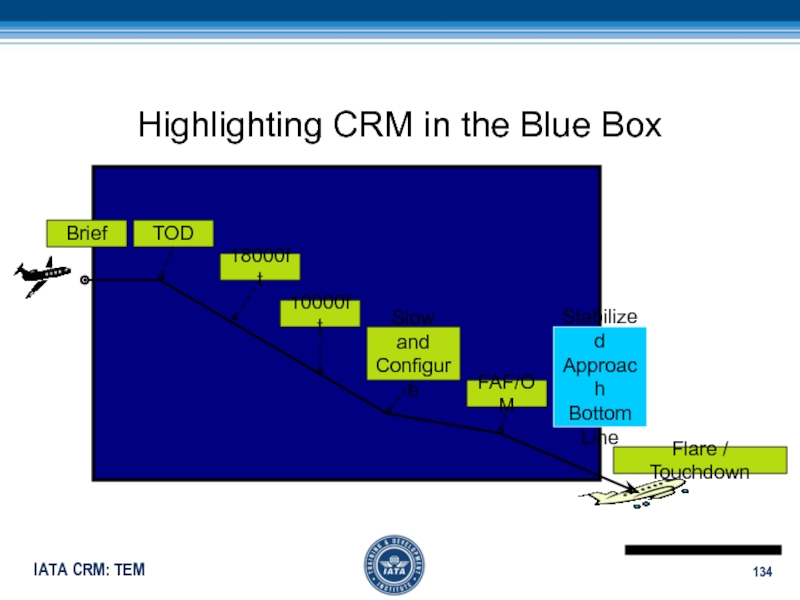
Слайд 134Highlighting CRM in the Blue Box
Brief
TOD
18000ft
10000ft
Slow and
Configure
FAF/OM
Stabilized
Approach
Bottom
Line
Flare / Touchdown
Слайд 135Blue Box
Most crew errors (LOSA)
Most consequential crew errors (LOSA)
Most accidents
worldwide (ALAR)
CFIT
Errors dealing with automated systems represent the largest source
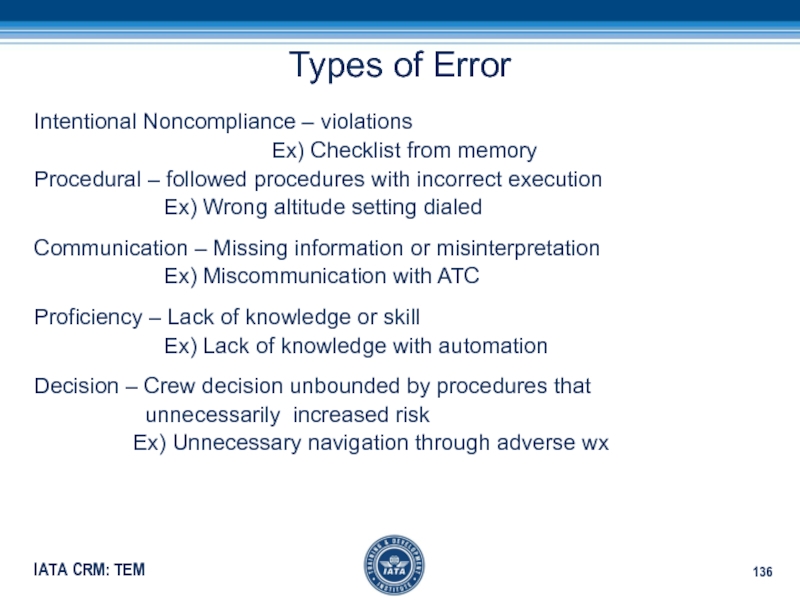
of errorСлайд 136Types of Error
Intentional Noncompliance – violations
Ex) Checklist from memory
Procedural –
followed procedures with incorrect executionEx) Wrong altitude setting dialed
Communication – Missing information or misinterpretation
Ex) Miscommunication with ATC
Proficiency – Lack of knowledge or skill
Ex) Lack of knowledge with automation
Decision – Crew decision unbounded by procedures that
unnecessarily increased risk
Ex) Unnecessary navigation through adverse wx
Слайд 137Barriers to Manage Error
External Alerting Systems
Aircraft Warning Systems
Team Climate
Execution
Error Management
Слайд 138Managing Errors
Once an error is committed, it is difficult to
catch (trap) your own error
Other people are more likely to
catch your errorTherefore redundancy is one strong defense against error
Слайд 139Managing Error Topics
Pilot invulnerability?
Culture?
Team Climate is important also
Distractions?
Execution
Monitor crosscheck
Workload management
Vigilance
Automation
management
Слайд 140 - Timely
- With respect
- Constructive intent
- Specific
- Use questionsGuidelines and Techniques for
EFFECTIVE CHALLENGING
Слайд 141Summary
What error management is
Why we need it
How are we going
to accomplish this
Team Building
leadership
Communication environment
Execution
Monitor / crosscheck
Workload management
Vigilance
Automation management
Слайд 144Undesired Aircraft State Management
UAS - Aircraft deviations at edge of
the
safety envelopeIncorrect aircraft configurations
Vertical deviations
Lateral deviations
Speed too high
Speed too low
Abrupt aircraft handling
Path/glide slope deviations
Unstable approach
Long landing
Firm landing
Wrong taxiway/runway
Runway incursion
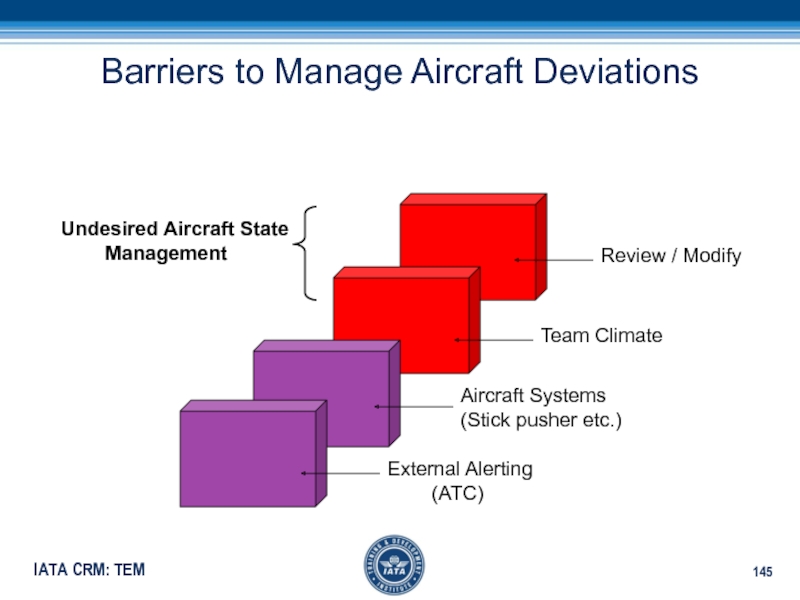
Слайд 145Barriers to Manage Aircraft Deviations
Aircraft Systems
(Stick pusher etc.)
Team Climate
Review /
Modify
Undesired Aircraft State
Management
External Alerting
(ATC)Слайд 150Threat
Latent Threats – National Culture,
Organizational Culture &
Policies
Professional Culture
Regulation
Overt Threats – Environmental Factors
Organizational Factors
Individual Factors
Team / Crew Factors
Aircraft Factors
External Error
Threat
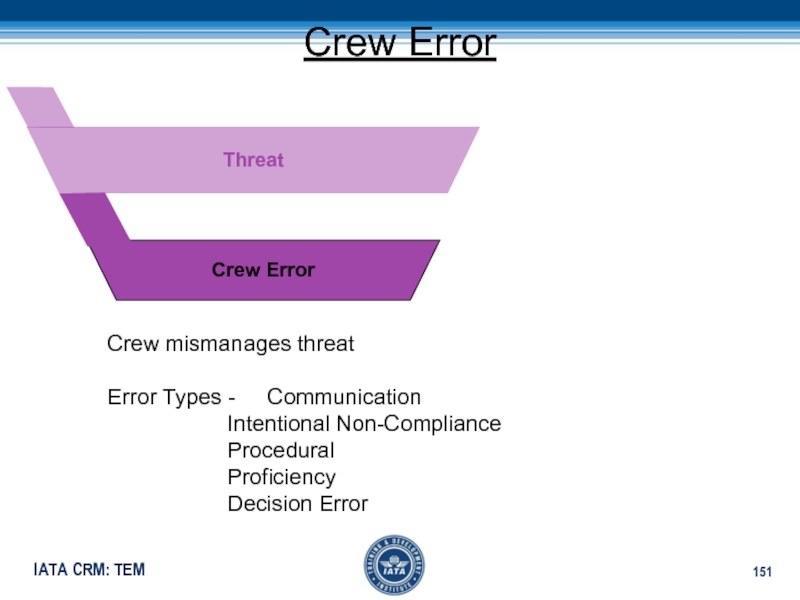
Слайд 151Crew Error
Crew mismanages threat
Error Types - Communication
Intentional Non-Compliance
ProceduralProficiency
Decision Error
Crew Error
Threat
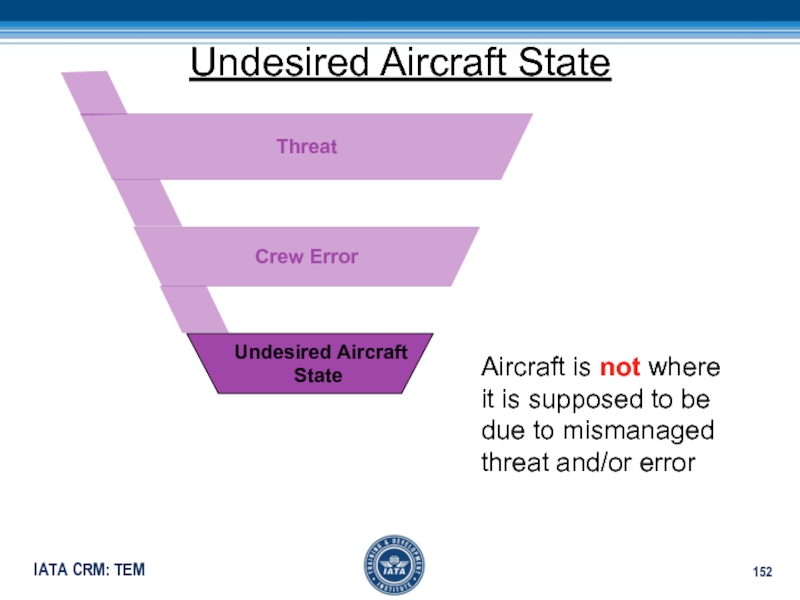
Слайд 152Undesired Aircraft State
Aircraft is not where it is supposed to
be due to mismanaged threat and/or error
Crew Error
Threat
Undesired AircraftState
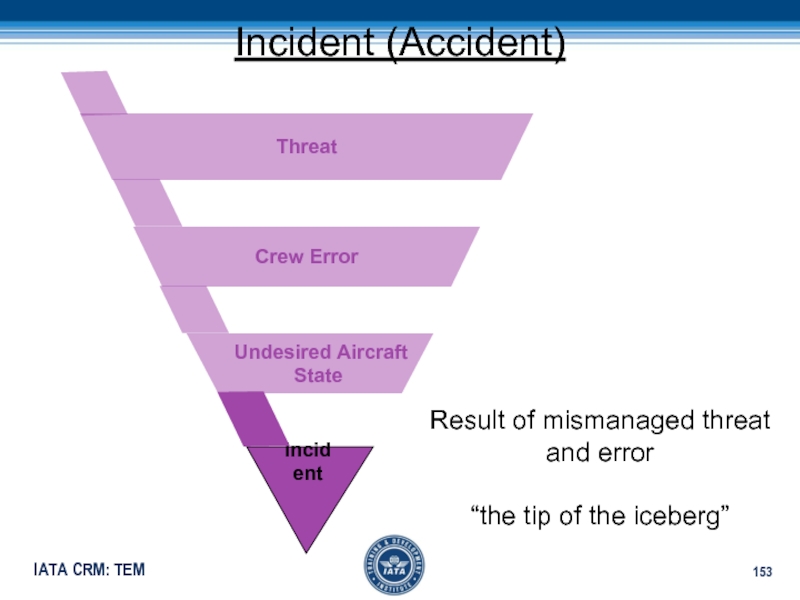
Слайд 153Incident (Accident)
Crew Error
Threat
Undesired Aircraft
State
Incident
Result of mismanaged
threat and error
“the tip of the iceberg”
Слайд 157How to Manage Threat and Error
Countermeasures
Error Avoidance
Threat Management
Error Management
Undesired Aircraft
State
Management
Слайд 160Error Avoidance
Proactive strategies to avoid committing errors
Planning
Following Sop’s and checklists
Team
climate behaviours such as active leadership and establishing a team
environmentSMS?
Complete avoidance is impossible – errors are inevitable
Must look for sources of error to strengthen system defenses
Слайд 161Error Avoidance
Human limitations lead to error
Limited memory capacity
Limited processing capacity
Multi-tasking
capability
Limits imposed by stressors
Tunnel vision
Limits imposed by fatigue or other
physiological factorsPoor group dynamics
Cultural influences
Organizational
Professional
National
Слайд 163Threat Management
Manage operational complexity, which translates into threat management.
Team climate
behaviours such as active leadership and establishing a team environment
planning
Review and modify countermeasures which include evaluation of plans, inquiry and assertiveness
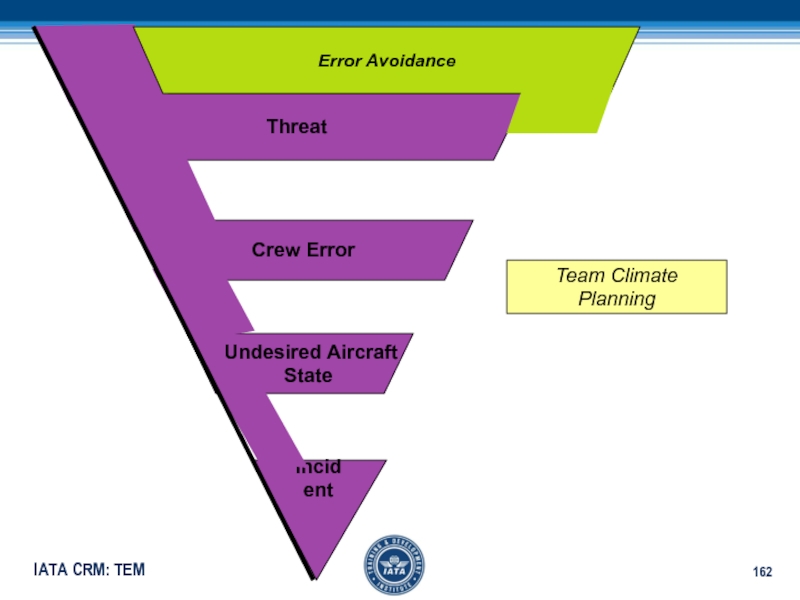
Слайд 164Threat
Crew Error
Undesired Aircraft
State
Incident
Error Avoidance
Threat Management
Team Climate, Planning
Review /Modify
Слайд 165Error Management
Manage crew errors.
Error is an inevitable result of human
limitations such as fatigue and other physiological factors, limited memory
and processing capacity, external stressors, poor group dynamics and cultural influencesTask execution behaviours such as monitoring and workload management are central to error management
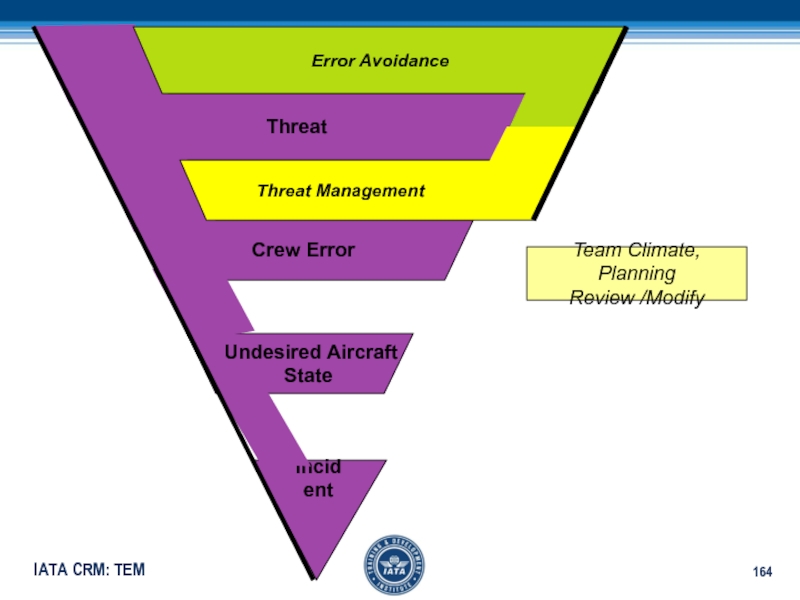
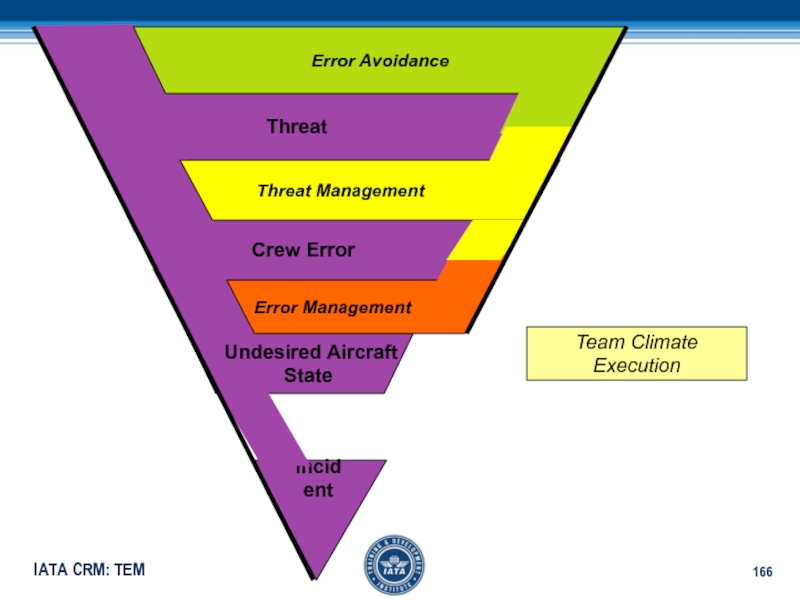
Слайд 166Threat
Crew Error
Undesired Aircraft
State
Incident
Error Avoidance
Threat Management
Error Management
Team Climate
Execution
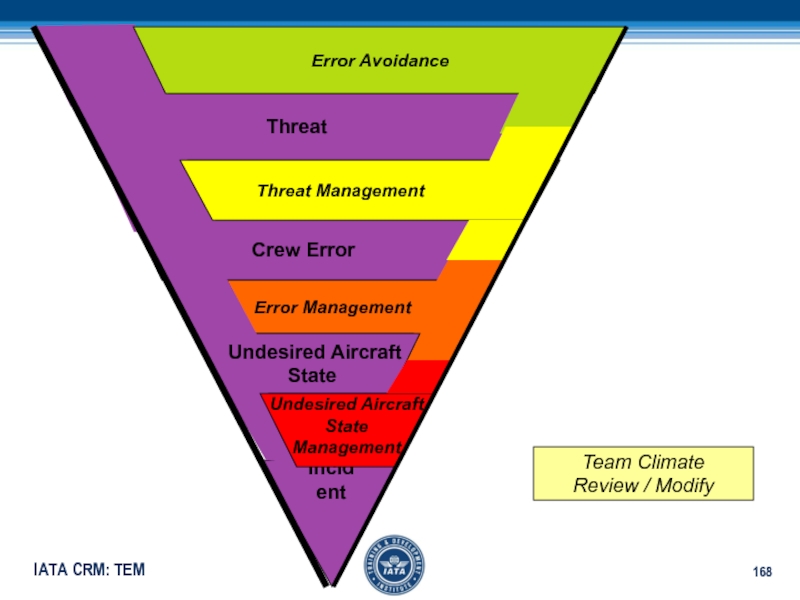
Слайд 167Undesired Aircraft State Management
Manage aircraft deviations, wrong configurations, speed etc.
Review
and modify countermeasures which include evaluation of plans, inquiry and
assertivenessСлайд 168Threat
Crew Error
Incident
Error Avoidance
Threat
Management
Error Management
Undesired Aircraft
State
Undesired Aircraft
State
Management
Team Climate
Review
/ ModifyСлайд 169 Threat
Crew Error
Undesired Aircraft
State
Incident
Error Avoidance
Threat ManagementError Management
Undesired Aircraft
State
Management
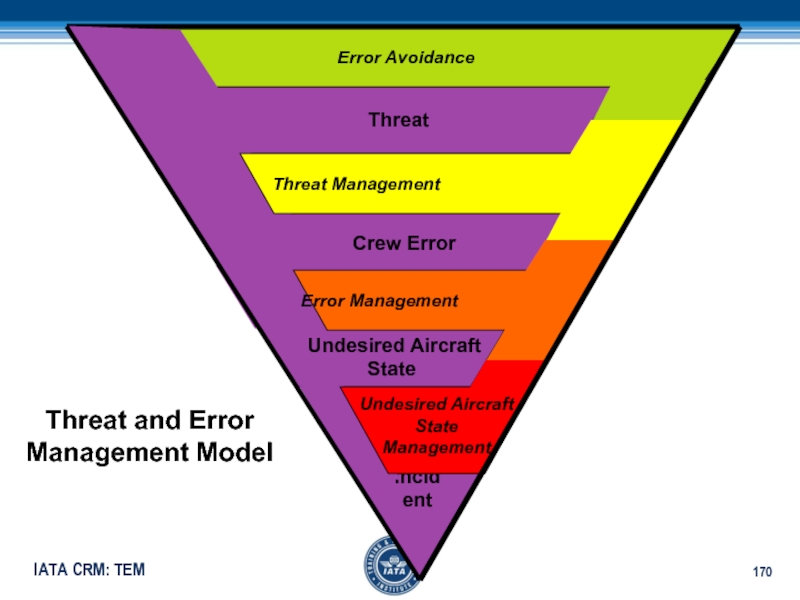
Threat and Error
Management Model
Слайд 170 Threat
Crew Error
Undesired Aircraft
State
Incident
Error
Avoidance Threat Management
Error Management
Undesired Aircraft
State
Management
Threat and Error
Management Model
Слайд 174Productivity
Errors cost money
Find out where mistakes are being made
and
adjust resources
Better use of training
Слайд 175Expose Yourself!!!
How can management better understand what is happening
on the line?
By fostering a culture where
crews can confess honest mistakes without fearing reprisal Using your own incidents for training
Слайд 176Management’s Role
establish trust, which includes
a commitment to reduce
error-inducing conditions.
adopt
a non-punitive policy toward error
provide training
collect ongoing data?
Слайд 177Feedback
Need a process to identify and feedback threat and error
information, not only from the crew but from the other
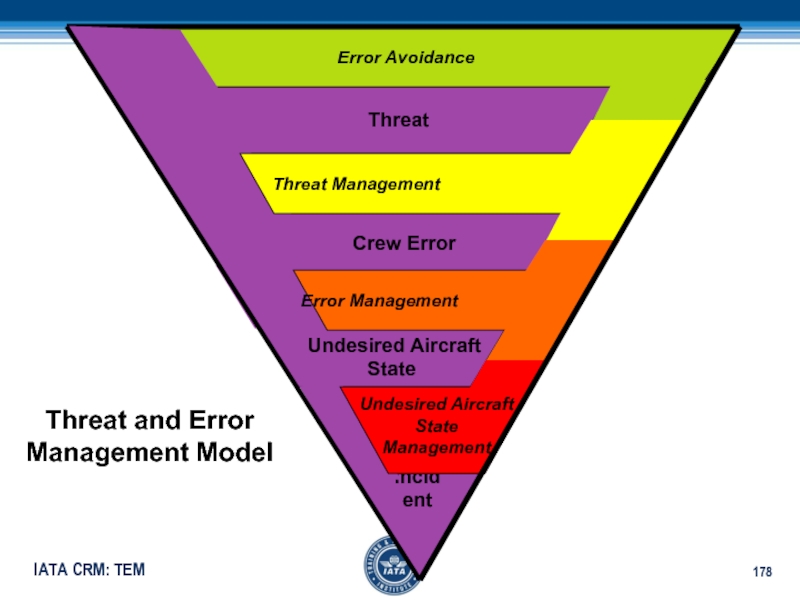
safety barriersСлайд 178 Threat
Crew Error
Undesired Aircraft
State
Incident
Error
Avoidance Threat Management
Error Management
Undesired Aircraft
State
Management
Threat and Error
Management Model
Слайд 179How does TEM fit into a
Safety Management System?
TEM supports
SMS by bringing in hard data
Linkage between Safety and CRM
/TEM Safety change process
TEM can be used for a focus group at an airline
Слайд 180TEM at the Organizational level
Recognize dangers of threat and error
Provide
training in threat and error management
Understand limitations of crew
Collect
data - LOSA and Latent threatsMistakes will be made, reward crew for pointing it out and correcting it
Слайд 181Data Collection
Company, industry and regulating authorities get information of the
“real” problems that line pilots face
Cannot prevent the creation of
latent threats but make their adverse consequence visible to those who manage and operate the systemСлайд 182 More Realistic Training
Focus on Threat and Error Recognition
Provide
countermeasure skills to crews
Feedback-help management understand
line operation Слайд 183Tools to Improve Safety
SOP’s and Checklists
- strategies put forth by the company
Training - Technical
proficiency - Countermeasure (CRM) skills
TEM model as an analytical tool of incidents