Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Informatics Class 2
Содержание
- 1. Informatics Class 2
- 2. Chapter 1Class objectives 1 Describe the
- 3. Digital Economy – New EconomyE-Business: The
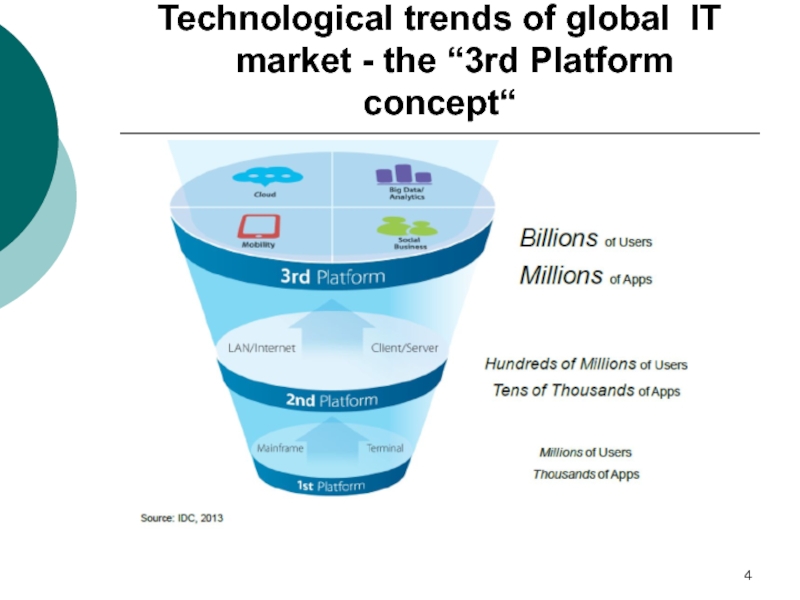
- 4. Technological trends of global
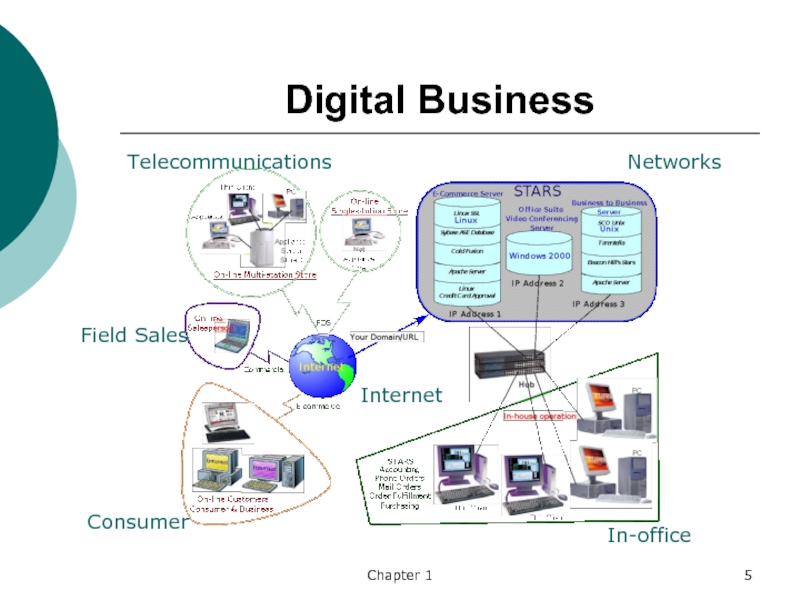
- 5. Chapter 1Digital BusinessNetworksInternetTelecommunicationsConsumerIn-officeField Sales
- 6. Chapter 1The Old Economy – Taking Photo’sBuy
- 7. Chapter 1The New Economy – Taking Photo’s1st
- 8. Business ModelsA business model is a method
- 9. Chapter 1Digital Age Business ModelsName-Your-Own PriceReverse AuctionsAffiliate MarketingE-Marketplaces and ExchangesElectronic aggregation (buying groups)
- 10. Chapter 1Drivers Forcing Changes In Business ModelsEnvironmental,
- 11. Chapter 1The Drivers of changeBusiness Pressures on an Organization that force change.MarketTechnologySociety
- 12. Chapter 1The Drivers of change ContinuedBusiness Pressures on an Organization.MarketSocietyTechnology
- 13. Chapter 1Organizational Response to these DriversStrategic SystemsContinuous
- 14. Chapter 1Information SystemAn information system (IS) collects,
- 15. Chapter 1Information System as a sequence of processes
- 16. Chapter 1Computer Based Information SystemHardwareSoftwareDataNetworkProceduresPeopleHardwareSoftwarePeopleDataApplicationMore than hardware and software
- 17. Chapter 1Applications and OperationsRetail operationsWholesaleManufacturingHuman ResourcesMarketingContent management…
- 18. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectiveMarketingIdentify customersDetermine what they wantPlanning productsAdvertising and promoting productsDetermine prices for products
- 19. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectiveSalesContact customersSell the productTake the orderFollow-up on the sale1-2 year sales forecast
- 20. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectiveManufacturingControl Equipment and machineryDesign
- 21. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectivePurchasing ( procurement)Which vendorsQuantity to purchaseRebate trackingHandle delivery mismatchesGenerate the purchase order
- 22. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectiveFinanceFinancial AssetsInvestment managementBankingLong term budgets
- 23. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectiveAccountingAccounts ReceivableDisbursementsPayrollDepreciationEarned Rebates…
- 24. Chapter 1Information SystemsFunctional PerspectiveHuman ResourcesEmployee wages, salaries
- 25. Chapter 1Trends in TechnologyCost-performance ratio of chips
- 26. Chapter 1 Trends in TechnologyInternetMobile Computing and M-CommerceWireless networksUbiquitous ComputingSmart Devices
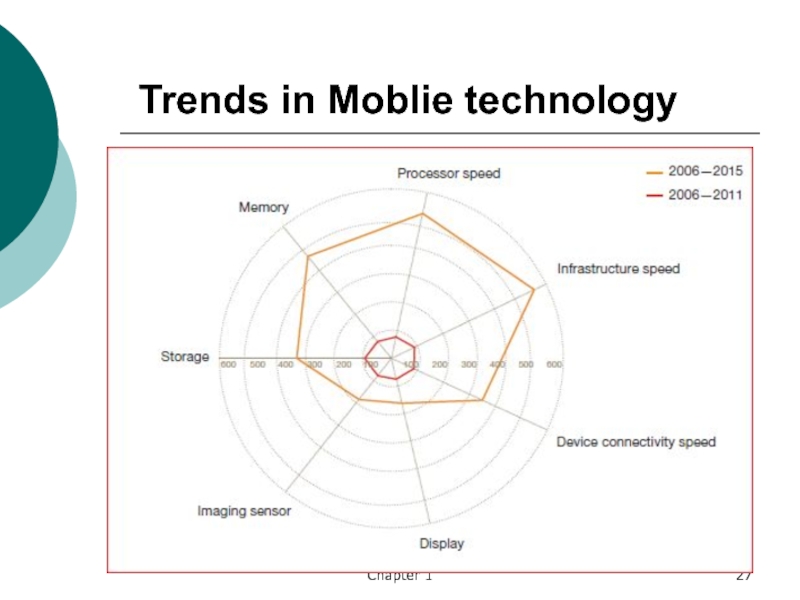
- 27. Trends in Moblie technology Chapter 1
- 28. Chapter 1Trends in Technology (continued)The Network ComputerOptical NetworksStorage Area NetworksIntranets & ExtranetsThe InternetThe Networked Enterprise
- 29. Chapter 1Why Study Information Technology ?You will
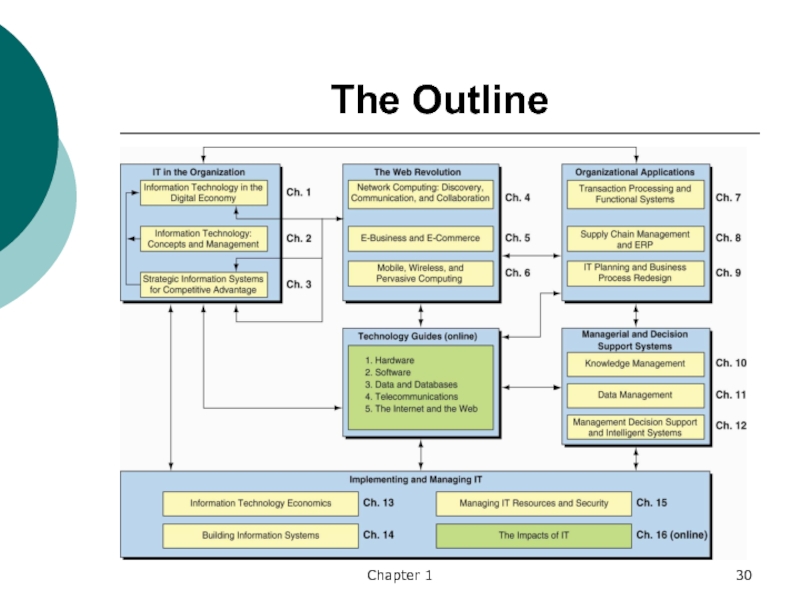
- 30. Chapter 1The Outline
- 31. Chapter 1MANAGERIAL ISSUESRecognizing opportunities for using IT
- 32. Chapter 1MANAGERIAL ISSUES ContinuedEthics and social issues.
- 33. Chapter 1 Questions ?
- 34. Скачать презентанцию
Chapter 1Class objectives 1 Describe the characteristics of the digital economy and e-business.2 Recognize the relationships between business pressures, organizational responses, and information systems.3 Identify the
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Chapter 1
Class objectives
1 Describe the characteristics of the
digital economy and e-business.
2 Recognize the relationships between
business pressures, organizational responses, and information systems.3 Identify the major pressures in the business environment and describe the major organizational responses to them.
4 Define computer-based information systems and information technology.
5 Describe the role of information technology in supporting the functional areas, public services and specific industries
6 List the new technology development in the areas of generic and networked computing and Web-based systems.
7 Understand the importance of learning about information technology.
Слайд 3
Digital Economy – New Economy
E-Business: The use of electronic technologies
to transact business.
Collaboration: People and Organizations interact, communicate, collaborate and
search for informationInformation Exchange: Storing, processing and transmission of information.
Слайд 6Chapter 1
The Old Economy – Taking Photo’s
Buy film in a
store
Load your camera
Take pictures
Take roll of film to store for
processingPickup the film when ready
Select specific photos for enlargement
Mail to family and friends
Слайд 7Chapter 1
The New Economy – Taking Photo’s
1st Generation Digital Photography
Old
economy except 6 and 7 were replaced by using a
scanner and emailing2nd Generation Digital Photography
Use a Digital Camera, no film, no processing.
3rd Generation Digital Photography
Your Digital Camera is now your mobile phone, in your binoculars or a palmtop computer.
Слайд 8Business Models
A business model is a method of doing business
by which a company can generate revenue to sustain itself.
The model spells out how the company adds value to create a product or service. (Value- add Chain model )Apple makes and sells smart phones
A TV station provides free broadcasting. Its survival depends on a complex model involving advertisers and content providers.
Internet portals, such as Yandex, use a complex business model.
Changing
Слайд 9Chapter 1
Digital Age Business Models
Name-Your-Own Price
Reverse Auctions
Affiliate Marketing
E-Marketplaces and Exchanges
Electronic
aggregation (buying groups)
Слайд 10Chapter 1
Drivers Forcing Changes In Business Models
Environmental, organizational, and technological
factors are creating a highly competitive business environment ; these
factors or forces can change quickly, sometimes in an unpredictable manner.Therefore, companies need to react frequently and quickly to both the threats and the opportunities resulting from this new business environment. A response can be a reaction to a pressure already in existence, an initiative intended to defend an organization against future pressures, or an activity that exploits an opportunity created by changing conditions.
Business Pressures
Business Critical Response Activities
Слайд 11Chapter 1
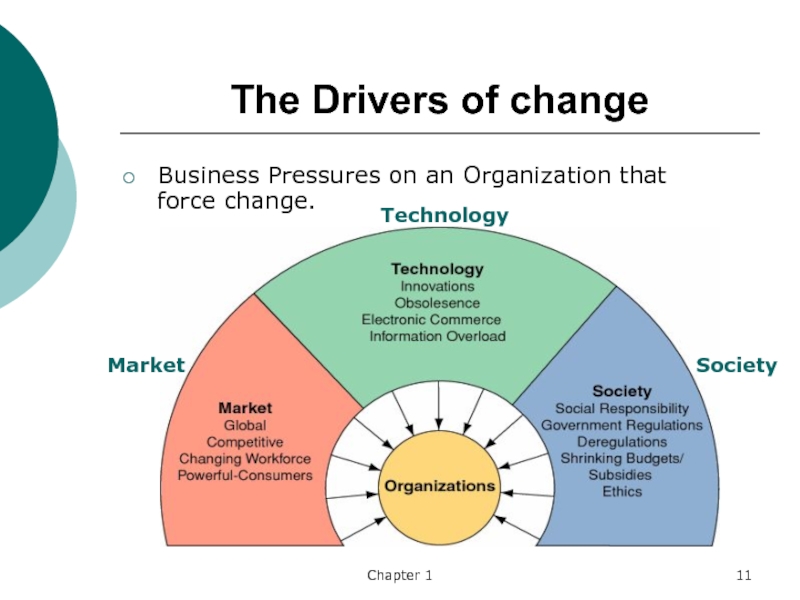
The Drivers of change
Business Pressures on an Organization that
force change.
Market
Technology
Society
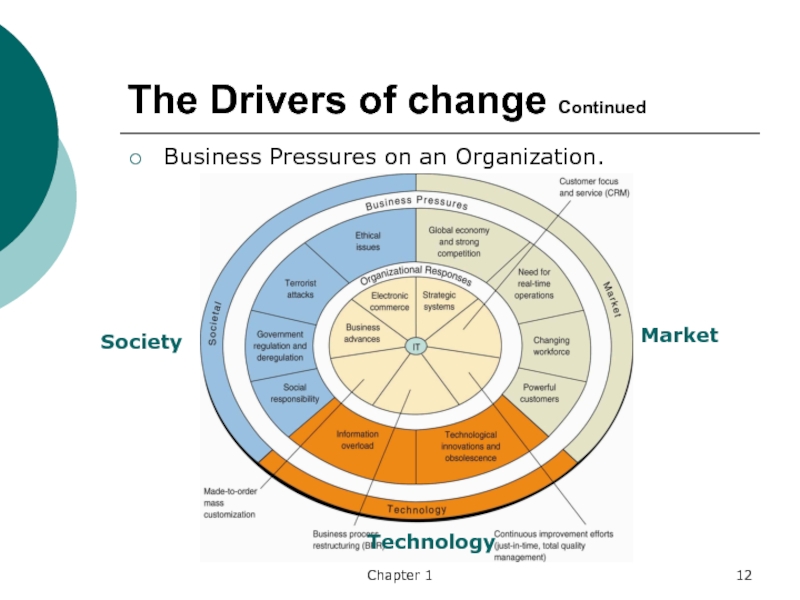
Слайд 12Chapter 1
The Drivers of change Continued
Business Pressures on an Organization.
Market
Society
Technology
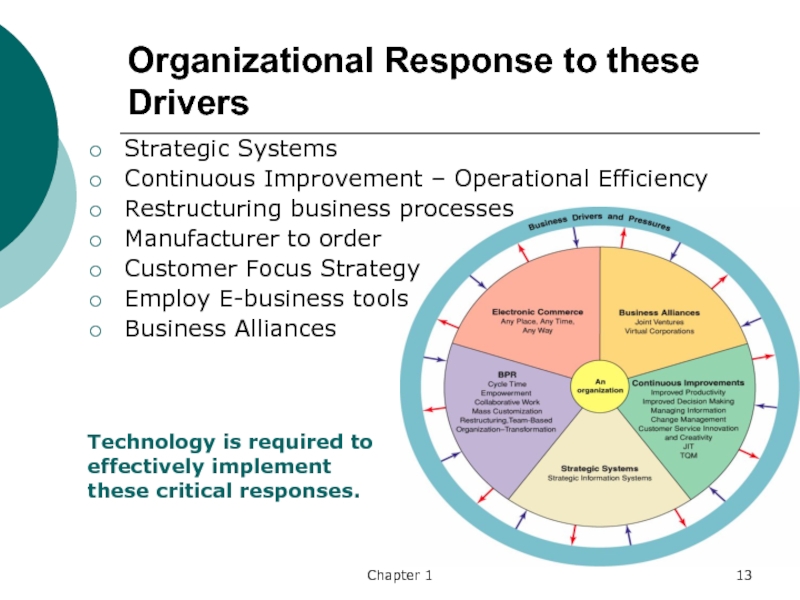
Слайд 13Chapter 1
Organizational Response to these Drivers
Strategic Systems
Continuous Improvement – Operational
Efficiency
Restructuring business processes
Manufacturer to order
Customer Focus Strategy
Employ E-business tools
Business Alliances
Technology
is required to effectively implement these critical responses. Слайд 14Chapter 1
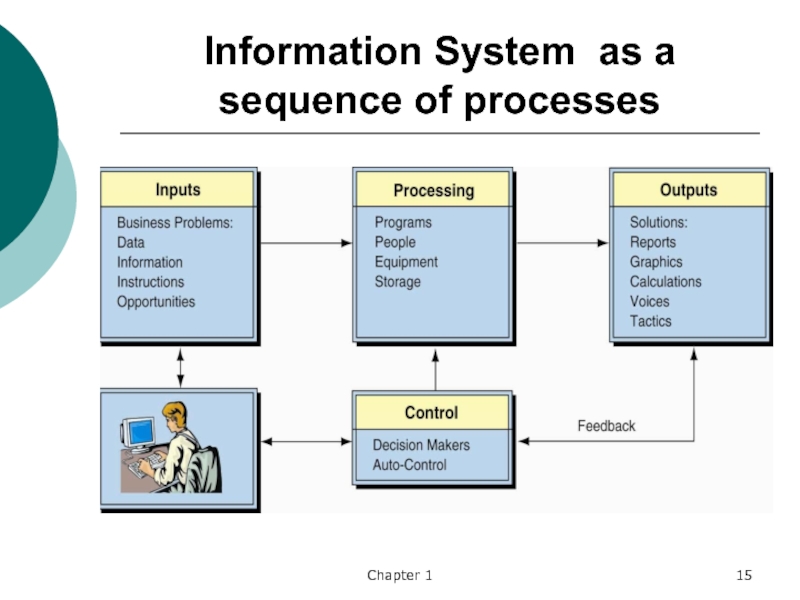
Information System
An information system (IS) collects, processes, stores, analyzes,
and disseminates information for a specific purpose. Like any other
system, an information system includes inputs (data, instructions) and outputs (reports, calculations). It processes the inputs by using technology such as PCs and produces outputs that are sent to users or to other systems via electronic networks and a feedback mechanism that controls the operation.Input
Output
Process
Feedback
Control
Слайд 16Chapter 1
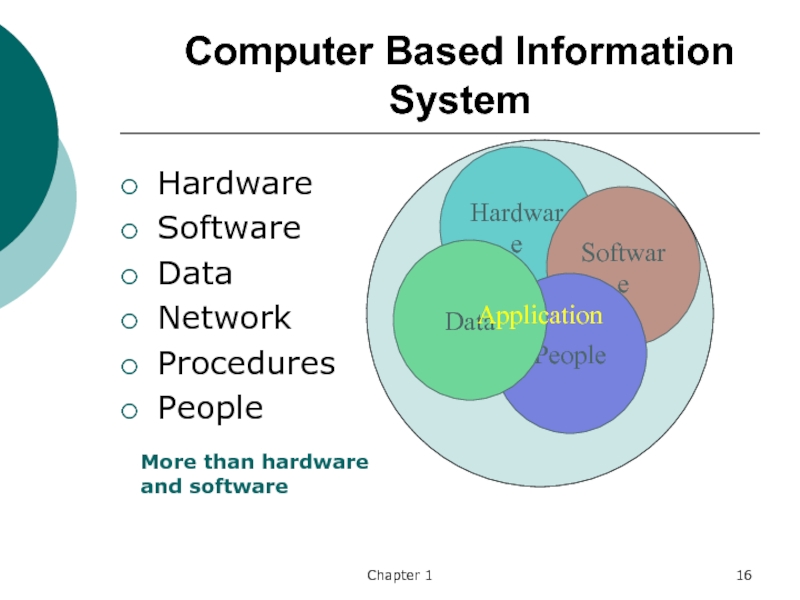
Computer Based Information System
Hardware
Software
Data
Network
Procedures
People
Hardware
Software
People
Data
Application
More than hardware and software
Слайд 17Chapter 1
Applications and Operations
Retail operations
Wholesale
Manufacturing
Human Resources
Marketing
Content management
…
Слайд 18Chapter 1
Information Systems
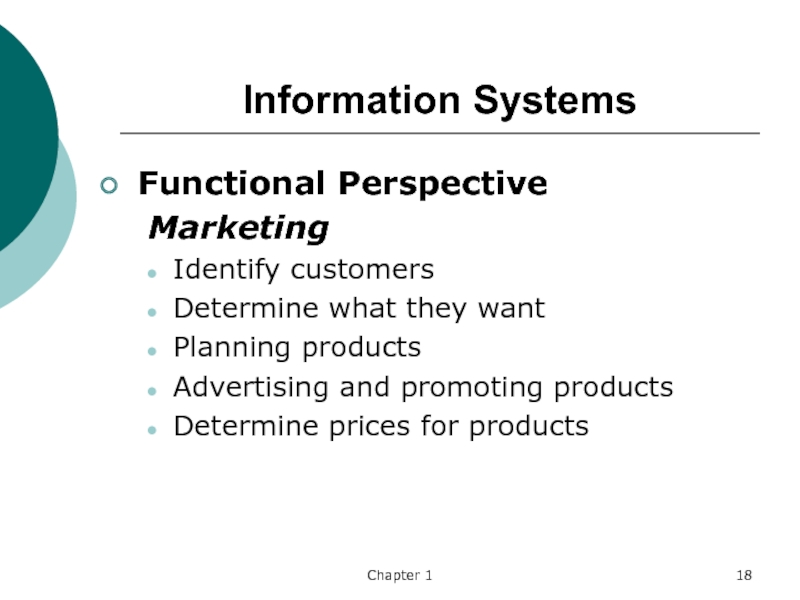
Functional Perspective
Marketing
Identify customers
Determine what they want
Planning products
Advertising and
promoting products
Determine prices for products
Слайд 19Chapter 1
Information Systems
Functional Perspective
Sales
Contact customers
Sell the product
Take the order
Follow-up on
the sale
1-2 year sales forecast
Слайд 20Chapter 1
Information Systems
Functional Perspective
Manufacturing
Control Equipment and machinery
Design new products
Quantity of
components to produce
New production facilities
Generate the work order
Слайд 21Chapter 1
Information Systems
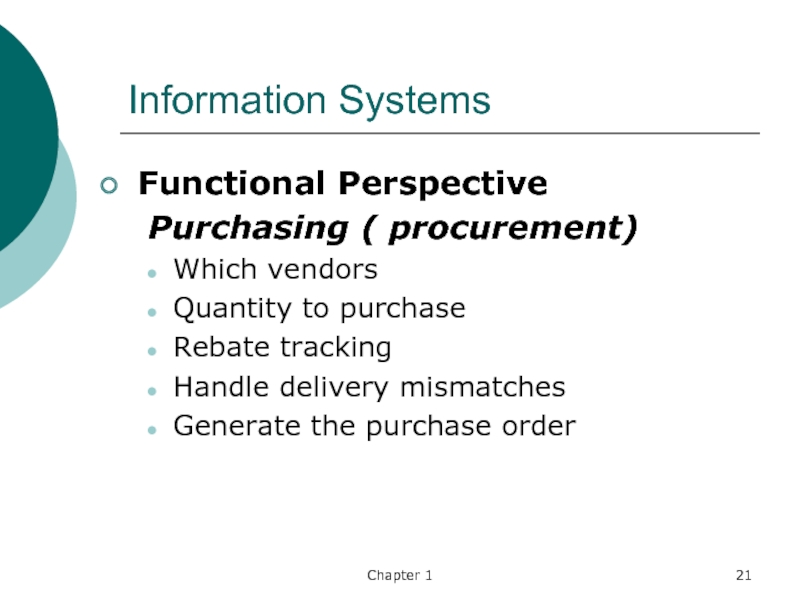
Functional Perspective
Purchasing ( procurement)
Which vendors
Quantity to purchase
Rebate tracking
Handle
delivery mismatches
Generate the purchase order
Слайд 22Chapter 1
Information Systems
Functional Perspective
Finance
Financial Assets
Investment management
Banking
Long term budgets
Слайд 23Chapter 1
Information Systems
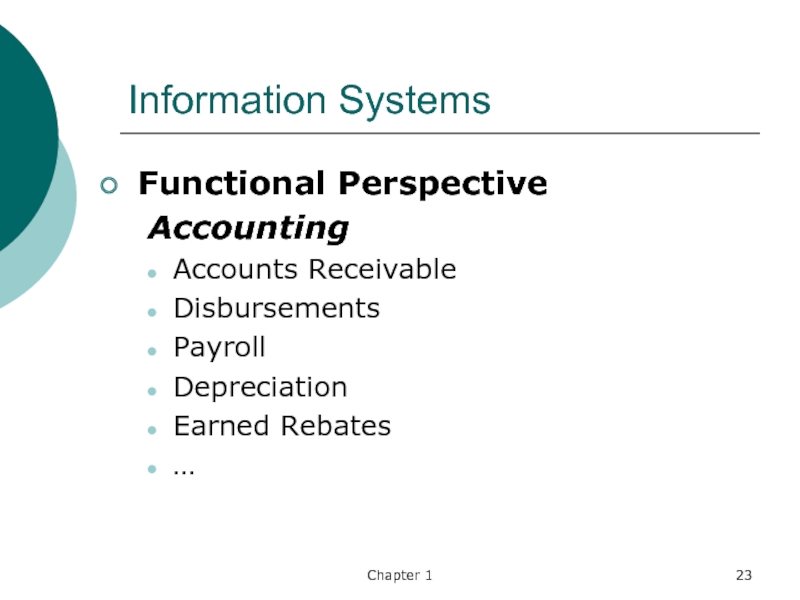
Functional Perspective
Accounting
Accounts Receivable
Disbursements
Payroll
Depreciation
Earned Rebates
…
Слайд 24Chapter 1
Information Systems
Functional Perspective
Human Resources
Employee wages, salaries & benefits
Long term
labor requirements
Tracking vacation, sick,
Track employee skills
Interviewing employees
Слайд 25Chapter 1
Trends in Technology
Cost-performance ratio of chips keeps improving. Moore’s
Law, his prediction was that the processing power of silicon
chips would double every 18 months.According to McGarvey & tenornetworks.com, states that the performance of optical communication networks is growing by a factor of 10 every three years
Several new devices and methods to increase storage capacity price performance
Object technology enables the development of self-contained units of software that can be shared
Networked and distributed computing is emerging rapidly Metcalfe’s Law.
Слайд 26Chapter 1
Trends in Technology
Internet
Mobile
Computing and M-Commerce
Wireless networks
Ubiquitous Computing
Smart Devices
Слайд 28Chapter 1
Trends in Technology (continued)
The Network Computer
Optical Networks
Storage Area Networks
Intranets
& Extranets
The Internet
The Networked Enterprise
Слайд 29Chapter 1
Why Study Information Technology ?
You will be more effective
in your chosen career if you understand how successful information
systems are built, used, and managed.You also will be more effective if you know how to recognize and avoid unsuccessful systems and failures.
Developing “Computer” Literacy will only enhance your “Information” Literacy
Слайд 31Chapter 1
MANAGERIAL ISSUES
Recognizing opportunities for using IT and Web-based systems.
Who will build, operate, and maintain the information systems. This
is a critical issue because management wants to minimize the cost of IT while maximizing its benefits. Some alternatives are to outsource portions, or even all, of the IT activities, and to divide the remaining work between the IS department and the end users. How much IT? This is a critical issue related to IT planning. IT does not come free, but not having it may be much costlier.
How important is IT? In some cases, IT is the only approach that can help organizations. As time passes, the comparative advantage of IT increases.
Is the situation going to change? Yes, the pressures will be stronger as time passes. Therefore, the IT role will be even more important.
Globalization. Global competition will have an impact on many companies. However, globalization opens many opportunities, ranging from selling and buying products and services online in foreign markets, to conducting joint ventures or investing in them. IT supports communications, collaboration, and discovery of information regarding all the above.
Слайд 32Chapter 1
MANAGERIAL ISSUES Continued
Ethics and social issues. The implementation of
IT involves many ethical and social issues that are constantly
changing due to new developments in technologies and environments. These topics should be examined any time an IT project is undertaken.Transforming the organization to the digital economy. The transformation can be done on several fronts. Management should study the opportunities, consider alternatives and prioritize them.