Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Kazakh National Medical University named after S.D. Asfendiayrov Department
Содержание
- 1. Kazakh National Medical University named after S.D. Asfendiayrov Department
- 2. Infection (infectious process) - a
- 3. Infectious diseases - is the extreme manifestation
- 4. Pathogens - is the potential
- 5. Exotoxins - labile proteins secreted by microbes
- 6. The degrees of pathogenicity of a microbe
- 7. For origin and development of infectious disease
- 8. Source of infection:SoilAirFoodhousehold objectsBacteria carriager
- 9. TransmissionAirborneFecal-oralBy ContactПарантеральныйGenitalTransmissivetransplacentalФАКТОРЫ ПЕРЕДАЧИ:
- 10. Factors of transmission
- 11. PERIODS OF INFECTIONIncubation - from infection to
- 12. CLASSIFICATION OF INFECTIONSBY THE CAUSATIVE AGENT bacterial
- 13. BY DURATION: acute chronic persistent (long-term experience
- 14. source of infection: anthroponoses (of people) –
- 15. ON the spread of germs and toxins:
- 16. Pathogenicy factorsHyaluronidase - cleaves hyaluronic acid intercellular
- 17. Particular viral infectionsObligate parasitism of the virus,
- 18. FORMS OF VIRAL INFECTIONProductive - acute, accompanied
- 19. Immunity
- 20. What is immunity?It is the capability of
- 21. Слайд 21
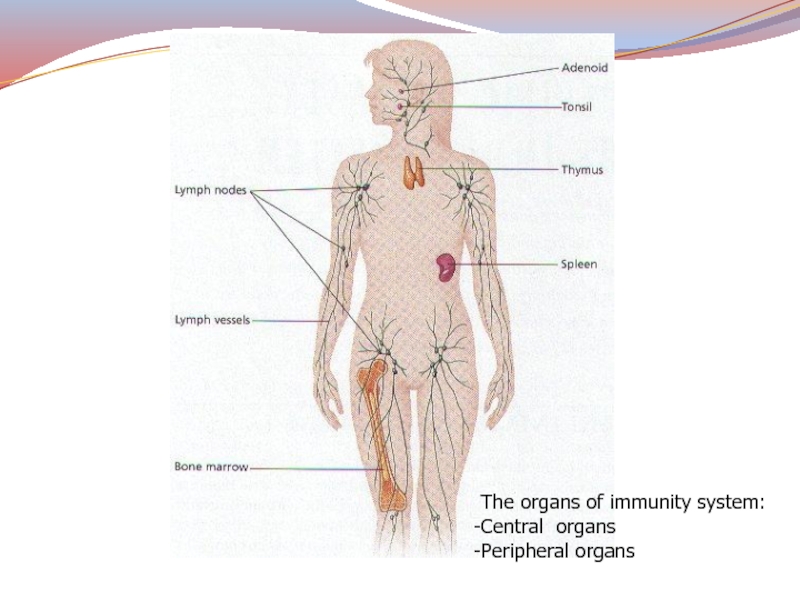
- 22. The organs of immunity system:Central organsPeripheral organs
- 23. I Innate immunity II Adaptive immunityNaturalsterile (after
- 24. Cellular immunity - this is the function
- 25. Humoral immunity - this is the function
- 26. Initial immune response occurs when you first
- 27. The immune response to all types of
- 28. First-Line Defenses /Innate Immune System- The body's first
- 29. Inflammatory response causes Redness - due to
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Skin and mucosaThe barrier functionThe bactericidal propertiesMechanical
- 32. PhagocytosisThe functions of phagocytes:ProtectiverepresentingSecretory (IL-1)Stages of phagocytosis:chemotaxisAdhesionendocytosisEducation
- 33. humoral factorsLysozyme - thermo-stable protein (muramidase). Produced
- 34. THE IMMUNE SYSTEMThe hierarchical unity of organs
- 35. The Cells of Immunity SystemImmunocompetent - capable
- 36. lymphocytesLM T - cell immune responseLM B
- 37. В- ЛМ (20 % of lymphocytes in
- 38. Antigens - substances of any origin, can
- 39. Types of AntigensGeteroantigens- common Antigens, found in
- 40. Immunological tolerance - the body does not
- 41. An antibody is a protein produced in
- 42. types of immunoglobulins5 types of immunoglobulins:Ig GIg MIg A (sIg A)Ig EIg D
- 43. Ig G (80% serum Ig). They are
- 44. applied immunologyVaccines and toxoids - drugs to
- 45. Vaccination: A vaccination is an injection of
- 46. REQUIREMENTS FOR VACCINESHigh immunogenicity (ability to provide reliable anti-infectious protection)AREAKTOGENNOST (no significant side reactions)HARMLESSNESSMINIMUM sensitizing effect
- 47. CLASSIFICATION OF VACCINESAccording to methods preparationLive (attenuated)InactivatedanatoxinsChemicalsRecombinantGenetic engineeringAnti-idiotype in progressliposomal developmentBacterialviral
- 48. Living vaccineThese drugs are made from live
- 49. Killed vaccineThis suspension of killed microbes in
- 50. CHEMICAL VACCINEThis product containing the active bacteria
- 51. ANATOXINSIt is neutralized exotoxin which produced by
- 52. Immune serum and immunoglobulinsThis preparations the introduction
- 53. Serum products are divided into:Heterologous (obtained from
- 54. ImmunoglobulinsIt is highly purified, concentrated gamma globulin
- 55. diagnostic drugsThis diagnostic serum and diagnostic tools
- 56. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1 Kazakh National Medical University named after S.D. Asfendiayrov Department of
Microbiology, Virology and Immunology
infection. Immunity. Types and forms of umminity. Factors specific and nonspecific defense. Serological reaction. Antigens. Antibodies. The Basic principles of immunization and immunotherapyСлайд 2 Infection (infectious process) - a set of physiological and
pathological processes, emerging and developing in the body when introducing
him pathogens that cause a violation of the constancy of its internal environment and physiological responses (Timakov). - invasion of a host organism by microorganism, proliferation of the invading organism, and host reactionFor the development of the infectious process must be 3 factors:
The pathogenic microbe
The susceptible microorganism
Certain environmental conditions
Слайд 3Infectious diseases - is the extreme manifestation of infection.
It is
distinguished from other diseases::
The presence of a pathogenic microbe
The contagiousness
Cyclicality (proceeds periods)
Specific reactions of the organism to the pathogen
Development of immunity
Bacteria carriage
Слайд 4 Pathogens - is the potential ability to cause disease
(species characteristic). VIRULENCE of microbes - is the degree of pathogenicity
(the strain sign).
Pathogenicity factors of microbes:
Adhesion
COLONIZATION – presence of microorganisms on skin or mucosa, no penetration into tissues.
Invasions - the penetration and proliferation associated with the introduction of live tissue (due to the enzyme hyaluronidase, neuraminidase, plasma coagulase)
Suppression of phagocytosis (by capsule, M protein from streptococcal protein A from Staphylococcus, cord factor in the tubercle bacillus)
AGRESSINS - substances that suppress the body's defenses and enhancing pathogens
Toxin - a poisonous substance produced by pathogenic microbes. Divided into exo-and endotoxins.
Слайд 5Exotoxins - labile proteins secreted by microbes in the environment,
are highly toxic. Characterized Organotropona, virulence, antigenicity, immunogenicity. By the
mechanism of action are divided into : - Neurotoxins (tetanus) - Histo toxins (diphtheria) - Enterotoxins (cholera) - Hemolysin (lysis of red blood cells - strep) -leycocidins (staph) Can be transformed into anatoxin - exotoxin is deprived of toxicity, but has antigenic and immunogenic properties. It is used to prevent infections. Endotoxins - thermostable lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a part of the cell wall, gram (-) are detection of the destruction of bacteria. They do not have specificity. The antigenicity and immunogenicity is the weak. The cause of cardiac depression and low body temperature.Слайд 6The degrees of pathogenicity of a microbe - VIRULENCE denoted:
Dlm
- dosis letalis minima - min. mortality. dose - the
smallest number of living microbes, causing the death of 80% -95% of the animalsDlc - dosis letalis certa - certainly lethal dose - from which killed 100% of infected animals.
LD50 - dose of dies which 50% of infected animals
DI - dosis infectionis - infective dose (the minimum number of microbial cells that can cause infectious process).
Слайд 7For origin and development of infectious disease are essential:
The infectious
dose of pathogens (the minimum number of microbial cells capable
of causing infectious process)Portal of entry - the body's tissues through which the organism enters the macro-organism.
Слайд 9Transmission
Airborne
Fecal-oral
By Contact
Парантеральный
Genital
Transmissive
transplacental
ФАКТОРЫ ПЕРЕДАЧИ:
Слайд 11PERIODS OF INFECTION
Incubation - from infection to the first signs
of the disease (not contagious)
Prodromal - nonspecific common manifestations
(can be dangerous) Height - the period of the development of clinical symptoms
Outcome:
recovery
death
bacteriocarrier
Слайд 12CLASSIFICATION OF INFECTIONS
BY THE CAUSATIVE AGENT
bacterial
viral
fungal
protozoal
BY PRESENT CLINICAL SYMPTOMS
typical
atypical
BY LOCATION
total (generalized)
local
(alopecia)Слайд 13BY DURATION:
acute
chronic
persistent (long-term experience and microbial growth
within the cells, such as macrophages)
bacteriocarrier
DEGREE IN CLINICAL
EXPRESSION: symptomatic (symptomatic)
abortive
latent
BY DESCENT:
exogenous
endogenous
autoinfection
Слайд 14source of infection:
anthroponoses (of people) – Gonorrhea
Zoonoses (of
animals) - brucelosis
anthropozoonoses (of people and animals) – plague
Sapronoses (dead
matter) - Legionella pneumophilaBY INTENSITY DISTRIBUTION:
Sporadic – isolated occurrence with no apparent connections between localities or times of occurrence
Group - a small number of cases in one community
Epidemic – significantly increased occurrence within a given localities and time periods
Pandemic - significantly increased occurrence within a given localities and time periods without restriction
The number of species of agent:
monoinfection (1 microbe)
mixed infections (mixed) - tank + virus
Слайд 15ON the spread of germs and toxins:
bacteremia - bacteria
circulating in the blood
viremia - the virus circulates in
the blood toxinemia (exotokisn) and toxemia (endo)
septicemia - microbes multiply in the blood
pyosepticemia - microbes multiply in the blood, are carried to the organs and tissues, there form secondary purulent foci.
sepsis (proliferation of microbes in the blood)
Reccurent infection:
secondary - to the existing inf-ii + new Notices
reinfection - sick with the same disease after complete recovery
superinfection - the patient during the illness are infected by the same pathogen
relapse - a return wedge. manifestations due to microbial residues after the first infection
Слайд 16Pathogenicy factors
Hyaluronidase - cleaves hyaluronic acid intercellular substance increases the
permeability of the mucous membranes and conjunctive tissues
Neuraminidase –penetrates inside
the cell are distributed in the intercellular space.Coagulase (thicken blood plasma)
Plasmin (dissolves fibrin clots)
Leukocidin (destroys white blood cells)
Lecithinase destroys cell membranes
Слайд 17Particular viral infections
Obligate parasitism of the virus, its pathogenicity of
infectious its NC - "infectivity"
The high specificity, Organotropona (there are
neurotropic viruses, hepatotropic viruses)Blood viruses - transport environment, the presence of viremia stage.
Interaction of the viral genome and the genome of the cell
Infectious viruses - self-reproduce its genotype
Integration viruses - viral genes integrated into the chromosome of the cell and cause degeneration of cells (oncoviruses)
virus in immune system cells (lymphocytes) -virus influenza, measles, herpes, polio, AIDS, etc. Lymphotropic reflected in the outcome of the pathogenesis and viral infections (immunodeficiency)
The formation of intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions - smallpox, rabies, herpes, measles, etc. Have diagnostic value.
Слайд 18FORMS OF VIRAL INFECTION
Productive - acute, accompanied by a reproduction
of the virus in the cell and their rapid release:
focal
generalized
persistent
The
latent (asymptomatic) - the lack of virus isolationChronic -vydelenie virus from the body
Abortive - suspension of production
The development of neoplastic degeneration of cells (oncogenic viral infection)
Слайд 20What is immunity?
It is the capability of the body to
resist harmful microorganisms or viruses from entering it.
The immune system
produces antibodies or cells that can deactivate pathogens.Fungi, protozoans, bacteria, and viruses are all potential pathogens.
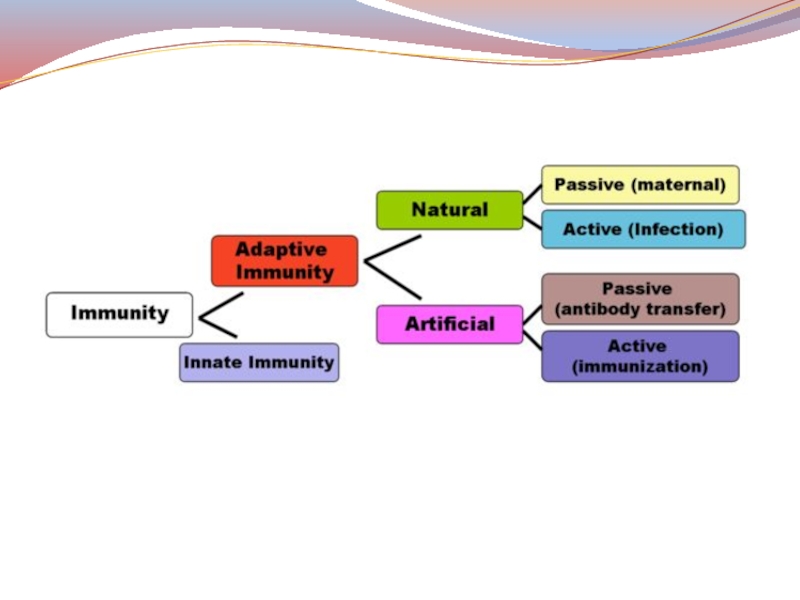
Слайд 23I Innate immunity
II Adaptive immunity
Natural
sterile (after the establishment of the
immunity germs are eliminated from the body) and non-sterile (produced
in the presence of germs)a) an antimicrobial
b) antitoxic
c) antiviral
g) Antifungal
Natural passive (placental)
Artificial active (post-vaccination) - formed in a few weeks and lasts for several years
Artificial passive (postserum) - formed after a few hours and lasts for several weeks or months
Слайд 24Cellular immunity - this is the function of T-lymphocytes. T-killer
cells destroy antigens by direct cytotoxicity and by the synthesis
of lymphokines.The regulation of the immune response involves two subtypes of T cells: T helper enhance the immune response of T-suppressors have the opposite effect.
Слайд 25Humoral immunity - this is the function of B cells.
T
helper B
LM clone antibody-producing cells (plasma cells) immunoglobulins (antibodies) (Ig)AH AT complex.
Слайд 26Initial immune response occurs when you first meeting with an
antigen. His expression reaches a maximum of 7 - 8
th day, persists for 2 weeks, and then decreases; (Ig M)secondary immune response occurs at the second meeting with the antigen by the cells of immunological memory. The secondary immune response is developing rapidly due to the memory cells and reaches more (3 - 4 times) intensity;(Ig G)
Слайд 27The immune response to all types of passes 2 Phases
:
1st, nonproductive - antigen recognition and interaction of immune cells;
2nd,
productivity - the proliferation of effector cells and antibody production.Слайд 28First-Line Defenses /Innate Immune System- The body's first line of defense
against pathogens uses mostly physical and chemical barriers such as
Skin – acts as a barrier to invasion
Sweat – has chemicals which can kill different pathogens.
Tears - have lysozyme which has powerful digestive abilities that render antigens harmless.
Saliva – also has lysozyme.
Mucus - can trap pathogens, which are then sneezed, coughed, washed away, or destroyed by chemicals.
Stomach Acid – destroys pathogens
Слайд 29Inflammatory response causes
Redness - due to capillary dilation resulting
in increased blood flow
Heat - due to capillary dilation
resulting in increased blood flowSwelling – due to passage of plasma from the blood stream into the damaged tissue
Pain – due mainly to tissue destruction and, to a lesser extent, swelling.
Слайд 31Skin and mucosa
The barrier function
The bactericidal properties
Mechanical protection
Normal microflora
Mechanical protection
Antagonism
It
promotes the maturation of the immune system
Слайд 32Phagocytosis
The functions of phagocytes:
Protective
representing
Secretory (IL-1)
Stages of phagocytosis:
chemotaxis
Adhesion
endocytosis
Education phagolysosome
Intracellular digestion
NK cells
(natural killer cells)
lymfocit-shared population of cells possessing the natural
cytotoxicityAntiviral
Antitumor
Antiprotozoal
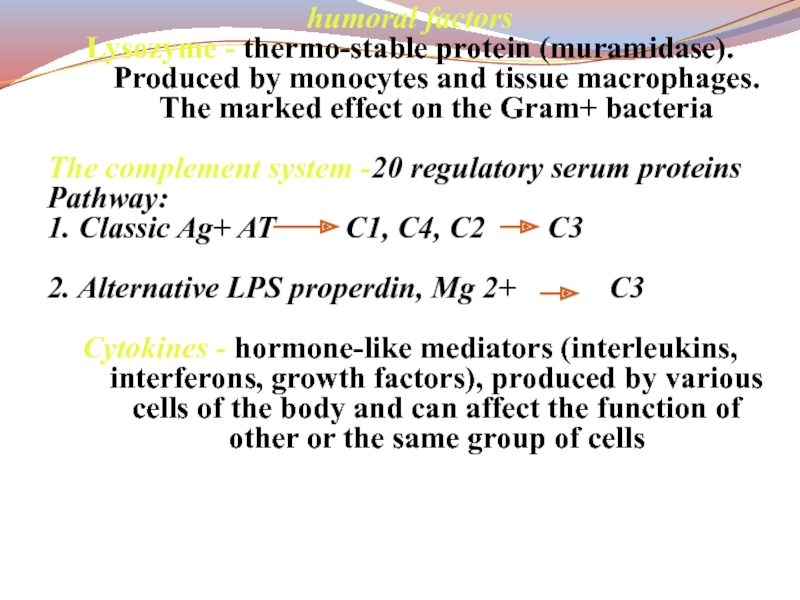
Слайд 33humoral factors
Lysozyme - thermo-stable protein (muramidase). Produced by monocytes and
tissue macrophages. The marked effect on the Gram+ bacteria
The complement
system -20 regulatory serum proteinsPathway:
1. Classic Ag+ AT C1, C4, C2 C3
2. Alternative LPS properdin, Mg 2+ C3
Cytokines - hormone-like mediators (interleukins, interferons, growth factors), produced by various cells of the body and can affect the function of other or the same group of cells
Слайд 34THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
The hierarchical unity of organs and cells that
function as a single unit, protecting the body against infections
and foreign agentsFeatures of the immune system:
The cells are spread throughout the body
The cells are circulating in the blood
Constantly develops AT
It consists of 1012 lymphoid cells
The total weight of 1.5-2 kg
The central figure - lymphocyte
Слайд 35
The Cells of Immunity System
Immunocompetent - capable of specific immune
responses, which have receptors AG
Auxiliary - (antigen) - the ability
to distinguish foreign cells from their own and submit them to immunocompetent cells.Cells AG-nonspecific defense that distinguish the body's own components from foreign particles and destroy them
Слайд 36lymphocytes
LM T - cell immune response
LM B - the humoral
immune response
T LM (80% lymphocytes)
T - effectors
T - killers
T -
helpersT – suppressor
Features:
cell-mediated immunity;
regulation of the activity of B-cells (immunologic memory and tolerance);
hypersensitivity (IV) type.
graft rejection;
antitumor immunity
Слайд 37
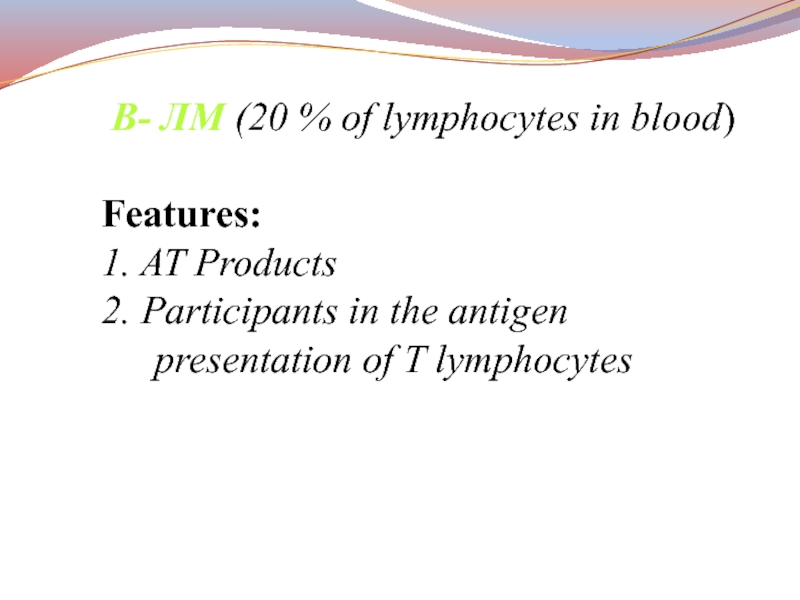
В- ЛМ (20 % of lymphocytes in blood)
Features:
1. AT Products
2.
Participants in the antigen presentation of T lymphocytes
Слайд 38Antigens - substances of any origin, can cause the body's
specific immune response and to participate in its implementation
Properties:
Alien
The antigenicity
Specificity
Immunogenicity
Protein
natureHigh MR
Types AG
Full - capable of inducing the formation of specific antibodies and to react with them
Haptens - failed to induce the formation of specific antibodies and to react with them
The structure of the AG 2 components:
Protein - defines the antigenicity
The amino acid residues (determinant group) located on the surface of the protein - specificity.
белок
Слайд 39Types of Antigens
Geteroantigens- common Antigens, found in representatives of different
types of microorganisms, animals and plants. For example, Antigens Forsman
- guinea pig, e / c sheep and Salmonella.Cross-react AG (PRA) - found in a number of micro-organisms and in human tissues. For example, hypertension hemolytic streptococcus, the human myocardium and renal glomerulus, so provokes rheumatic heart disease and glomerulonephritis.
Izoantigens - some of them individuals or groups of individuals differ (ABO blood)
Tumor - as a result of malignant transformation
Viral - linked to the nucleocapsid or envelope glycoproteins
HLA - Antigens major histocompatibility complex
Somatic - thermostable O Antigens
The flagellar - labile H Antigens
Capsule - labile K - Antigens
Antigens virulence - Vi - Antigens
Autoantigens (glass. Body, the thyroid gland)
Слайд 40Immunological tolerance - the body does not respond to the
AG and does not produce antibodies. Occurs when the body
met with antigens in the embryonic period, when the defects of the lymphoid tissue, when very high or very low doses of antigen in an organism with a weak Immunity system.Immunological paralysis - the inability organism produce AT form when very high doses of antigen. Due to blockade of immunocompetent cells. After removing unnecessary AG products AT resumes.
Immunodeficiency - reduction or absence of humoral and cellular defense. congenital and acquired.
Слайд 41An antibody is a protein produced in response to an
antigen.
Structure of Antibodies
L Н Н LFab-фрагмент V участок
s-s
s-s
Fc-фрагмент С участок
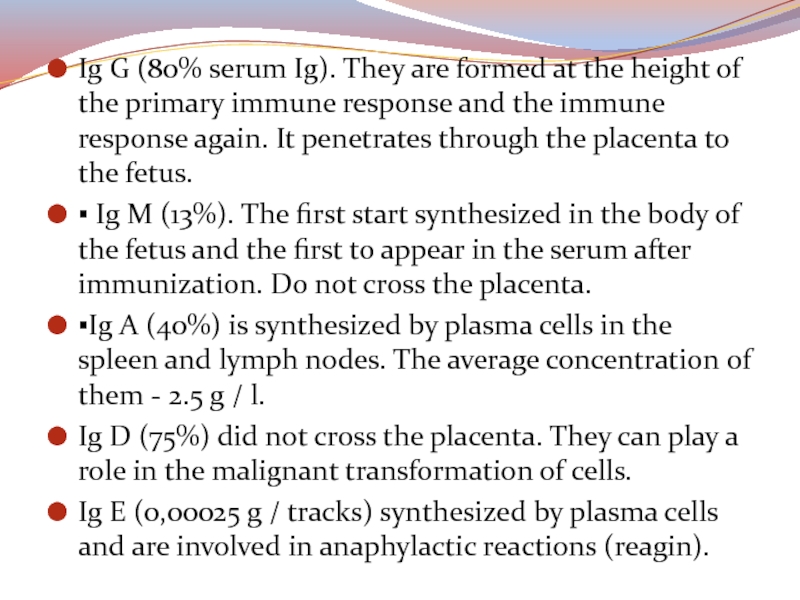
Слайд 43Ig G (80% serum Ig). They are formed at the
height of the primary immune response and the immune response
again. It penetrates through the placenta to the fetus.▪ Ig M (13%). The first start synthesized in the body of the fetus and the first to appear in the serum after immunization. Do not cross the placenta.
▪Ig A (40%) is synthesized by plasma cells in the spleen and lymph nodes. The average concentration of them - 2.5 g / l.
Ig D (75%) did not cross the placenta. They can play a role in the malignant transformation of cells.
Ig E (0,00025 g / tracks) synthesized by plasma cells and are involved in anaphylactic reactions (reagin).
Слайд 44applied immunology
Vaccines and toxoids - drugs to induce the body's
specific immune response by mobilizing mechanisms of immunological memory
Immune serum
and immunoglobulins - preparations containing completespecific antibodies, the introduction of which in the organism leads to the immediate acquisition of passive humoral immune response.Слайд 45Vaccination: A vaccination is an injection of a weakened form
of the actual antigen that causes the disease. The injection
is too weak to make you sick, but your B lymphocytes will recognize the antigen and react as if it were the "real thing". Thus, you produce MEMORY cells for long term immunity.Слайд 46REQUIREMENTS FOR VACCINES
High immunogenicity (ability to provide reliable anti-infectious protection)
AREAKTOGENNOST
(no significant side reactions)
HARMLESSNESS
MINIMUM sensitizing effect
Слайд 47CLASSIFICATION OF VACCINES
According to methods preparation
Live (attenuated)
Inactivated
anatoxins
Chemicals
Recombinant
Genetic engineering
Anti-idiotype in progress
liposomal
development
Bacterial
viral
Слайд 48Living vaccine
These drugs are made from live but weakened (attenuated
virulence) microbes retained immunogenicity. These vaccines are characterized by high
efficiency, as cause in the body similar to the natural process of infection, but without clinical manifestations. When this vaccine strain may persist and multiply in the body. Typically, once introduced.Benefits:
A single injection
Prolonged immunity
Disadvantages:
- In a weakened organism can cause infections
Слайд 49Killed vaccine
This suspension of killed microbes in nat. solution. To
inactivate microbes are used:
1. Elevated Temperature (56-58 ° C)
2. The
chemicals (ethyl alcohol, formalin, acetone, phenol)3. UFO
Benefits:
They do not cause infectious disease in a weakened body
Disadvantages:
repeated administration
Immunity non-durable
Слайд 50CHEMICAL VACCINE
This product containing the active bacteria derived from bacteria
by various treatments, in particular by enzymes (pancreatin, trypsin). These
less reactogenic vaccine, a storage stable, more immunogenic. They are made of several kinds of microbes, i.e. they are integrated (associates). The advantage of them in a sharp reduction in the number of injections, while maintaining the amount of antigen administered. Usually they are administered singly.In order to antigens not quickly absorbed into the body and provide long-lasting immunity, they added absorbent material (aluminum hydroxide adjuvant, phosphate, aluminum)
Слайд 51ANATOXINS
It is neutralized exotoxin which produced by the action of
formalin solution. It contains many ballast substances. Currently uses purified
toxoids adsorbed to the adjuvant. This toxin loses its virulence, but retains the ability to induce the synthesis of antitoxic antibodies.Diphtheria toxoid adsorbed purified
Staphylococcal toxoid
Tetanus toxoid adsorbed purified
DT - toxoid
Polianatoksin peeled
Anatoxins connected with corpuscular AG (DTP cholera vaccine)
Слайд 52Immune serum and immunoglobulins
This preparations the introduction in the body
which creates artificial passive immunity acquired. Immunity is created quickly,
but lasts a short time, because introduced protein is rapidly degraded.Sera have immediate effect, neutralizing toxins, destroying the bacteria themselves. Therefore, they are mainly used for the treatment and prophylaxis less.
Often introduced by intramuscular injection.
Слайд 53Serum products are divided into:
Heterologous (obtained from blood of animals)
Homologous
(derived from human blood)
heterologous:
Immunization of animals
The high concentration of antibodies
Unlimited
selection of producersThe high immunogenicity of the (alien) -
especially when using
homologous:
are not immunogenic
From the donor or from placental blood
AT concentration is not great. This may include other antibodies.
Слайд 54Immunoglobulins
It is highly purified, concentrated gamma globulin human and animal.
2
types:
Normal (obtained from the donor, abortive, placental blood)
measles
polio
pertussis
2. The direction
of action (immune sera obtained from human donors and animals)Against rabies
smallpox
tetanus
Слайд 55diagnostic drugs
This diagnostic serum and diagnostic tools designed for the
production of diagnostic reactions.
Diagnosticums - a suspension of killed bacteria
of some kind. Their variety - erythrocyte diagnostic tools (bacterial AG adsorbed on erythrocytes).Diagnostic serum - antibodies obtained by immunizing animals (rabbits, sheep) the relevant AG.
Allergens - preparations for the production of skin tests and detection of allergic conditions. Show infection of the body.