Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Law in Kazakhstan
Содержание
- 1. Law in Kazakhstan
- 2. Introduction
- 3. Sources:ConstitutionCivil CodeNumerous laws (Law on JSC, Law
- 4. Fundamental Principles of Civil LegislationProtection of Civil
- 5. Principles:Equality of the participantsInviolability of propertyFreedom of
- 6. Protection of civil rights:restitution of status quocompensation
- 7. Subjects of civil relations:Natural personsLegal entitiesAdministrative-territorial unitsState.
- 8. Natural persons
- 9. Natural persons:Citizens of KazakhstanForeign citizensStateless persons.
- 10. Legal capacity is one’s capacity to have civil rights and obligations [art.13 CC]
- 11. Legal capacityAll citizens have equal LC [art.13(1)
- 12. Active capacity (deed capacity, dispositive legal capacity) citizen’s
- 13. Active capacityFull AC begins with attaining one’s
- 14. Full AC age reduction:Marriage at the age
- 15. Active capacity of minors…… of 14 –
- 16. Active capacity of minors……under 14 [art. 23
- 17. Limitation of active capacityWhy: alcoholic or drug
- 18. Ceasing of active capacityWhy: mental decease due
- 19. Legal entities
- 20. Legal entity:It is an organization which: has
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Commercial organizationAimed on the receiving of profitThe
- 23. Non-commercial organizationDoes not have the receiving of
- 24. Legal capacity of legal entityBegins from the
- 25. Business partnership:It is a commercial organization, the
- 26. Types of business partnershipsgeneral partnership its participants (general
- 27. Joint stock companyIt is a legal entity,
- 28. Property right
- 29. Property rightThe right to possessThe right to useThe right to dispose (art.188 CC)
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Right of business authorityIt is a material
- 32. Right of business authorityDoes not include the
- 33. The right of operational management:It is a
- 34. The right of operational managementDoes not include
- 35. Grounds for acquisition of property rightPrimary GroundsDerivative Grounds
- 36. Primary Grounds Manufacture or creation of things;Fruits,
- 37. Derivative GroundsContract of purchase/sale, barter, gift, or
- 38. Grounds for termination of property right Alienation
- 39. Compulsory deprival of property rightSatisfaction of claims
- 40. Не конец
- 41. Скачать презентанцию
Introduction
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Sources:
Constitution
Civil Code
Numerous laws (Law on JSC, Law on LLP and
PAL, Law on consumer rights protection etc.)
Слайд 4
Fundamental Principles of Civil Legislation
Protection of Civil Rights
Subjects of Civil
Law
Property right
Objects of Civil Law
Transactions
Representation and Power of Attorney
Law of
Obligations.General Part
Слайд 5Principles:
Equality of the participants
Inviolability of property
Freedom of agreement
Restitution for violated
rights and their defense in the court
Unrestricted circulation of goods,
services and monetary resources in the entire territory of the RK. Note: Restrictions are allowed only in accordance with the legislative acts, where it is necessary for ensuring security, protection of life and health of the people, protection of the natural environment and cultural valuables.
Слайд 6Protection of civil rights:
restitution of status quo
compensation of material damage
(real damage + lost profit) and moral damage.
Слайд 7Subjects of civil relations:
Natural persons
Legal entities
Administrative-territorial units
State.
Слайд 11Legal capacity
All citizens have equal LC [art.13(1) CC]
LC begins from
one’s birth and ends with one’s death. [art.13(2) CC]
Content of
LC: to owe any property, inherit, choose place of residence, to have intellectual property etc. [art.14 CC]Слайд 12Active capacity (deed capacity, dispositive legal capacity)
citizen’s capacity by his
own actions to obtain and to exercise his civil rights,
to create for himself civil obligations and to fulfill them [art.17 CC]Слайд 13Active capacity
Full AC begins with attaining one’s majority, 18 years.
[art.17(1) CC]
Marriage at 16 years old or emancipation – full
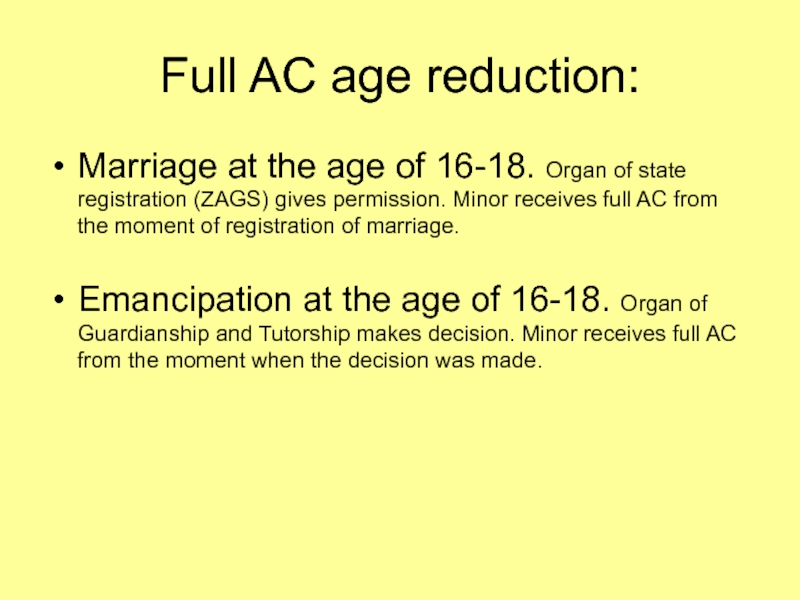
AC at 16. [art.17(2) CC]Слайд 14Full AC age reduction:
Marriage at the age of 16-18. Organ
of state registration (ZAGS) gives permission. Minor receives full AC
from the moment of registration of marriage.Emancipation at the age of 16-18. Organ of Guardianship and Tutorship makes decision. Minor receives full AC from the moment when the decision was made.
Слайд 15Active capacity of minors…
… of 14 – 18 years old
[art.22 CC]
All bargains – with the consent of parents, adopters
or tutorsDispose own income and objects of their intellectual property, make day-to-day bargains
Слайд 16Active capacity of minors…
…under 14 [art. 23 CC]
For them all
the bargains are made by parents, adopters and guardians
Simple day-to-day
bargains correspondent to their ageСлайд 17Limitation of active capacity
Why:
alcoholic or drug addiction which puts
one’s family in difficult financial situation [art.27 CC]
Слайд 18Ceasing of active capacity
Why:
mental decease due to which a
person does not realize own actions [art. 26 CC]
Слайд 20Legal entity:
It is an organization which:
has its separate property
on the basis of property right, right of business authority
or right of operational management;is liable for its obligations with this property;
can in its own name acquire and exercise property and personal non-property rights and obligations;
can be a plaintiff and a defendant in the court;
has independent balance-sheet or budget.
A legal entity has a seal with its name. (art. 33 CC)
Слайд 22Commercial organization
Aimed on the receiving of profit
The income is distributed
between the participants
Types of commercial organizations:
state enterprise
business partnership
joint stock company
production
cooperative society (art. 34 (1,2) CC)Слайд 23Non-commercial organization
Does not have the receiving of profit as the
main aim
The income is not distributed between the participants
Types of
non-commercial organizations:Institution
Public foundation
Non-commercial joint-stock company
Religious association
Consumer cooperative society
Social fund
Other types (art. 34 (1,3) CC)
Слайд 24Legal capacity of legal entity
Begins from the moment of its
creation (registration) or from the moment of the obtaining of
a license, if the license is required for that activity.Finishes at the moment of the end of its liquidation or at the moment of expiry of the license, if the license was required for that activity (art. 35 (1,2) CC )
Слайд 25Business partnership:
It is a commercial organization, the charter fund of
which is divided into shares of the founders.
The property of
the business partnership, created on the basis of investments of the founders as well as the property that was produced or acquired by the business partnership during the period of its activity belongs to that business partnership on the basis of property right (art. 58 (1) CC)Слайд 26Types of business partnerships
general partnership
its participants (general partners), in the
case of insufficiency of the property of the partnership, bare
the joint liability for the obligations of the partnership with all their property (art. 63 CC)kommandit partnership
besides one or more general partners there are also one or more participants with limited liability; only general partners can manage the business activity of the partnership (art.72 CC)
limited liability partnership
its partners bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the partnership within the limits of the contributions made by themselves (art.77 CC)
partnership with additional liability
its participants are liable for the obligations of the partnership with their investments to the charter fund and in the case those are insufficient – additionally with the property that belongs to them in the amount proportionate to the contributions made by them (art.84 CC)
Слайд 27Joint stock company
It is a legal entity, which makes the
emission of shares with the scope to attract the money
for executing of its activity (art.3 (1) of the Law of RK on JSC)its participants (shareholders) bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of company within the limits of the shares that belong to them.
Слайд 31Right of business authority
It is a material right of a
state enterprise, which has received the property from the state
and which exercises the right to possess, to use and to dispose towards that property, as it is provided for by the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan. (art.196 CC)Слайд 32Right of business authority
Does not include the right to:
sell or
transmit the property to the other people
exchange
give in a long-term
lease (over 3 years)give on the non-paid basis the right to use the property to the other people
create branches of the state enterprise
establish joint productions and joint companies together with private entrepreneurs, invest therein their production and monetary capital
give credits to the private entrepreneurs with the interest lower than the one constituted by the National bank of the RK. (art.200 CC)
Слайд 33The right of operational management:
It is a material right of
an institution, state institution, financed by the owner, or of
a budget enterprise, which has received the property from the owner and which exercises the right to use, to possess and to dispose of the property in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan, with the aims of its activity, with the tasks of the owner and with the destination of this property. (art.202 CC)Слайд 34The right of operational management
Does not include the right to
determine the legal destiny of the property which the company
had received on the basis of the balance-sheet. (art. 206 CC)Слайд 36Primary Grounds
Manufacture or creation of things;
Fruits, products, and revenues received
as a result of the use of property.
Find, treasure
Acquisitive prescription
– a person or legal entity, who is not the owner of property but in good faith, openly, and uninterruptedly possesses immovable property as his own for fifteen years or other property for five years acquires the right of ownership in such property.Слайд 37Derivative Grounds
Contract of purchase/sale, barter, gift, or other transaction concerning
the alienation of this property.
Inheritance
Reorganization of a juridical person the
right of ownership in the property belonging to it passes to the juridical persons-legal successors of the reorganized juridical person.Слайд 38Grounds for termination of property right
Alienation by the owner
of his property to other persons;
Renunciation of the property
right by the owner; Perishing or destruction of the property;
Loss of the property right to property in other instances provided for by legislation.
Слайд 39Compulsory deprival of property right
Satisfaction of claims of creditor
Compulsory alienation
of property which by virtue of legislative acts can not
belong to the particular personRequisition (in cases of emergency)
Confiscation (by court decision as punishment)
Withdrawal of a land plot;
Purchase of improvidently maintained cultural and historical values.









![Law in Kazakhstan Legal capacity is one’s capacity to have civil rights and obligations [art.13 CC] Legal capacity is one’s capacity to have civil rights and obligations [art.13 CC]](/img/thumbs/68b49a61c56905546acaa03c67be9e4f-800x.jpg)
![Law in Kazakhstan Legal capacityAll citizens have equal LC [art.13(1) CC]LC begins from one’s Legal capacityAll citizens have equal LC [art.13(1) CC]LC begins from one’s birth and ends with one’s death.](/img/thumbs/977318a7a62ad75f2940715285a03b53-800x.jpg)

![Law in Kazakhstan Active capacityFull AC begins with attaining one’s majority, 18 years. [art.17(1) Active capacityFull AC begins with attaining one’s majority, 18 years. [art.17(1) CC]Marriage at 16 years old or](/img/thumbs/56b301e69313974207e77fb12beaa443-800x.jpg)
![Law in Kazakhstan Active capacity of minors…… of 14 – 18 years old [art.22 Active capacity of minors…… of 14 – 18 years old [art.22 CC]All bargains – with the consent](/img/thumbs/1a084aaa3448bc8a0ea6b5834b38df5f-800x.jpg)
![Law in Kazakhstan Active capacity of minors……under 14 [art. 23 CC]For them all the Active capacity of minors……under 14 [art. 23 CC]For them all the bargains are made by parents, adopters](/img/thumbs/187f0776f6179a9544b4490f6eb52171-800x.jpg)