Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture 6. Financial markets: Debt market in details
Содержание
- 1. Lecture 6. Financial markets: Debt market in details
- 2. ©Ella KhromovaFinancial marketsBondsFinancial InstrumentsFinancial marketsLecture 6Primary marketsSecondary
- 3. ©Ella KhromovaMajor Types of Financial InstrumentsBondsFinancial InstrumentsFinancial marketsLecture 6
- 4. ©Ella KhromovaKey terminologies of debt/bonds (fixed income
- 5. ©Ella KhromovaDebt ValuationLecture 6N – Years to
- 6. ©Ella KhromovaDebt Valuation: ExampleLecture 6French government bonds,
- 7. ©Ella KhromovaClassification of bonds based on cash-flowLecture
- 8. ©Ella KhromovaYTMLecture 6N – Years to maturityC
- 9. ©Ella KhromovaYTM: ExampleLecture 6French government bonds, known
- 10. ©Ella KhromovaYTM: Quick calculationLecture 6French government bonds,
- 11. ©Ella KhromovaExercise 2Practice 4What is the intrinsic
- 12. ©Ella KhromovaInvestment strategyLecture 6How to compare bonds?
- 13. ©Ella KhromovaBloombergLecture 6BondsFinancial InstrumentsFinancial markets
- 14. ©Ella KhromovaBloombergLecture 6BondsFinancial InstrumentsFinancial marketsChange in price (modified duration)
- 15. ©Ella KhromovaExercise 1Practice 4BondsLIBOR (London Interbank Offered
- 16. ©Ella KhromovaPractice 4Exercise 1Bonds
- 17. ©Ella KhromovaPractice 4Exercise 1Bonds
- 18. ©Ella KhromovaBuckle, M. and E. Beccalli Principles
- 19. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Lecture 6.
Financial markets: Debt market in details
©Ella Khromova
Lecture 6
International
finance and globalization
Слайд 2©Ella Khromova
Financial markets
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Lecture 6
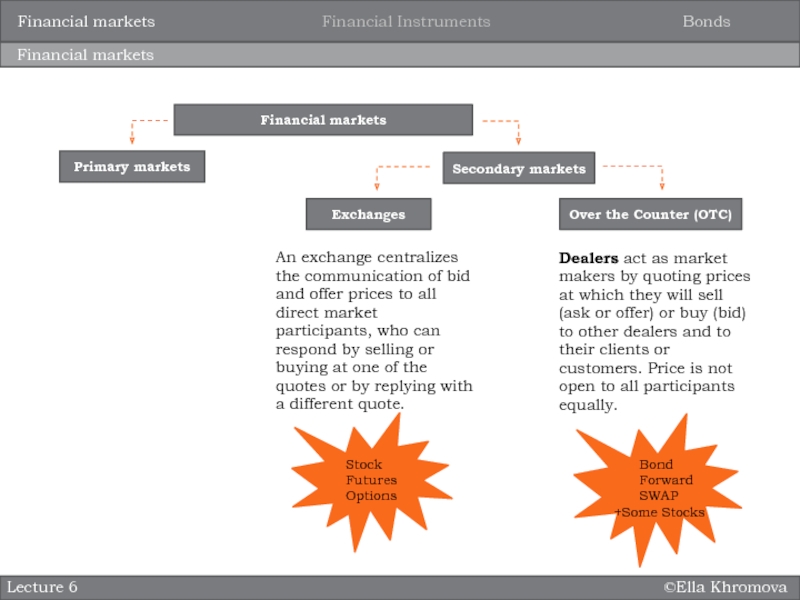
Primary markets
Secondary markets
Over the Counter
(OTC)
An exchange centralizes the communication of bid and offer prices
to all direct market participants, who can respond by selling or buying at one of the quotes or by replying with a different quote.Exchanges
Dealers act as market makers by quoting prices at which they will sell (ask or offer) or buy (bid) to other dealers and to their clients or customers. Price is not open to all participants equally.
Stock
Futures
Options
Bond
Forward
SWAP
+Some Stocks
Слайд 3©Ella Khromova
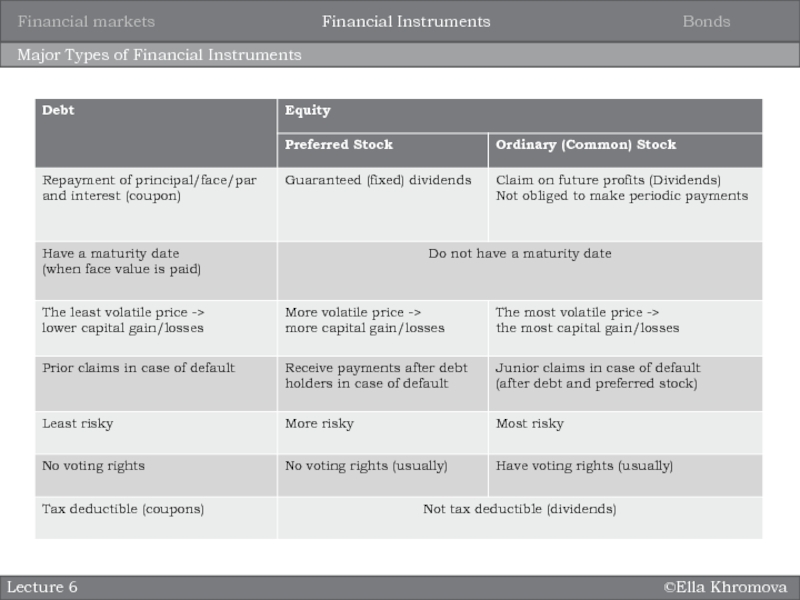
Major Types of Financial Instruments
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Lecture 6
Слайд 4©Ella Khromova
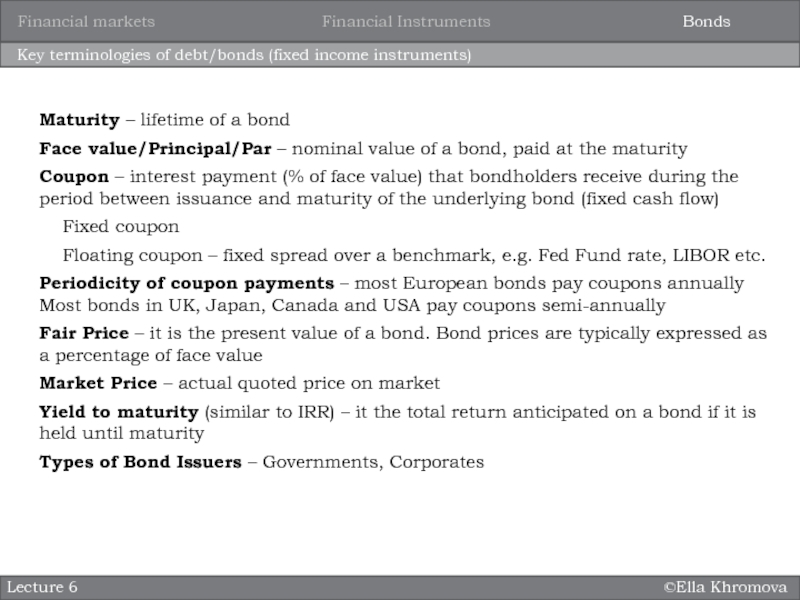
Key terminologies of debt/bonds (fixed income instruments)
Lecture 6
Maturity –
lifetime of a bond
Face value/Principal/Par – nominal value of a
bond, paid at the maturityCoupon – interest payment (% of face value) that bondholders receive during the period between issuance and maturity of the underlying bond (fixed cash flow)
Fixed coupon
Floating coupon – fixed spread over a benchmark, e.g. Fed Fund rate, LIBOR etc.
Periodicity of coupon payments – most European bonds pay coupons annually Most bonds in UK, Japan, Canada and USA pay coupons semi-annually
Fair Price – it is the present value of a bond. Bond prices are typically expressed as a percentage of face value
Market Price – actual quoted price on market
Yield to maturity (similar to IRR) – it the total return anticipated on a bond if it is held until maturity
Types of Bond Issuers – Governments, Corporates
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Слайд 5©Ella Khromova
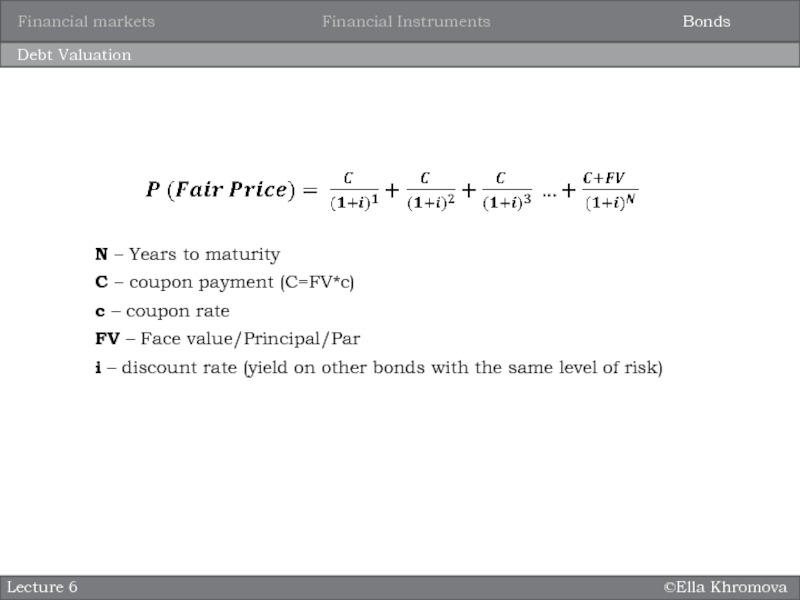
Debt Valuation
Lecture 6
N – Years to maturity
C – coupon
payment (C=FV*c)
c – coupon rate
FV – Face value/Principal/Par
i –
discount rate (yield on other bonds with the same level of risk)Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Слайд 6©Ella Khromova
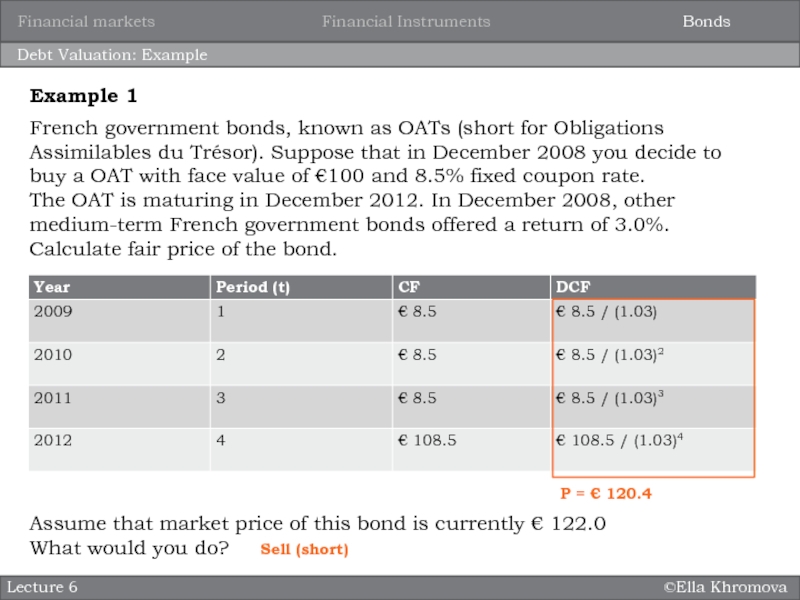
Debt Valuation: Example
Lecture 6
French government bonds, known as OATs
(short for Obligations Assimilables du Trésor). Suppose that in December
2008 you decide to buy a OAT with face value of €100 and 8.5% fixed coupon rate.The OAT is maturing in December 2012. In December 2008, other medium-term French government bonds offered a return of 3.0%.
Calculate fair price of the bond.
Example 1
P = € 120.4
Assume that market price of this bond is currently € 122.0
What would you do?
Sell (short)
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Слайд 7©Ella Khromova
Classification of bonds based on cash-flow
Lecture 6
Straight/Bullet coupon bond
– Periodic payments with single payment at maturity
Annuity bond –
It pays a mix of interest and principal for a finite period of time, i.e. no balloon payment at the endZero coupon bond – No periodic payment; single payment at maturity
Perpetuity bond – It lasts forever and only interest is paid every period (much closer to stocks)
Floating rate coupon bond –coupon depends on some interest rate (LIBOR, etc)
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Слайд 8©Ella Khromova
YTM
Lecture 6
N – Years to maturity
C – coupon payment
(C=FV*c)
c – coupon rate
FV – Face value/Principal/Par
ytm – yield
to maturity (total annual return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until it matures)Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Слайд 9©Ella Khromova
YTM: Example
Lecture 6
French government bonds, known as OATs (short
for Obligations Assimilables du Trésor). Suppose that in December 2008
you decide to buy a OAT with face value of €100 and 8.5% fixed coupon rate.The OAT is maturing in December 2012. In December 2008, other medium-term French government bonds offered a return of 4.0%.
The market price is € 122.0.
Calculate yield to maturity of the bond.
Example 1: cont’d
ytm = 2.63%
Compare the ytm with opportunity cost of capital. What would you do?
Sell (short) the bond and invest in other medium-term French government bonds offered a return of 4.0%
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Слайд 10©Ella Khromova
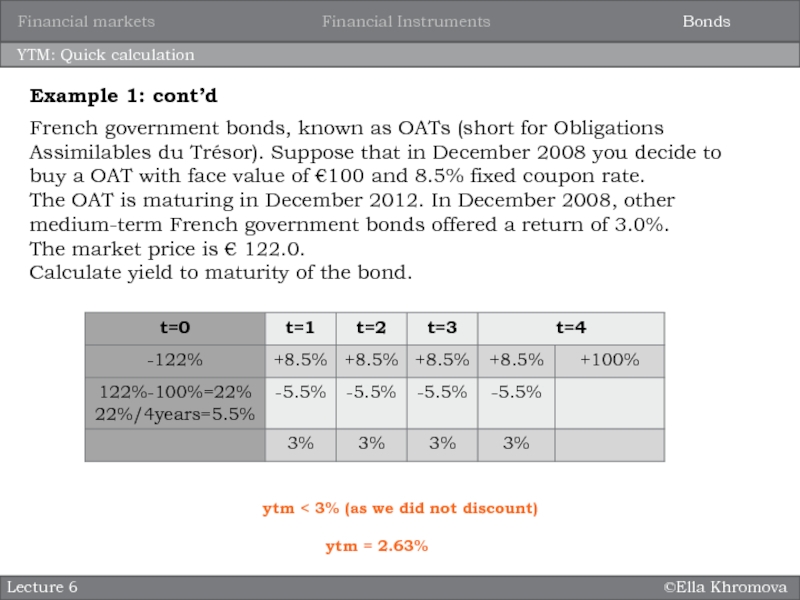
YTM: Quick calculation
Lecture 6
French government bonds, known as OATs
(short for Obligations Assimilables du Trésor). Suppose that in December
2008 you decide to buy a OAT with face value of €100 and 8.5% fixed coupon rate.The OAT is maturing in December 2012. In December 2008, other medium-term French government bonds offered a return of 3.0%.
The market price is € 122.0.
Calculate yield to maturity of the bond.
Example 1: cont’d
ytm < 3% (as we did not discount)
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
ytm = 2.63%
Слайд 11©Ella Khromova
Exercise 2
Practice 4
What is the intrinsic (fair) value for
a 2 year 5% annual riskless coupon bond given the
following data with par value of bond £1,000? Assume you know some facts:1 year zero coupon Treasury bill is traded at £90,9
2 year zero coupon Treasury bill is traded at £79,7
Demonstrate your strategy (long or short), if current market price for the bond from the first question is 90% of par.
Bonds
Слайд 12©Ella Khromova
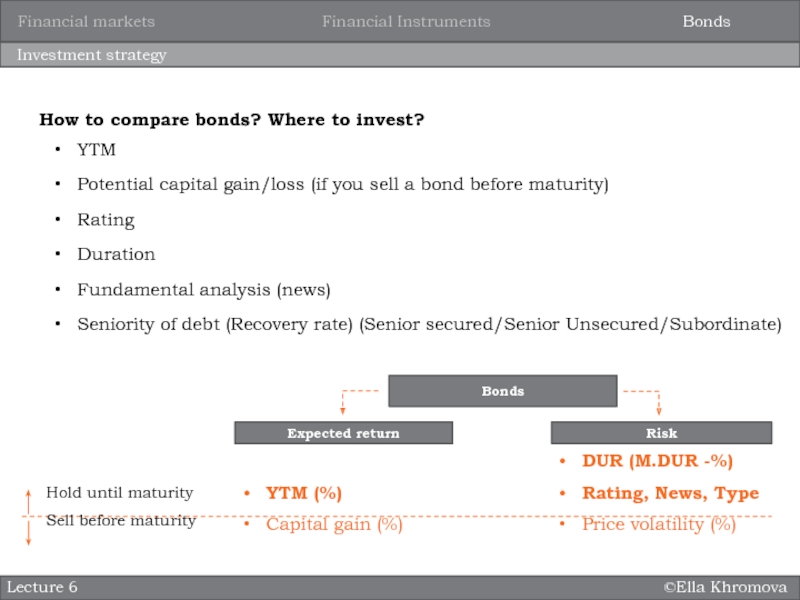
Investment strategy
Lecture 6
How to compare bonds? Where to invest?
YTM
Potential
capital gain/loss (if you sell a bond before maturity)
Rating
Duration
Fundamental analysis
(news)Seniority of debt (Recovery rate) (Senior secured/Senior Unsecured/Subordinate)
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Bonds
Expected return
Risk
YTM (%)
Capital gain (%)
DUR (M.DUR -%)
Rating, News, Type
Price volatility (%)
Hold until maturity
Sell before maturity
Слайд 14©Ella Khromova
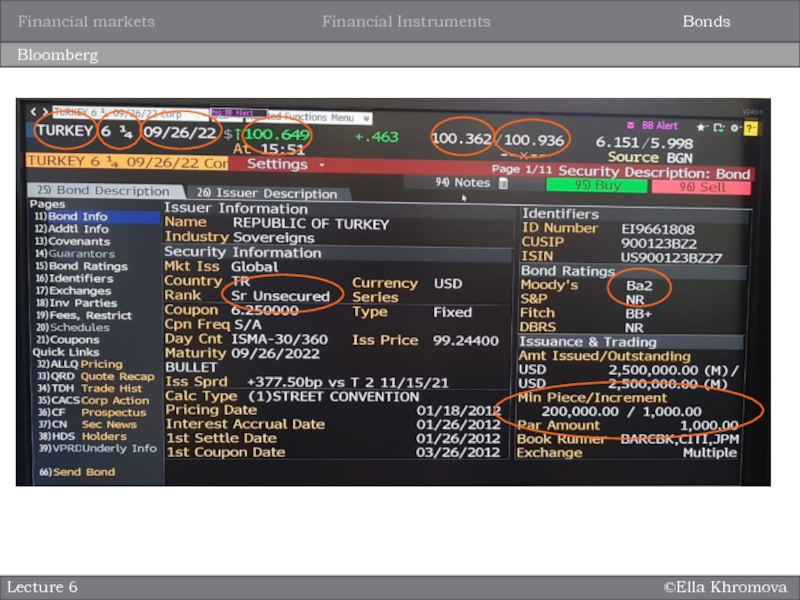
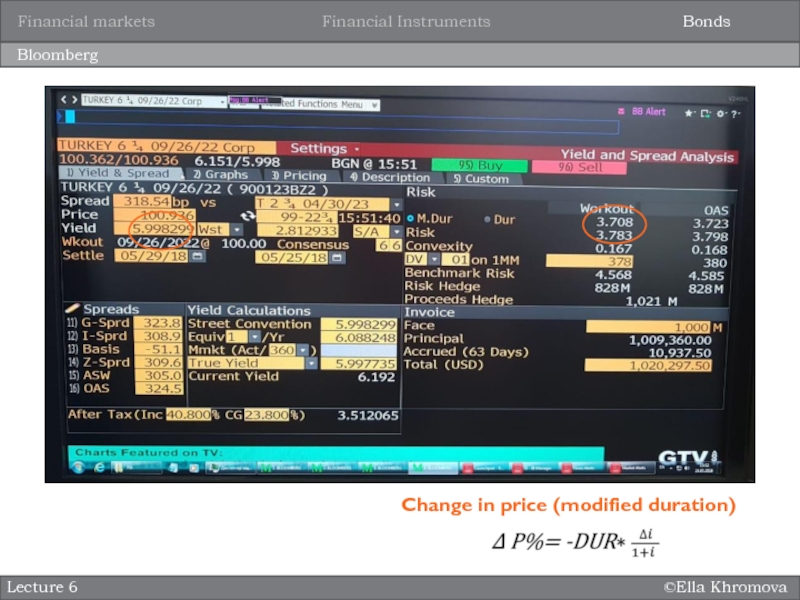
Bloomberg
Lecture 6
Bonds
Financial Instruments
Financial markets
Change in price (modified duration)
Слайд 15©Ella Khromova
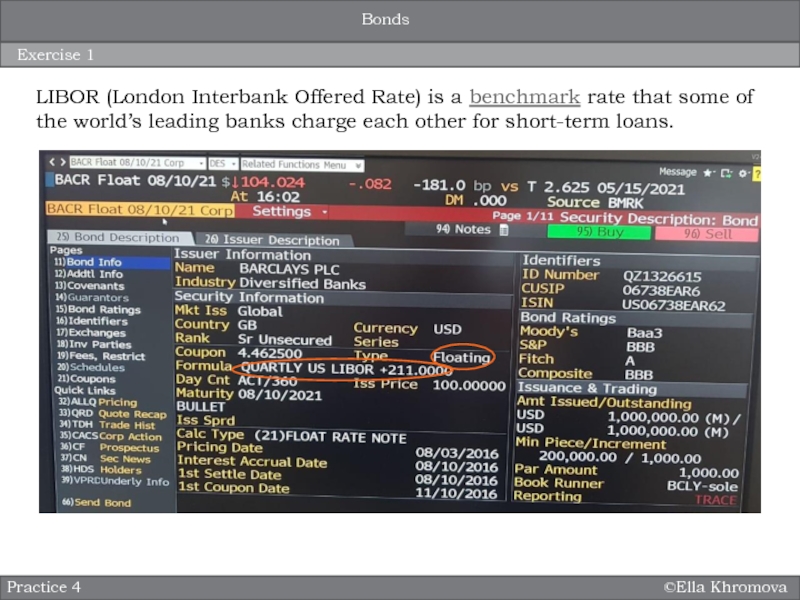
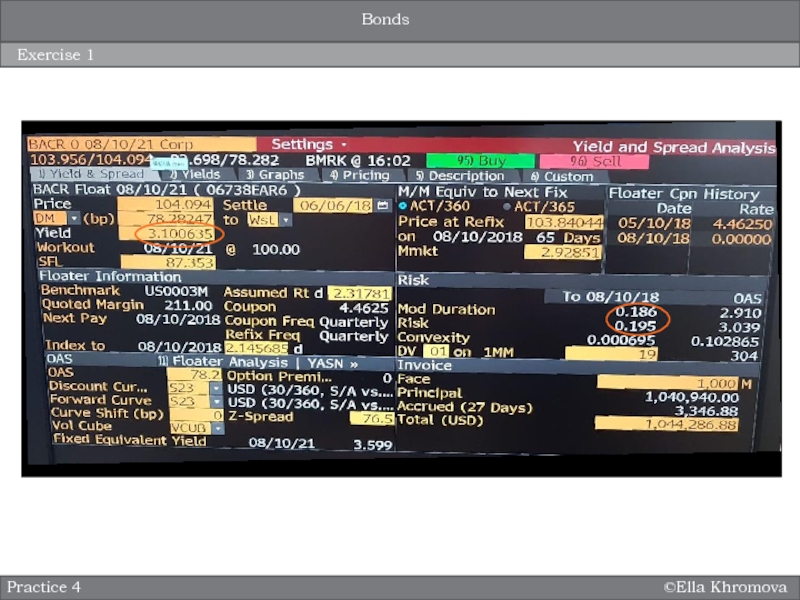
Exercise 1
Practice 4
Bonds
LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) is a benchmark rate
that some of the world’s leading banks charge each other
for short-term loans.Слайд 18©Ella Khromova
Buckle, M. and E. Beccalli Principles of banking and
finance (UOL study guide) pp. 26-30 (excluding The term structure
of interest rates), 32-36, 150-151Brealey, Myers and Allen. Principles of Corporate finance. Chapter 3
Mishkin, F. and S. Eakins Financial Markets and Institutions. (Addison Wesley) Chapter 12
Essential reading for Lecture 6:
Lecture 6