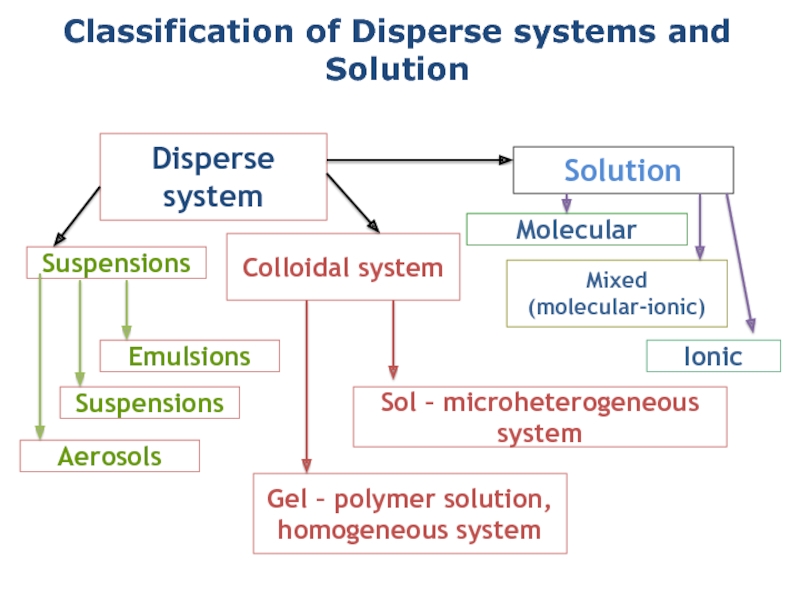
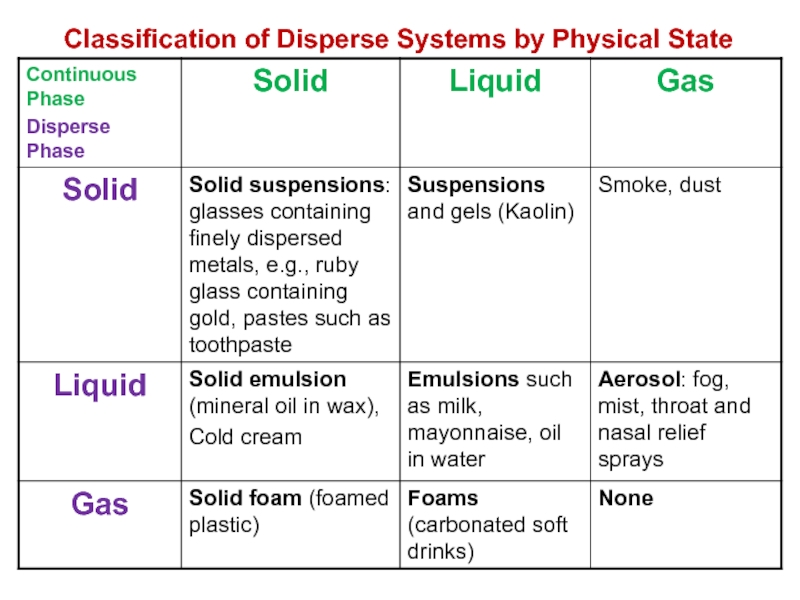
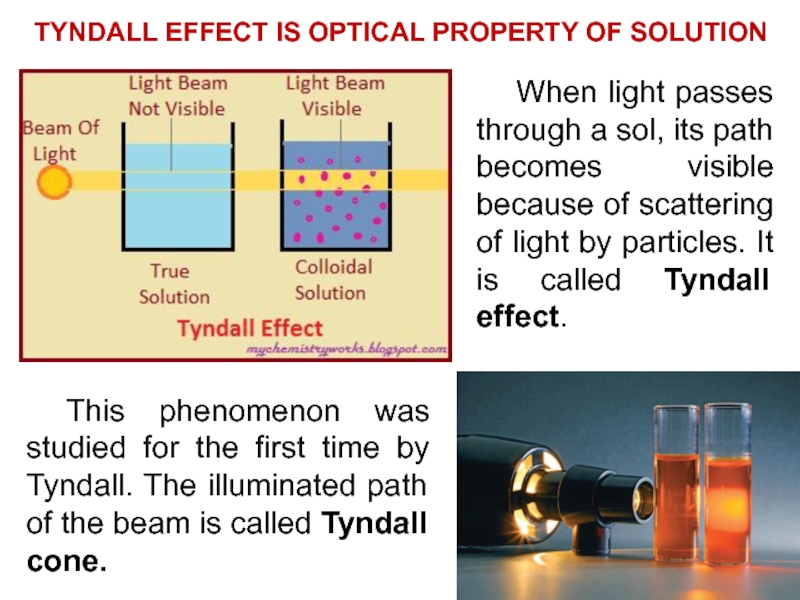
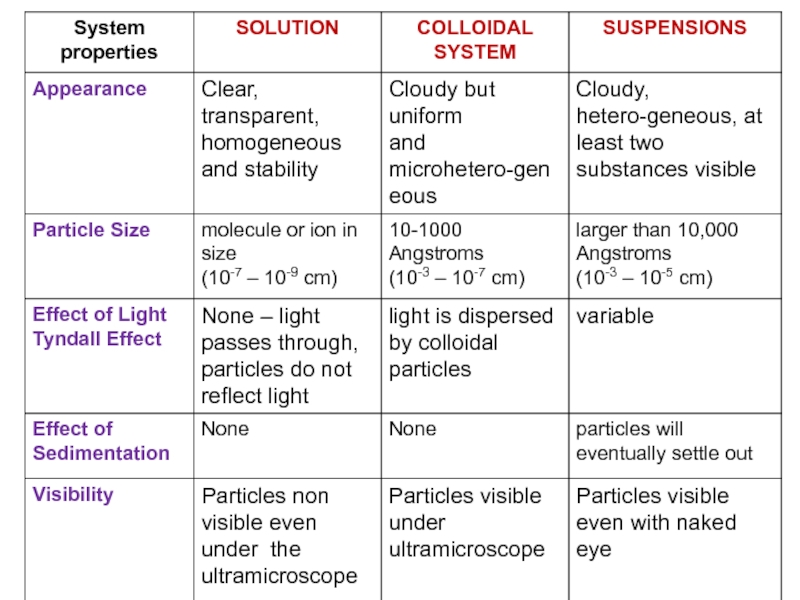
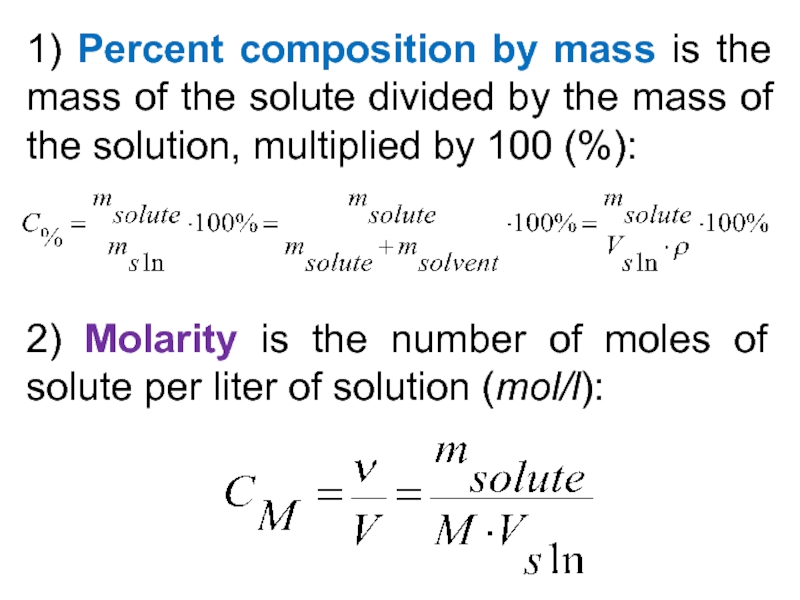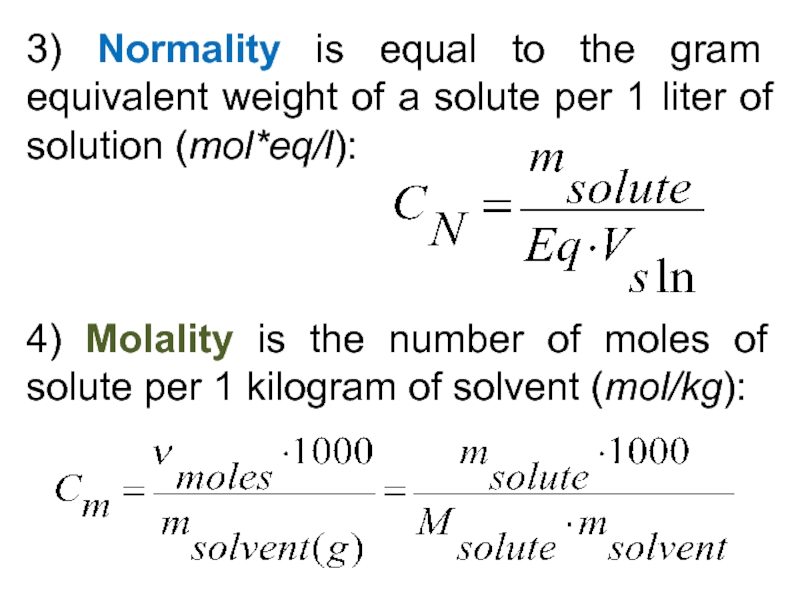and colloids.
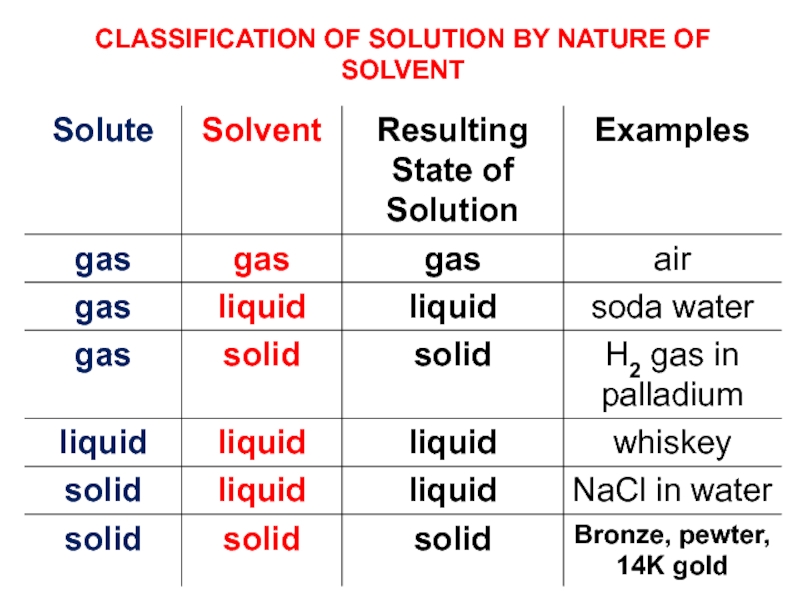
2) Understand, compare, and contrast the terms homogeneous mixture
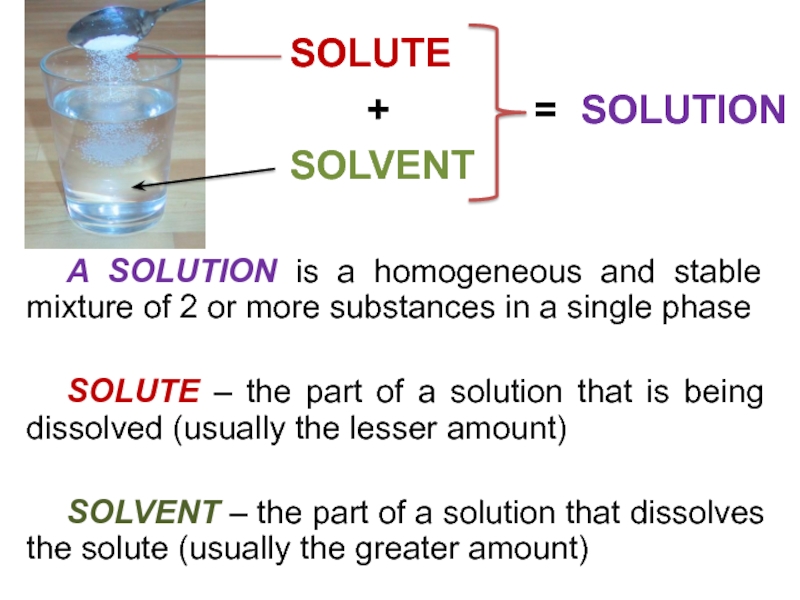
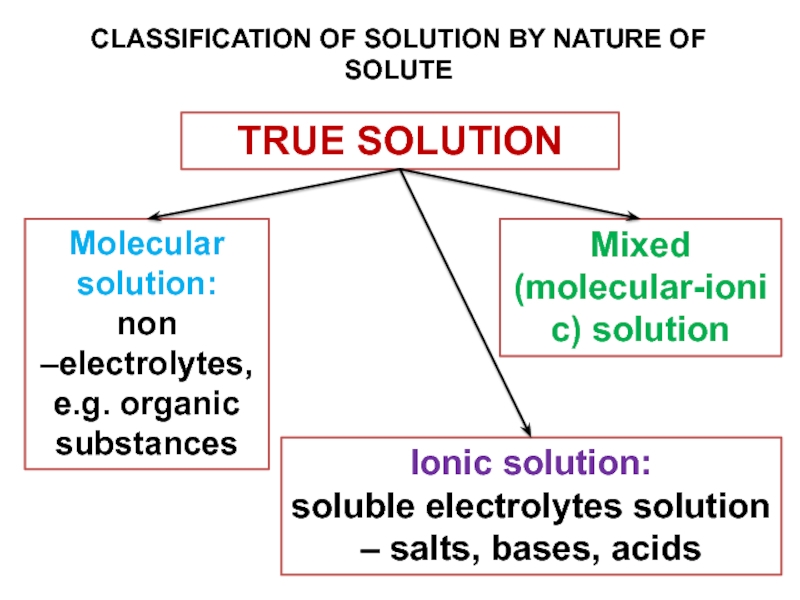
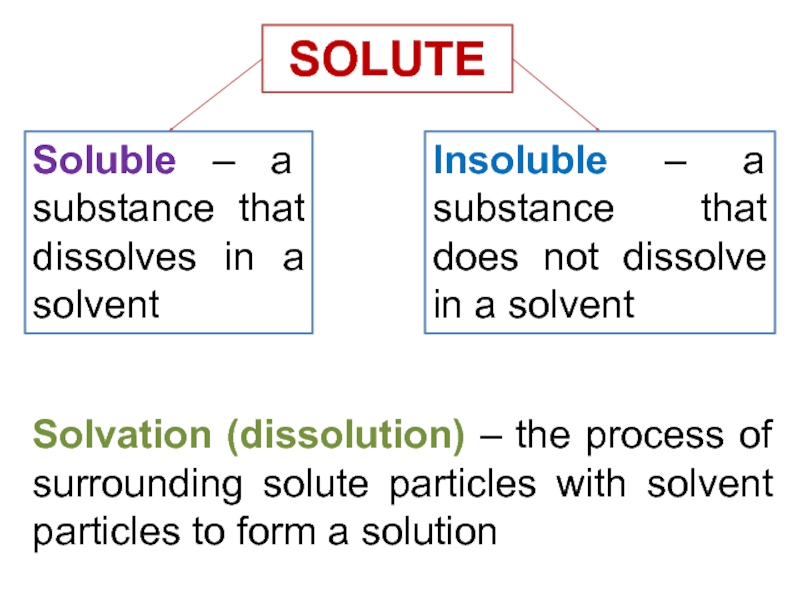
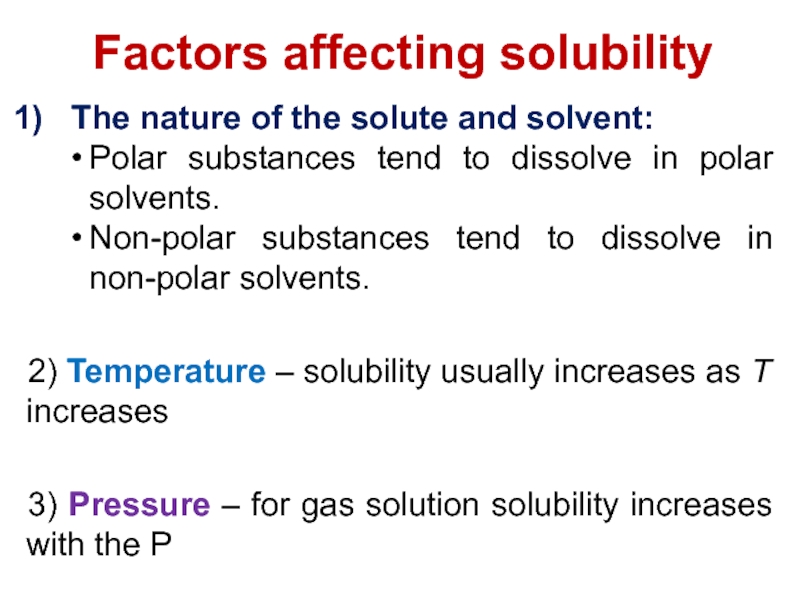
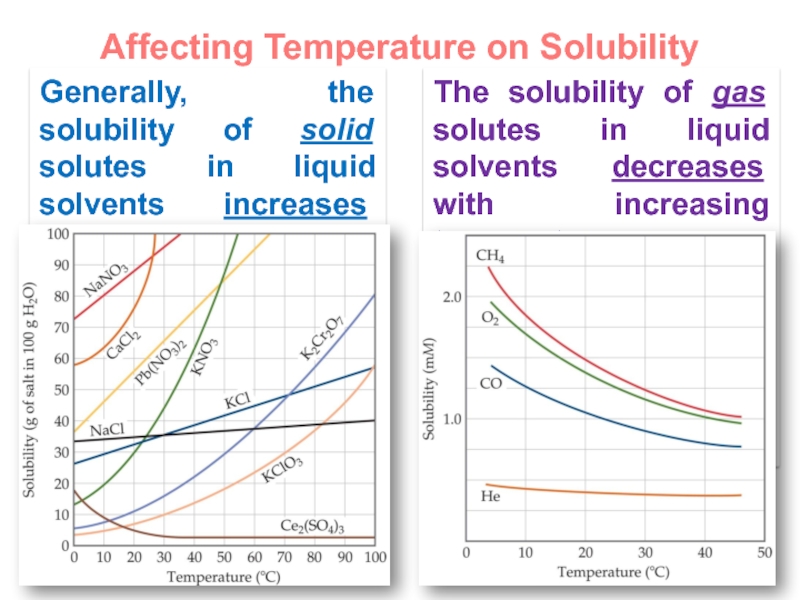
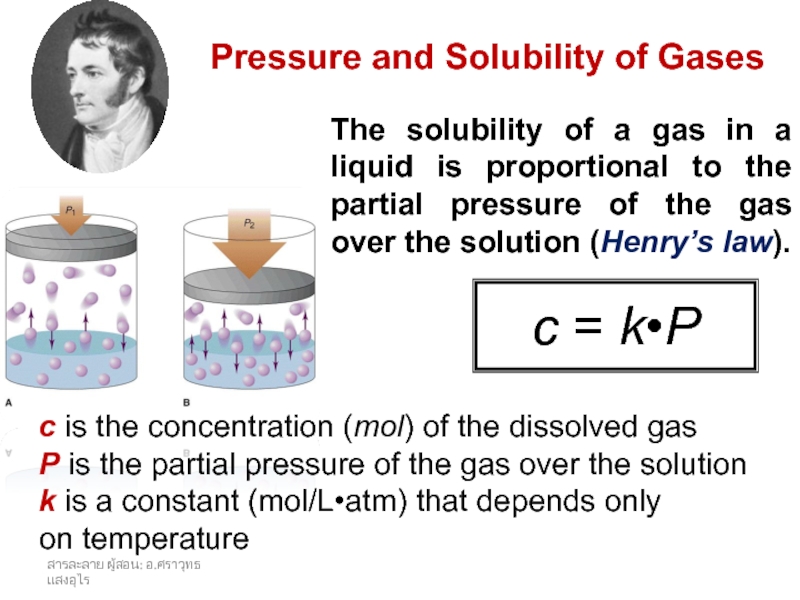
and heterogeneous mixture. For a homogeneous mixture, explain the difference between solute(s) and solvent. 3) Predict the effect of temperature and pressure on the solubility of gases in water and the effect of temperature on the solubility of solids in water.
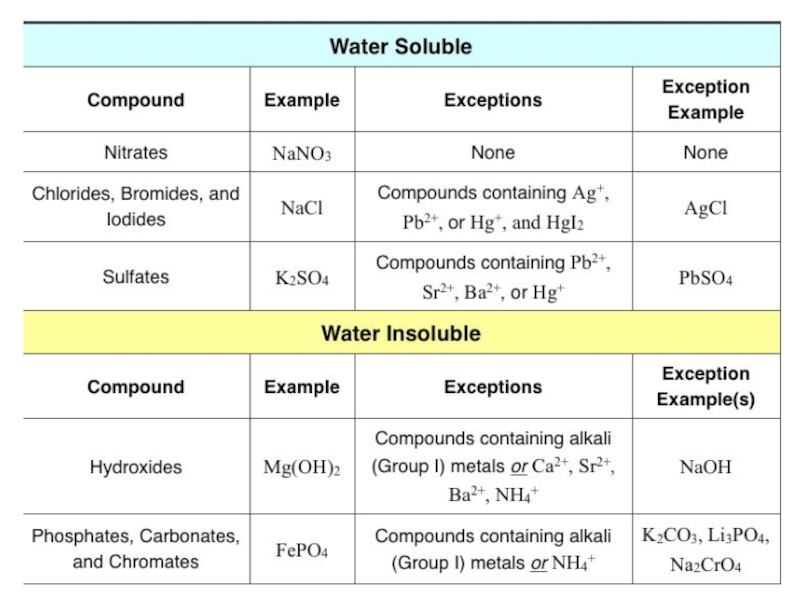
4) Be able to use the Solubility Rules Table to determine if an ionic compound will significantly dissolve in water.
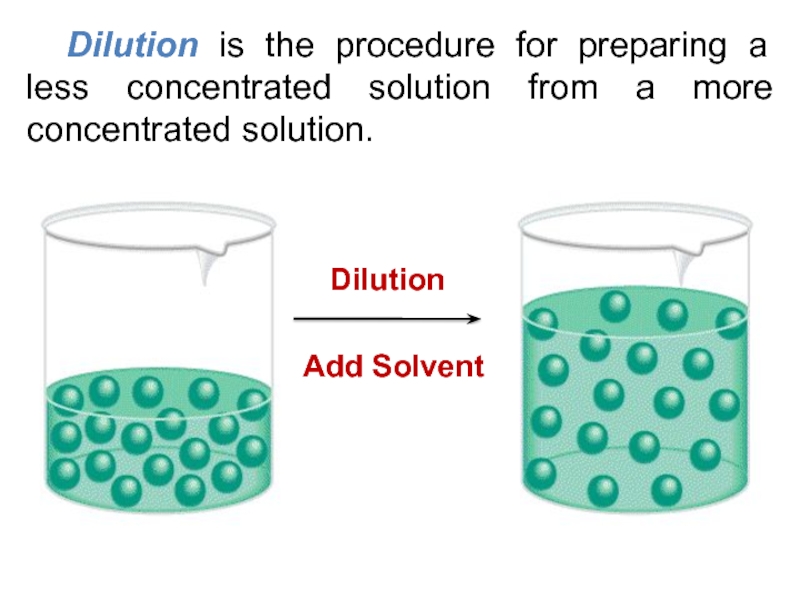
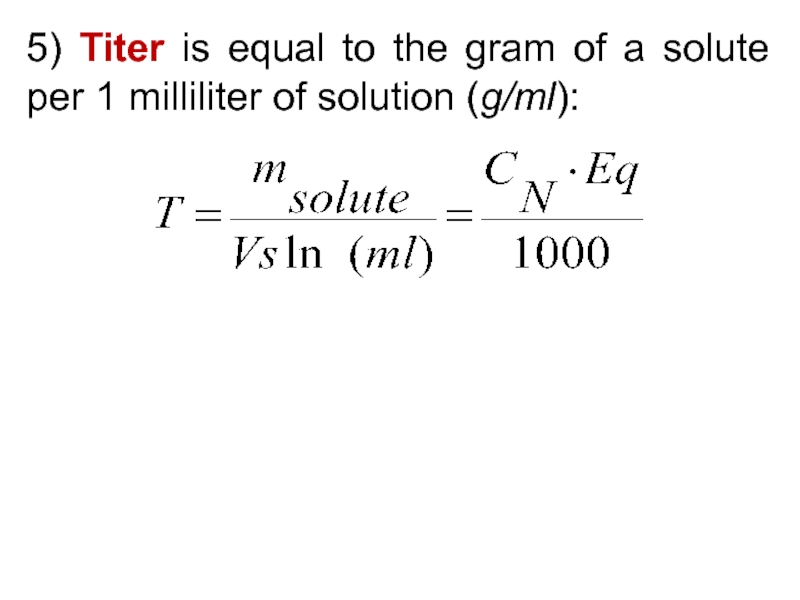
5) Be able to calculate the concentration of a solution using various concentration units of measurements. (%, parts per thousand, molarity, molality, normality and titer)