Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Managing in a Global Environment
Содержание
- 1. Managing in a Global Environment
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall4–Exhibit 4–1 European Union
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall4–Exhibit 4–3 How Organizations Go Global
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall4–Hofstede’s Framework for Assessing Cultures
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Managing
in a Global Environment
Слайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.4.1 What’s Your Global perspective?
Define parochialism.
Contrast ethnocentric, polycentric, and geocentric attitudes towards global business.
4.2 Understanding The global Environment
Describe the current status of the EU, NAFTA, ASEAN and other Regional Trade Allowances.
Discuss the role of the WTO.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Learning
Outcomes
4.3 Doing Business Globally
Contrast multinational, multidomestic, global, transnational, and born
global organizations.Describe the different ways organizations can go international.
4.4 Managing In A Global Environment.
Explain how the global legal-political and economic environments affect managers.
Discuss Hofstede’s five dimensions for assessing cultures.
Describe the challenges of doing business globally in today’s world.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Learning
Outcomes
4.4 Managing In A Global Environment.
Explain how the global legal-political
and economic environments affect managers.Discuss Hofstede’s five dimensions for assessing cultures.
Describe the challenges of doing business globally in today’s world.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
The
Global Marketplace
Opportunities and Challenges
Coping with the sudden appearance of new
competitorsAcknowledging cultural, political, and economic differences
Dealing with increased uncertainty, fear, and anxiety
Adapting to changes in the global environment
Avoiding parochialism
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
What’s
Your Global Perspective?
Parochialism
Is viewing the world solely through one’s own
eyes and perspectives.Is not recognizing that others have different ways of living and working.
Is a significant obstacle for managers working in a global business world.
Is falling into the trap of ignoring others’ values and customs and rigidly applying an attitude of “ours is better than theirs” to foreign cultures.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Adopting
a Global Perspective
Ethnocentric Attitude
The parochialistic belief that the best work
approaches and practices are those of the home country.Polycentric Attitude
The view that the managers in the host country know the best work approaches and practices for running their business.
Geocentric Attitude
A world-oriented view that focuses on using the best approaches and people from around the globe.
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Regional
Trading Agreements
The European Union (EU)
A unified economic and trade entity
Belgium, Denmark, France, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, the United Kingdom, Germany, Austria, Finland, and Sweden
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
Eliminated barriers to free trade (tariffs, import licensing requirements, and customs user fees)
United States, Canada, and Mexico
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Exhibit
4–1 European Union
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Regional
Trading Agreements
U.S.-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA)
Free Trade Area of
the AmericasSouthern Cone Common Market (Mercosur)
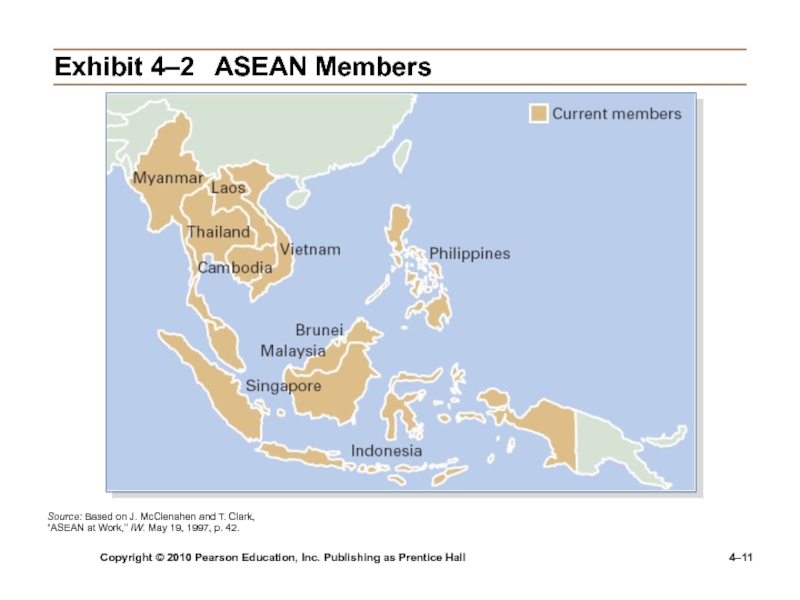
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Trading alliance of 10 Southeast Asian nations
African Union
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SARRC)
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Exhibit
4–2 ASEAN Members
Source: Based on J. McClenahen and T. Clark, “ASEAN
at Work,” IW. May 19, 1997, p. 42.Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
The
World Trade Organization (WTO)
Evolved from the General Agreement on Tariffs
and Trade (GATT) in 1995.Functions as the only global organization dealing with the rules of trade among nations.
Has 149 member nations and 32 observer governments.
Monitors and promotes world trade.
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Different
Types of International Organizations
Multinational Corporation (MNC)
Maintains operations in multiple countries.
Multidomestic
CorporationIs an MNC that decentralizes management and other decisions to the local country.
Global Company
Is an MNC that centralizes its management and other decisions in the home country.
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Different
Types of International Organizations (cont’d)
Transnational Corporation (Borderless Organization)
Is an MNC
that has eliminated structural divisions that impose artificial geographic barriers and is organized along business lines that reflect a geocentric attitude.Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
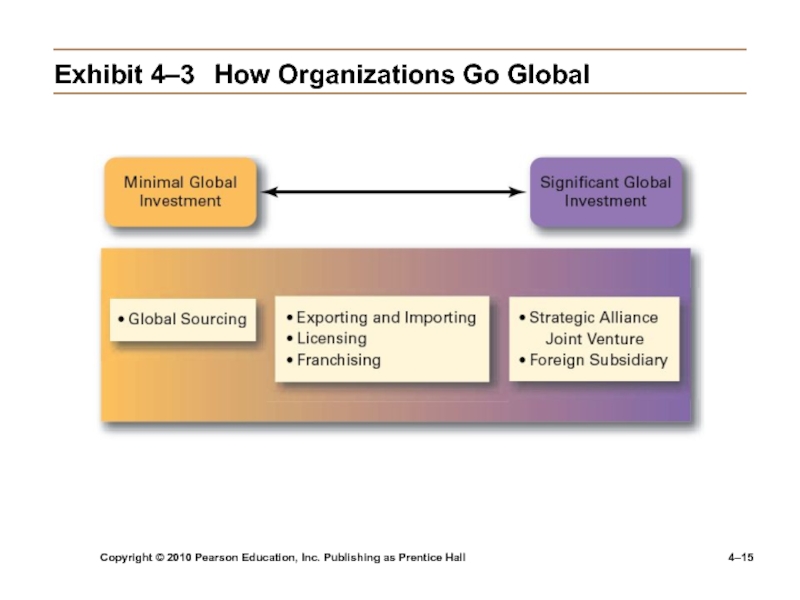
Exhibit
4–3 How Organizations Go Global
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Other
Forms of Globalization
Strategic Alliances
Partnerships between and organization and a foreign
company in which both share resources and knowledge in developing new products or building new production facilities.Joint Venture
A specific type of strategic alliance in which the partners agree to form a separate, independent organization for some business purpose.
Foreign Subsidiary
Directly investing in a foreign country by setting up a separate and independent production facility or office.
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Managing
in A Global Environment
The Legal Environment
Stability or instability of legal
and political systemsLegal procedures are established and followed
Fair and honest elections held on a regular basis
Differences in the laws of various nations
Effects on business activities
Effects on delivery of products and services
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
The
Economic Environment
Economic Systems
Free market economy
An economy in which resources are
primarily owned and controlled by the private sector.Planned economy
An economy in which all economic decisions are planned by a central government.
Monetary and Financial Factors
Currency exchange rates
Inflation rates
Diverse tax policies
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
The
Cultural Environment
National Culture
Is the values and attitudes shared by individuals
from a specific country that shape their behavior and their beliefs about what is important.May have more influence on an organization than the organization culture.
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Exhibit
4–4 What Are Americans Like
Americans are very informal.
Americans are direct.
Americans
are competitive.Americans are achievers.
Americans are independent and individualistic.
Americans are questioners.
Americans dislike silence.
Americans value punctuality.
Americans value cleanliness.
Sources: Based on M. Ernest (ed.), Predeparture Orientation Handbook: For Foreign Students and Scholars Planning to Study in the United States (Washington, DC: U.S. Information Agency, Bureau of Cultural Affairs, 1984), pp. 103–05; A. Bennett, “American Culture Is Often a Puzzle for Foreign Managers in the U.S.,” Wall Street Journal, February 12, 1986, p. 29; “Don’t Think Our Way’s the Only Way,” The Pryor Report, February 1988, p. 9; and B.J. Wattenberg, “The Attitudes behind American Exceptionalism,” U.S. News & World Report, August 7, 1989, p. 25.
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Hofstede’s
Framework for Assessing Cultures
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
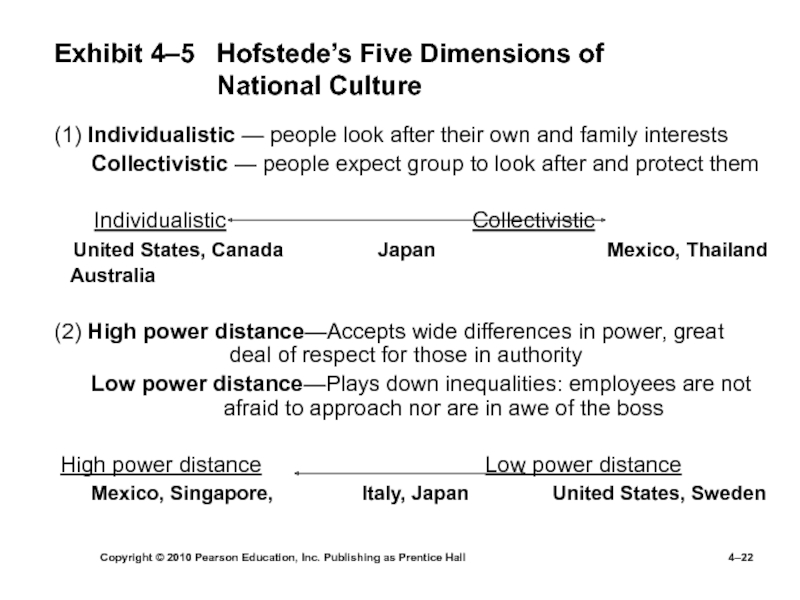
Exhibit
4–5 Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of
National Culture(1) Individualistic — people look after their own and family interests
Collectivistic — people expect group to look after and protect them
Individualistic Collectivistic
United States, Canada Japan Mexico, Thailand
Australia
(2) High power distance—Accepts wide differences in power, great deal of respect for those in authority
Low power distance—Plays down inequalities: employees are not afraid to approach nor are in awe of the boss
High power distance Low power distance
Mexico, Singapore, Italy, Japan United States, Sweden
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Exhibit
4–5 Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of
National Culture(3) High uncertainty avoidance—Threatened with ambiguity and experience high levels of anxiety
Low uncertainty avoidance— Comfortable with risks; tolerant of different behavior and opinions
High uncertainty avoidance Low uncertainty avoidance
Italy, Mexico, France United Kingdom Canada, United States, Singapore
(4) Achievement—Values such as assertiveness, acquiring money and goods, and competition prevail
Nurturing—Values such as relationships and concern for others prevail
Achievement Nurturing
United States, Japan, Canada, Greece France, Sweden
Mexico
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Exhibit
4–5 Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of
National Culture(5) Long-term orientation—People look to the future and value thrift and persistence
Short-term orientation — People value tradition and the past
Short-term thinking Long-term thinking
Germany, Australia, China, Taiwan, Japan
United States, Canada
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Exhibit
4–6 GLOBE Highlights
Source: M. Javidan and R. J. House, “Cultural Acumen
for the Global Manager: Lessons from Project GLOBE,” Organizational Dynamics, Spring 2001, pp. 289–305. Copyright © 2001. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier.Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Global
Management in Today’s World
Challenges
Openness associated with globalization
Significant cultural differences (e.g.,
Americanization)Adjusting leadership styles and management approaches
Risks
Loss of investments in unstable countries
Increased terrorism
Economic interdependence
Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
4–
Terms
to Know
parochialism
ethnocentric attitude
polycentric attitude
geocentric attitude
European Union (EU)
Euro
North American Free Trade
Agreement (NAFTA)Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
World Trade Organization (WTO)
multinational corporations (MNCs)
multidomestic corporation
global company
transnational or borderless organization
born globals
global sourcing
exporting
importing
licensing
franchising
strategic alliances
joint venture
foreign subsidiary
market economy
command economy
national culture
GLOBE
wikis
blogs