Слайд 1мараках марван якин нажи
Department of Dermatovenerology
Слайд 2Lection 3
Eczema
Etiology and pathogenesis of eczema. It is necessary to
comprehend that eczema is a polyetiological disease with complex pathogenesis,
where the main role is played by allergic factors, affecting the organisms with changed reactivity of the central and vegetative nervous systems. The autoallergic phenomenon is of certain significance, which is due to the presence of focal infection, visceral and endocrinopathy, immune conditions. Eczema starts with the formation of monovalent sensitization (increased sensitivity towards a certain allergen) which afterwards may transfer into polyvalent sensitization.
The word eczema means 'to boil over.'
Слайд 3Pathogenic types of eczema
True eczema
Microbial eczema
Nummular eczema
Varicose eczema
Posttraumatic eczema
Seborrheic eczema
Infantile eczema
Слайд 4Classification of dermatitis
Simple dermatitis
Physical
Mechanical
Chemical
Biological
Allergic dermatitis
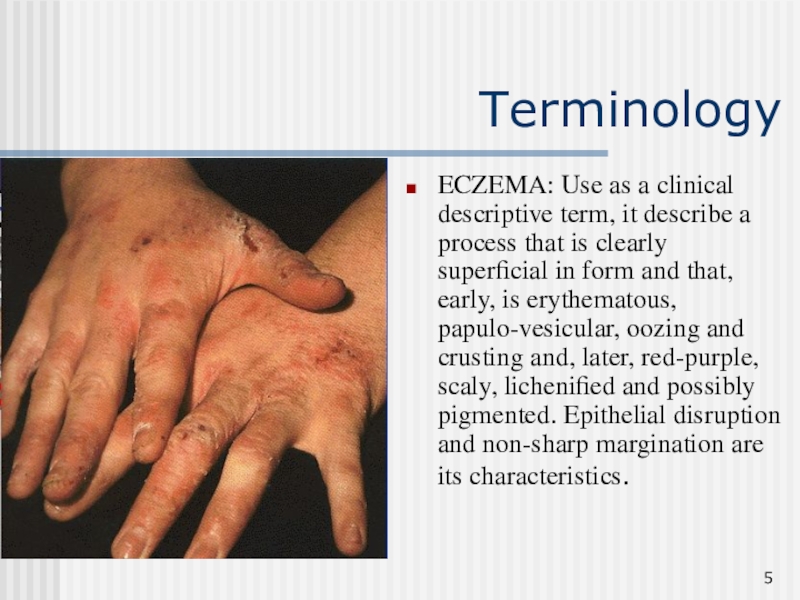
Слайд 5Terminology
ECZEMA: Use as a clinical descriptive term, it describe a
process that is clearly superficial in form and that, early,
is erythematous, papulo-vesicular, oozing and crusting and, later, red-purple, scaly, lichenified and possibly pigmented. Epithelial disruption and non-sharp margination are its characteristics.
Слайд 6True eczema
True eczema – the main role in pathogenesis is
played by a polyvalent sensitization and pronounced neurogenic disturbances. Clinical
features: disseminated, symmetric and blunt borders of the lesions, intense itching; primary lesion is a punctulated microvesicle (“serous wells”), crusts with small foci, fine-laminar desquamation.
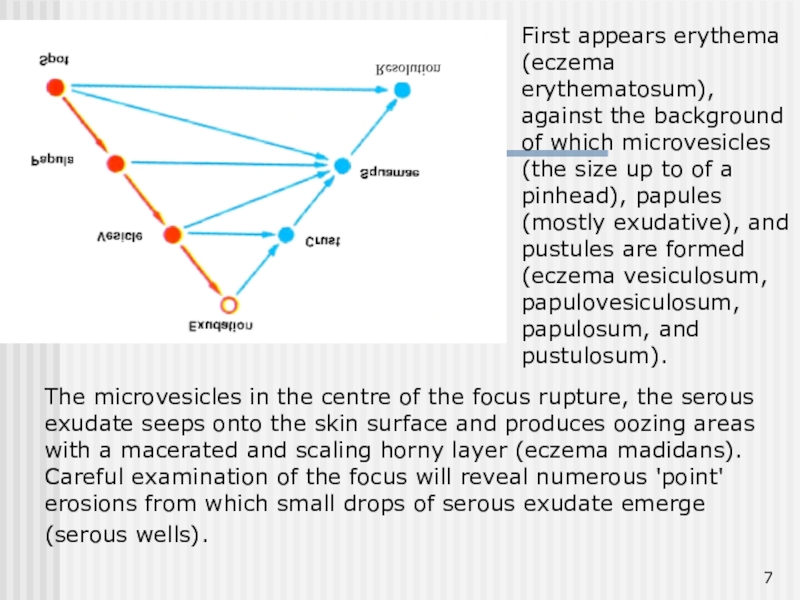
Слайд 7The microvesicles in the centre of the focus rupture, the
serous exudate seeps onto the skin surface and produces oozing
areas with a macerated and scaling horny layer (eczema madidans). Careful examination of the focus will reveal numerous 'point' erosions from which small drops of serous exudate emerge (serous wells).
First appears erythema (eczema erythematosum), against the background of which microvesicles (the size up to of a pinhead), papules (mostly exudative), and pustules are formed (eczema vesiculosum, papulovesiculosum, papulosum, and pustulosum).
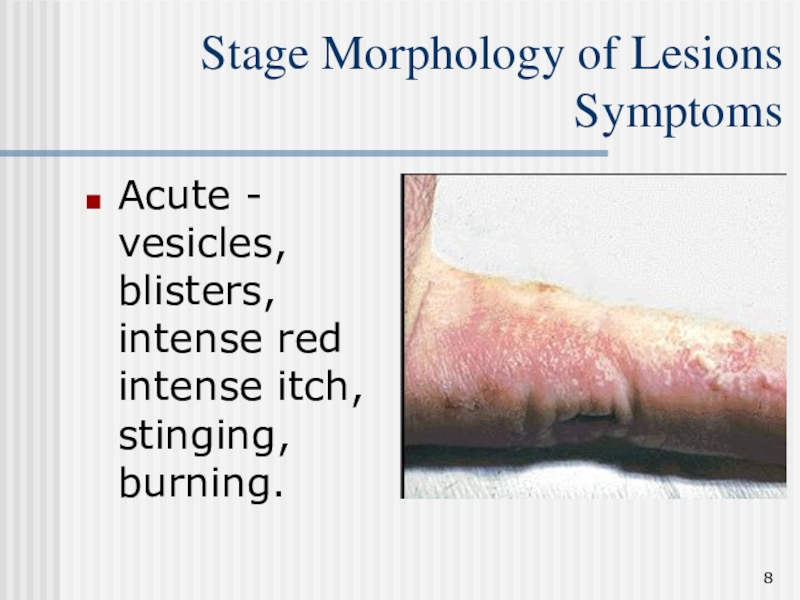
Слайд 8Stage Morphology of Lesions Symptoms
Acute - vesicles, blisters, intense
red intense itch, stinging, burning.
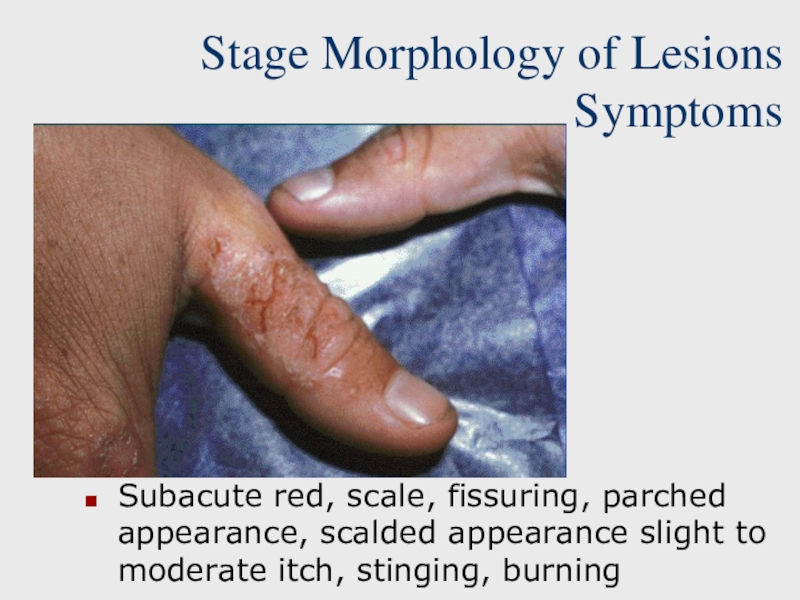
Слайд 9Stage Morphology of Lesions Symptoms
Subacute red, scale, fissuring, parched appearance,
scalded appearance slight to moderate itch, stinging, burning
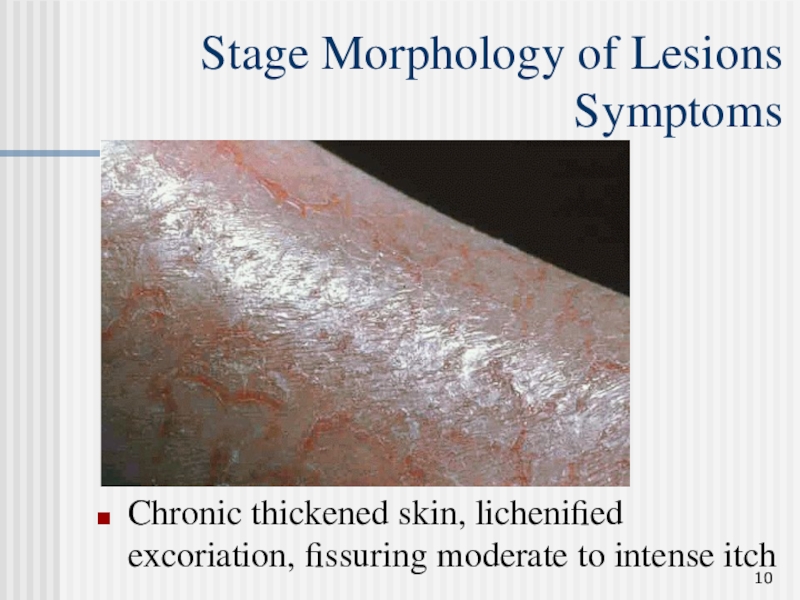
Слайд 10Stage Morphology of Lesions Symptoms
Chronic thickened skin, lichenified excoriation, fissuring
moderate to intense itch
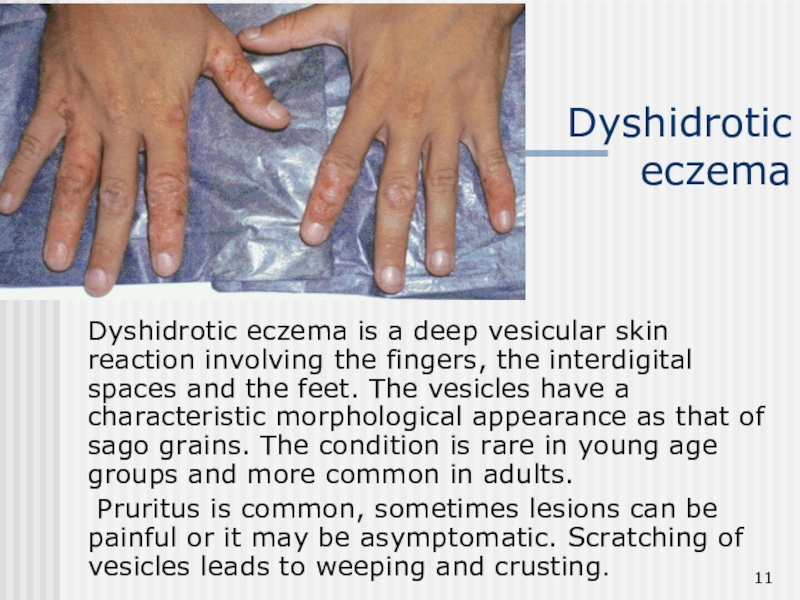
Слайд 11Dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is a deep vesicular skin reaction involving
the fingers, the interdigital spaces and the feet. The vesicles
have a characteristic morphological appearance as that of sago grains. The condition is rare in young age groups and more common in adults.
Pruritus is common, sometimes lesions can be painful or it may be asymptomatic. Scratching of vesicles leads to weeping and crusting.
Слайд 12Microbial eczema
Microorganisms or their products that clear when the organisms
are eradicated may cause microbial eczema. This should be distinguished
from infected eczema, in which eczema is complicated by secondary bacterial or viral invasion of the broken skin. The skin becomes sensitized to bacterial products or chemicals present in the exudates. Infectious eczematoid dermatitis is considered as an example of autosensitisation.
The mechanism by which microorganisms can cause eczema is not understood. Bacterial antigens can promote a cytotoxic reaction in the skin.
Слайд 13Microbial eczema.
Clinical features.
The distinction between infective and infected eczema
is difficult.
Infected eczema shows erythema with exudation and crusting. The
exudation may be profuse with crusting, or slight, with the accumulation of layers of somewhat greasy moist scale, below the surface is raw and red.
The margin is characteristically sharply defined. There may be small pustules and fissures in the advancing edge .
Infective eczema usually presents as an area of advancing erythema, sometimes with micro vesicles. It is seen predominantly around discharging wounds or ulcers, or moist skin lesions of other types.
Infective dermatitis is relatively common in patients with venous leg ulcers, but care must be taken to distinguish it from contact dermatitis due to topical preparations .
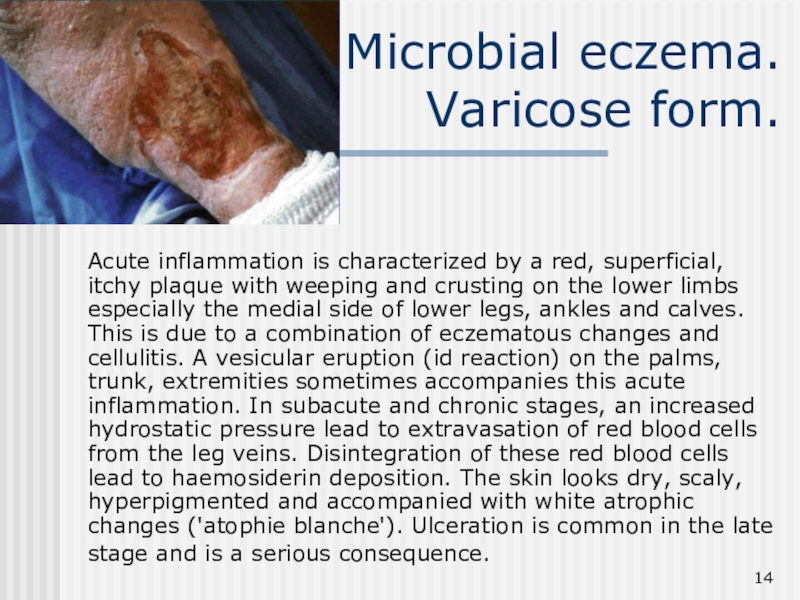
Слайд 14Microbial eczema.
Varicose form.
Acute inflammation is characterized by a red,
superficial, itchy plaque with weeping and crusting on the lower
limbs especially the medial side of lower legs, ankles and calves. This is due to a combination of eczematous changes and cellulitis. A vesicular eruption (id reaction) on the palms, trunk, extremities sometimes accompanies this acute inflammation. In subacute and chronic stages, an increased hydrostatic pressure lead to extravasation of red blood cells from the leg veins. Disintegration of these red blood cells lead to haemosiderin deposition. The skin looks dry, scaly, hyperpigmented and accompanied with white atrophic changes ('atophie blanche'). Ulceration is common in the late stage and is a serious consequence.
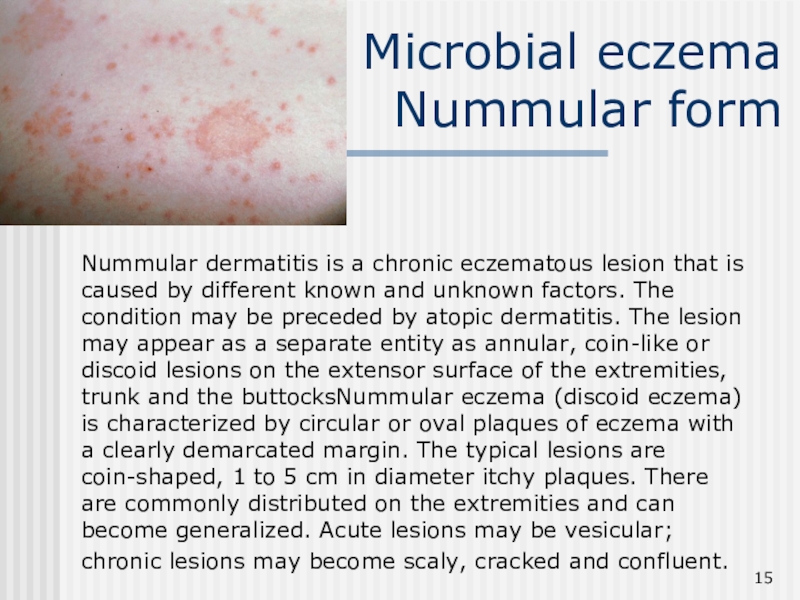
Слайд 15Microbial eczema
Nummular form
Nummular dermatitis is a chronic eczematous lesion
that is caused by different known and unknown factors. The
condition may be preceded by atopic dermatitis. The lesion may appear as a separate entity as annular, coin-like or discoid lesions on the extensor surface of the extremities, trunk and the buttocksNummular eczema (discoid eczema) is characterized by circular or oval plaques of eczema with a clearly demarcated margin. The typical lesions are coin-shaped, 1 to 5 cm in diameter itchy plaques. There are commonly distributed on the extremities and can become generalized. Acute lesions may be vesicular; chronic lesions may become scaly, cracked and confluent.
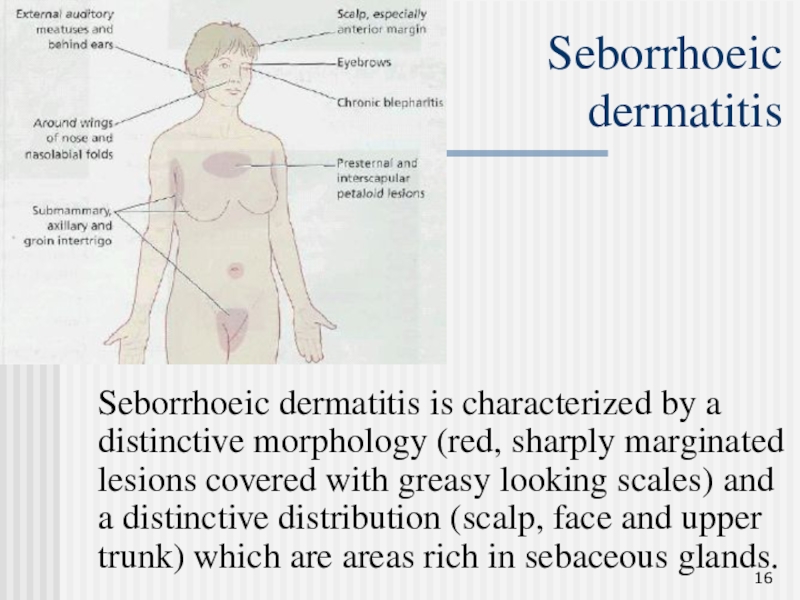
Слайд 16Seborrhoeic
dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is characterized by a distinctive morphology (red,
sharply marginated lesions covered with greasy looking scales) and a
distinctive distribution (scalp, face and upper trunk) which are areas rich in sebaceous glands.
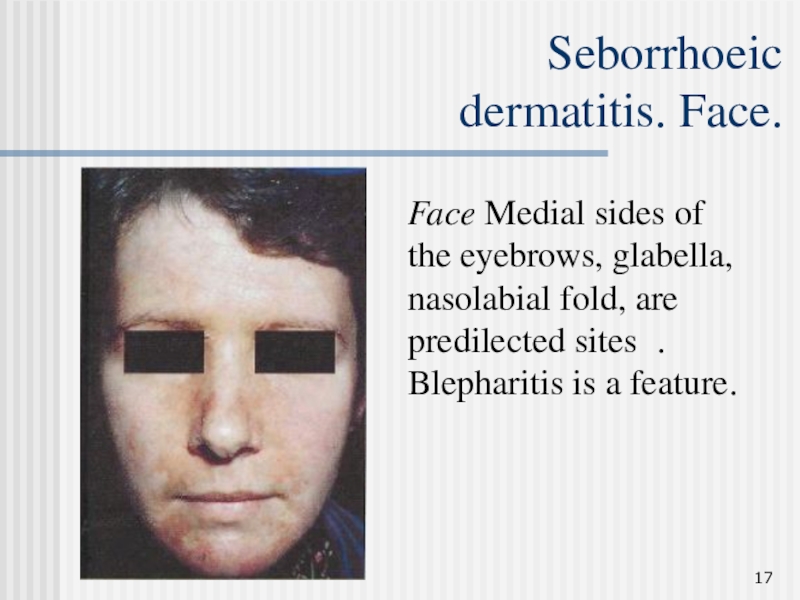
Слайд 17Seborrhoeic
dermatitis. Face.
Face Medial sides of the eyebrows, glabella, nasolabial
fold, are predilected sites . Blepharitis is a feature.
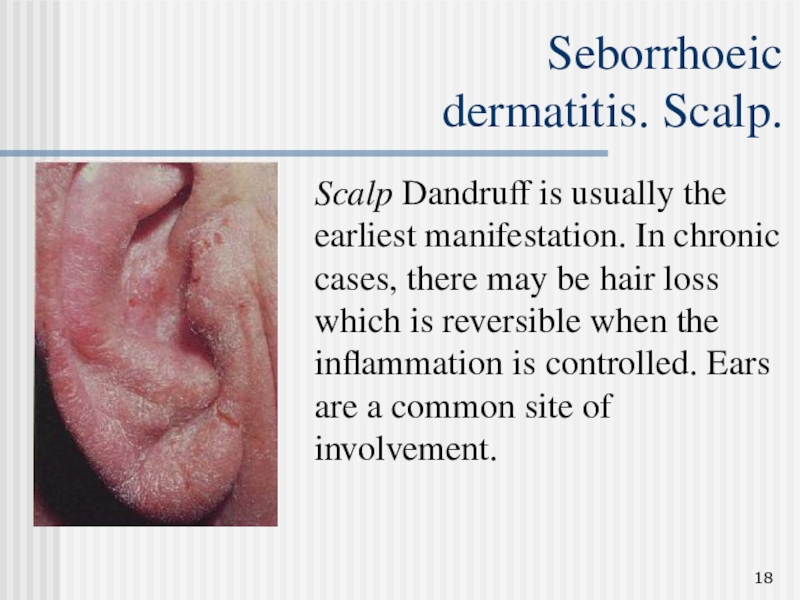
Слайд 18Seborrhoeic
dermatitis. Scalp.
Scalp Dandruff is usually the earliest manifestation. In
chronic cases, there may be hair loss which is reversible
when the inflammation is controlled. Ears are a common site of involvement.
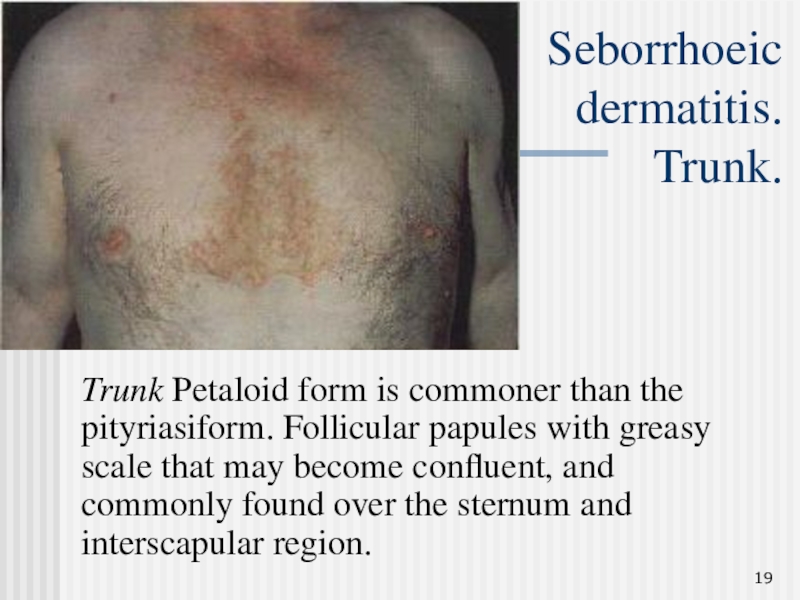
Слайд 19Seborrhoeic
dermatitis.
Trunk.
Trunk Petaloid form is commoner than the pityriasiform.
Follicular papules with greasy scale that may become confluent, and
commonly found over the sternum and interscapular region.
Слайд 20Seborrhoeic
dermatitis.
Infantile.
The eruptions in infants frequently first appear between
the third and eighth weeks of life. It may start
in the napkin area, the face and scalp, and occasionally on the trunk outside the napkin area. The rash comprises well-defined areas of erythema and scaling with tiny vesicles. Papular and lichenified lesions are not seen. Typically the infant is well and not irritable (c/w atopic dermatitis). The prognosis is usually good. Most uncomplicated cases clear in 3 to 4 weeks.
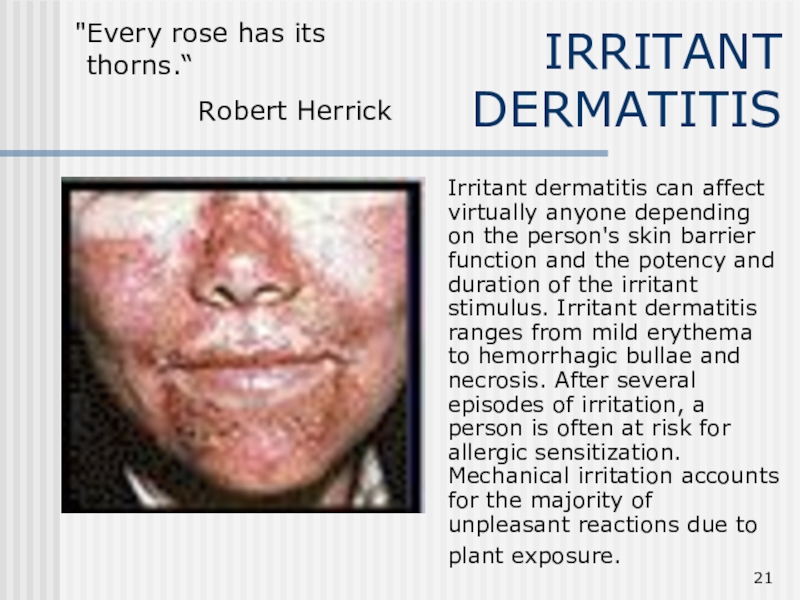
Слайд 21IRRITANT DERMATITIS
Irritant dermatitis can affect virtually anyone depending on
the person's skin barrier function and the potency and duration
of the irritant stimulus. Irritant dermatitis ranges from mild erythema to hemorrhagic bullae and necrosis. After several episodes of irritation, a person is often at risk for allergic sensitization. Mechanical irritation accounts for the majority of unpleasant reactions due to plant exposure.
"Every rose has its
thorns.“
Robert Herrick
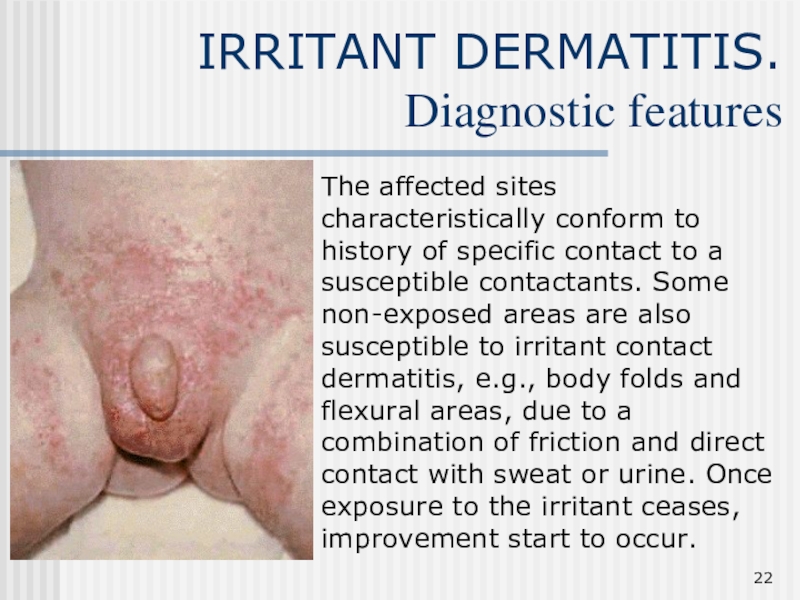
Слайд 22IRRITANT DERMATITIS.
Diagnostic features
The affected sites characteristically conform to history
of specific contact to a susceptible contactants. Some non-exposed areas
are also susceptible to irritant contact dermatitis, e.g., body folds and flexural areas, due to a combination of friction and direct contact with sweat or urine. Once exposure to the irritant ceases, improvement start to occur.
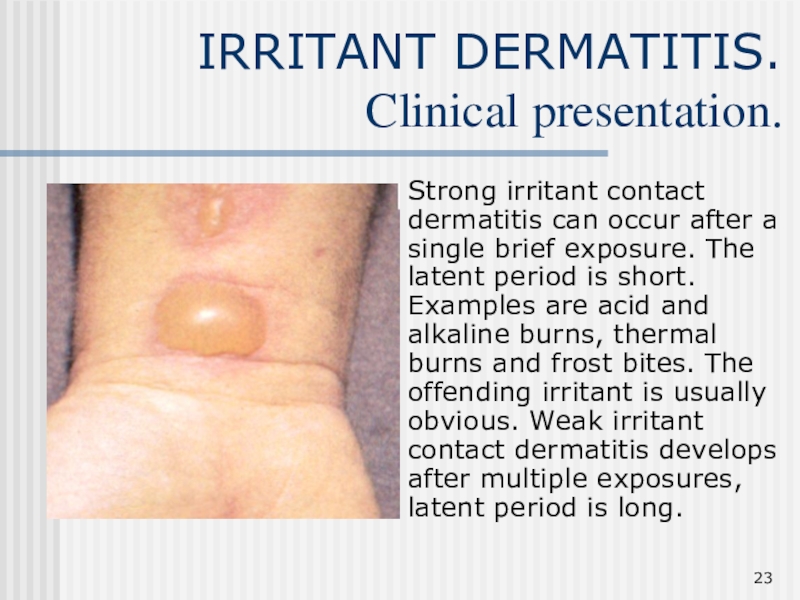
Слайд 23IRRITANT DERMATITIS.
Clinical presentation.
Strong irritant contact dermatitis can occur after a
single brief exposure. The latent period is short. Examples are
acid and alkaline burns, thermal burns and frost bites. The offending irritant is usually obvious. Weak irritant contact dermatitis develops after multiple exposures, latent period is long.
Слайд 24IRRITANT DERMATITIS.
Management.
The offending irritant should be identified and removed. Soap
and detergents should appropriately be minimized. Cool water is less
detrimental than hot water. Advice on the use of protective barriers whilst at work, e.g., gloves, protective clothes etc. should be strictly followed by the patient. Restoration of the lipid layer can be accomplished by frequent application of emollients. In case of maceration, wet clothing should be changed frequently, non-porous clothing to be avoided. Inflammatory element can be controlled with topical steroid.
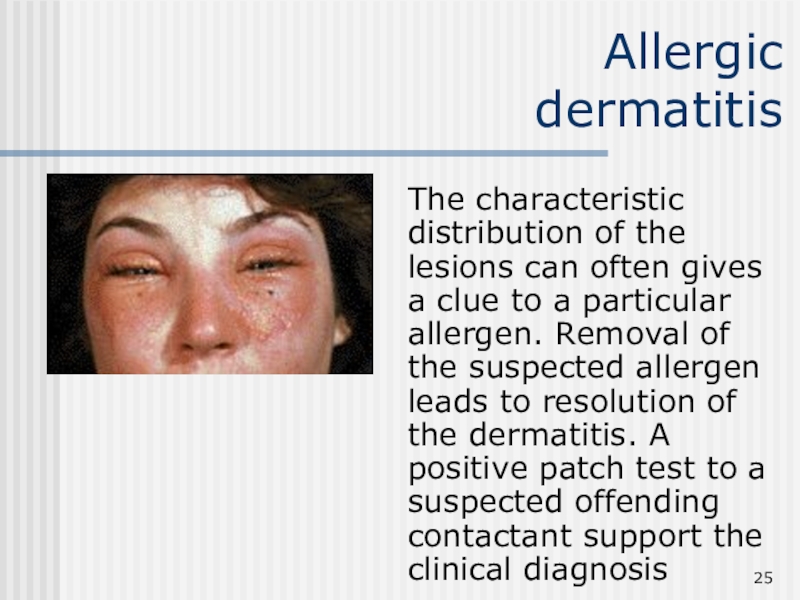
Слайд 25Allergic
dermatitis
The characteristic distribution of the lesions can often gives
a clue to a particular allergen. Removal of the suspected
allergen leads to resolution of the dermatitis. A positive patch test to a suspected offending contactant support the clinical diagnosis
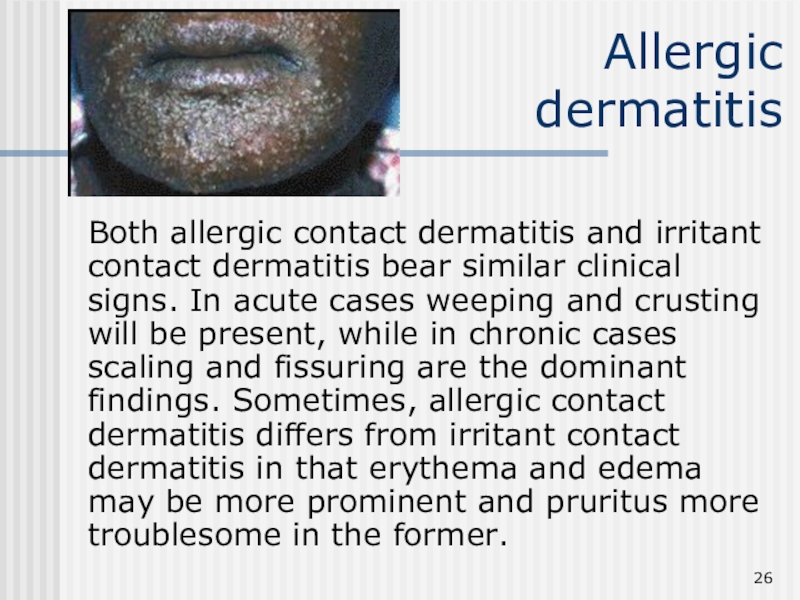
Слайд 26Allergic
dermatitis
Both allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis bear
similar clinical signs. In acute cases weeping and crusting will
be present, while in chronic cases scaling and fissuring are the dominant findings. Sometimes, allergic contact dermatitis differs from irritant contact dermatitis in that erythema and edema may be more prominent and pruritus more troublesome in the former.
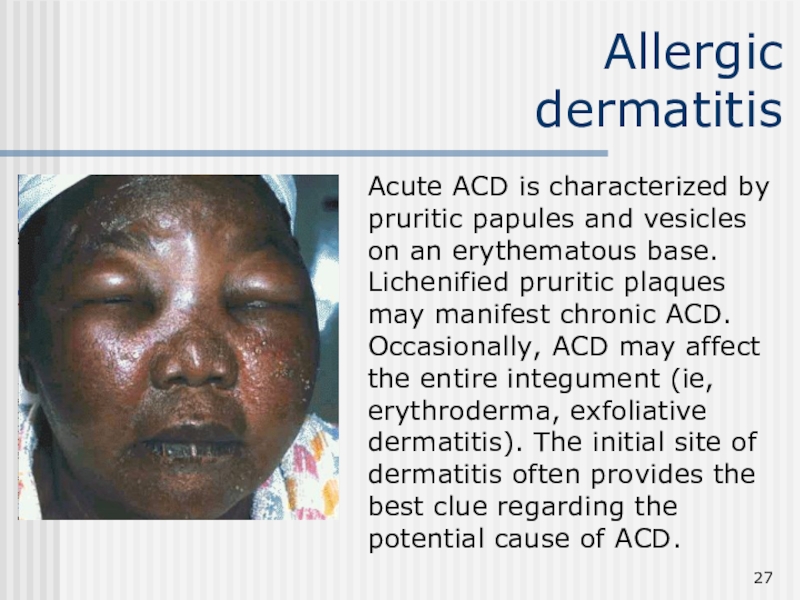
Слайд 27Allergic
dermatitis
Acute ACD is characterized by pruritic papules and vesicles
on an erythematous base. Lichenified pruritic plaques may manifest chronic
ACD. Occasionally, ACD may affect the entire integument (ie, erythroderma, exfoliative dermatitis). The initial site of dermatitis often provides the best clue regarding the potential cause of ACD.
Слайд 29Allergic dermatitis.
Management.
The first step is the identification and removal of
the contactant. A detailed history and a careful examination is
usually sufficient. Patch testing is indicated for cases in which inflammation persists despite avoidance and appropriate topical therapy.
For acute inflammation with blisters and intense erythema, cold wet compresses e.g. KMnO4 are highly effective. They should be used for 15 to 30 minutes several times a days until blistering and severe itching is controlled. Prednisolone, in dosage of around 30-40 mg a day in divided doses is used for extensive inflammation. Topical steroids for reduction of local inflammation.
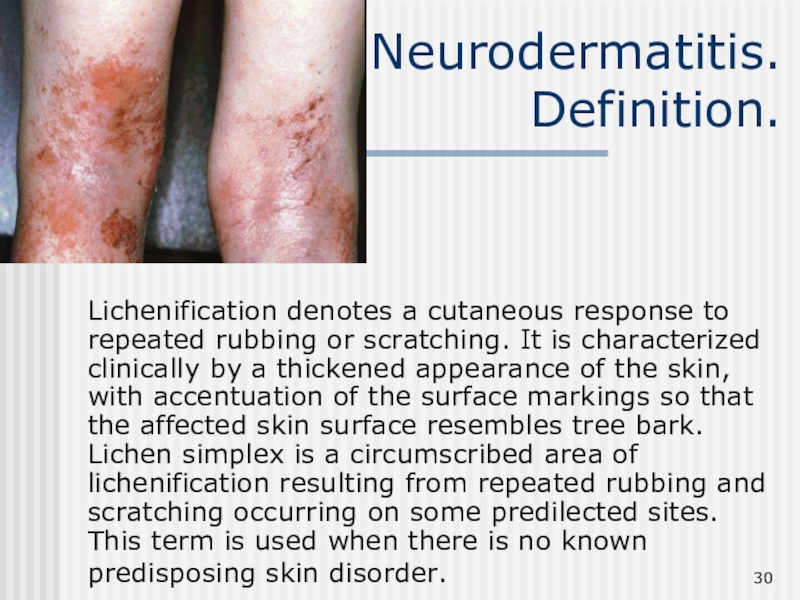
Слайд 30Neurodermatitis.
Definition.
Lichenification denotes a cutaneous response to repeated rubbing or
scratching. It is characterized clinically by a thickened appearance of
the skin, with accentuation of the surface markings so that the affected skin surface resembles tree bark. Lichen simplex is a circumscribed area of lichenification resulting from repeated rubbing and scratching occurring on some predilected sites. This term is used when there is no known predisposing skin disorder.
Слайд 31Neurodermatitis.
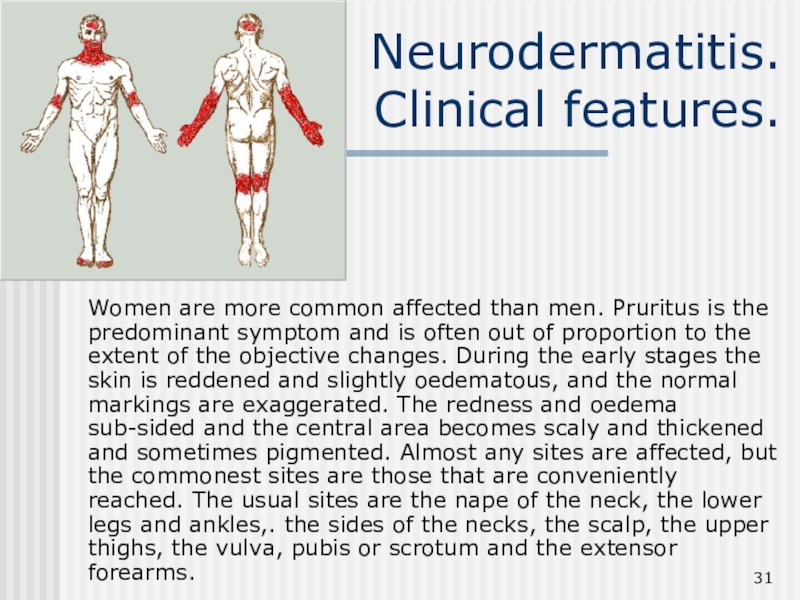
Clinical features.
Women are more common affected than men. Pruritus is
the predominant symptom and is often out of proportion to
the extent of the objective changes. During the early stages the skin is reddened and slightly oedematous, and the normal markings are exaggerated. The redness and oedema sub-sided and the central area becomes scaly and thickened and sometimes pigmented. Almost any sites are affected, but the commonest sites are those that are conveniently reached. The usual sites are the nape of the neck, the lower legs and ankles,. the sides of the necks, the scalp, the upper thighs, the vulva, pubis or scrotum and the extensor forearms.
Слайд 32Neurodermatitis.
Management.
A search for a causation should be made before the
lichenification is considered to be primary, then a careful psychological
history should be taken and the patient given some assistance in reducing her tensions. Topical steroid is the treatment of choice, sometimes with occlusion to enhance absorption and prevent further scratching. Intralesional triamcinolone is useful for circumscribed chronic lesions. Topical antibiotic may be prescribed if secondary infection is present.
Слайд 33AD
The aetiology is unknown and the pathogenetic mechanisms are speculative.
However, a number of clinical, pathological and immunological abnormalities are
frequently observed in these patients.
Elevated IgE occur in about 80 percent of AD patients and are directed against a wide variety of antigen like pollens, molds, foods, house dust mites and bacterial antigens etc. A high IgE level is not a unique feature of AD but appears to correlate with the clinical severity and falls with remission.
Слайд 34Atopic dermatitis.
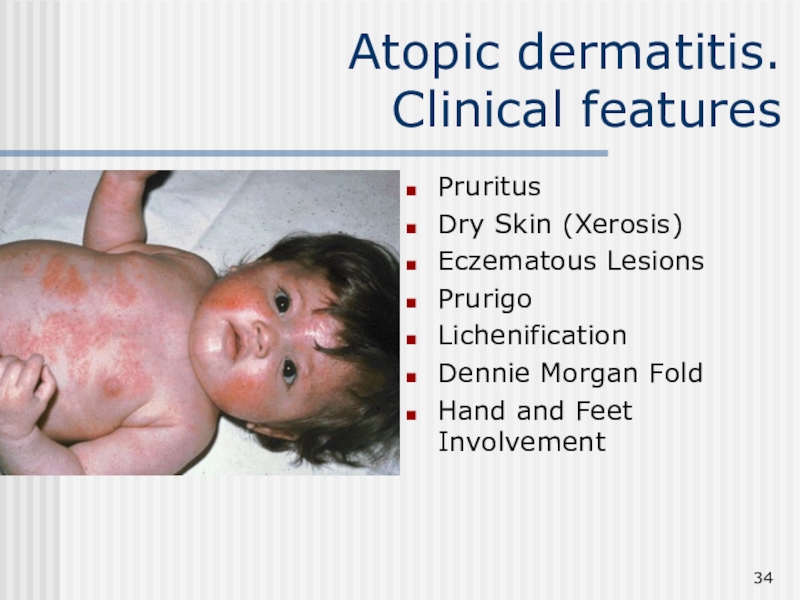
Clinical features
Pruritus
Dry Skin (Xerosis)
Eczematous Lesions
Prurigo
Lichenification
Dennie Morgan Fold
Hand and Feet Involvement
Слайд 35Atopic dermatitis.
Four Phases of AD
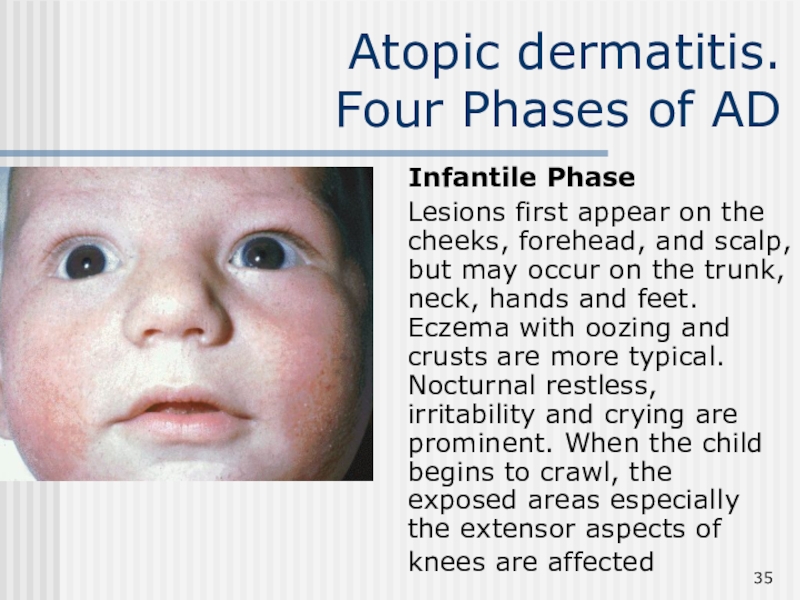
Infantile Phase
Lesions first
appear on the cheeks, forehead, and scalp, but may occur
on the trunk, neck, hands and feet. Eczema with oozing and crusts are more typical. Nocturnal restless, irritability and crying are prominent. When the child begins to crawl, the exposed areas especially the extensor aspects of knees are affected
Слайд 36Atopic dermatitis.
Four Phases of AD
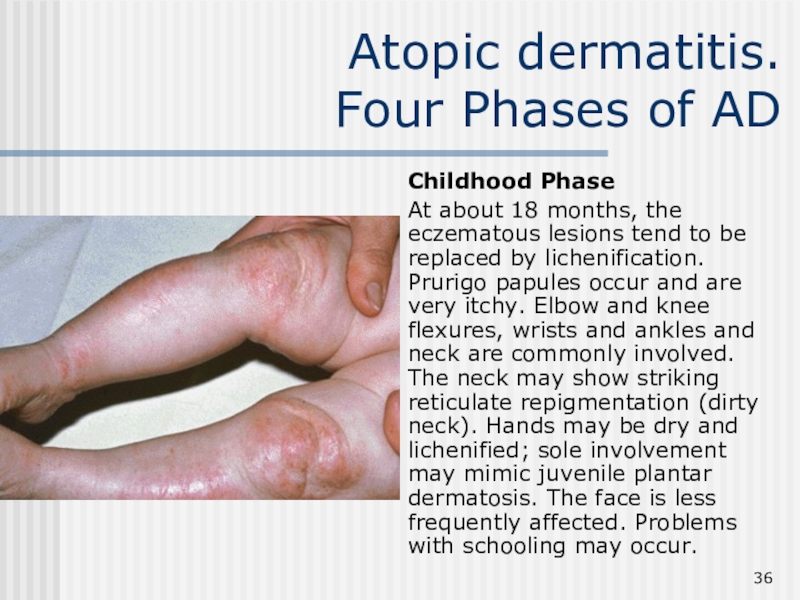
Childhood Phase
At about 18
months, the eczematous lesions tend to be replaced by lichenification.
Prurigo papules occur and are very itchy. Elbow and knee flexures, wrists and ankles and neck are commonly involved. The neck may show striking reticulate repigmentation (dirty neck). Hands may be dry and lichenified; sole involvement may mimic juvenile plantar dermatosis. The face is less frequently affected. Problems with schooling may occur.
Слайд 37AD.
Four Phases of AD
Adolescent/Young Adult Phase
Predominant features are
pruritus, lichenification, prurigo papules, scratch marks, and crusting. Lesions occur
mostly on the face, neck, flexures, and upper trunk. Localized patches of eczema around the nipple or vermillion of the lips can occur. Psychological difficulties occur in some.
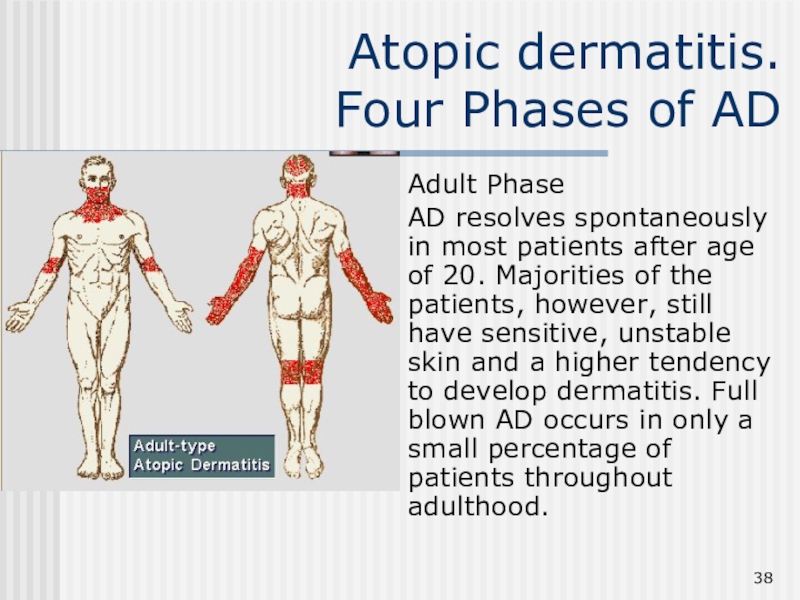
Слайд 38Atopic dermatitis.
Four Phases of AD
Adult Phase
AD resolves spontaneously
in most patients after age of 20. Majorities of the
patients, however, still have sensitive, unstable skin and a higher tendency to develop dermatitis. Full blown AD occurs in only a small percentage of patients throughout adulthood.