Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Medical Academy named after S.I. Georgievsky of Vernadsky CFU
Содержание
- 1. Medical Academy named after S.I. Georgievsky of Vernadsky CFU
- 2. NATURAL SELECTION OF HUMAN POPULATION REPRESENTED BY :DHRUV MANGAL195 b (LA-2)SUPERVISOR- ANNA ZHUKOVA
- 3. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
- 4. NATURAL SELECTIONthe process whereby organisms better adapted
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. HOW NATURAL SELECTION WORKS?To make natural selection
- 7. The original source of the new gene
- 8. FACT 1: Individuals in a population vary
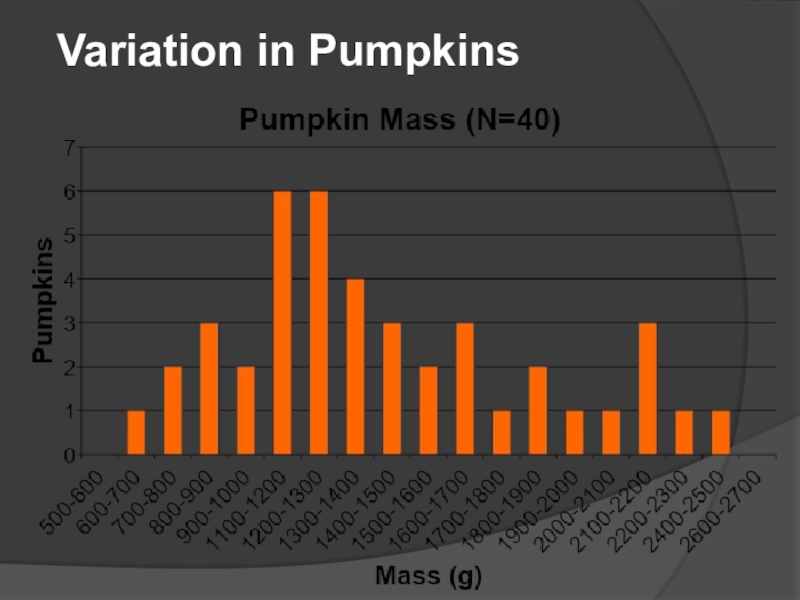
- 9. Variation in Pumpkins
- 10. Variation in Humans
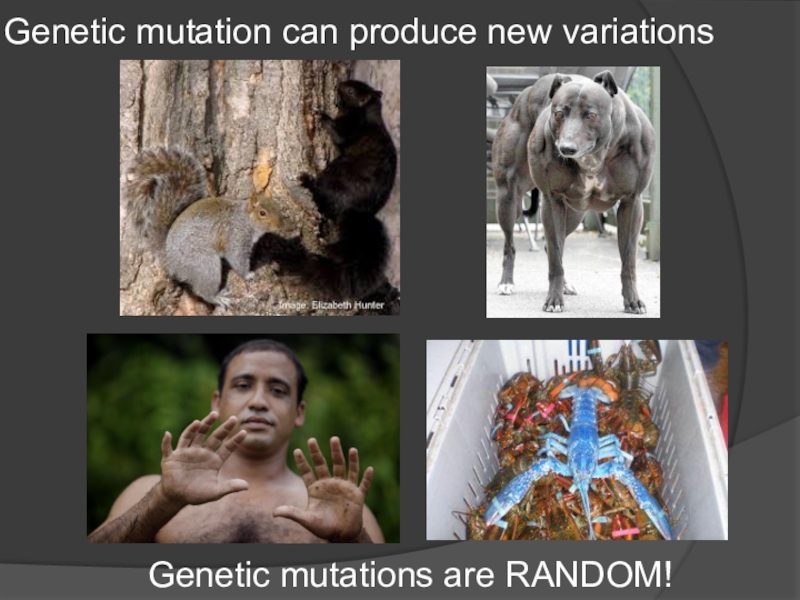
- 11. Genetic mutation can produce new variationsGenetic mutations are RANDOM!
- 12. Sexual (two parent) reproduction “shuffles” existing variations into new combinations
- 13. FACT 2: A population of any species
- 14. Inference 1: Certain inherited variations give some
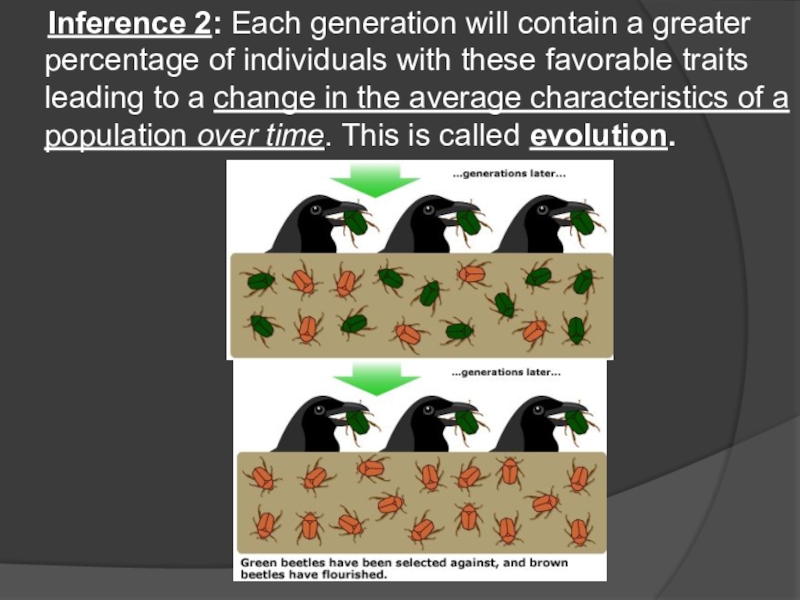
- 15. Inference 2: Each generation will contain a
- 16. Grant Finch Study: state and explain the
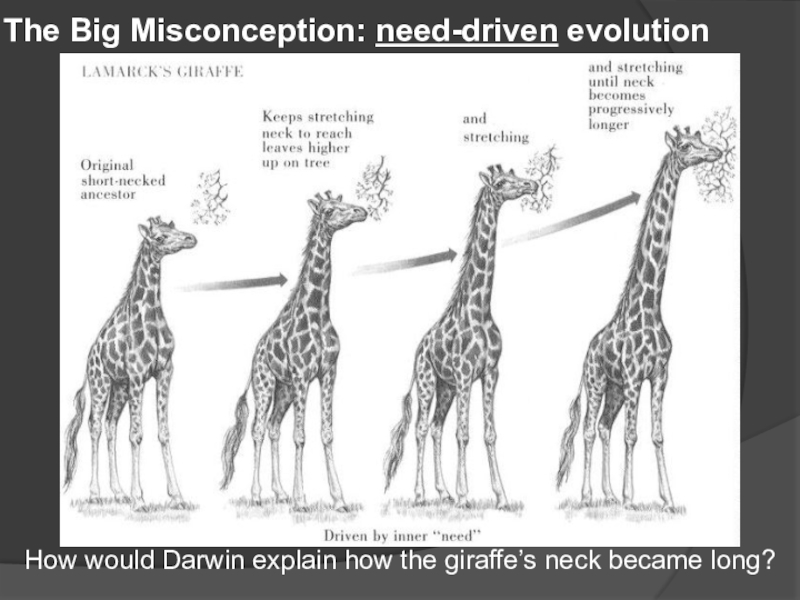
- 17. The Big Misconception: need-driven evolutionHow would Darwin explain how the giraffe’s neck became long?
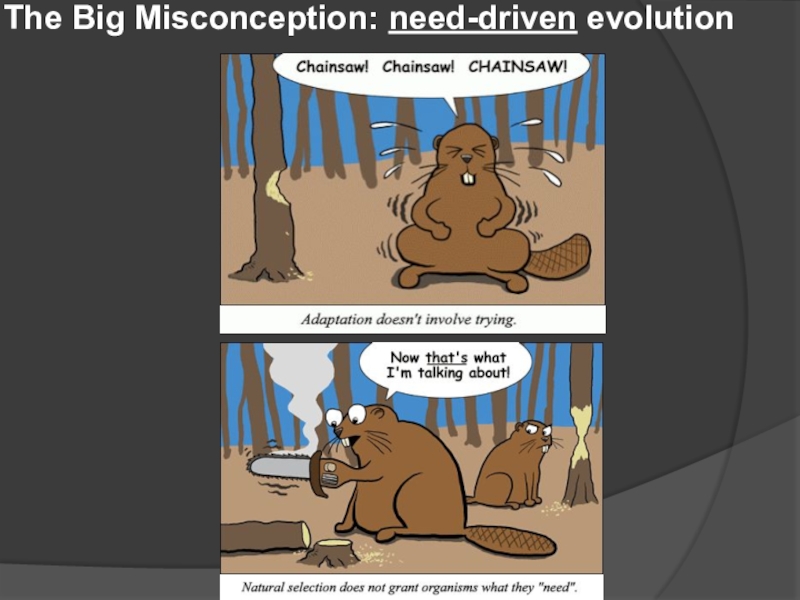
- 18. The Big Misconception: need-driven evolution
- 19. The Big Misconception: need-driven evolution
- 20. SUMMARYBy biological evolution we mean that many
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Скачать презентанцию
NATURAL SELECTION OF HUMAN POPULATION REPRESENTED BY :DHRUV MANGAL195 b (LA-2)SUPERVISOR- ANNA ZHUKOVA
Слайды и текст этой презентации
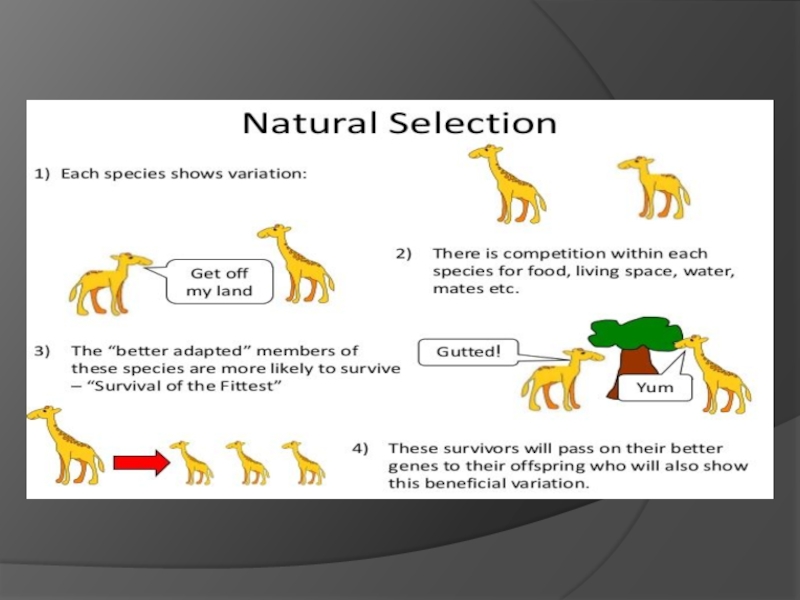
Слайд 4NATURAL SELECTION
the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment
tend to survive and produce more offspring. The theory of
its action was first fully expounded by Charles Darwin and is now believed to be the main process that brings about evolution.Слайд 6HOW NATURAL SELECTION WORKS?
To make natural selection more concrete, let's
consider a simplified, hypothetical example. In this example, a group
of mice with heritable variation in fur color (black vs. tan) has just moved into a new area where the rocks are black. This environment features hawks, which like to eat mice and can see the tan ones more easily than the black ones against the black rock.Because the hawks can see and catch the tan mice more easily, a relatively large fraction of the tan mice are eaten, while a much smaller fraction of the black mice are eaten. If we look at the ratio of black mice to tan mice in the surviving ("not-eaten") group, it will be higher than in the starting population.
Слайд 7
The original source of the new gene variants that produce
new heritable traits, such as fur colors, is random mutation
(changes in DNA sequence). Random mutations that are passed on to offspring typically occur in the germline, or sperm and egg cell lineage, of organisms. Sexual reproduction "mixes and matches" gene variants to make more variation.Слайд 8FACT 1: Individuals in a population vary or differ in
traits. Most of this variation is heritable (passed from parent
to offspring).Слайд 13FACT 2: A population of any species has the potential
to produce far more offspring than will survive to produce
offspring of their own.What are some of the challenges living things must overcome to survive?
Слайд 14 Inference 1: Certain inherited variations give some individuals a better
chance to survive in their environment. Those that survive will
produce more offspring. This is called natural selection.Слайд 15 Inference 2: Each generation will contain a greater percentage of
individuals with these favorable traits leading to a change in
the average characteristics of a population over time. This is called evolution.Слайд 16Grant Finch Study: state and explain the specific data that
supports each postulate in natural selection
Individuals in a population vary
in their traits2. Most of this variation is heritable – passed on to offspring
3. More offspring are produced than can survive (due to limited resources such as food)
4. Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce
Medium Ground Finch Geospiza fortis
Слайд 17The Big Misconception: need-driven evolution
How would Darwin explain how the
giraffe’s neck became long?
Слайд 20SUMMARY
By biological evolution we mean that many of the organisms
that inhabit the Earth today are different from those that
inhabited it in the past.Natural selection is one of several processes that can bring about evolution, although it can also promote stability rather than change. It follows that natural selection is not the same thing as evolution.
The four propositions underlying Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection are: (1) more individuals are produced than can survive; (2) there is therefore a struggle for existence; (3) individuals within a species show variation; and (4) offspring tend to inherit their parents' characters.
The three necessary and sufficient conditions for natural selection to occur are: (1) a struggle for existence; (2) variation; and (3) inheritance.
Endler's experiment with guppies demonstrated that evolution through natural selection can occur in relatively few generations.
Mutation is the ultimate source of variation.
The frequency of a particular character in a particular population may be due to chance events (e.g. the founder effect and/or genetic drift) rather than to natural selection.