Слайд 1Ministry education and Science of Republic of Kazakhstan
Karaganda State University
named after academician Ye.A. Buketov
Biological and geographical faculty
Botany Department
Course – Botany
Specialty - 5В011300 – «Biology»
Lecture № 21
Division Angiospermae, Magnoliophyta. Class Dicotyledones
(1 hour)
Lecturer: candidate of biological science, associated professor
Ishmuratova Margarita Yulaevna
Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 General characteristic of Angiosperm plants.
2 Bases of
systematic.
3 Characteristic of families Magnoliophyta, Schizandraceae, Lauraceae, Nimphaceae, typical species
and practical uses.
Слайд 3Basic literatures:
1 Еленевский А.Г., Соловьев М.П., Тихомиров В.Н. Ботаника:
систематика высших, или наземных, растений. 2 изд. - М.: Academіa,
2001. - 429 с.
2 Нестерова С.Г. Лабораторный практикум по систематике растений. - Алматы: Қазақ ун-ті, 2011. - 220 с.
3 Родман А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Additional literatures:
1 Билич Г.Л., Крыжановский В.А. Биология. Т. 2: Ботаника. - М.: Оникс 21 век, 2002. - 543 с.
2 Ишмуратова М.Ю. Систематика и интродукция растений (курс лекций). - Караганда: РИО Болашак-Баспа, 2015. - 100 с.
3 Тусупбекова Г.Т. Основы естествознания. Ч. 1. Ботаника. – Астана: Фолиант, 2013. – 321 с.
Слайд 4Flowering plants (angiosperms, Angiospermae) are sometimes referred to as “Spermatophyta
2.0.”, or “upgraded gymnosperms”. In fact, there is no single
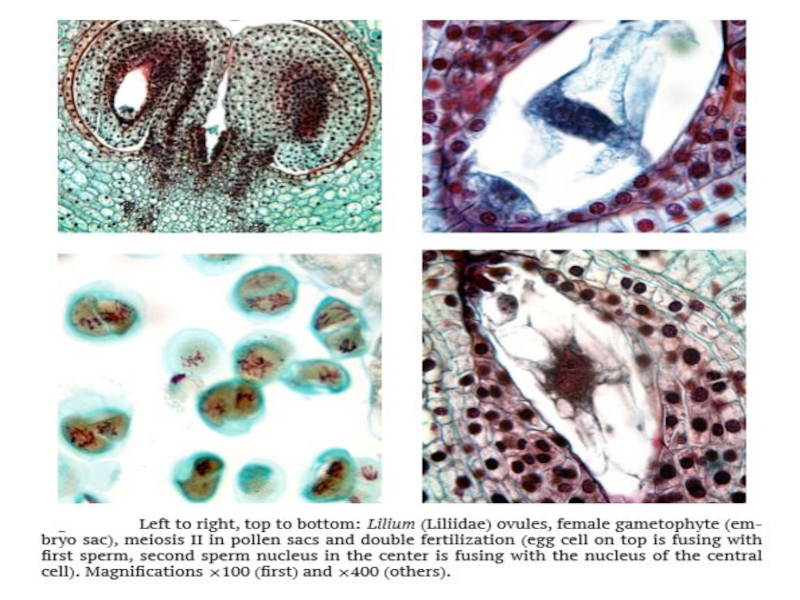
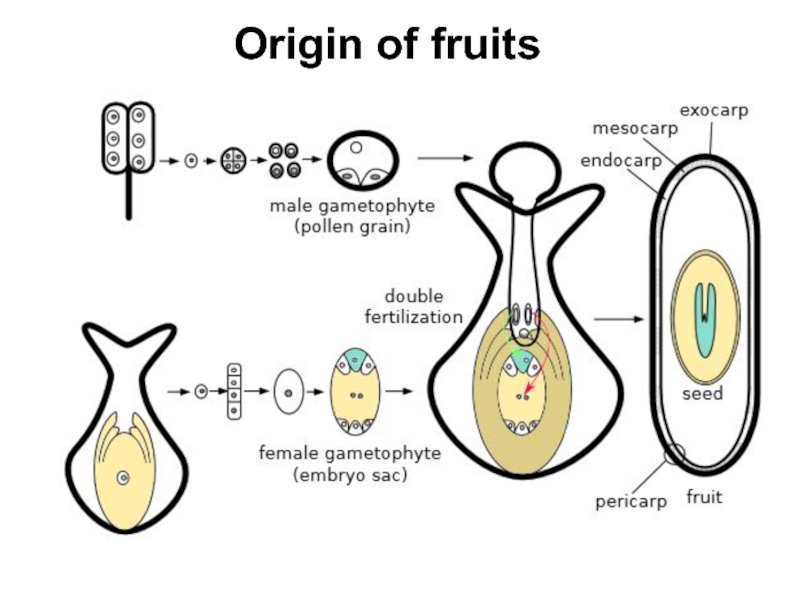
character which unequivocally differs flowering plants from other seed plants. Only several characteristics combined together will distinguish angiosperms. Flowering plants have their ovules inside an additional cover: pistil which corresponds with megasporophyll (sporangium-bearing leaf); later, the pistil develops into the fruit. These plants have an almost complete reduction of gametophytes: three or even two cell of the pollen (male gametophyte) and seven (sometimes even four) cells in embryo sac (female gametophyte), there are no archegonia or anteridia. Like gnetophytes, theyhavedoublefertilization. Thesperms(spermatia)comethroughthepollentube (like in conifers and gnetophytes). One sperm fertilizes the egg cell, and the other sperm fertilizes the biggest cell of embryo sac.
Слайд 6While the first fertilization results in a “normal” diploid zygote
which grows into embryo, the second fertilization ignites the process
of feeding tissue development. This feeding tissue is endosperm2, frequently triploid (3n) since it originates from the sperm and cell with two nuclei and sperm, or diploid (2n), if the biggest cell of embryo sac (central cell) had one nucleus only.
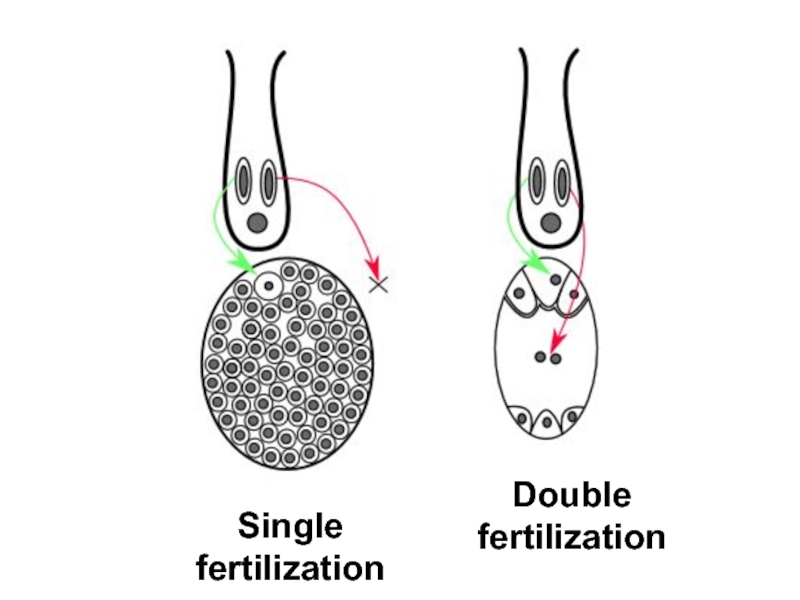
Слайд 7Double fertilization may be explained in several ways: (1) the
second fertilization results in second,“altruistic”embryo which sacrifices itself to feed
the“brother”; (2) second fertilization is only a signal which initiates the development of endosperm and it does not really matter which genotype it has; and/or (3) to make a functional nutrition tissue, angiosperms need a polyploid genome whereas its origin is not so important. Onewayoranother,floweringplantsabandonedthepre-fertilization development of the nutrition tissue, and changed endosperm 1 to endosperm 2.
Слайд 8Single fertilization
Double fertilization
Слайд 9In the Mesozoic era, gymnosperms were the dominating plants of
the tree story. However, in the uderstorey, herbaceous spore plants
did not surrender to seed plants and were still dominating. Amazingly, the rewereal most no herbaceous gymnosperms! The explanation is that gymnosperms, being quite advanced in general, had a slow and ineffective life cycle. Ineffectiveness was in part due to the absence of sophisticated cross-pollination like insect pollination (which requires edible parts like nectar or excess pollen).
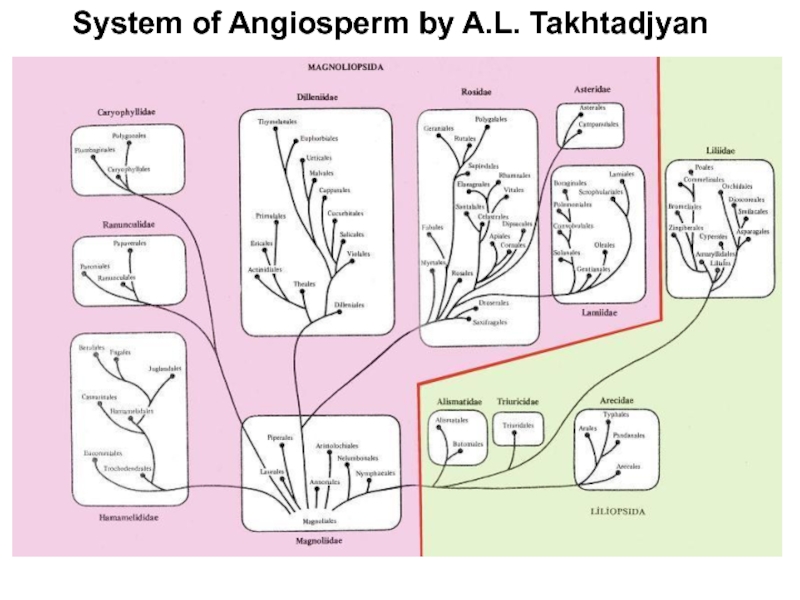
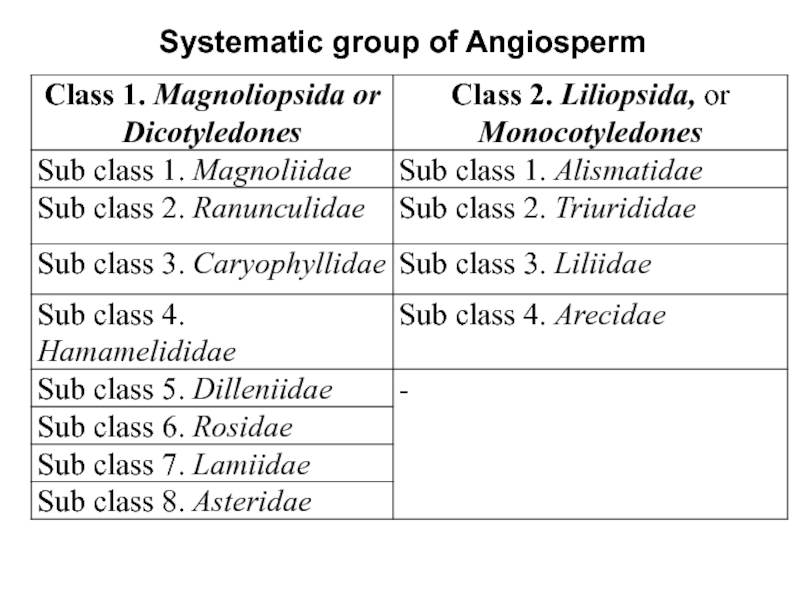
Слайд 13System of Angiosperm by A.L. Takhtadjyan
Слайд 14The most important signs of organization of flower plants:
flower;
much reduction
of gametophytes;
system of pollination;
creation of nucellus and fruits;
developed transport
system and system for water economy;
developed root system;
developed leafy apparatus;
diversity of life forms.
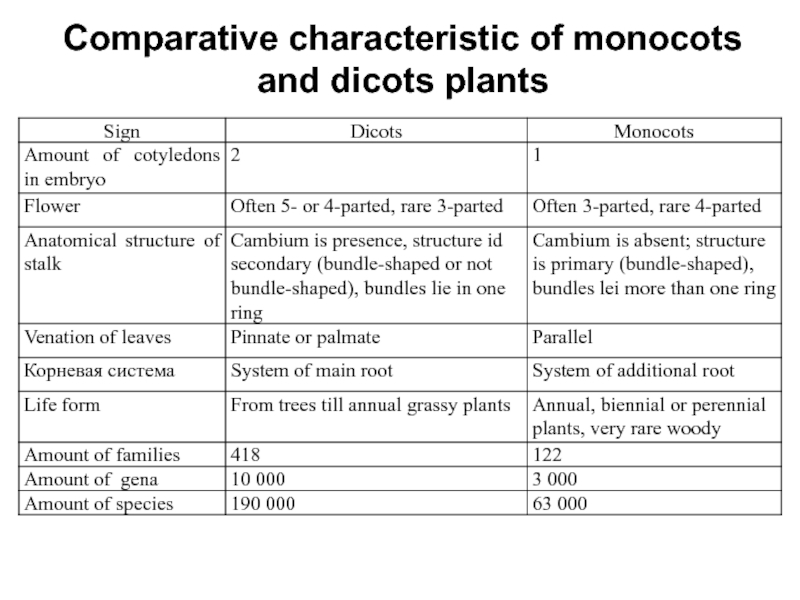
Слайд 16Comparative characteristic of monocots and dicots plants
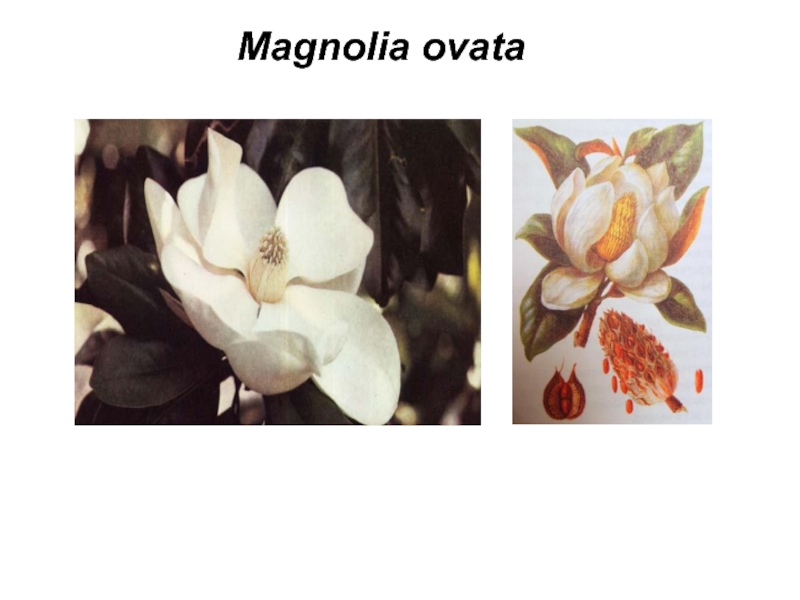
Слайд 17Family – Magnoliaceae
Family includes 12 gena and about 240
species. Spreading – sub-tropics and tropics, center of species diversity
– Southern-Eastern Asia.
Life forms – trees and bushes, usually evergreen.
Formula of flower - *P6AG
The important gena are Magnolia, and Liriodendron.
Practical uses:
Herb - Magnolia grandiflora, for treatment of hypertonia.
Decorative - M. grandiflora, is cultivated in gardens and parks.
Слайд 19Family Shisandraceae
Family include 2 gena and 47 species.
Spreading – countries
of Eastern Asia.
Life forms – evergreen bushes.
Formula of flower
*P5-24 A4-80 G (12-300)
The important genus is Schisandra.
Practical uses:
Medical – Schisandra chinensis, seeds and fruits are used for production of preparations with stimulate and tonic activity.
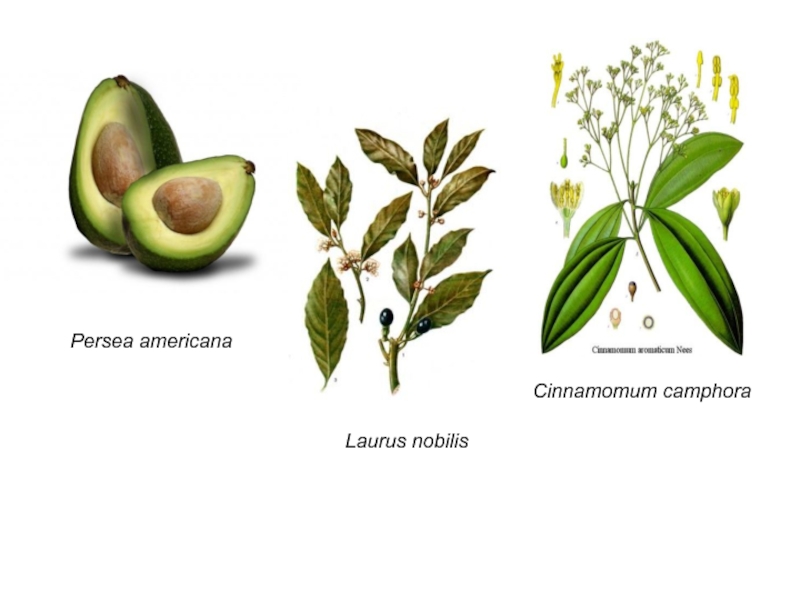
Слайд 21Family Lauraceae
Family include 45 gena and about 2500-3000 species.
Spreading
– sub-tropic and tropics.
Life forms – trees, bushes and
lianas.
Flower formula *P4-6 A 6 G 1
The important gena – Laurus, Cinnamomum and Persea .
Practical uses:
Medical – Laurus nobilis is used for extraction of essential oils for treatment of flue and organ of digestion system. Cinnamomum camphora) – is a source of natural camphora;
Food - Laurus nobilis is used as a spicy; cork of Cinnamomum zeylanicum is also used as a spicy; Persea americana is used for preparation of butter and salad, important dietary product.
Слайд 22Cinnamomum camphora
Persea americana
Laurus nobilis
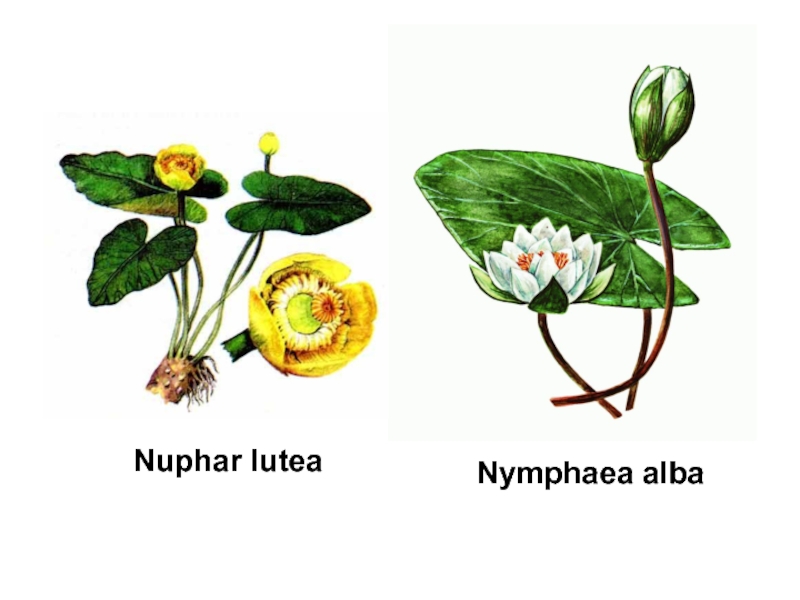
Слайд 23Family Nymphaeaceae
Family includes 5 gena and about 70 species.
Spreading
– lakes, ponds and rivers with fresh water of all
continents.
Life forms – annual or perennial grassy water plants.
Flower formula - *Ca4-5 Co A G (5-35)
Pollination – cross-pollination by bags and self-pollination.
The important gena – Nuphar, Nymphaea, Victoria.
Practical uses:
Decorative – cultivation in botanical gardens and parks.
Слайд 25Control questions:
1 What are the defects of artificial system
of classification of plants?
2 Define biosystematics.
3 What is
Binomial nomenclature?
4 Write the objectives of classification of plants.
5 What are the aims of biosystematics.
Слайд 26Testing questions:
Name of species is created from 2 names of
taxons:
A) Family
B) Genus
C) Class
D) Order
E) Species
epithet
F) Type
G) Division
H) Kingdom
Formula of lower *Ca4-5 Co A G (5-35) belongs to:
A) Trifolium
B) Nuphar
C) Nymphaea
D) Chamomilla
E) Rubus
F) Polygonum
G) Persea
H) Laurus