Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
MOTIVATION
Содержание
- 1. MOTIVATION
- 2. Objectives 1. A basic understanding of human motivation 2. Insights into
- 3. The Motivation ProcessDefining MotivationThe inner state that
- 4. Process Theories of MotivationNeeds - goal theoryVroom expectancy theoryEquity theoryPorter-Lawler theory
- 5. Implications for the organizationManager must know the
- 6. The Vroom Expectancy Theory of MotivationFelt needs
- 7. Equity Theory Theory consists of two parts:How
- 8. The Porter-Lawler TheoryA more complete description of
- 9. Content Theories of Motivation: Human Needs Maslow’s Hierarchy of NeedsAlderfer’s TheoryMcClelland’s needs theory
- 10. Maslow’s Hierarchy of NeedsFigure 9–1
- 11. Alderfer’s TheoryGrowthRelatedness ExistenceSecuritySafetyInternal esteemSocial Self-actualizationExternal esteem
- 12. Alderfer’s TheorySimilarity to Maslow:Hierarchy of needs: lower
- 13. McClelland’s Needs TheoryWe develop these 3 needs
- 14. Motivating Organization MembersStrategies for Motivating Organization MembersManagerial CommunicationTheory X–Theory YJob DesignBehavior Modification
- 15. Managerial CommunicationMost affordable!Gives employees sense of recognition, accomplishment, security and belonging
- 16. Theory X – Theory Y (Human Resources
- 17. Job DesignEarlier Job Design StrategiesJob Rotation –
- 18. Modified Work SchedulesWork share programsFlextime programs and alternative workplace strategiesTelecommuting and virtual offices
- 19. Motivating Organization Members
- 20. Скачать презентанцию
Objectives 1. A basic understanding of human motivation 2. Insights into various human needs 3. An appreciation for the importance of motivating organization members 4. An understanding of various motivation strategies
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Objectives
1. A basic understanding of human motivation
2. Insights into various human needs
3. An
appreciation for the importance of motivating organization members
various motivation strategiesСлайд 3The Motivation Process
Defining Motivation
The inner state that causes an individual
to behave in a way that ensures the accomplishment of
some goal.Therefore, it explains why people act as they do.
Two types of theories:
Process theories explain how people are motivated
Content theories emphasize people’s internal characteristics
Слайд 4Process Theories of Motivation
Needs - goal theory
Vroom expectancy theory
Equity theory
Porter-Lawler
theory
Слайд 5Implications for the organization
Manager must know the needs of the
employees. If the reward is not relevant to employee’s needs,
the employee will not be motivatedX
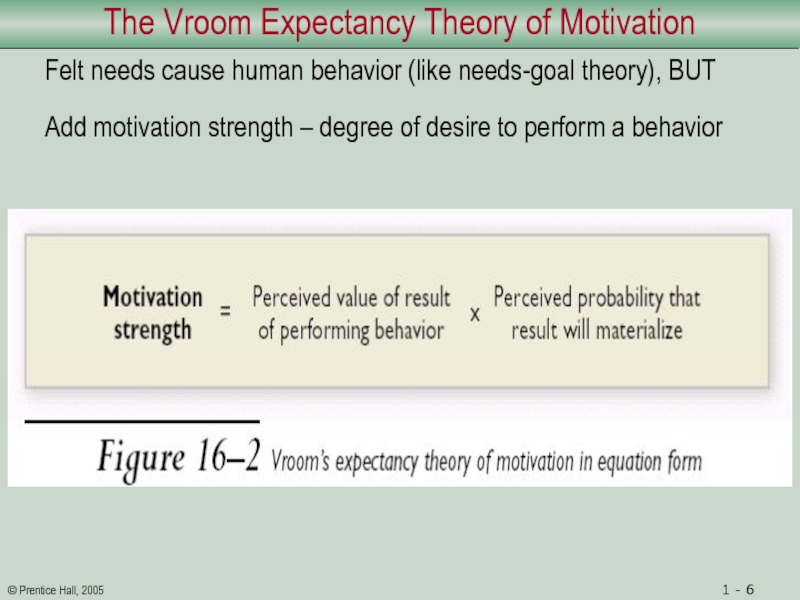
Слайд 6The Vroom Expectancy Theory of Motivation
Felt needs cause human behavior
(like needs-goal theory), BUT
Add motivation strength – degree of desire
to perform a behaviorСлайд 7Equity Theory
Theory consists of two parts:
How a person perceives
fairness of an employment situation
How perceived inequities lead to changes
in behaviorEmployees evaluate their treatment relative to the treatment of others
Inputs: Employee contributions to their jobs
Outputs: What employees receive in return
To right the inequity some will :
1. Change their work inputs
2. Try to change the compensation
3. Try to change their own perception
4. Leave the situation
Слайд 8The Porter-Lawler Theory
A more complete description of all process theories,
but it is consistent with the three theories.
1) Felt need
causes human behavior (needs-goal)2) Effort to satisfy the need depends on value of the reward and probability that the reward will be given (Vroom’s motivational strength)
3) The motivation process
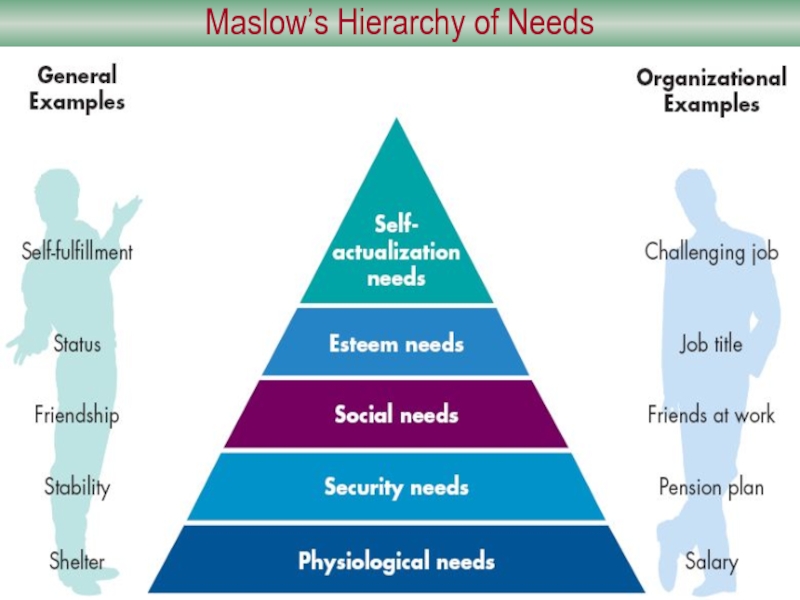
Слайд 9Content Theories of Motivation: Human Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Alderfer’s
Theory
McClelland’s needs theory
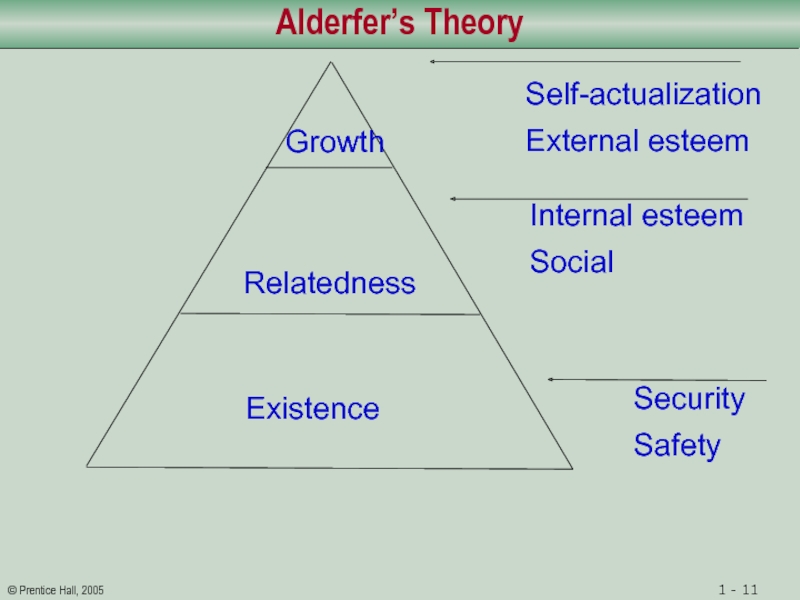
Слайд 11Alderfer’s Theory
Growth
Relatedness
Existence
Security
Safety
Internal esteem
Social
Self-actualization
External esteem
Слайд 12Alderfer’s Theory
Similarity to Maslow:
Hierarchy of needs: lower level needs have
priority over higher level needs:
Existence: Physiological and safety needs
Relatedness:
Social and external esteem needs Growth: Self-actualization and internal esteem needs
Difference from Maslow (textbook):
Only three levels of needs
Ability to pursue higher level needs before lower-level needs are satisfied
Frustration-regression principle – can go down the hierarchy
Difference from Maslow (management literature):
Allows for different levels of needs to be pursued simultaneously.
Allows the order of the needs be different for different people.
Acknowledges that if a higher level need remains unfulfilled, the person may regress to lower level needs that appear easier to satisfy. This is known as the frustration-regression principle.
Слайд 13McClelland’s Needs Theory
We develop these 3 needs in our lifetimes:
1.
Need for achievement (nAch) – the desire to do something
better or more efficiently than it has ever been done before2. Need for power (nPower) – the desire to control, influence, or be responsible for others
3. Need for affiliation (nAff) – the desire to maintain close, friendly, personal relationships
Our life experiences determine which of these needs will be highly developed and therefore dominate the personality
Слайд 14Motivating Organization Members
Strategies for Motivating Organization Members
Managerial Communication
Theory X–Theory Y
Job
Design
Behavior Modification
Слайд 15Managerial Communication
Most affordable!
Gives employees sense of recognition, accomplishment, security and
belonging
Слайд 16Theory X – Theory Y (Human Resources Model)
Theory X managers
who believe that people are inherently uncooperative and must be
constantly punished or rewarded,Theory Y managers who believe that people are naturally responsible and self-motivated to be productive.
Слайд 17Job Design
Earlier Job Design Strategies
Job Rotation – moving workers from
job to job
Job Enlargement – increase the number of job
operationsJob Enrichment
Herzberg’s two-factor theory of motivation
Job Enrichment and Productivity
Modified Work Schedules
Work share programs
Flextime
Telecommuting / Virtual office