Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
OLIGOPOLY
Содержание
- 1. OLIGOPOLY
- 2. Oligopoly1. Oligopoly Definition2. Concentration ratios3. The competitive spectrum4. The kinked demand curve5. Administered prices
- 3. 1. Oligopoly DefinitionAn oligopoly is an industry
- 4. Because the graph of the oligopolist is
- 5. The oligopolist, like the monopolist and unlike
- 6. 2. Concentration ratiosOne way of measuring how
- 7. A second way is to calculate the
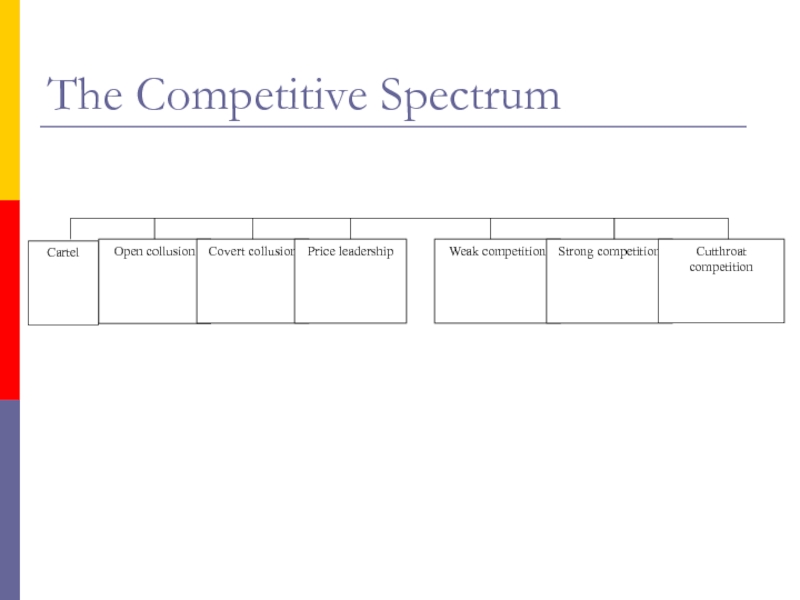
- 8. 3. The Competitive SpectrumCartelAn extreme case of
- 9. Open Collusion.Slightly less extreme than a cartel
- 10. This cozy arrangement would give each operation
- 11. These are extreme cases, but they would
- 12. Price Leadership1. The cigarette industry provided another
- 13. Whatever the degree of collusion, it would
- 14. The Competitive Spectrum
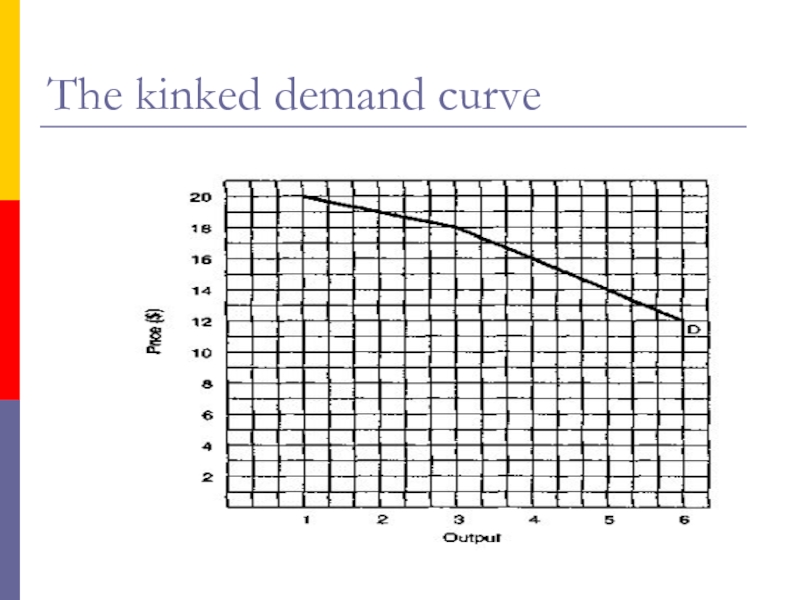
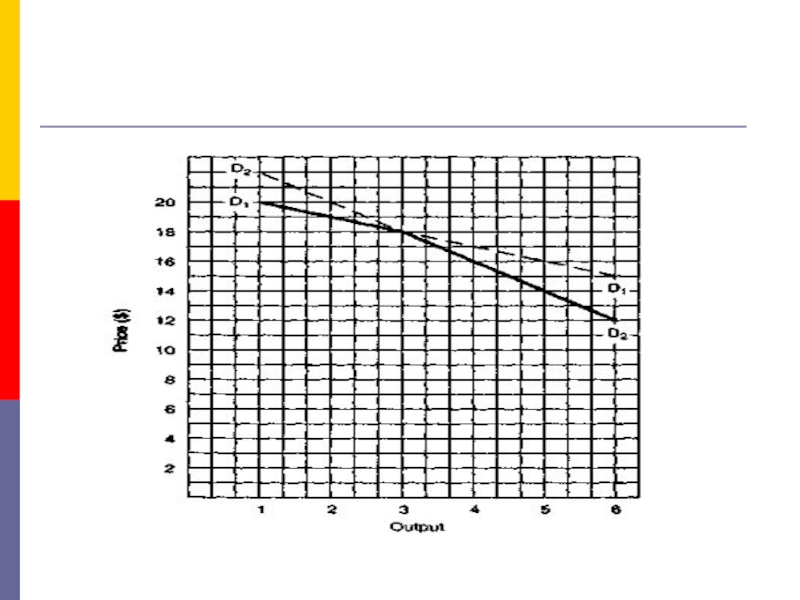
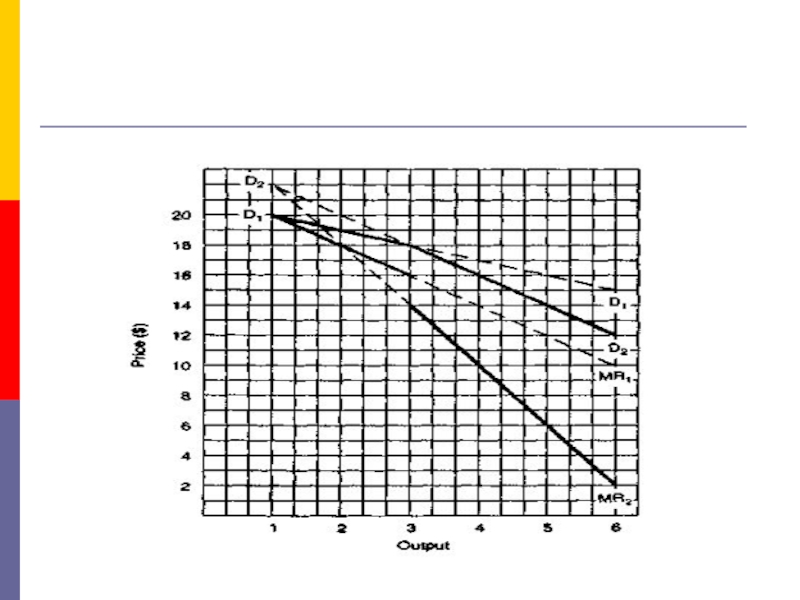
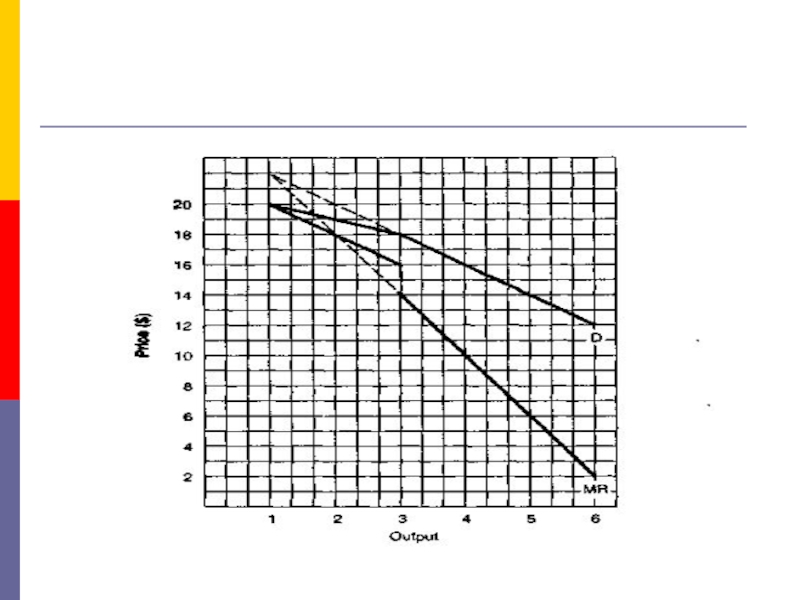
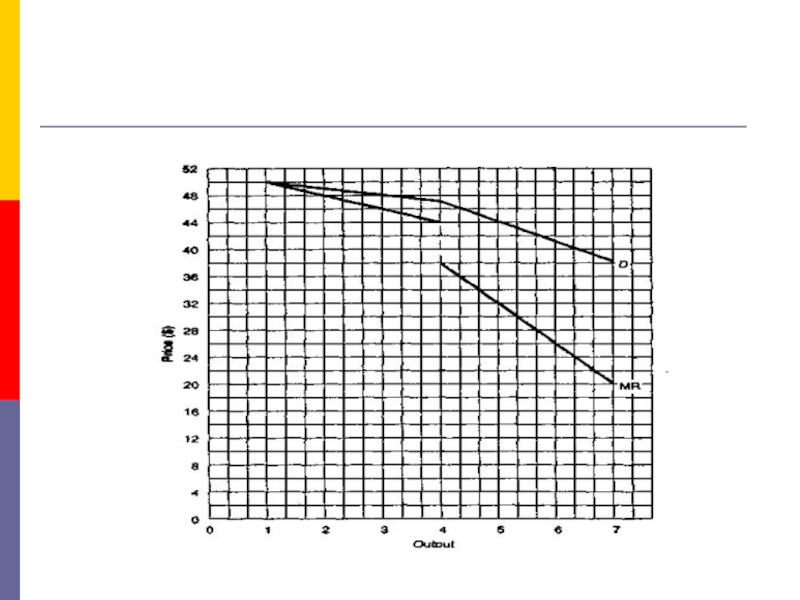
- 15. 4. The Kinked Demand CurveNow we deal
- 16. The kinked demand curve
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. 5. Administered PricesAdministered prices are set by
- 23. Administered prices are peculiar to oligopoly. Perfect
- 24. Thus, administered prices can occur only under
- 25. Скачать презентанцию
Oligopoly1. Oligopoly Definition2. Concentration ratios3. The competitive spectrum4. The kinked demand curve5. Administered prices
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Oligopoly
1. Oligopoly Definition
2. Concentration ratios
3. The competitive spectrum
4. The kinked
demand curve
Слайд 31. Oligopoly Definition
An oligopoly is an industry with just a
few sellers.
Is the product identical or differentiated? It doesn't
matter. The crucial factor under oligopoly is the small number of firms in the industry. Because there are so few firms, every competitor must think continually about the actions of his rivals, since what each does could make or break him. Thus there is a kind of interdependence among oligopolists.
Слайд 4Because the graph of the oligopolist is similar to that
of the monopolist, we will analyze it in exactly the
same manner with respect to price, output, profit, and efficiency. Price is higher than the minimum point of the ATC curve, and output is somewhat to the left of this point. And so, just like the monopolist, the oligopolist has a higher price and a lower output than the perfect competitor.Слайд 5The oligopolist, like the monopolist and unlike the perfect competitor,
makes a profit. With respect to efficiency, since the oligopolist
does not produce at the minimum point of its ATC, it is not as efficient as the perfect competitor.Слайд 62. Concentration ratios
One way of measuring how concentrated an industry
is, is to look at the percentage share of sales
of the leading firms. This is called the industry's concentration ratio.Economists use concentration ratios as a quantitative measure of oligopoly. The total percentage share of industry sales of the four leading firms is the industry concentration ratio. Industries with high ratios are very oligopolistic.
Слайд 7A second way is to calculate the Herfindahl-Hirschman index, which,
it turns out, is a lot easier to do than
to say.The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI). The Herfindahl-Hirschman index (HHI) is the sum of the squares of the market shares of each firm in the industry.
Слайд 83. The Competitive Spectrum
Cartel
An extreme case of oligopoly is a
cartel, where the firms behave as a monopoly in a
manner similar to that of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) in the world oil market.Слайд 9Open Collusion.
Slightly less extreme than a cartel would be a
territorial division of the market among the firms in the
industry.This would be a division similar to that of the Mafia, if indeed there really is such an organization. An oligopolistic division of the market might go something like this.
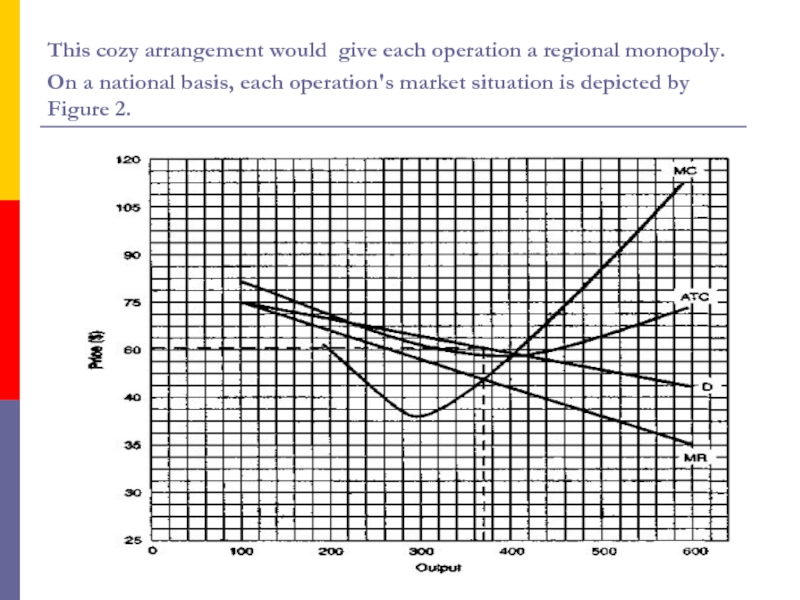
Слайд 10This cozy arrangement would give each operation a regional monopoly.
On a national basis, each operation's market situation is depicted
by Figure 2.Слайд 11These are extreme cases, but they would be illegal, even
during the last few years of less-than-stringent enforcement of the
antitrust laws.Now, as we move to somewhat less extreme cases of collusion, we begin to enter the real of reality. This brings us to the celebrated electric machinery conspiracy case.
Слайд 12Price Leadership
1. The cigarette industry provided another instance of price
leadership.
2. Another form of price leadership is the setting of
the prime rate of interest by the nation's leading banks. Слайд 13Whatever the degree of collusion, it would be hard for
firms in oligopolized industries to ignore each other's actions and
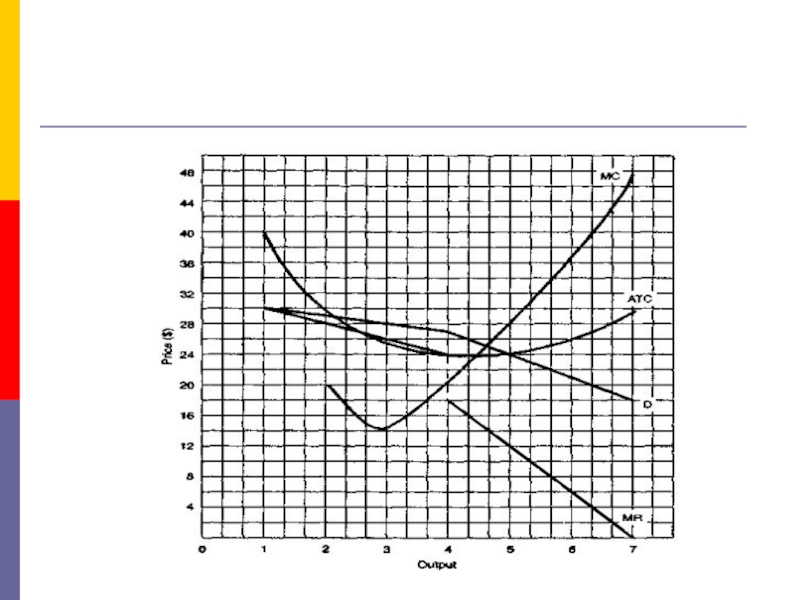
anticipated reactions with respect to price and output.Слайд 154. The Kinked Demand Curve
Now we deal with the extreme
case of oligopolists who are cutthroat competitors, firms that do
not exchange so much as a knowing wink.Each is out to maximize its profits. These oligopolists are ready to cut the throats of their competitors, figuratively speaking, of course.
Слайд 225. Administered Prices
Administered prices are set by large corporations for
relatively long periods of time, without responding to the normal
market forces, mainly, changes in demand.Слайд 23Administered prices are peculiar to oligopoly.
Perfect competitors and monopolistic
competitors would be too small to dictate price. Monopolists would
change their output and price in response to changes in demand to maximize their profits.But under competitive oligopoly, the firms would rarely shift output or price because they would continue to maximize profit as long as MC was within the range of MR.