Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Основы программирования ФИСТ 1 курс Власенко Олег Федосович
Содержание
- 1. Основы программирования ФИСТ 1 курс Власенко Олег Федосович
- 2. Динамические структуры данныхСписок односвязныйСписок двусвязныйЦиклический списокДеревоДвоичное деревоДвоичное дерево поискаГрафы…
- 3. Двоичное дерево поискаДвоичное дерево поиска (англ. binary search
- 4. Структура узла дереваstruct NodeTree { int data; struct NodeTree
- 5. Отрабатываем навыки рисованияvoid main() { struct NodeTree node1
- 6. Простейшая печать дереваvoid printTree(struct NodeTree * p){ if (p != NULL) { printTree(p->left); printf("(%d)\n", p->data); printTree(p->right); }}
- 7. Печать дерева c отображением структурыvoid printfShift(int shift)
- 8. Добавление элемента в деревоstruct NodeTree * addElement(struct
- 9. Добавление элемента в деревоvoid main() { root =
- 10. Добавление элемента в деревоvoid main() { root =
- 11. Очистка дереваvoid clearTree(struct NodeTree *p){ if (p != NULL) { clearTree(p->left); clearTree(p->right); free(p); }}...clearTree(root);root = NULL;...
- 12. А такой элемент есть в дереве?int contains(struct
- 13. А такой элемент есть в дереве? (2)void
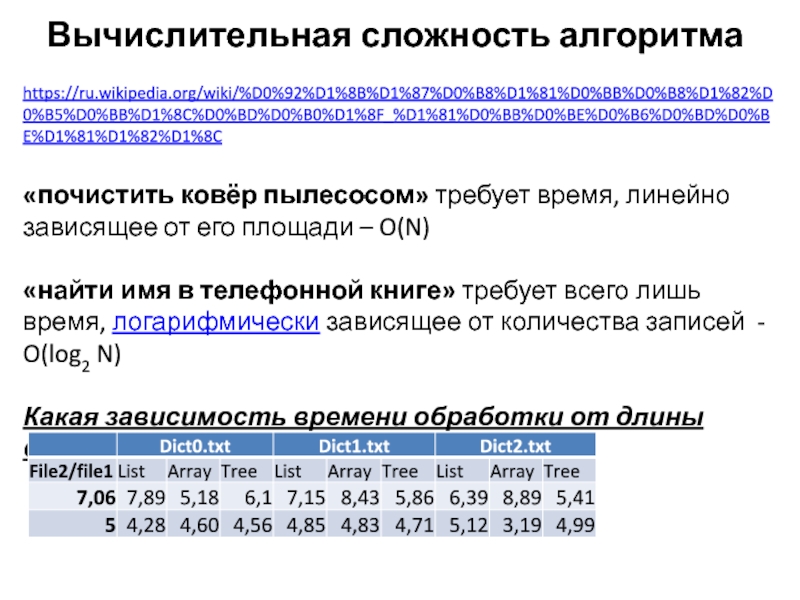
- 14. Сравнение скорости работы структур данных
- 15. Задача конвертации текстаНа входе 2 файла: Файл
- 16. Текст программы – решение на массиве (1)#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS#include #include #include #include #include
- 17. Текст программы – решение на массиве (2)#define
- 18. Текст программы – решение на массиве (3)struct
- 19. Текст программы – решение на массиве (4)void
- 20. Текст программы – решение на массиве (5)int
- 21. Текст программы – решение на массиве (6)int
- 22. Текст программы – решение на массиве (7) //
- 23. Текст программы – решение на массиве (8)int
- 24. Текст программы – решение на массиве (9)FILE
- 25. Текст программы – решение на массиве (10)char
- 26. Текст программы – решение на массиве (11)else
- 27. Текст программы – решение на массиве (12) }
- 28. Текст программы – решение на массиве (13)void
- 29. Текст программы – решение на массиве (14) destroy(dict); t2
- 30. Тестируем с массивомAlice.txt – 142 800 байтTolkien.txt
- 31. решение на списке (1)struct Node { char *
- 32. решение на списке (2)struct Dictionary * create(){ struct
- 33. решение на списке (3)void addWord(struct Dictionary *
- 34. решение на списке (4)void destroy(struct Dictionary *
- 35. решение на списке (5)int contains(struct Dictionary *
- 36. решение на списке (6)void main() { long t0,
- 37. Тестируем со спискомAlice.txt – 142 800 байтTolkien.txt
- 38. решение на дереве (1)struct NodeTree { char *
- 39. решение на дереве (2)struct Dictionary * create(){ struct
- 40. решение на дереве (3)struct NodeTree * addElement( struct
- 41. решение на дереве (4) else if ((cond =
- 42. решение на дереве (5)void addWord(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word){ dict->root = addElement(dict->root, word); dict->cnt_words++;}
- 43. решение на дереве (6)void clearTree(struct NodeTree *p){ if (p != NULL) { clearTree(p->left); clearTree(p->right); free(p->word); free(p); }}void destroy(struct Dictionary * dict) { clearTree(dict->root); free(dict);}
- 44. решение на дереве (7)int containElement(struct NodeTree *
- 45. решение на дереве (8)int contains(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word){ return containElement(dict->root, word);}
- 46. решение на дереве (9)void main() { long t0,
- 47. Тестируем с деревомAlice.txt – 142 800 байтTolkien.txt
- 48. Зависимость времени работы от длины текстового
- 49. Вычислительная сложность алгоритмаhttps://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%92%D1%8B%D1%87%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%8F_%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C«почистить ковёр пылесосом» требует время,
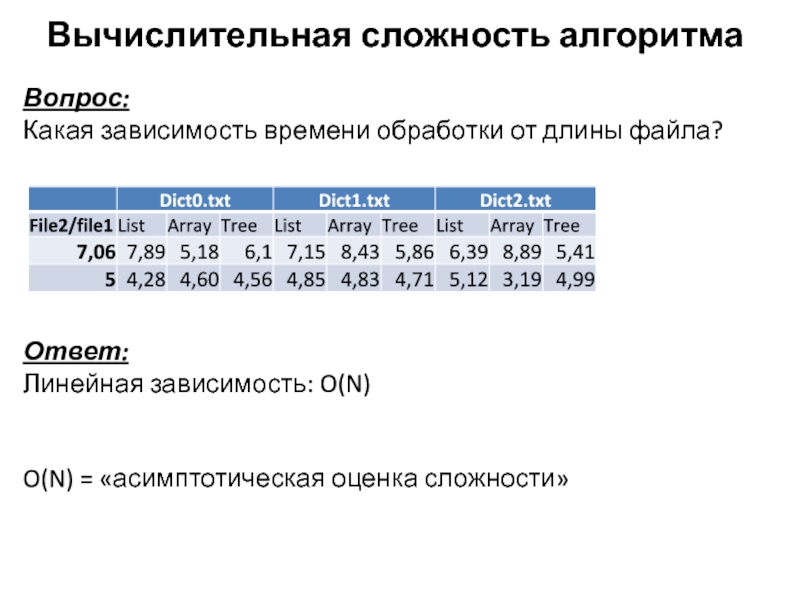
- 50. Вычислительная сложность алгоритмаВопрос:Какая зависимость времени обработки от длины файла?Ответ:Линейная зависимость: O(N)O(N) = «асимптотическая оценка сложности»
- 51. Вычислительная сложность поискаПоиск элемента– какая зависимость времени
- 52. Вычислительная сложность поискаПоиск в списке: O(N)Поиск в
- 53. Источники информацииhttp://c-spravochnik.ru/ https://msdn.microsoft.com/ru-ru/default.aspx http://habrahabr.ru/ https://www.google.ru/ http://rsdn.ru/
- 54. Скачать презентанцию
Динамические структуры данныхСписок односвязныйСписок двусвязныйЦиклический списокДеревоДвоичное деревоДвоичное дерево поискаГрафы…
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Основы программирования
ФИСТ 1 курс
Власенко
Олег
Федосович
Лекция 14
Бинарное дерево
Сравнение скорости работы
структур данных.
Слайд 2Динамические структуры данных
Список односвязный
Список двусвязный
Циклический список
Дерево
Двоичное дерево
Двоичное дерево поиска
Графы
…
Слайд 3Двоичное дерево поиска
Двоичное дерево поиска (англ. binary search tree, BST) — это
двоичное дерево, для которого выполняются следующие дополнительные условия (свойства дерева
поиска):Оба поддерева — левое и правое — являются двоичными деревьями поиска.
У всех узлов левого поддерева произвольного узла X значения ключей данных меньше, нежели значение ключа данных самого узла X.
В то время, как значения ключей данных у всех узлов правого поддерева (того же узла X) больше, нежели значение ключа данных узла X.
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%94%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B5_%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B2%D0%BE
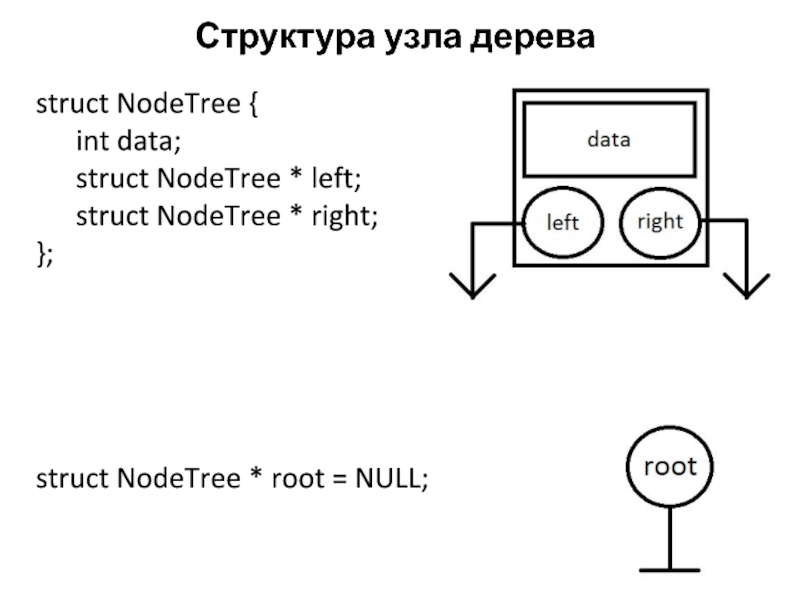
Слайд 4Структура узла дерева
struct NodeTree {
int data;
struct NodeTree * left;
struct NodeTree
* right;
};
struct NodeTree * root = NULL;
Слайд 5Отрабатываем навыки рисования
void main() {
struct NodeTree node1 = { 1,
NULL, NULL };
struct NodeTree node2 = { 2, NULL, NULL
};struct NodeTree node3 = { 3, NULL, NULL };
root = &node2;
node2.left = &node1;
node2.right = &node3;
printTree(root);
printTreeShifted(root, 0);
}
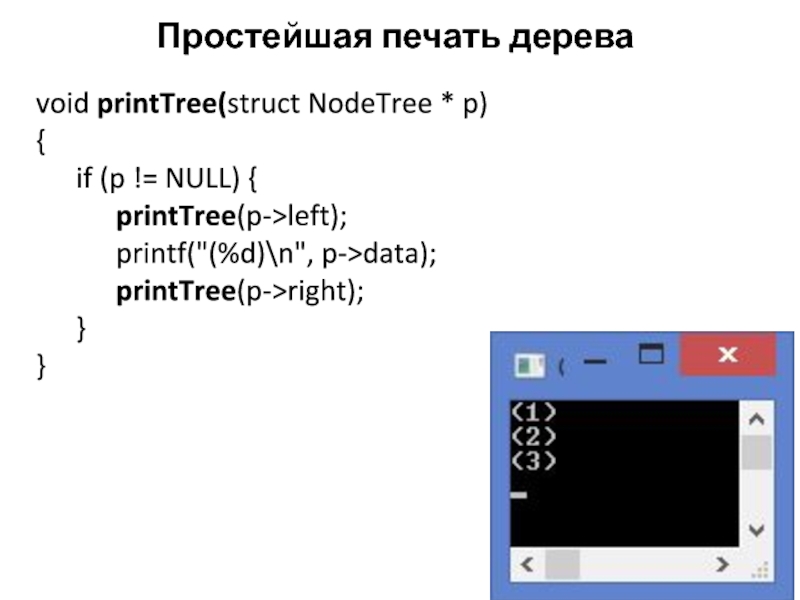
Слайд 6Простейшая печать дерева
void printTree(struct NodeTree * p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
printTree(p->left);
printf("(%d)\n", p->data);
printTree(p->right);
}
}
Слайд 7Печать дерева c отображением структуры
void printfShift(int shift) {
int i;
for (i
= 0; i < shift; i++) {
printf(" ");
}
}
void printTreeShifted(struct NodeTree
* p, int shift){
if (p != NULL) {
printTreeShifted(p->left, shift + 1);
printfShift(shift);
printf("(%d)\n", p->data);
printTreeShifted(p->right, shift + 1);
}
}
Слайд 8Добавление элемента в дерево
struct NodeTree * addElement(struct NodeTree *p, int
value)
{
if (p == NULL) {
p = (struct NodeTree*)malloc(
sizeof(struct NodeTree));
p->data
= value;p->left = p->right = NULL;
} else if (p->data == value) {
// НИЧЕГО НЕ ДЕЛАЕМ!!!
} else if (value < p->data) {
p->left = addElement(p->left, value);
} else {
p->right = addElement(p->right, value);
}
return p;
}
Слайд 9Добавление элемента в дерево
void main() {
root = addElement(root, 60);
root =
addElement(root, 40);
root = addElement(root, 20);
root = addElement(root, 10);
root = addElement(root,
30);root = addElement(root, 50);
root = addElement(root, 90);
root = addElement(root, 70);
root = addElement(root, 80);
printTreeShifted(root, 0);
}
Что будет выведено???
Слайд 10Добавление элемента в дерево
void main() {
root = addElement(root, 60);
root =
addElement(root, 40);
root = addElement(root, 20);
root = addElement(root, 10);
root = addElement(root,
30);root = addElement(root, 50);
root = addElement(root, 90);
root = addElement(root, 70);
root = addElement(root, 80);
printTreeShifted(root, 0);
}
Слайд 11Очистка дерева
void clearTree(struct NodeTree *p)
{
if (p != NULL) {
clearTree(p->left);
clearTree(p->right);
free(p);
}
}
...
clearTree(root);
root =
NULL;
...
Слайд 12А такой элемент есть в дереве?
int contains(struct NodeTree * p,
int value)
{
if (p == NULL) {
return 0;
} else if (value
== p->data) {return 1;
} else if (value < p->data) {
return contains(p->left, value);
} else {
return contains(p->right, value);
}
}
Слайд 13А такой элемент есть в дереве? (2)
void main() {
root =
addElement(root, 60);
root = addElement(root, 40);
root = addElement(root, 20);
root = addElement(root,
10);root = addElement(root, 30);
root = addElement(root, 50);
root = addElement(root, 90);
root = addElement(root, 70);
root = addElement(root, 80);
printTreeShifted(root, 0);
printf("contains(10) = %d\n", contains(root, 10));
printf("contains(15) = %d\n", contains(root, 15));
printf("contains(20) = %d\n", contains(root, 20));
}
Слайд 15Задача конвертации текста
На входе 2 файла:
Файл 1: Файл словаря
– в каждой строке по 1 слову
Файл 2: Текстовый файл
– большой текст (книга)Оба файла содержат текст на английском языке.
Нужно создать третий файл - HTML файл, где есть весь текст из файла 2. Причем все слова, встречающиеся в файле 1, в файле 3 должны быть помечены как жирные.
Слайд 16Текст программы – решение на массиве (1)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
Слайд 17Текст программы – решение на массиве (2)
#define MAX_WORDS 10000
#define MAX_LEN
25
struct Dictionary {
char words[MAX_WORDS][MAX_LEN];
int cnt_words;
};
struct Dictionary * create();
void destroy(struct Dictionary
* dict);void addWord(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word);
int contains(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word);
Слайд 18Текст программы – решение на массиве (3)
struct Dictionary * create()
{
struct
Dictionary * dict = (struct Dictionary *)
malloc(sizeof(struct Dictionary));
dict->cnt_words =
0;return dict;
}
void destroy(struct Dictionary * dict) {
free(dict);
}
Слайд 19Текст программы – решение на массиве (4)
void addWord(struct Dictionary *
dict, char * word)
{
if (dict->cnt_words < MAX_WORDS) {
strncpy(dict->words[dict->cnt_words],
word, MAX_LEN -
1);++dict->cnt_words;
}
}
Слайд 20Текст программы – решение на массиве (5)
int contains(struct Dictionary *
dict, char * word)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i
dict->cnt_words; ++i){
if (strcmp(word, dict->words[i]) == 0)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Слайд 21Текст программы – решение на массиве (6)
int loadDictionary(struct Dictionary *
dict,
char * filename) {
// открыть файл
FILE * fin;
char s[MAX_LEN];
fin
= fopen(filename, "rt");if (fin == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
Слайд 22Текст программы – решение на массиве (7)
// в цикле для
всех строк
while (!feof(fin)) {
// загрузить строку
if (fgets(s, MAX_LEN - 1,
fin) != NULL) {if (s[strlen(s) - 1] == '\n')
s[strlen(s) - 1] = '\0';
addWord(dict, s);
}
}
// закрыть файл
fclose(fin);
return 1;
}
Слайд 23Текст программы – решение на массиве (8)
int convertTextToHtml(
struct Dictionary *
dict,
char * text_in_filename,
char * text_out_filename)
{
char s[MAX_LEN];
// открыть
файлыFILE *fin = fopen(text_in_filename, "rt");
if (fin == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
Слайд 24Текст программы – решение на массиве (9)
FILE *fout = fopen(text_out_filename,
"wt");
if (fout == NULL)
{
fclose(fin);
return 0;
}
fprintf(fout, "");
fprintf(fout, "");
fprintf(fout, "");
fprintf(fout, "
http - equiv = \"Content-Type\" content = \"text/html; charset=utf-8\" />");fprintf(fout, "
fprintf(fout, "");
fprintf(fout, "");
Слайд 25Текст программы – решение на массиве (10)
char ch;
int is_letter =
0;
char word[81];
int word_len = 0;
while ((ch = getc(fin)) != EOF)
{if (isalpha((unsigned char)ch)) {
if (!is_letter) {
word_len = 0;
}
is_letter = 1;
word[word_len++] = ch;
}
else { // if (!isalpha(ch)) {
Слайд 26Текст программы – решение на массиве (11)
else { // if
(!isalpha(ch)) {
if (is_letter) {
word[word_len] = '\0';
if (contains(dict, word))
fprintf(fout, "%s ",
word);else
fprintf(fout, "%s", word);
}
is_letter = 0;
fprintf(fout, "%c", ch);
if (ch == '\n')
fprintf(fout, "
");
}
Слайд 27Текст программы – решение на массиве (12)
} // while ((ch
= getc(fin)) != EOF)
fclose(fin);
fprintf(fout, "");
fprintf(fout, "");
fclose(fout);
return 1;
} // convertTextToHtml- конец!!!
Слайд 28Текст программы – решение на массиве (13)
void main() {
long t0,
t1, t2;
t0 = clock();
printf("t0 = %f sec \n", t0 /
(float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);struct Dictionary *dict = create();
loadDictionary(dict, "c:\\Temp\\lection16\\dict0.txt");
t1 = clock();
printf("t1 = %f sec \n", t1 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
convertTextToHtml(dict,
"c:\\Temp\\lection16\\alice.txt",
"c:\\Temp\\lection16\\alice_out_array.html");
Слайд 29Текст программы – решение на массиве (14)
destroy(dict);
t2 = clock();
printf("t2 =
%f sec \n",
t2 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("Run time = t2 -
t0 = %f sec \n", (t2 - t0) / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
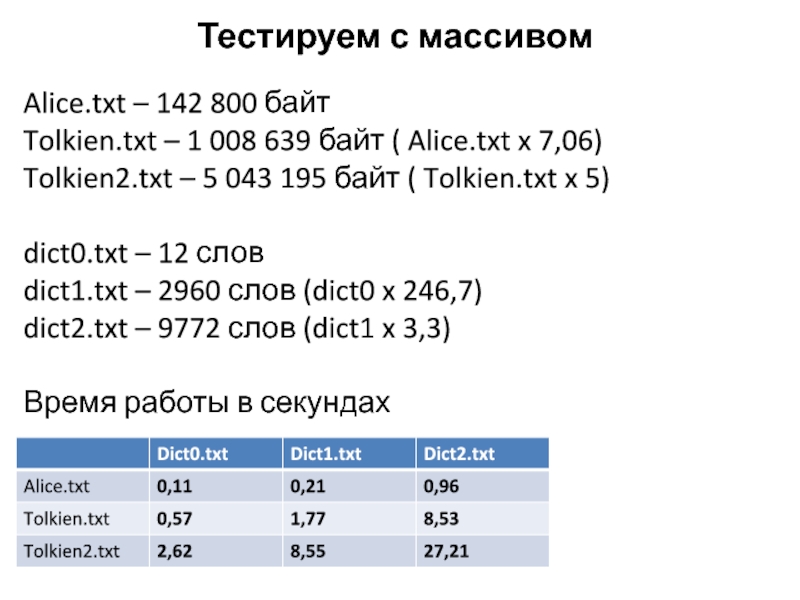
Слайд 30Тестируем с массивом
Alice.txt – 142 800 байт
Tolkien.txt – 1 008
639 байт ( Alice.txt x 7,06)
Tolkien2.txt – 5 043 195
байт ( Tolkien.txt x 5) dict0.txt – 12 слов
dict1.txt – 2960 слов (dict0 x 246,7)
dict2.txt – 9772 слов (dict1 x 3,3)
Время работы в секундах
Слайд 31решение на списке (1)
struct Node {
char * word;
struct Node *
next;
};
struct Dictionary {
struct Node * first;
int cnt_words;
};
struct Dictionary * create();
void
destroy(struct Dictionary * dict);void addWord(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word);
int contains(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word);
Слайд 32решение на списке (2)
struct Dictionary * create()
{
struct Dictionary * dict
= (struct Dictionary *)
malloc(sizeof(struct Dictionary));
dict->first = NULL;
dict->cnt_words = 0;
return
dict;}
Слайд 33решение на списке (3)
void addWord(struct Dictionary * dict, char *
word)
{
struct Node * newNode = (struct Node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->next =
dict->first;newNode->word = (char *)calloc(strlen(word) + 1,
sizeof(char));
strcpy(newNode->word, word);
dict->cnt_words++;
dict->first = newNode;
}
Слайд 34решение на списке (4)
void destroy(struct Dictionary * dict) {
while (dict->first
!= NULL)
{
struct Node * delNode = dict->first;
dict->first = dict->first->next;
free(delNode->word);
free(delNode);
}
free(dict);
}
Слайд 35решение на списке (5)
int contains(struct Dictionary * dict, char *
word)
{
struct Node * ptr = dict->first;
while (ptr != NULL) {
if
(strcmp(ptr->word, word) == 0) {return 1;
}
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return 0;
}
Слайд 36решение на списке (6)
void main() {
long t0, t1, t2;
t0 =
clock();
printf("t0 = %f sec \n", t0 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
struct Dictionary *dict
= create();loadDictionary(dict, "c:\\Temp\\lection16\\dict2.txt");
t1 = clock();
printf("t1 = %f sec \n", t1 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
convertTextToHtml(dict, "c:\\Temp\\lection16\\Tolkien2.txt",
"c:\\Temp\\lection16\\Tolkien2_out_list.html");
destroy(dict);
t2 = clock();
printf("t2 = %f sec \n", t2 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("Run time = t2 - t0 = %f sec \n", (t2 - t0) / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
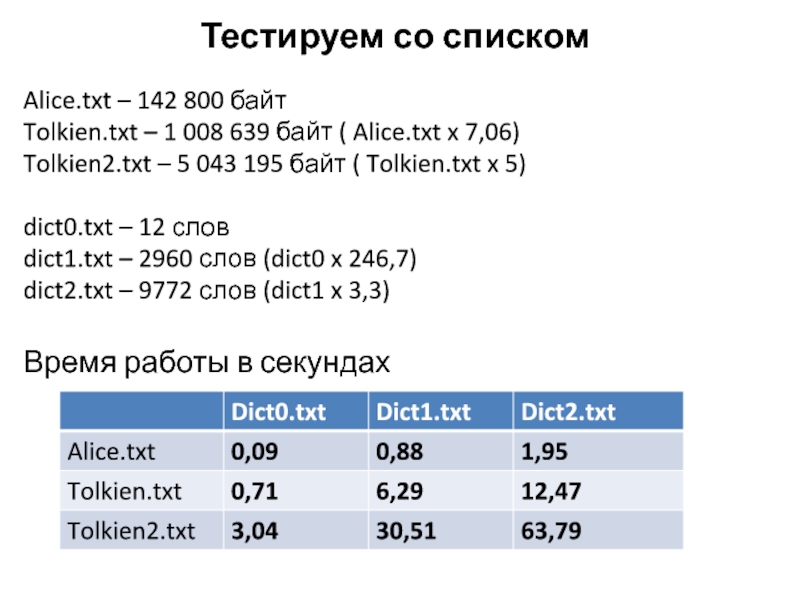
Слайд 37Тестируем со списком
Alice.txt – 142 800 байт
Tolkien.txt – 1 008
639 байт ( Alice.txt x 7,06)
Tolkien2.txt – 5 043 195
байт ( Tolkien.txt x 5) dict0.txt – 12 слов
dict1.txt – 2960 слов (dict0 x 246,7)
dict2.txt – 9772 слов (dict1 x 3,3)
Время работы в секундах
Слайд 38решение на дереве (1)
struct NodeTree {
char * word;
struct NodeTree *
left;
struct NodeTree * right;
};
struct Dictionary {
struct NodeTree * root;
int cnt_words;
};
struct
Dictionary * create();void destroy(struct Dictionary * dict);
void addWord(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word);
int contains(struct Dictionary * dict, char * word);
Слайд 39решение на дереве (2)
struct Dictionary * create()
{
struct Dictionary * dict
= (struct Dictionary *)
malloc(sizeof(struct Dictionary));
dict->root = NULL;
dict->cnt_words = 0;
return
dict;}
Слайд 40решение на дереве (3)
struct NodeTree * addElement(
struct NodeTree *p,
char*
word)
{
int cond;
if (p == NULL) {
p = (struct NodeTree*)malloc(
sizeof(struct NodeTree));
p->word = (char *)calloc(strlen(word) + 1,
sizeof(char));
strcpy(p->word, word);
p->left = p->right = NULL;
}
Слайд 41решение на дереве (4)
else if ((cond = strcmp(word, p->word)) ==
0) {
// вставляемое слово совпадает
// с уже имеющимся - ничего
не делаем} else if (cond < 0) {
// вставляемое слово меньше
// корня поддерева
p->left = addElement(p->left, word);
} else {
// вставляемое слово больше
// корня поддерева
p->right = addElement(p->right, word);
}
return p;
}
Слайд 42решение на дереве (5)
void addWord(struct Dictionary * dict, char *
word)
{
dict->root = addElement(dict->root, word);
dict->cnt_words++;
}
Слайд 43решение на дереве (6)
void clearTree(struct NodeTree *p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
clearTree(p->left);
clearTree(p->right);
free(p->word);
free(p);
}
}
void destroy(struct Dictionary * dict) {
clearTree(dict->root);
free(dict);
}
Слайд 44решение на дереве (7)
int containElement(struct NodeTree * p, char *word)
{
int
cond;
if (p == NULL) {
return 0;
} else if ((cond =
strcmp(word, p->word)) == 0) {return 1;
} else if (cond < 0) {
return containElement(p->left, word);
} else {
return containElement(p->right, word);
}
}
Слайд 45решение на дереве (8)
int contains(struct Dictionary * dict, char *
word)
{
return containElement(dict->root, word);
}
Слайд 46решение на дереве (9)
void main() {
long t0, t1, t2;
t0 =
clock();
printf("t0 = %f sec \n", t0 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
struct Dictionary *dict
= create();loadDictionary(dict, "c:\\Temp\\lection16\\dict1.txt");
t1 = clock();
printf("t1 = %f sec \n", t1 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
convertTextToHtml(dict, "c:\\Temp\\lection16\\Tolkien.txt",
"c:\\Temp\\lection16\\Tolkien_out_tree.html");
destroy(dict);
t2 = clock();
printf("t2 = %f sec \n", t2 / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("Run time = t2 - t0 = %f sec \n", (t2 - t0) / (float)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
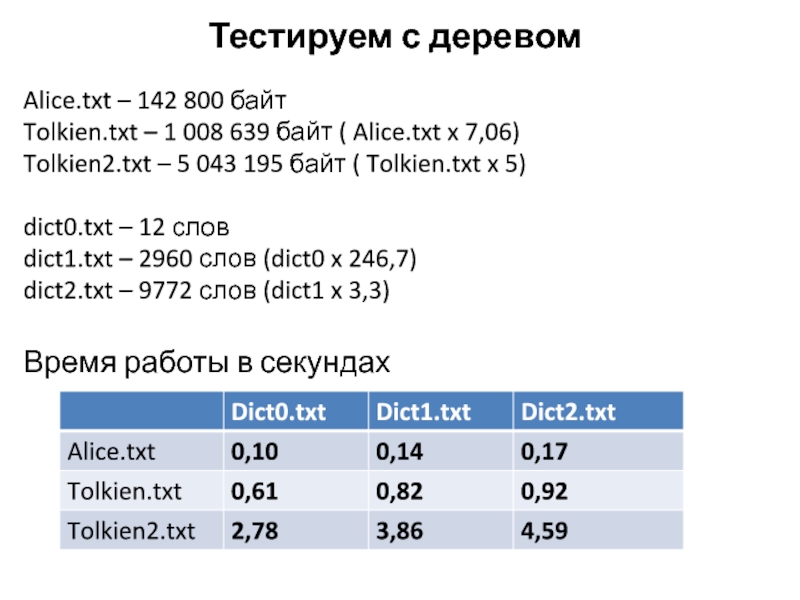
Слайд 47Тестируем с деревом
Alice.txt – 142 800 байт
Tolkien.txt – 1 008
639 байт ( Alice.txt x 7,06)
Tolkien2.txt – 5 043 195
байт ( Tolkien.txt x 5) dict0.txt – 12 слов
dict1.txt – 2960 слов (dict0 x 246,7)
dict2.txt – 9772 слов (dict1 x 3,3)
Время работы в секундах
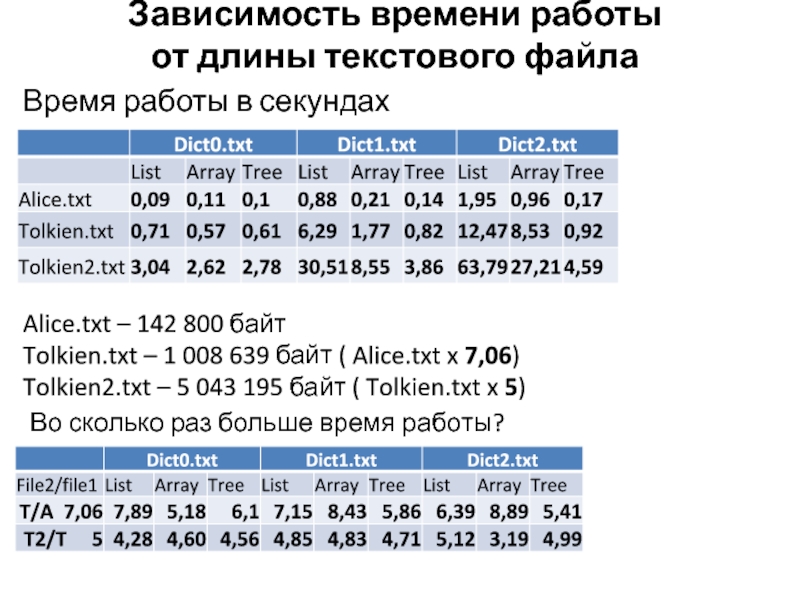
Слайд 48Зависимость времени работы
от длины текстового файла
Время работы в секундах
Alice.txt
– 142 800 байт
Tolkien.txt – 1 008 639 байт (
Alice.txt x 7,06)Tolkien2.txt – 5 043 195 байт ( Tolkien.txt x 5)
Во сколько раз больше время работы?
Слайд 49Вычислительная сложность алгоритма
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%92%D1%8B%D1%87%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%8F_%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C
«почистить ковёр пылесосом» требует время, линейно зависящее от
его площади – O(N)
«найти имя в телефонной книге» требует всего
лишь время, логарифмически зависящее от количества записей - O(log2 N)Какая зависимость времени обработки от длины файла?
Слайд 50Вычислительная сложность алгоритма
Вопрос:
Какая зависимость времени обработки от длины файла?
Ответ:
Линейная зависимость:
O(N)
O(N) = «асимптотическая оценка сложности»
Слайд 51Вычислительная сложность поиска
Поиск элемента
– какая зависимость времени поиска от количества
элементов в списке?
– какая зависимость времени поиска от количества элементов
в массиве?– какая зависимость времени поиска от количества элементов в дереве?
Варианты ответа:
O(1)
O(N)
O(N2)
O(log N)
O(2N)
Слайд 52Вычислительная сложность поиска
Поиск в списке: O(N)
Поиск в массиве (неотсортированном) :
O(N)
Поиск в двоичном дереве поиска: O(log N)
Поиск в отсортированном массиве
(при использовании двоичного поиска) : O(log N)Поиск в хэш-таблице: O(1)




 data); printTree(p->right); }}" alt="Простейшая печать дереваvoid printTree(struct NodeTree * p){ if (p != NULL) { printTree(p->left); printf("(%d)\n", p->data); printTree(p->right); }}">
data); printTree(p->right); }}" alt="Простейшая печать дереваvoid printTree(struct NodeTree * p){ if (p != NULL) { printTree(p->left); printf("(%d)\n", p->data); printTree(p->right); }}">









![Основы программирования ФИСТ 1 курс Власенко Олег Федосович Текст программы – решение на массиве (2)#define MAX_WORDS 10000#define MAX_LEN 25struct Текст программы – решение на массиве (2)#define MAX_WORDS 10000#define MAX_LEN 25struct Dictionary { char words[MAX_WORDS][MAX_LEN]; int cnt_words;};struct Dictionary *](/img/thumbs/d3d0907a066188312be4940564e095b5-800x.jpg)







![Основы программирования ФИСТ 1 курс Власенко Олег Федосович Текст программы – решение на массиве (10)char ch;int is_letter = 0;char Текст программы – решение на массиве (10)char ch;int is_letter = 0;char word[81];int word_len = 0;while ((ch =](/img/thumbs/0694f9b0c6328a933d4a31916f79a2e1-800x.jpg)
![Основы программирования ФИСТ 1 курс Власенко Олег Федосович Текст программы – решение на массиве (11)else { // if (!isalpha(ch)) Текст программы – решение на массиве (11)else { // if (!isalpha(ch)) { if (is_letter) { word[word_len] = '\0'; if (contains(dict,](/img/thumbs/40b190e9af86f746cdebec1fb2d5c8f1-800x.jpg)