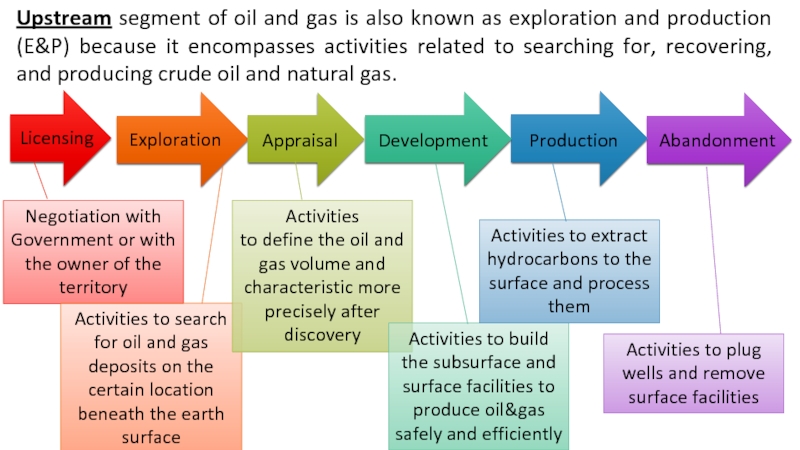
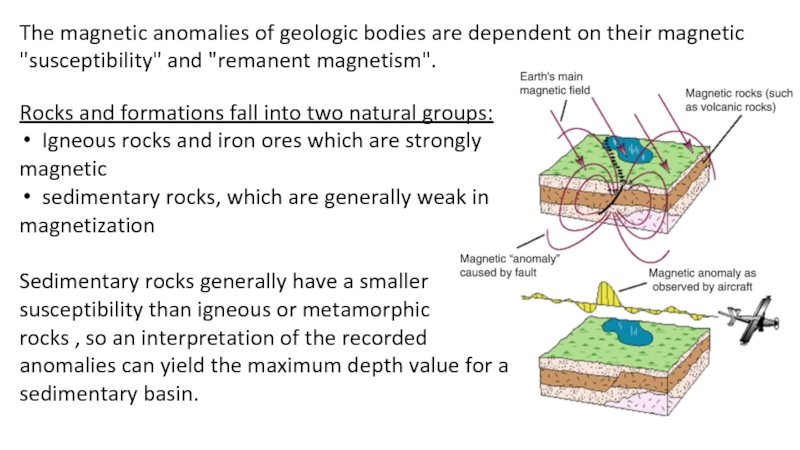
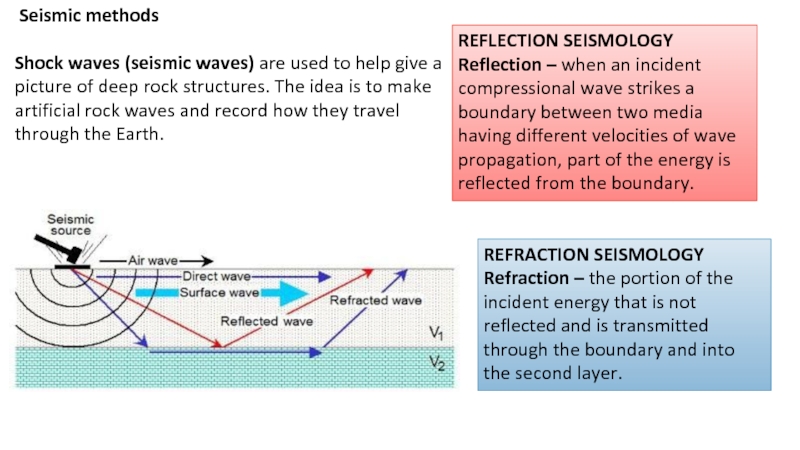
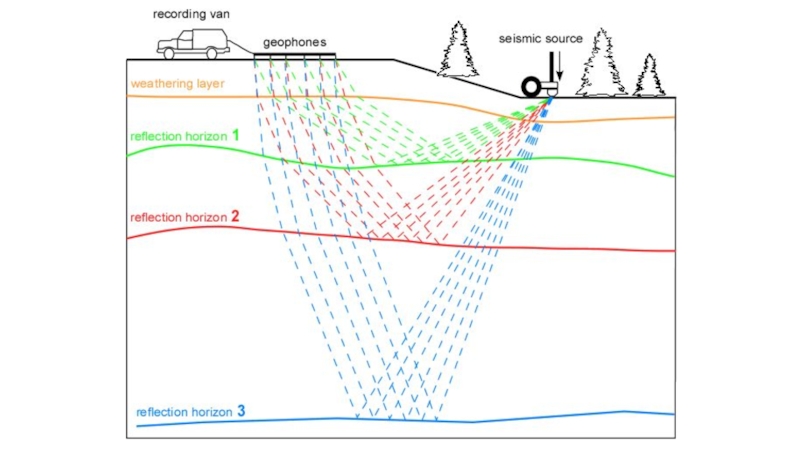
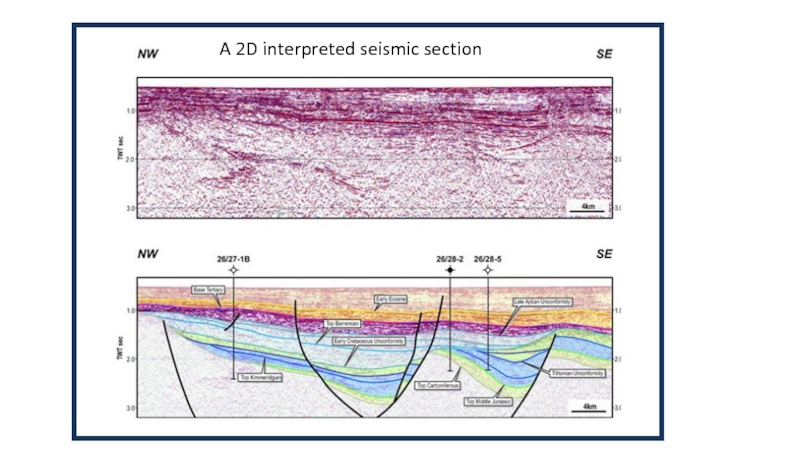
exploration and production (E&P) because it encompasses activities related to
searching for, recovering, and producing crude oil and natural gas. Licensing
Exploration
Appraisal
Development Production Abandonment
Negotiation with Government or with the owner of the territory
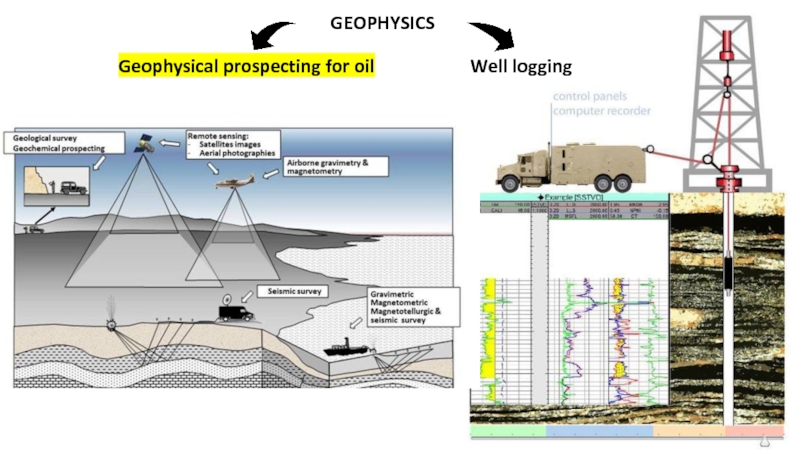
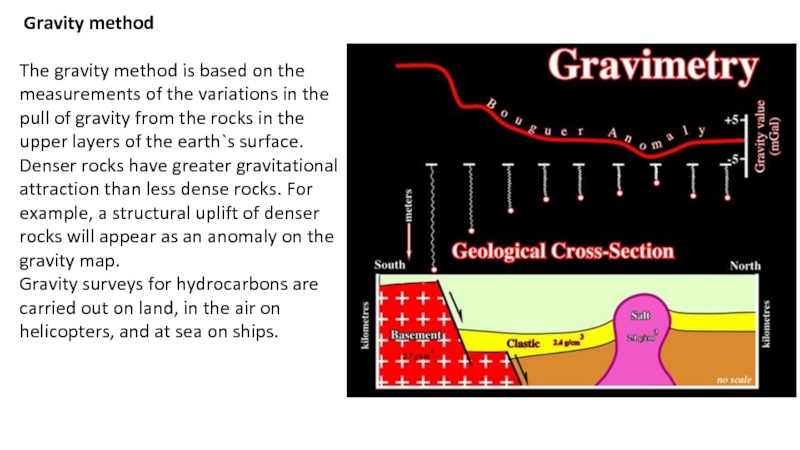
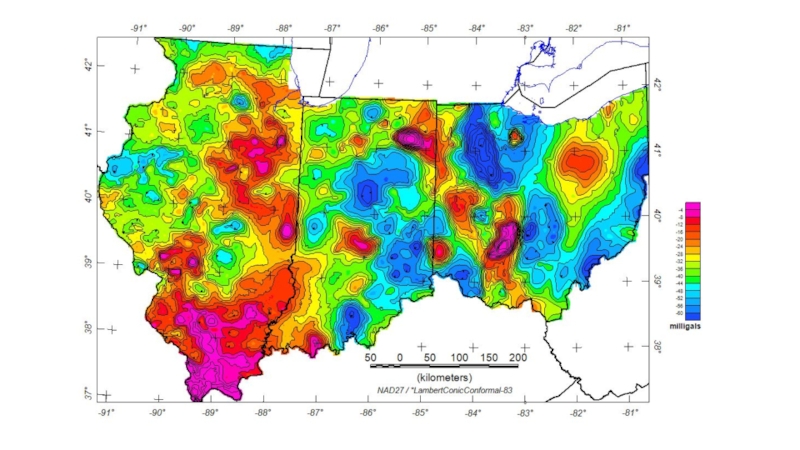
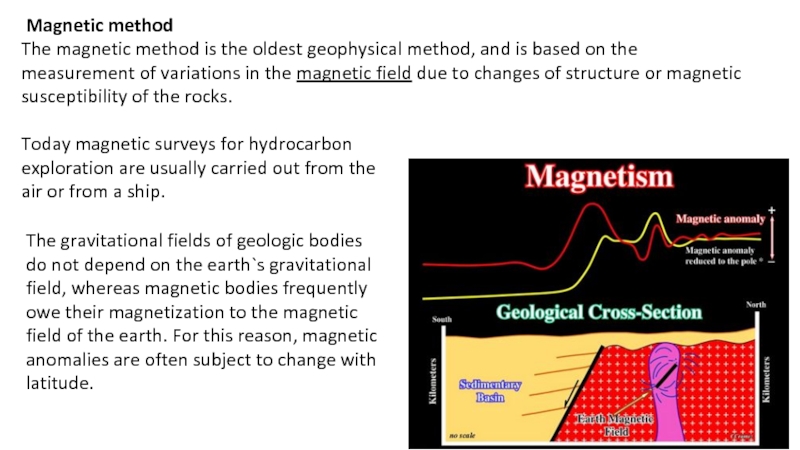
Activities to search for oil and gas deposits on the certain location beneath the earth surface
Activities to define the oil and gas volume and characteristic more precisely after discovery
Activities to build the subsurface and surface facilities to produce oil&gas safely and efficiently
Activities to extract hydrocarbons to the surface and process them
Activities to plug wells and remove surface facilities