Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
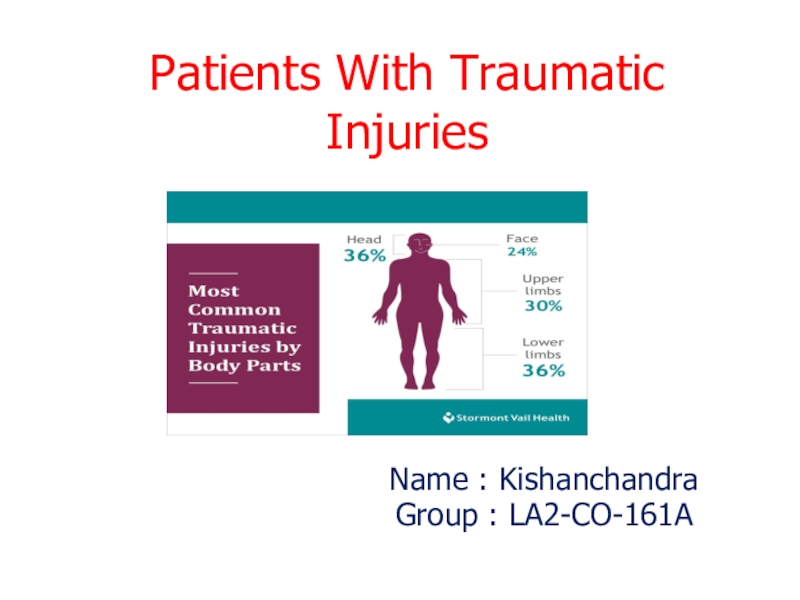
Patients With Traumatic Injuries
Содержание
- 1. Patients With Traumatic Injuries
- 2. Objectives of Trauma InvestigationDetermine :Activity With Lethal
- 3. Objectives contd..In order to:Identify the differences between
- 4. Classification of TraumaAnatomic Location of Injury Manner of Production Method of Production
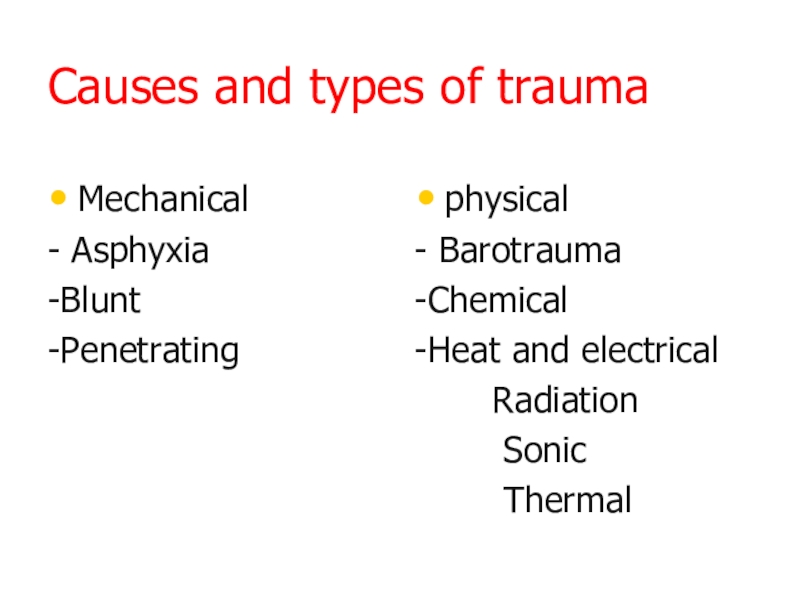
- 5. Causes and types of traumaMechanical- Asphyxia-Blunt -Penetrating
- 6. Level I Trauma Centers Prepared and committed
- 7. Level II Trauma CentersIncreased commitment to trauma
- 8. Trauma TransportSystolic B/P < 90 on 2
- 9. Trauma Transport...Traumatic arrest, isolated burns >20%Transport
- 10. Mechanism of InjuryThe process and forces that
- 11. Injury Patterns – PedestriansAdultsGenerally turn away &
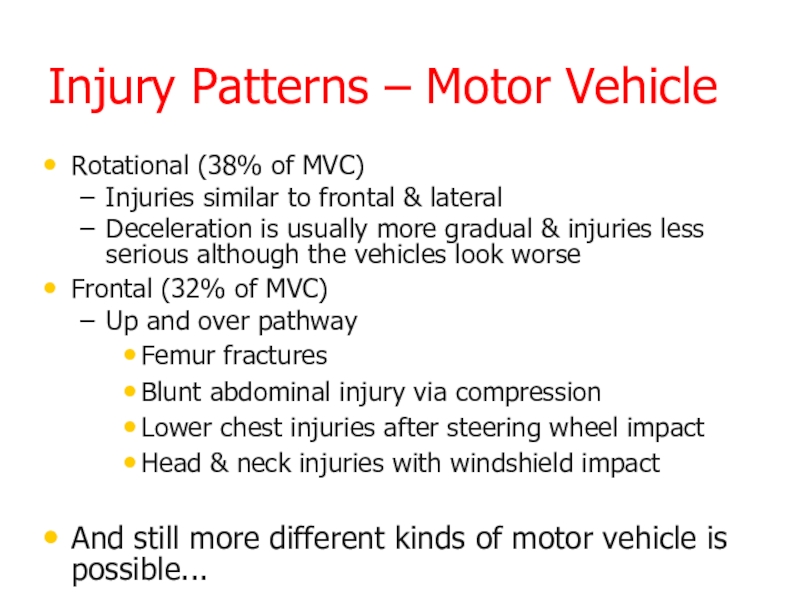
- 12. Injury Patterns – Motor VehicleRotational (38% of
- 13. Index of SuspicionYour anticipation of injury to
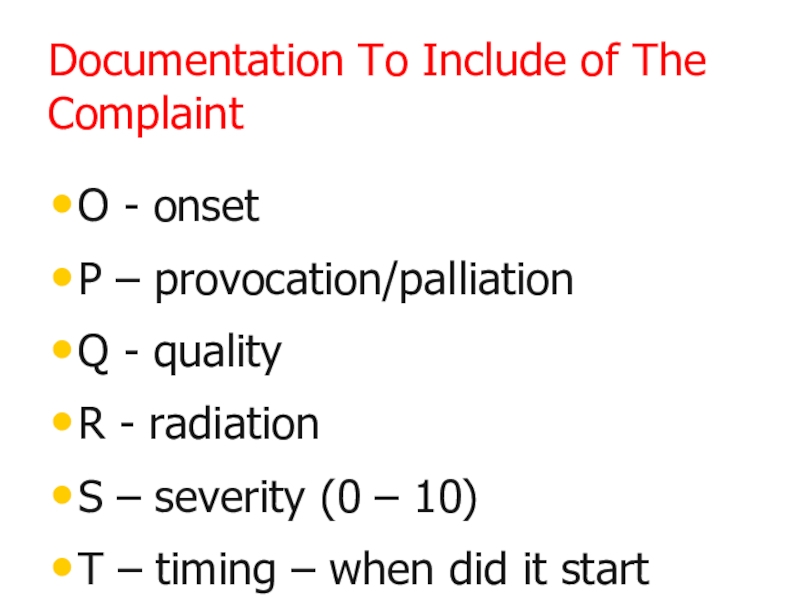
- 14. Documentation To Include of The ComplaintO -
- 15. Trauma Care – Amputated PartsRoutine trauma careTo
- 16. Care of Amputated PartsPlace part in a
- 17. GCS – Motor Response 1-6 PointsObeys command
- 18. Скачать презентанцию
Objectives of Trauma InvestigationDetermine :Activity With Lethal Injury Cause of Death Cause and Effect Manner of Death Survival Time Time of Death
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Objectives of Trauma Investigation
Determine :
Activity With Lethal Injury
Cause of
Death
of DeathСлайд 3Objectives contd..
In order to:
Identify the differences between a Category I,
II and III trauma patient.
Understand what the mechanism of injury
is and the information it providesUnderstand the difference between the index of suspicion and the general impression
Слайд 4Classification of Trauma
Anatomic Location of Injury
Manner of Production
Method
of Production
Слайд 5Causes and types of trauma
Mechanical
- Asphyxia
-Blunt
-Penetrating
physical
- Barotrauma
-Chemical
-Heat and
electrical
Radiation
SonicThermal
Слайд 6Level I Trauma Centers
Prepared and committed to handle all
types of specialty trauma 24/7
Provides leadership and resources to other
levels of trauma care in the RegionParticipates in data collection, research, continuing education, and public education programs.
Слайд 7Level II Trauma Centers
Increased commitment to trauma care for the
most common trauma emergencies with surgical capability available 24/7
Participates in
data collection, continuing education, and public education programsСлайд 8Trauma Transport
Systolic B/P < 90 on 2 consecutive readings (or
peds < 80)
Transport to the highest level Trauma
Center within 25 minutes25 minute clock starts from the time of injury
Слайд 9 Trauma Transport...
Traumatic arrest, isolated burns >20%
Transport to the closest
Trauma Center
No airway
Transport to the closest Emergency Department
Слайд 10Mechanism of Injury
The process and forces that cause trauma
Mentally recreate
the incident from the evidence noted
Identify strength of forces involved
Identify
direction forces came fromIdentify areas of the patient’s body most likely affected by the forces
Start to identify the mechanism of injury during the scene size-up
Слайд 11Injury Patterns – Pedestrians
Adults
Generally turn away & present lateral surfaces
Anatomically,
impact is low on the body
Injuries to tibia, fibula, femur,
knee, lateral chest, upper extremity, then head & neckPediatrics
Generally turn and face the vehicle
Injuries anatomically higher on the body than adults
Injuries to femur, pelvis and then those sustained when run over or pushed aside by the vehicle
Слайд 12Injury Patterns – Motor Vehicle
Rotational (38% of MVC)
Injuries similar to
frontal & lateral
Deceleration is usually more gradual & injuries less
serious although the vehicles look worseFrontal (32% of MVC)
Up and over pathway
Femur fractures
Blunt abdominal injury via compression
Lower chest injuries after steering wheel impact
Head & neck injuries with windshield impact
And still more different kinds of motor vehicle is possible...
Слайд 13Index of Suspicion
Your anticipation of injury to a body, region,
organ, or structure based on identification of the mechanism of
injuryYour index of suspicion is honed from experience and time on the job
Слайд 14Documentation To Include of The Complaint
O - onset
P – provocation/palliation
Q
- quality
R - radiation
S – severity (0 – 10)
T –
timing – when did it startСлайд 15Trauma Care – Amputated Parts
Routine trauma care
To remove gross contamination,
gently rinse with normal saline
DO NOT use distilled water to
irrigate open woundsNormal saline is isotonic and less harmful to tissue
Cover stump with damp (normal saline) sterile dressing and ace wrap
Ace provides uniform pressure to stump
Cover wounds with sterile dressing
Слайд 16Care of Amputated Parts
Place part in a plastic zip lock
bag
Place bag in larger bag or container over ice and
waterDo not ice the part alone
Слайд 17GCS – Motor Response 1-6 Points
Obeys command (6)
Localizes pain (5)
Patient
who pulls equipment off; pushes your hands away; purposeful movement
This
patient knows where the obnoxious stimuli is contacting his bodyWithdraws to pain (4)
Pt cannot isolate where they feel the noxious stimuli so just pulls back/withdraws
Flexion (3) – arms bent towards midline when stimulated
Extension (2) – arms extended when stimulated
None (1) – remains flaccid