Слайд 1Project Management
Concepts and Applications
January - 2014
Слайд 3Key Outcomes
Upon completion of this course participants will be able
to:
Appreciate the benefits of using a sound project management approach
to manage projects
Understand the overall framework of projects and project management
Have a good understanding of the language and key terms and concepts in project management
Have an appreciation of industry best practice project management tools, techniques and methodologies
Слайд 5Module 1
Project Management
Framework
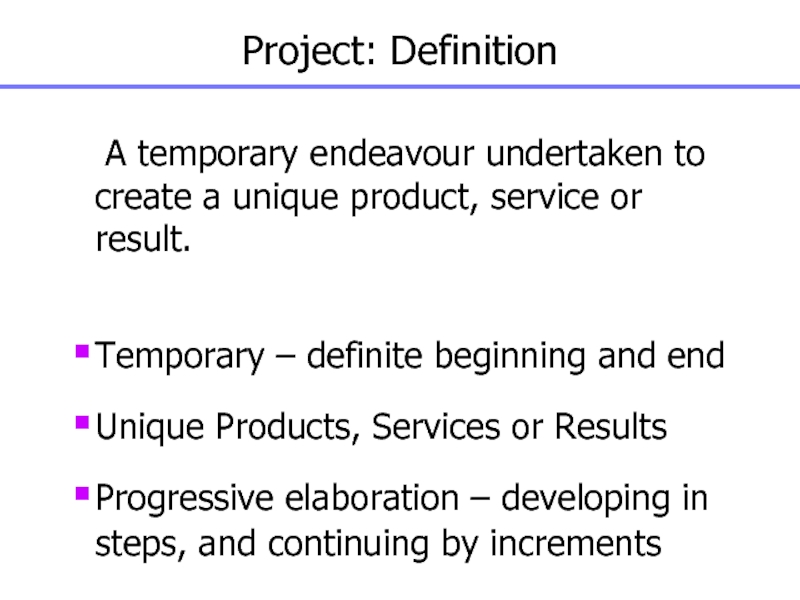
Слайд 6Project: Definition
A temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product,
service or result.
Temporary – definite beginning and end
Unique Products, Services
or Results
Progressive elaboration – developing in steps, and continuing by increments
Слайд 7Projects: Examples
Developing a new product or service
Effecting a change in
structure, staffing or style of an organisation
Designing a new transportation
vehicle
Developing or acquiring a new or modified information system
Constructing a building or facility
Implementing a new business procedure or process
Responding to a contract solicitation
Слайд 8What is Project Management?
Project Management is the application of skills,
knowledge, tools and techniques to meet the needs and expectations
of stakeholders for a project.
The purpose of project management is prediction and prevention, NOT recognition and reaction
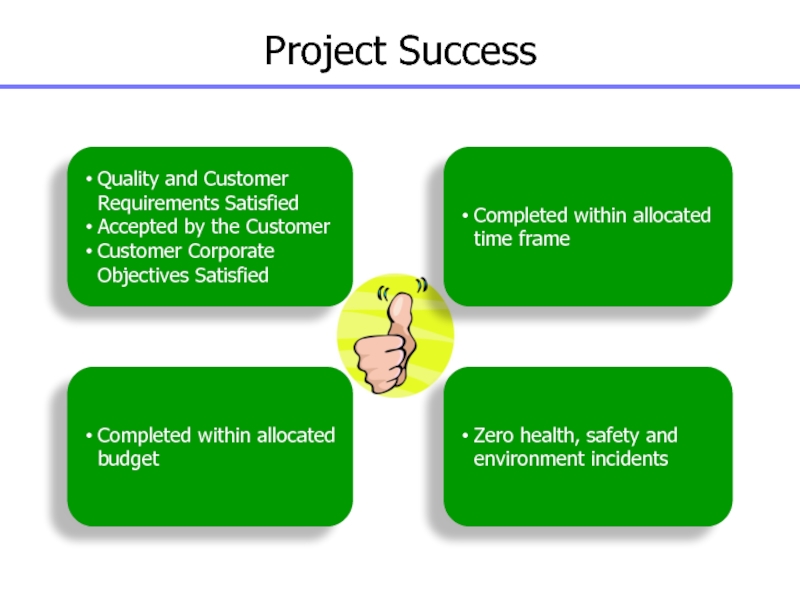
Слайд 9Project Success
Quality and Customer Requirements Satisfied
Accepted by the Customer
Customer Corporate
Objectives Satisfied
Completed within allocated time frame
Completed within allocated budget
Zero health,
safety and environment incidents
Слайд 10Projects Critical Success Factors
Agreement among the project team, customer and
management on the goals of the project
Good definition of project
scope
A plan that shows an overall path and clear responsibilities and will be used to measure progress during the project
Constant, effective communication amongst everyone involved in the project
A controlled scope
Management support
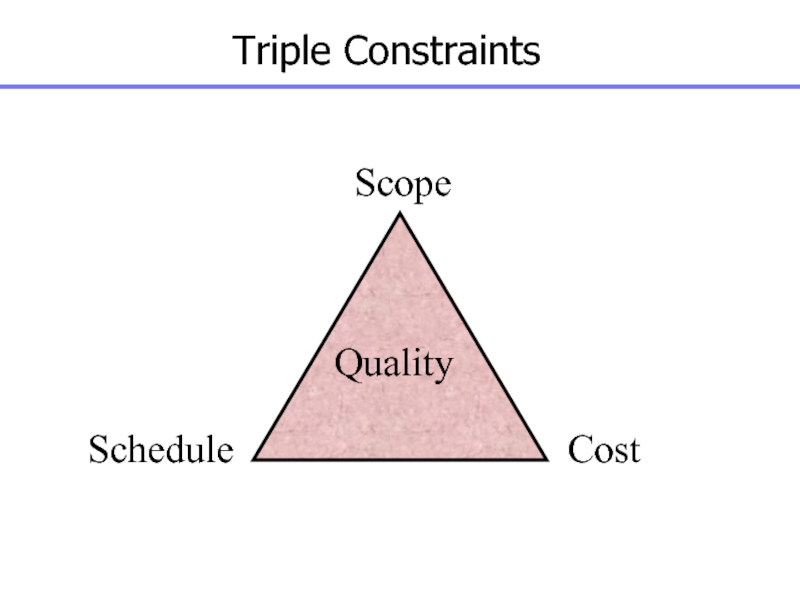
Слайд 11Triple Constraints
Scope
Schedule
Cost
Quality
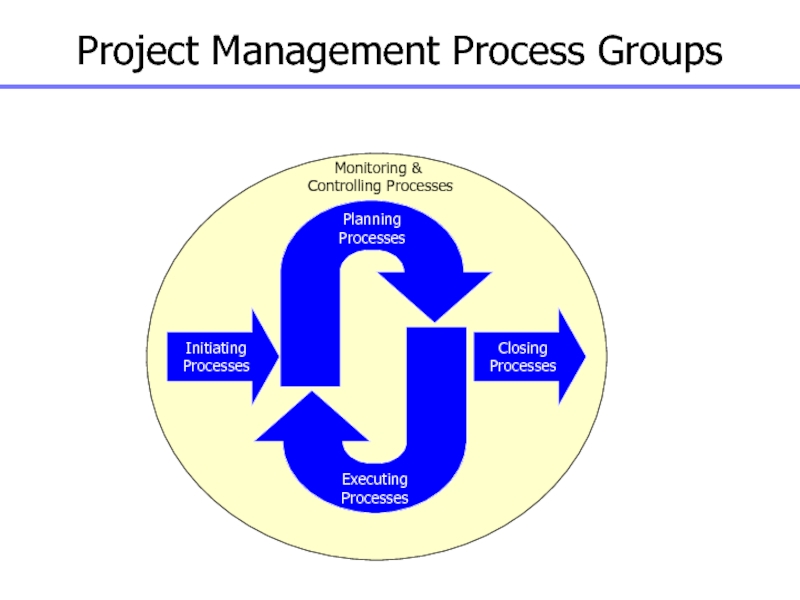
Слайд 13Project Management Process Groups
Initiating
Processes
Planning
Processes
Executing
Processes
Closing
Processes
Monitoring &
Controlling Processes
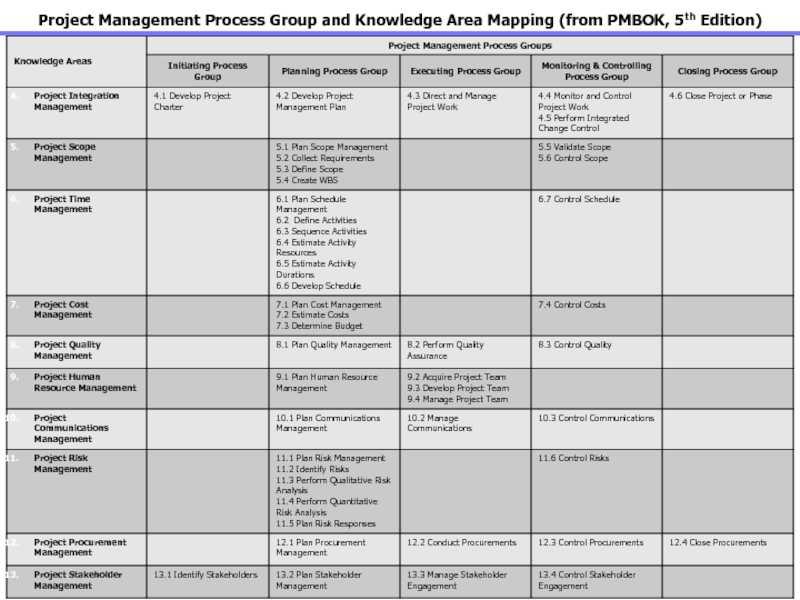
Слайд 14Project Management Process Group and Knowledge Area Mapping (from PMBOK,
5th Edition)
Cost
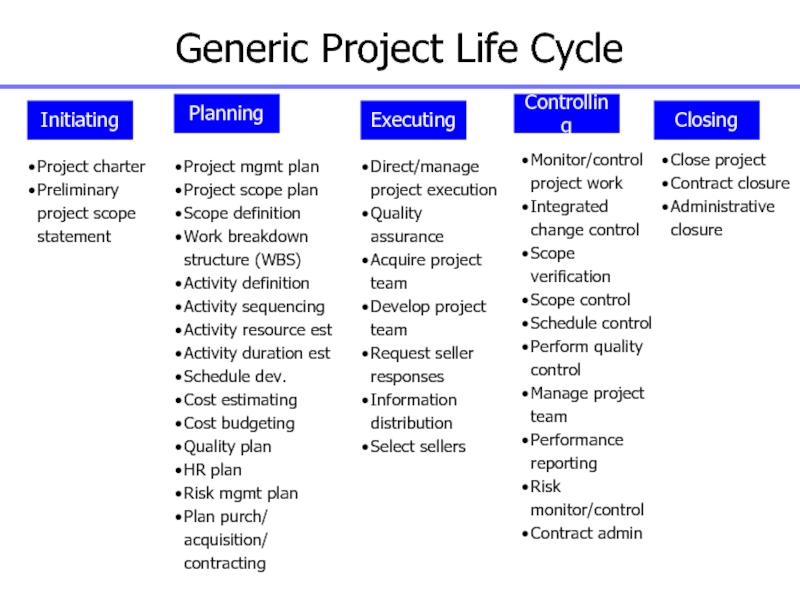
Слайд 15Generic Project Life Cycle
Initiating
Planning
Project mgmt plan
Project scope plan
Scope definition
Work breakdown
structure (WBS)
Activity definition
Activity sequencing
Activity resource est
Activity duration est
Schedule dev.
Cost estimating
Cost
budgeting
Quality plan
HR plan
Risk mgmt plan
Plan purch/ acquisition/ contracting
Project charter
Preliminary project scope statement
Executing
Direct/manage project execution
Quality assurance
Acquire project team
Develop project team
Request seller responses
Information distribution
Select sellers
Controlling
Monitor/control project work
Integrated change control
Scope verification
Scope control
Schedule control
Perform quality control
Manage project team
Performance reporting
Risk monitor/control
Contract admin
Closing
Close project
Contract closure
Administrative closure
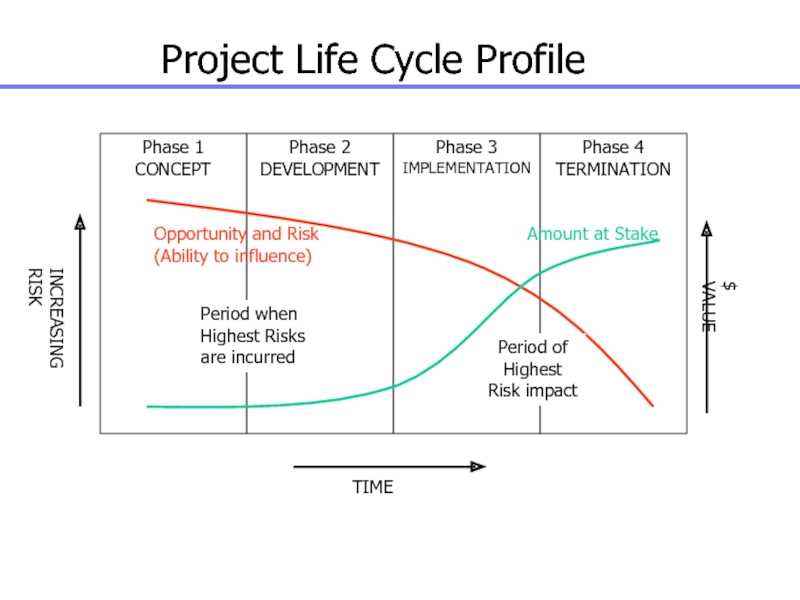
Слайд 16Project Life Cycle Characteristics
Cost and staffing levels are low at
start, higher towards the end and drops rapidly as the
project draws to a conclusion
Risk and uncertainty is highest at start of the project
Ability to influence the final characteristics of the project’s product and project final cost is highest at the start and gets progressively lower as the project continues
Слайд 17Phase 1
CONCEPT
Phase 2
DEVELOPMENT
Phase 3
IMPLEMENTATION
Phase 4
TERMINATION
Opportunity and Risk
(Ability to influence)
Amount at
Stake
Period when
Highest Risks
are incurred
Period of
Highest
Risk impact
$ VALUE
INCREASING RISK
TIME
Project Life
Cycle Profile
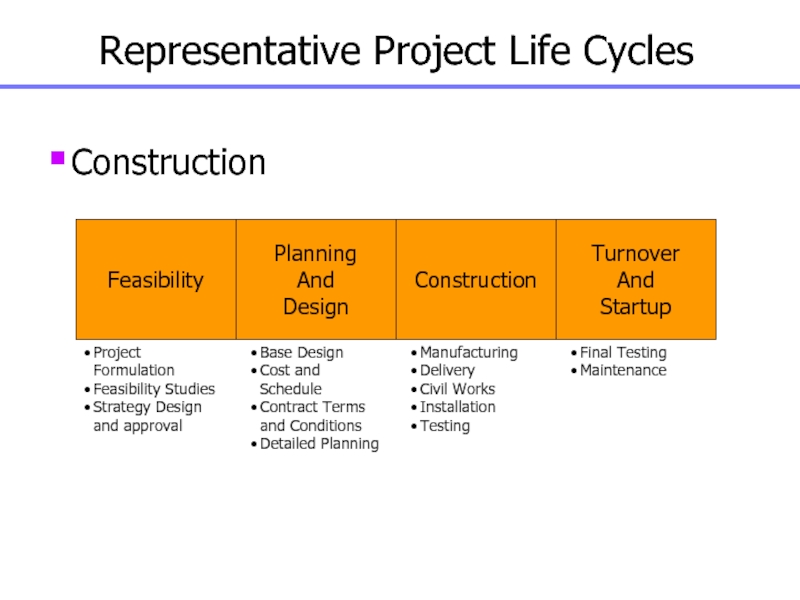
Слайд 18Representative Project Life Cycles
Construction
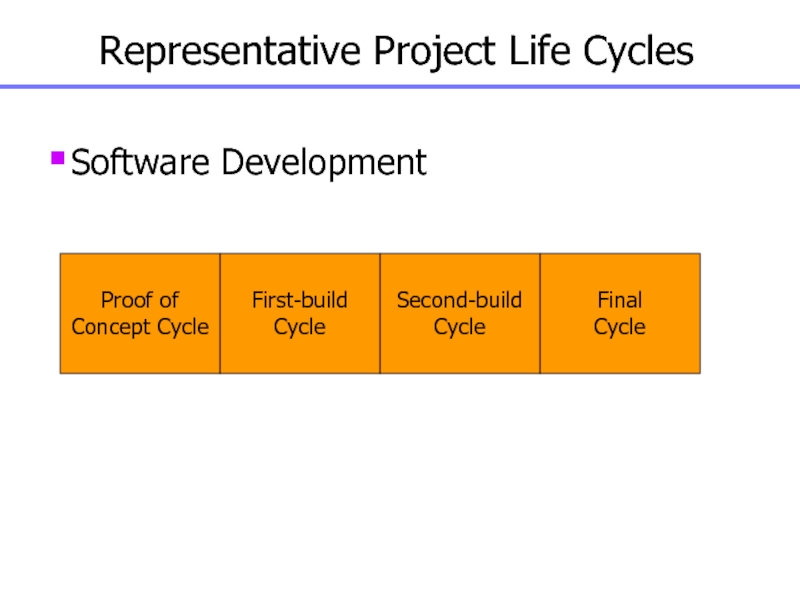
Слайд 19Representative Project Life Cycles
Software Development
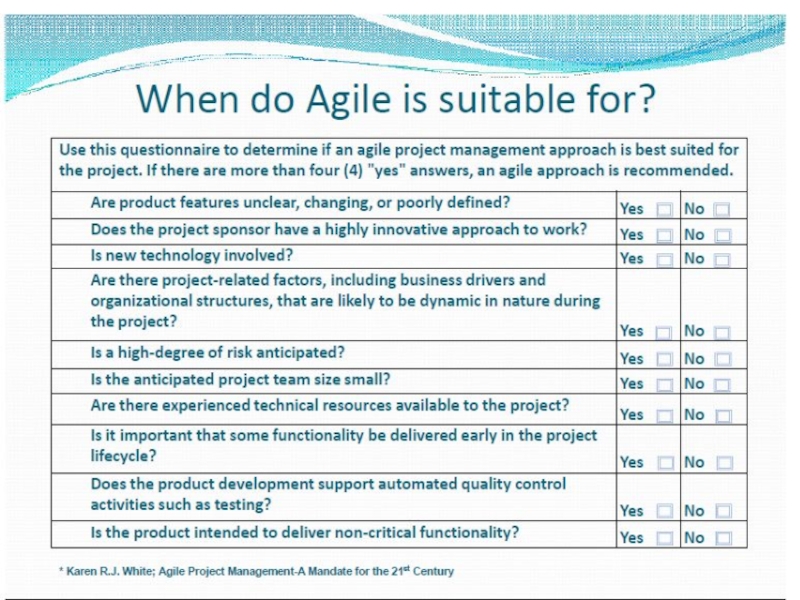
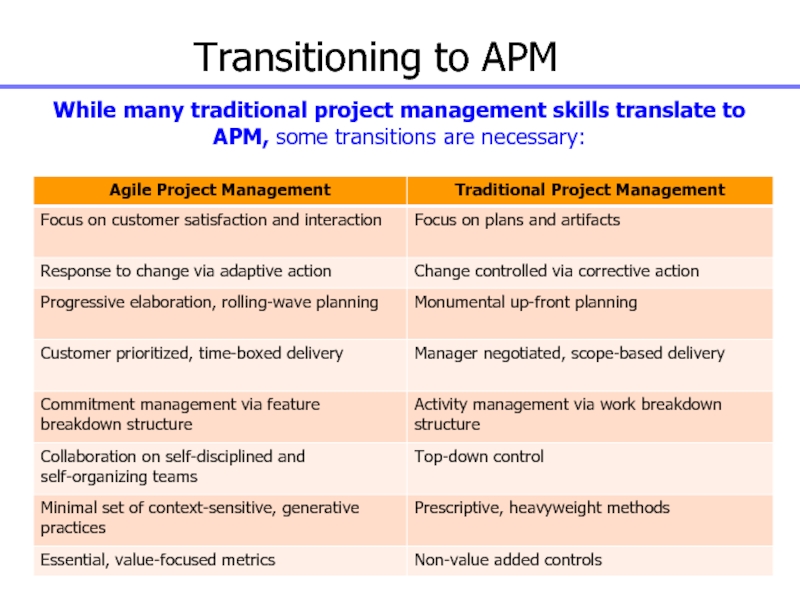
Слайд 22Transitioning to APM
While many traditional project management skills translate to
APM, some transitions are necessary:
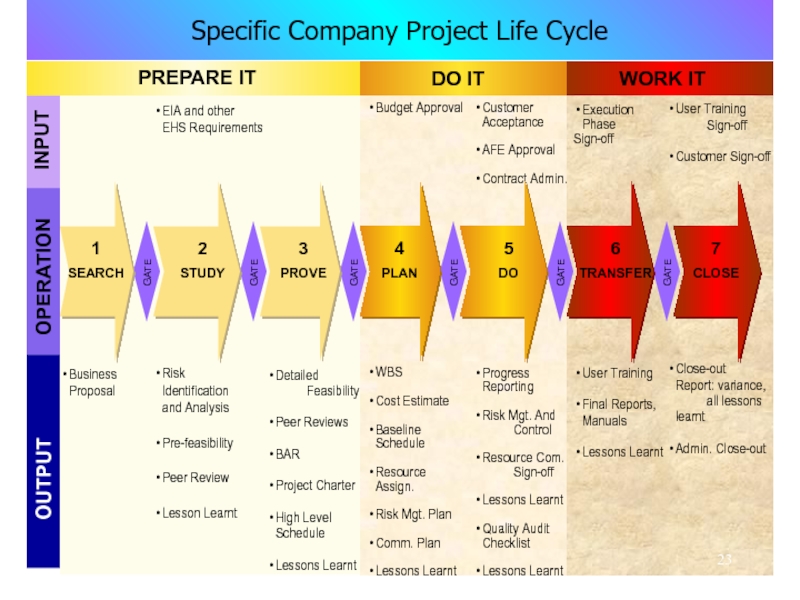
Слайд 23Specific Company Project Life Cycle
Budget Approval
WBS
Cost Estimate
Baseline
Schedule
Resource
Assign.
Risk
Mgt. Plan
Comm. Plan
Lessons Learnt
EIA and other
EHS Requirements
Risk
Identification
and
Analysis
Pre-feasibility
Peer Review
Lesson Learnt
Detailed
Feasibility
Peer Reviews
BAR
Project Charter
High Level Schedule
Lessons Learnt
Business
Proposal
Customer Acceptance
AFE Approval
Contract Admin.
Progress Reporting
Risk Mgt. And Control
Resource Com. Sign-off
Lessons Learnt
Quality Audit Checklist
Lessons Learnt
Execution
Phase Sign-off
User Training
Final Reports,
Manuals
Lessons Learnt
User Training Sign-off
Customer Sign-off
Close-out Report: variance, all lessons learnt
Admin. Close-out
GATE
DO IT
WORK IT
INPUT
OPERATION
OUTPUT
PREPARE IT
1
SEARCH
GATE
2
STUDY
GATE
1
SEARCH
GATE
4
PLAN
GATE
5
DO
GATE
6
TRANSFER
7
CLOSE
3
PROVE
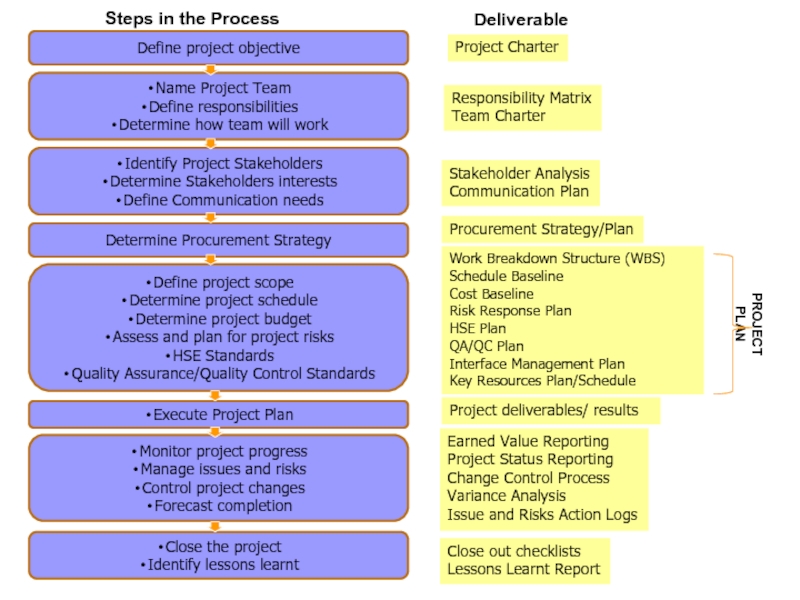
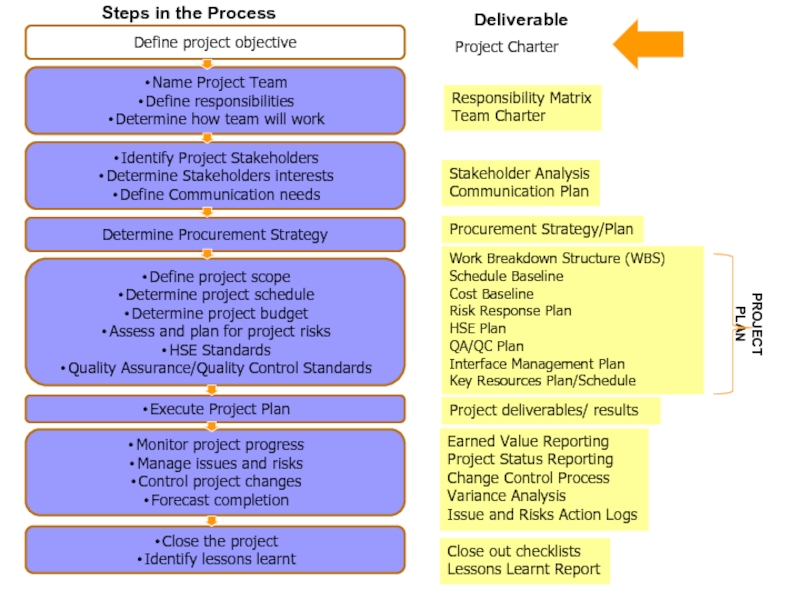
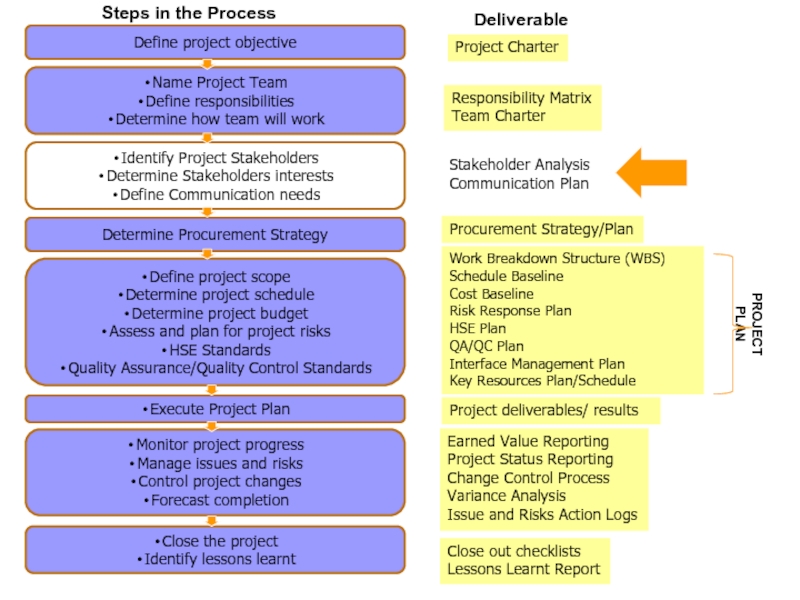
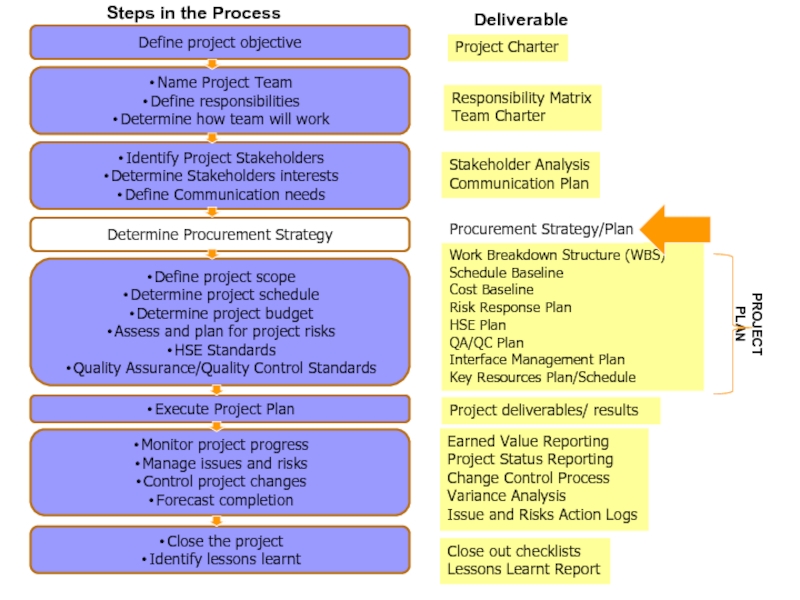
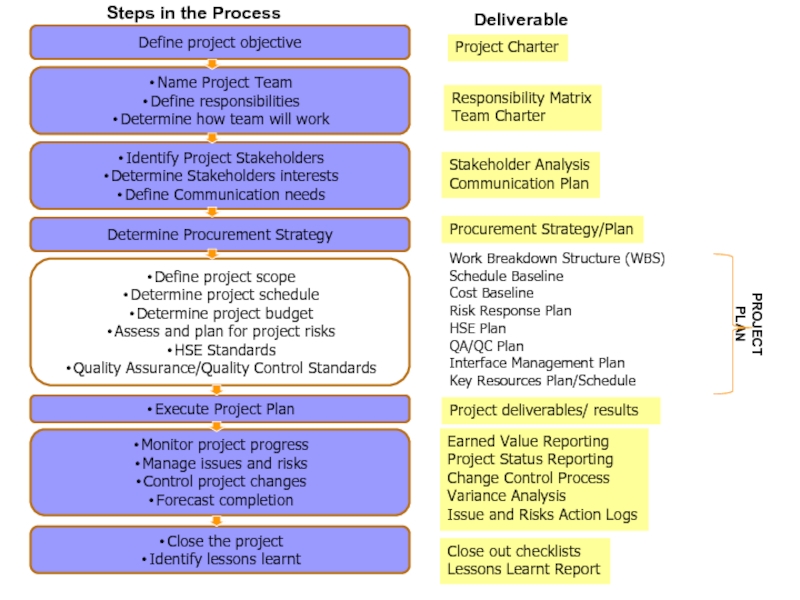
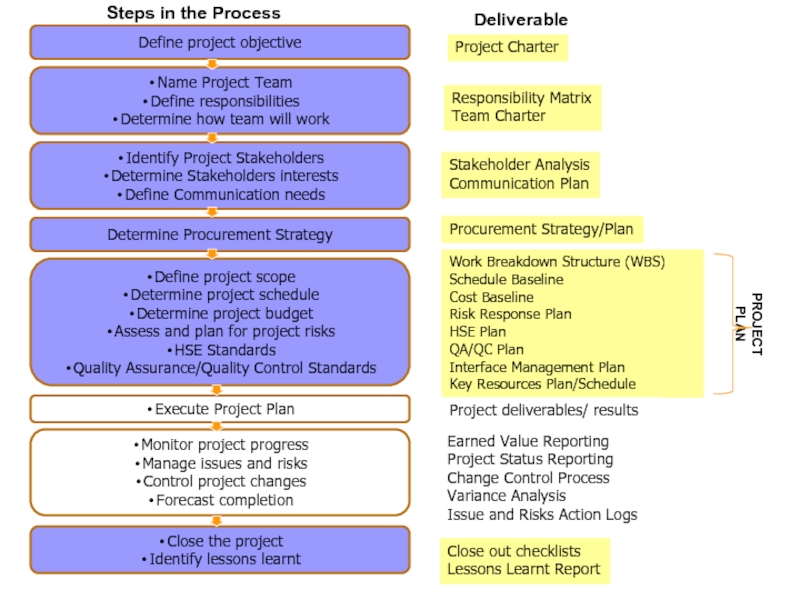
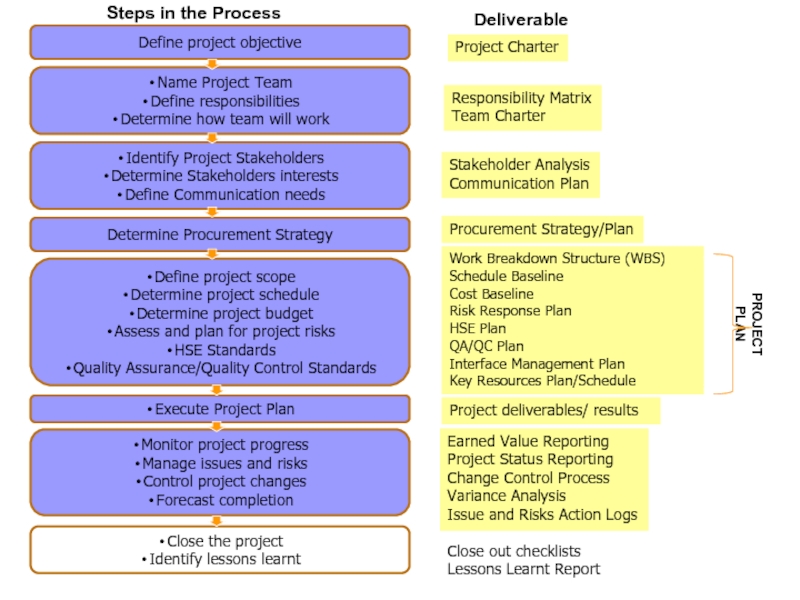
Слайд 24Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
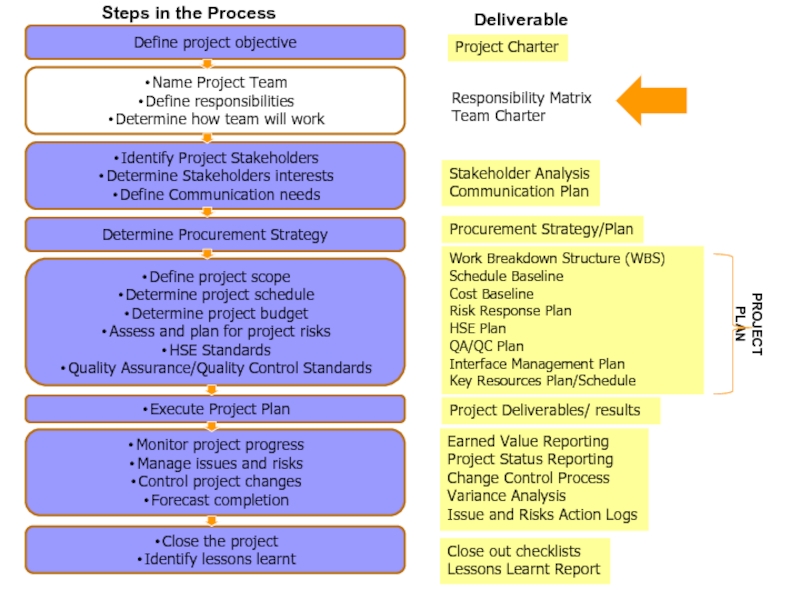
Слайд 26Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
Слайд 28Project Objective
Project Charter
Is sent out by the Project Sponsor
The document
that formally authorises a project
Provides the project manager with the
authority to apply organisational resources to project activities
Слайд 29Project Charter
Should provide the following info:
Project purpose or justification
Measurable project
objectives and related success criteria
High level requirements/deliverables
Assumptions and constraints
High level
project description and boundaries (in scope; out of scope)
High level risks
Summary milestone schedule
Summary budget
Stakeholder list
Project approval requirements (i.e. what constitutes project success, who decides the project is successful, and who signs off on the project
Assigned project manager, responsibility, and authority level, and
Name and authority of the sponsor or other person(s) authorising the project charter
Слайд 30Exercise 1: Project Charter
Use the information provided in the handout
to prepare a Project Charter for the House Renovation Project
Слайд 32Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project Deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
Слайд 33Responsibility Matrix
The responsibility matrix will document precisely the responsibility of
each group or individual in the project.
The purpose of the
Responsibility Matrix is to clearly define the responsibilities of team members and principal stakeholders in accomplishing the activities of the project.
The Responsibility Matrix is organised by Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) elements and used to determine what resources are needed on a project.
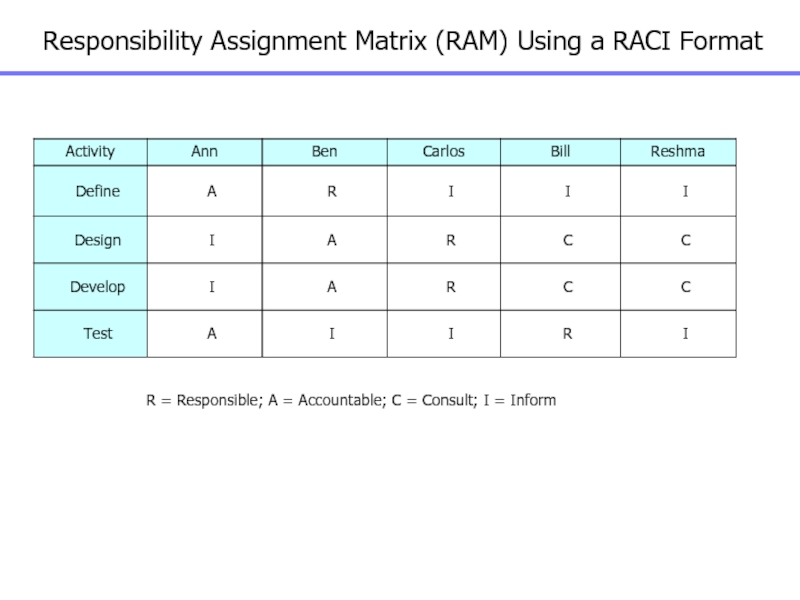
Слайд 34Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Using a RACI Format
R = Responsible;
A = Accountable; C = Consult; I = Inform
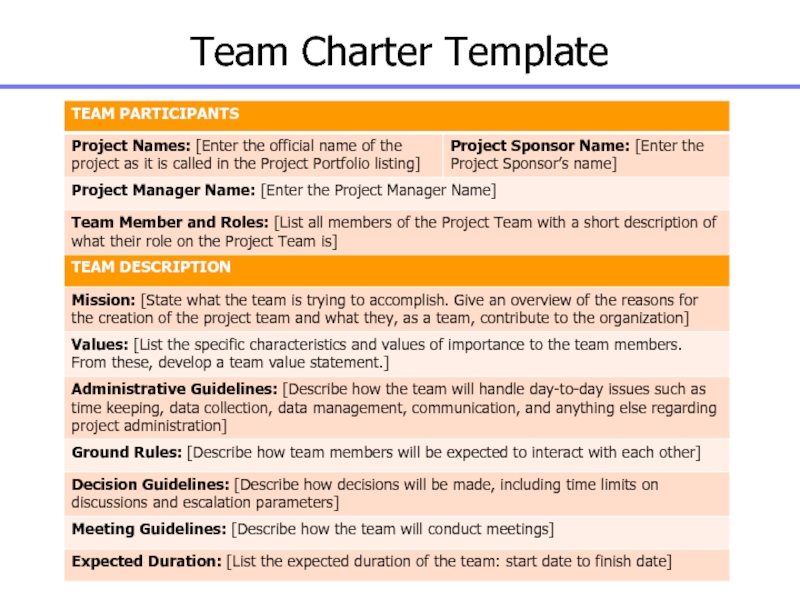
Слайд 35Team Charter
Development of the Team Charter is necessary as it
formally recognizes the existence of a project team.
It lists
all participants on the Project Team and their reporting relationships.
It describes the methods by which the Project Team will conduct business, meetings, etc.
It describes the conditions under which the project team is organized: individual roles within the team, and the operating agreement under which the entire team works.
It is a mutually agreed upon contract of behaviour for the team.
Слайд 39Module 4
Stakeholders and Communication
Слайд 40Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
Слайд 41Project Stakeholders
Individuals and organisations that are actively involved in the
project, or whose interests may be positively or negatively affected
as a result of project execution or project completion; they may also exert influence over the project and its results.
Слайд 42Project Stakeholders
Key stakeholders on every project:
Project manager – responsible for
project results
Customer – individual/organisation that will use the project’s product
Project
team members – the group that is performing the work of the project
Project Sponsor or Champion – provides financial resources, supports the project
Слайд 43Project Stakeholders
Other stakeholders
Line managers
Unions
Contractors and vendors
External funders
Government agencies
Community
Managing stakeholder expectations
is a key responsibility of the project manager
Слайд 44Project Stakeholders
Aim
Identify the stakeholders and assess how are they likely
to be impacted by the project and/or how they can
impact the project
Goal
Develop cooperation between the stakeholders and the project team, and ultimately assuring successful project outcomes
Identify, Analyse, Prioritise, Plan Response/Communication, Monitor & Control
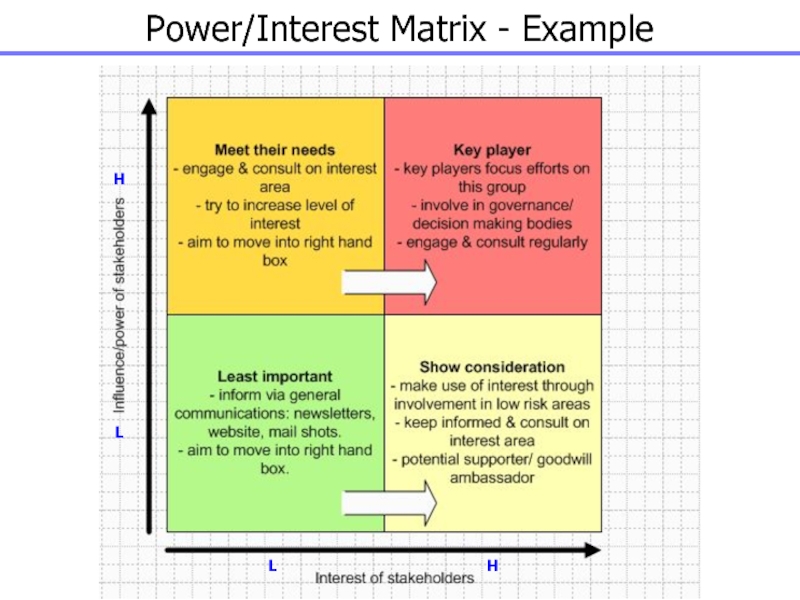
Слайд 45Power/Interest Matrix
Classifies stakeholders in relation to their power and the
extent to which they are likely to show interest in
the actions of the organisation
Can be used to indicate the nature of the relationship which should be adopted with each group
Слайд 46Stakeholder Interests
What are their expectations and what benefits do they
seek
What resources will they commit (or avoid committing) to the
project
Do they have other interests that might conflict with the project
How do they regard other stakeholders on the list
Слайд 47Stakeholder Power/Influence
Legal or statutory authority
Control of strategic resources
Social, economic and
political status
Possession of specialist knowledge
Negotiating position and ability to influence
other stakeholders
Formal/informal links to other stakeholders
Degree of dependence on other stakeholders
Leadership/Authority
Слайд 48Power/Interest Matrix - Example
L
L
H
H
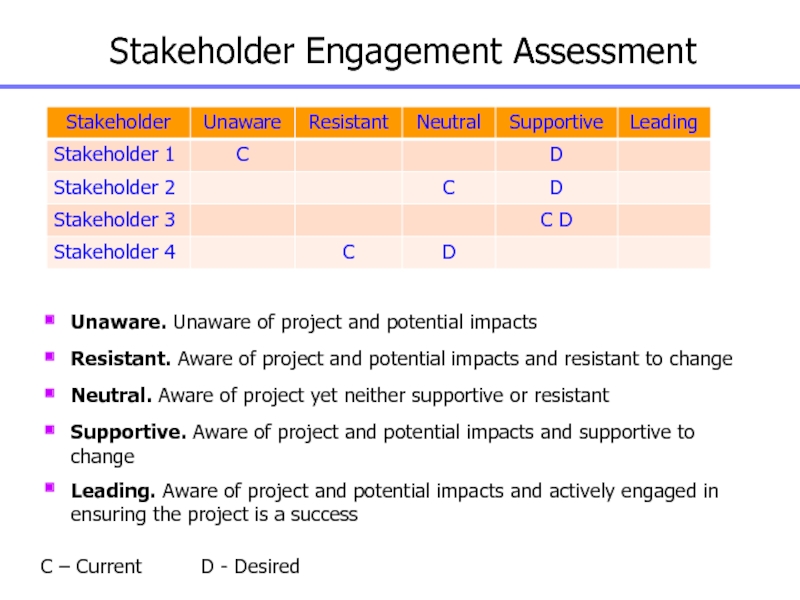
Слайд 49Stakeholder Engagement Assessment
Unaware. Unaware of project and potential impacts
Resistant. Aware
of project and potential impacts and resistant to change
Neutral. Aware
of project yet neither supportive or resistant
Supportive. Aware of project and potential impacts and supportive to change
Leading. Aware of project and potential impacts and actively engaged in ensuring the project is a success
C – Current D - Desired
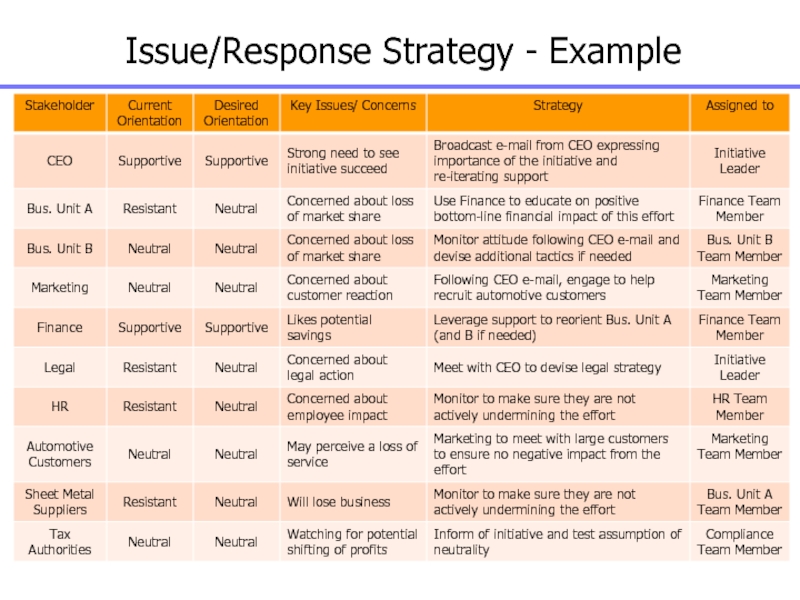
Слайд 50Issue/Response Strategy - Example
Слайд 52Exercise 2: Stakeholders
Identify the key and other stakeholders in the
House Renovation Project
Carry out a Stakeholder Analysis
Outline a high level
Communication Plan for the Project, as applicable
Слайд 54Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
Слайд 55Procurement Strategy
Describes the processes required to acquire goods and services
from outside the performing organization
Determining what to procure and when
Documenting
product requirements and identifying potential sources
Obtaining quotations, bids, offers or proposals
Selecting seller from among potential sellers
Managing the relationship with the seller
Completion and settlement of the contract, including resolution of any open issues
Слайд 56Project Procurement Management
Buyer’s goal
To place maximum performance risk on
the seller
To maintain incentive for economical and efficient performance
Seller’s goal
Minimise
risks
Maximise profits
Key issues
Transparency in transactions/processes
Clear contract specifications
Contract types
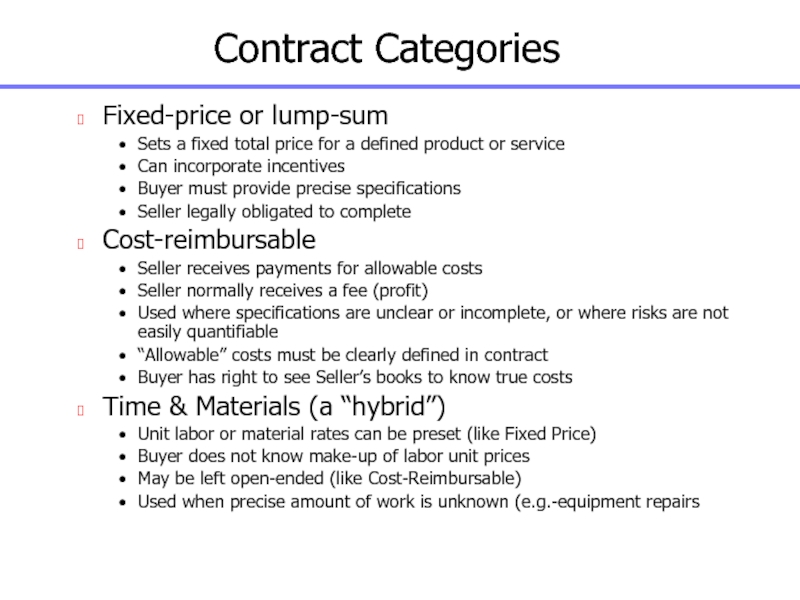
Слайд 57Contract Categories
Fixed-price or lump-sum
Sets a fixed total price for
a defined product or service
Can incorporate incentives
Buyer must provide precise
specifications
Seller legally obligated to complete
Cost-reimbursable
Seller receives payments for allowable costs
Seller normally receives a fee (profit)
Used where specifications are unclear or incomplete, or where risks are not easily quantifiable
“Allowable” costs must be clearly defined in contract
Buyer has right to see Seller’s books to know true costs
Time & Materials (a “hybrid”)
Unit labor or material rates can be preset (like Fixed Price)
Buyer does not know make-up of labor unit prices
May be left open-ended (like Cost-Reimbursable)
Used when precise amount of work is unknown (e.g.-equipment repairs
Слайд 58FIDIC Documents
Short Form of Contract (Green Book)
These Conditions of Contract
are recommended for engineering and building work of relatively small
capital value. However, depending on the type of work and the circumstances, the Conditions may be suitable for contracts of considerably greater value.
They are considered most likely to be suitable for fairly simple or repetitive work or work of short duration without the need for specialist sub-contracts. This form may also be suitable for contracts which include, or wholly comprise, contractor-designed civil engineering, building, mechanical and/or electrical works.
Слайд 59FIDIC Documents
Construction Contract (Red Book)
Conditions of Contract for Construction, which
are recommended for building or engineering works designed by the
Employer or by his representative, the Engineer.
Under the usual arrangements for this type of contract, the Contractor constructs the works in accordance with a design provided by the Employer.
However, the works may include some elements of Contractor-designed civil, mechanical, electrical and/or construction works
Слайд 60FIDIC Documents
Plant and Design-Build Contract (Yellow Book)
Conditions of Contract for
Plant and Design-Build, which are recommended for the provision of
electrical and/or mechanical plant, and for the design and execution of building or engineering works.
Under the usual arrangements for this type of contract, the Contractor designs and provides, in accordance with the Employer’s requirements, plant and/or other works; which may include any combination of civil, mechanical, electrical and/or construction works.
Слайд 61FIDIC Documents
EPC Turnkey Contract (Silver Book)
Conditions of Contract for EPC
Turnkey Projects, which are recommended where one entity takes total
responsibility for the design and execution of an engineering project.
Under the usual arrangements for this type of contract, the entity carries out all the Engineering, Procurement and Construction: providing a fully-equipped facility, ready for operation (at the "turn of the key"). This type of contract is usually negotiated between the parties.
DBO Contract (Gold Book)
Conditions of Contract for Design, Build and Operate Projects
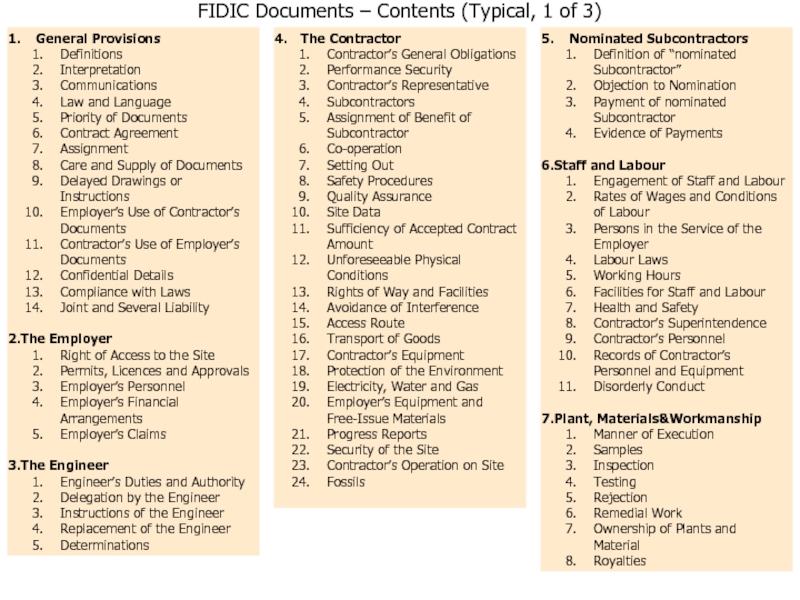
Слайд 62FIDIC Documents – Contents (Typical, 1 of 3)
Слайд 63FIDIC Documents – Contents (Typical, 2 of 3)
Слайд 64FIDIC Documents – Contents (Typical, 3 of 3)
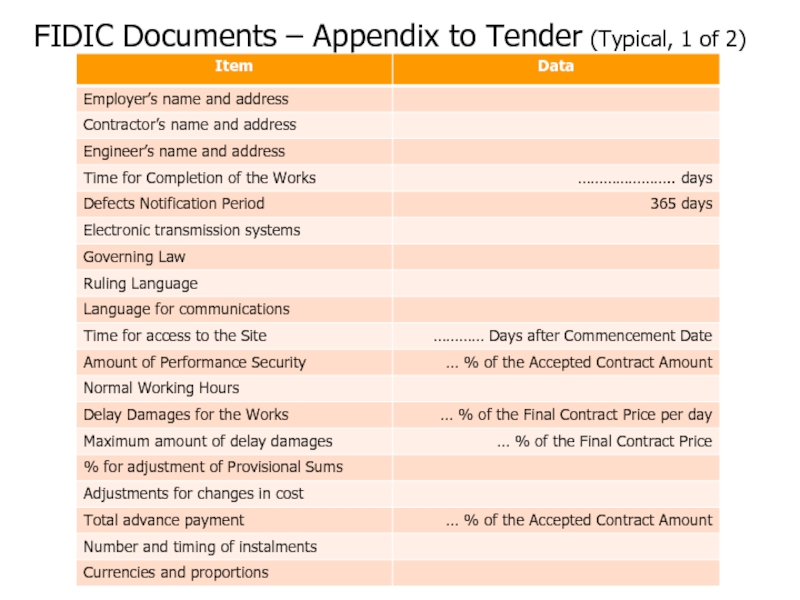
Слайд 65FIDIC Documents – Appendix to Tender (Typical, 1 of 2)
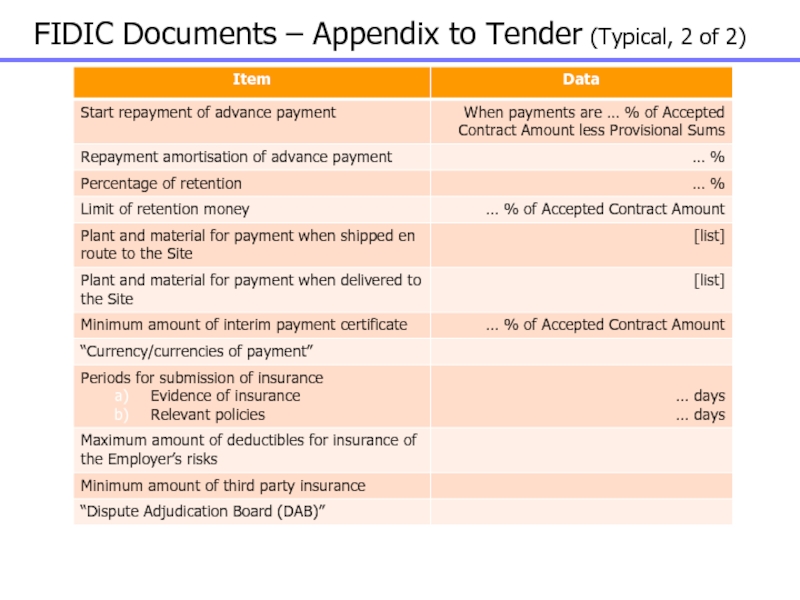
Слайд 66FIDIC Documents – Appendix to Tender (Typical, 2 of 2)
Слайд 67Bonds: Bid Bonds
Bid (Tender) Bonds
An indication of your Company’s ability
to carry out the work being bid on
Sought by the
Buyer to provide a surety should the successful bidder fail to proceed with the contract for any reason
Used as a financial fall-back in the event the successful contracting party is unable/unwilling to accept the award of the contract or meet any of its conditions, and it becomes necessary to place the project, or any part of it, out for bid again
Benefits
Demonstrates to the Buyer that the bidder is reliable, a sound business and has the ability to carry out the work being bid for
Indicates that your bid is genuine and you have a firm commitment to the project
Secures payment for the Buyer of the guaranteed amount in the event of:
Withdrawal of offer before its expiration date
Repudiation of the contract by the bidder after being awarded
Failure of the successful bidder to provide a replacement Performance Bond
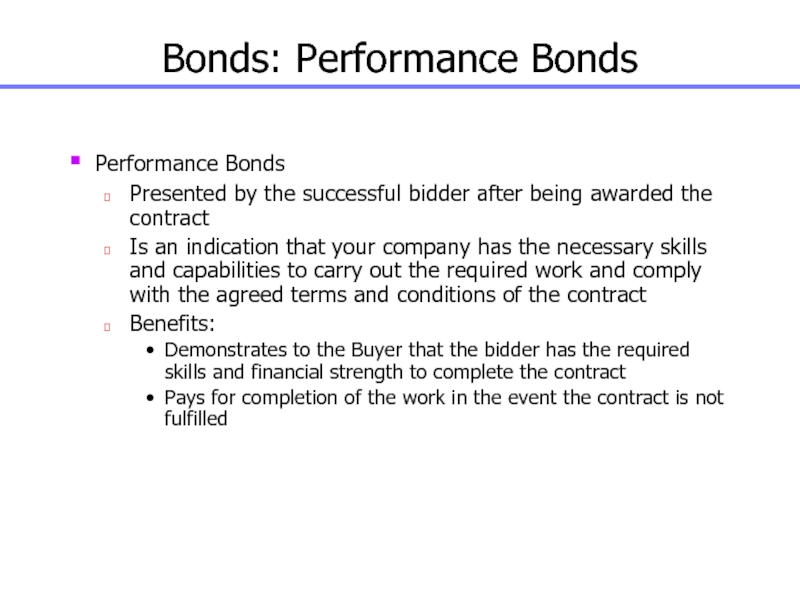
Слайд 68Bonds: Performance Bonds
Performance Bonds
Presented by the successful bidder after being
awarded the contract
Is an indication that your company has the
necessary skills and capabilities to carry out the required work and comply with the agreed terms and conditions of the contract
Benefits:
Demonstrates to the Buyer that the bidder has the required skills and financial strength to complete the contract
Pays for completion of the work in the event the contract is not fulfilled
Слайд 69Bonds: Advance Bonds, Maintenance Bond
Advance Payment Bond is a Guarantee
supplied by a party receiving an advance payment to the
party advancing the payment. It provides that the advanced sum will be returned if the agreement under which the advance was made cannot be fulfilled.
Payment Bond protects subcontractors and suppliers by guaranteeing that all claimants will be paid for labor and materials supplied to the contractor for use on the bonded job
Maintenance bond guarantees that for a stated period, usually one year, that any defective workmanship or material will be repaired
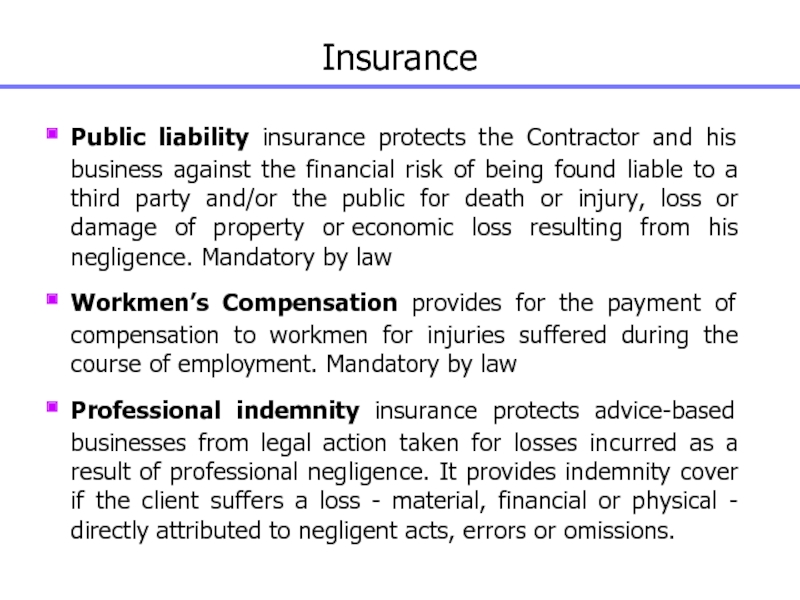
Слайд 70Insurance
Public liability insurance protects the Contractor and his business against
the financial risk of being found liable to a third
party and/or the public for death or injury, loss or damage of property or economic loss resulting from his negligence. Mandatory by law
Workmen’s Compensation provides for the payment of compensation to workmen for injuries suffered during the course of employment. Mandatory by law
Professional indemnity insurance protects advice-based businesses from legal action taken for losses incurred as a result of professional negligence. It provides indemnity cover if the client suffers a loss - material, financial or physical - directly attributed to negligent acts, errors or omissions.
Слайд 71Insurance: Builder’s Risk
Builder's Risk insurance, also known as "course of
construction", "construction all risk", and "contractor's all risk insurance", is
designed to insure buildings or projects against repair or replacement costs while they are under construction and, in some cases, for a specified period afterwards.
This insurance will usually also cover build materials, fixtures and appliances all of which are intended to become an integral part of the structure under construction as well as temporary works to facilitate construction.
Can be procured by Contractor or Client
Слайд 72Exercise 3: Procurement Strategy
Suggest a high level procurement strategy for
the provision of goods and services to accomplish the House
Renovation Project
Слайд 74Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
Слайд 75Project Scope
Definition
Project scope defines the services, equipment, and materials to
be provided and the work to be accomplished based on
contract parameters
Purpose
To develop an understanding of the project’s content and complexity; to determine what work will be done for the project and how it will be done
Слайд 77Scope Management
Primarily it is the definition and control of what
IS and
IS NOT included in the project.
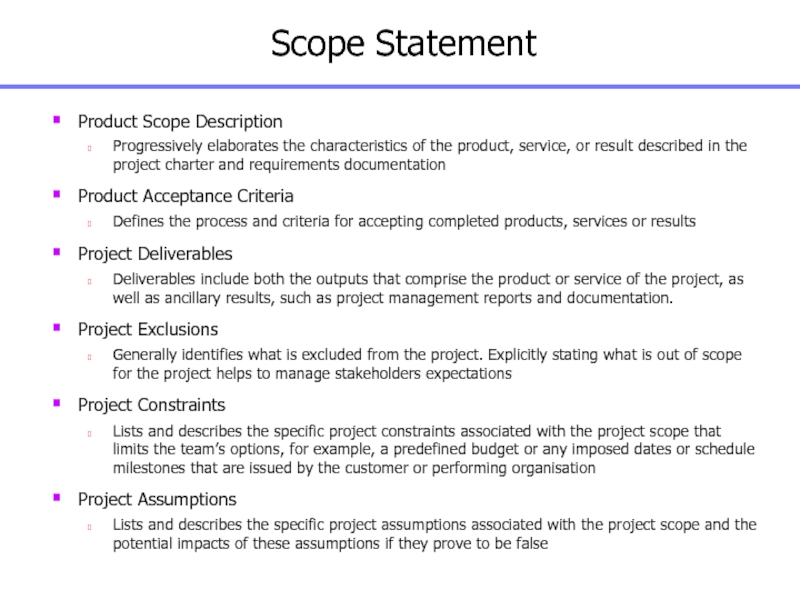
Слайд 78Product Scope Description
Progressively elaborates the characteristics of the product, service,
or result described in the project charter and requirements documentation
Product
Acceptance Criteria
Defines the process and criteria for accepting completed products, services or results
Project Deliverables
Deliverables include both the outputs that comprise the product or service of the project, as well as ancillary results, such as project management reports and documentation.
Project Exclusions
Generally identifies what is excluded from the project. Explicitly stating what is out of scope for the project helps to manage stakeholders expectations
Project Constraints
Lists and describes the specific project constraints associated with the project scope that limits the team’s options, for example, a predefined budget or any imposed dates or schedule milestones that are issued by the customer or performing organisation
Project Assumptions
Lists and describes the specific project assumptions associated with the project scope and the potential impacts of these assumptions if they prove to be false
Scope Statement
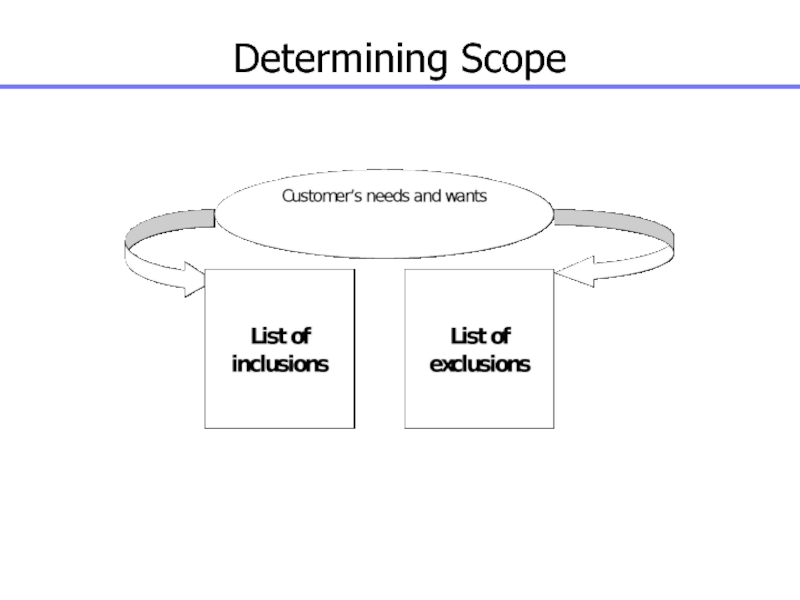
Слайд 79Create WBS
Subdividing the major project deliverables and project work into
smaller, more manageable components
Слайд 80Work Breakdown Structure
The WBS
Is the scope of work
The WBS helps
The
customer, management, and the technical team visualize the project
The project
team communicate
Build the foundation for the schedule and cost performance measurement
Facilitate assignment of task accountability
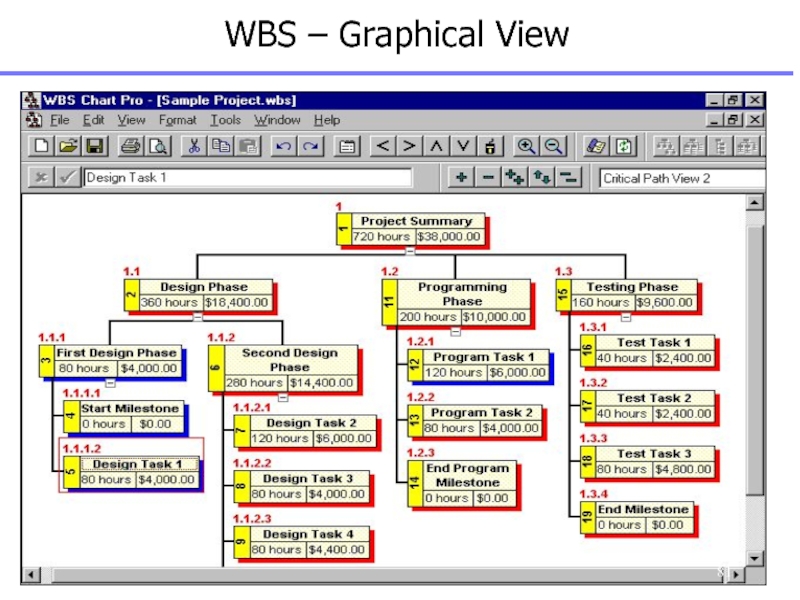
Слайд 82WBS – Outline View
Project Summary
1.1 Design
Phase
1.1.1 First Design Phase
1.1.1.1 Start Milestone
1.1.1.2 Design Task 1
1.1.2 Second Design Phase
1.1.2.1 Design Task 2
1.1.2.2 Design Task 3
1.1.2.3 Design Task 4
1.1.2.4 End Design Milestone
1.2 Programming Phase
1.2.1 Program Task 1
1.2.2 Program Task 2
1.2.3 End Program Milestone
1.3 Testing Phase
1.3.1 Test Task 1
1.3.2 Test Task 2
1.3.3 Test Task 3
1.3.4 End Milestone
Слайд 83WBS – Steps/Factors to Consider
Begin at the top using the
scope statement or by listing the major project deliverables
Use the
project team to develop the WBS
Each element represents a single tangible deliverable
The work package is the lowest level of the WBS
Слайд 86
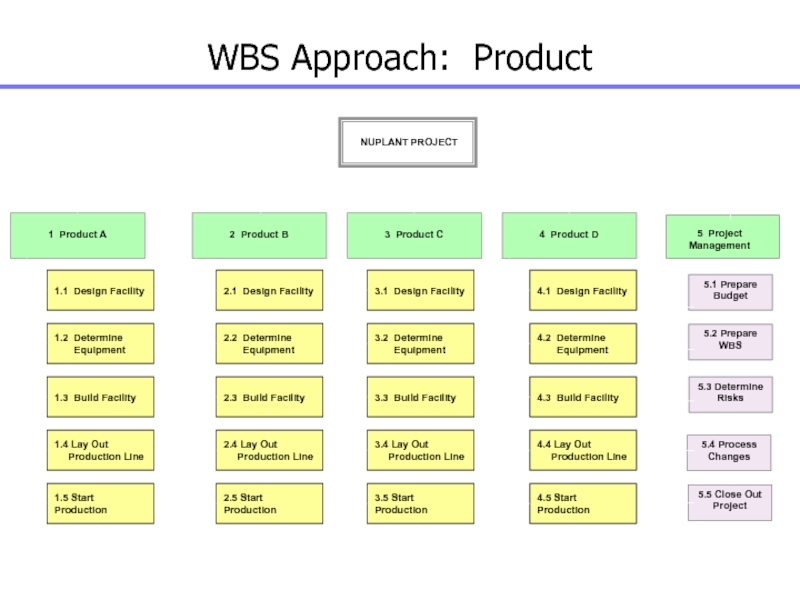
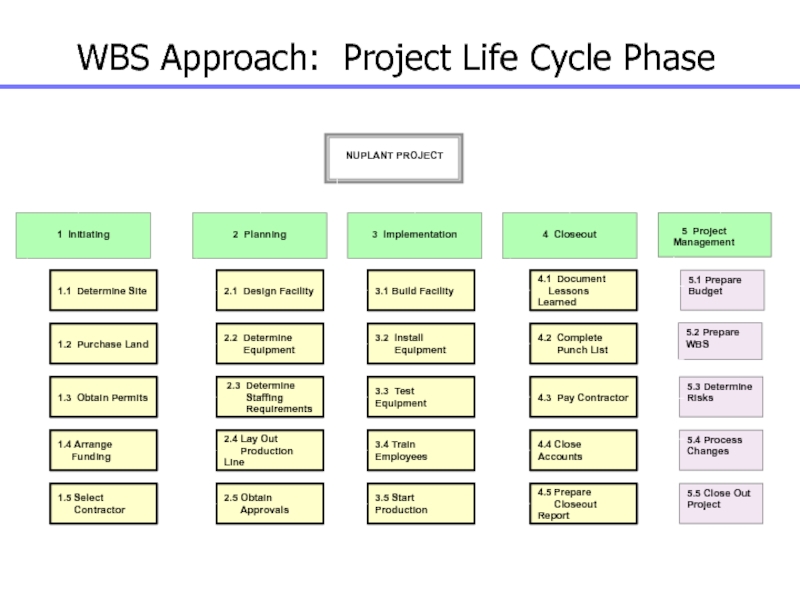
1 Initiating
WBS Approach: Project Life Cycle Phase
Слайд 87Exercise 4: Work Breakdown Structure
Use the sample Project Charter provided
by the facilitator and your own knowledge and experience to
prepare a WBS for the House Renovation Project
Слайд 88Project Schedule
Develop Schedule is the process of analysing activity sequences,
durations, resource requirements, and schedule constraints to create the project
schedule
Purpose
To determine whether it is possible to meet the project objectives
To track and communicate on project progress and status
To determine how possible changes could impact on the project
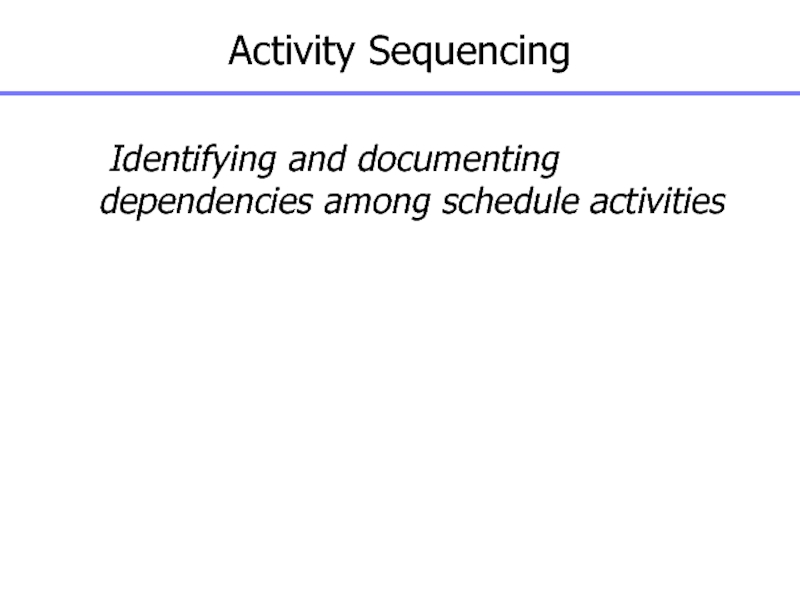
Слайд 89Activity Sequencing
Identifying and documenting dependencies among schedule activities
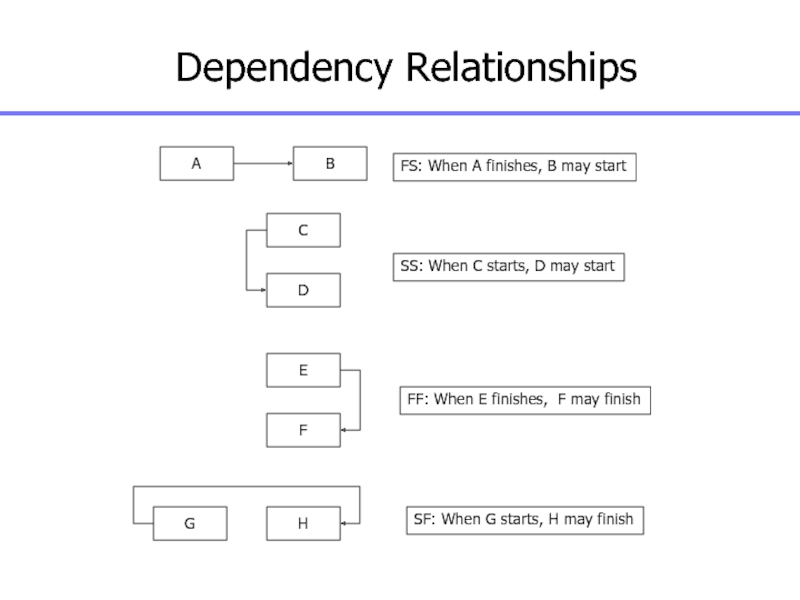
Слайд 91Dependency Relationships
A
B
FS: When A finishes, B may start
C
D
SS: When C
starts, D may start
E
F
FF: When E finishes, F may finish
G
H
SF:
When G starts, H may finish
Слайд 92Lag and Lead
Lag
A fixed duration between a predecessor and successor
Lead
Overlap
between successor and predecessor (Negative lag)
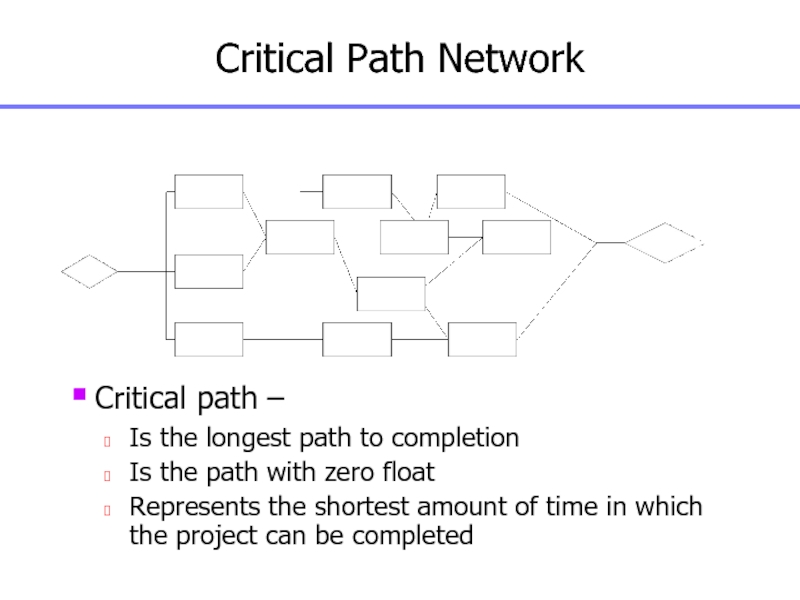
Слайд 93Critical Path Network
Critical path –
Is the longest path to completion
Is
the path with zero float
Represents the shortest amount of time
in which the project can be completed
Start
Finish
Слайд 94Schedule Terminology
Activity – a work element that consumes time and
resources
Relationships – dependencies that exist between activities
Early start/early finish –
earliest that a task can begin or finish based on the forward pass
Late start/late finish – the latest that a task can begin or finish based on the backward pass
Слайд 95Schedule Terminology (Cont’d)
Float – amount of time an activity can
be delayed from its early start and/or early finish without
delaying the project finish date
Critical Path – longest path through network; also the shortest possible duration of the project
Lag/lead time – fixed delay/overlap between activity start/finish
Predecessor – the “from” activity
Successor – the “to” activity
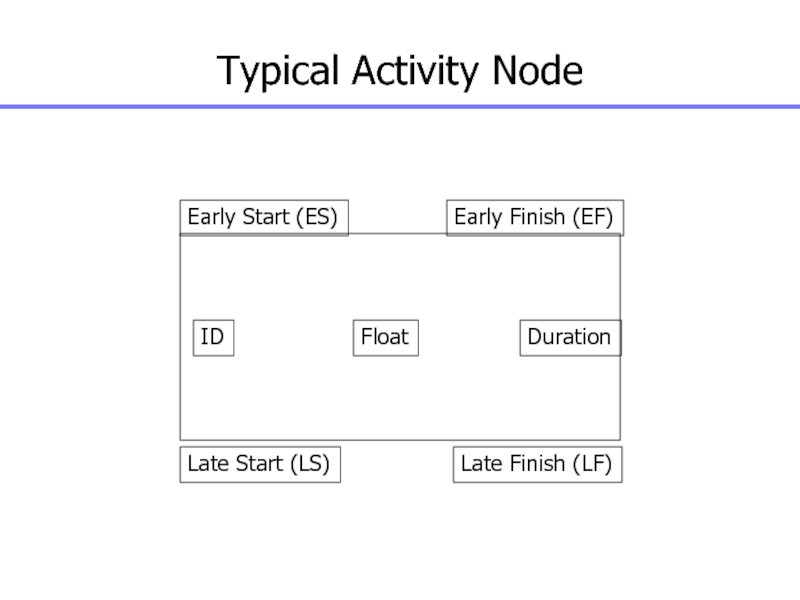
Слайд 96Typical Activity Node
Early Start (ES)
Early Finish (EF)
Late Start (LS)
Late Finish
(LF)
ID
Float
Duration
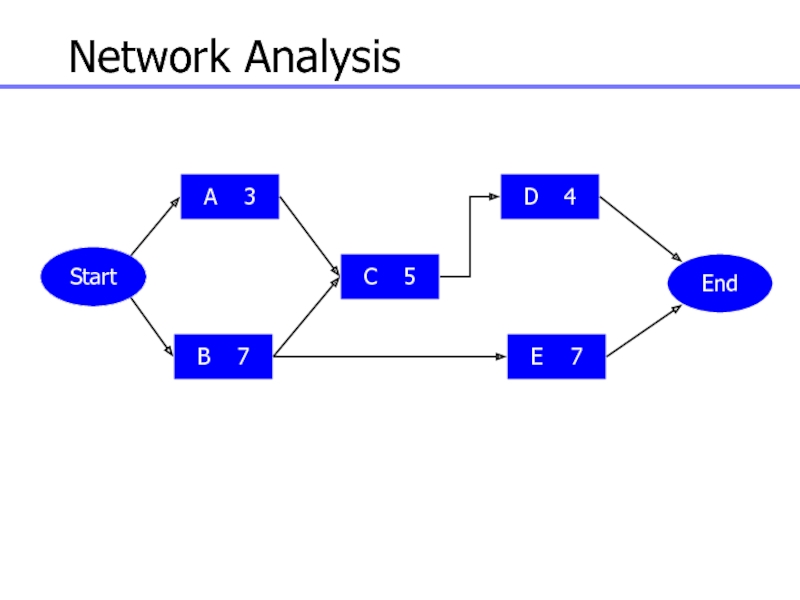
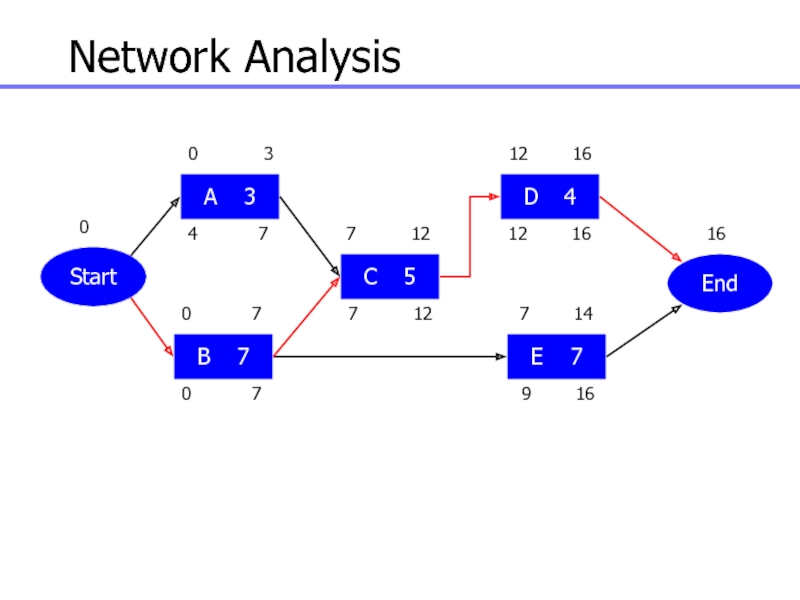
Слайд 97Network Analysis
Start
A 3
B 7
C 5
D 4
E 7
End
Слайд 98Network Analysis
Start
A 3
B 7
C 5
D 4
E 7
End
0 3
4
7
0 7
0
7
7 12
7 12
12 16
12 16
7 14
9 16
16
0
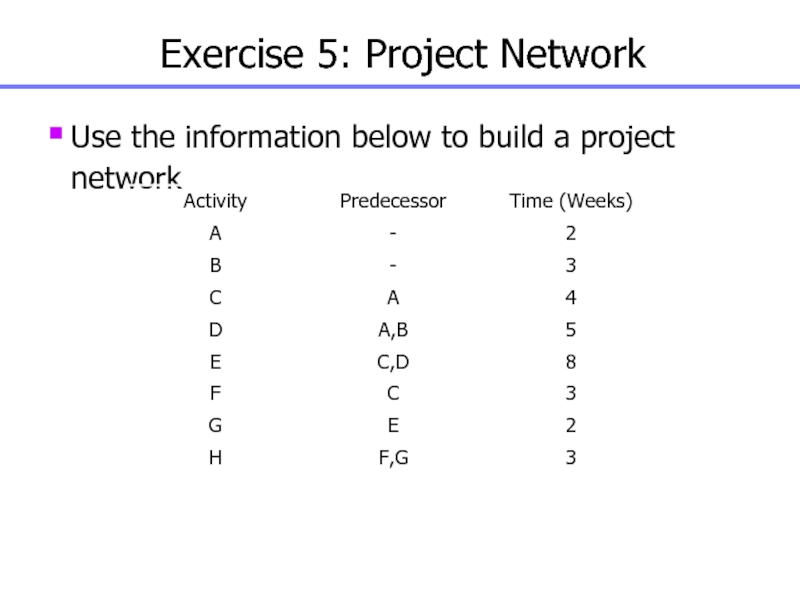
Слайд 99Exercise 5: Project Network
Use the information below to build a
project network
Слайд 100Activity & Milestone Schedule
Project team and customer know what is
expected and when
Provides baseline for performance measurement
Easily displays planned vs.
actual progress
Needed to determine accurate resource estimates
Used by high-level management to track the project
Task 1
Task 2
Task 3
Task 4
Слайд 103Exercise 6: Project Schedule
Use the sample WBS provided by the
facilitator and your own knowledge and experience to identify the
sequence of activities and develop a preliminary schedule for the project
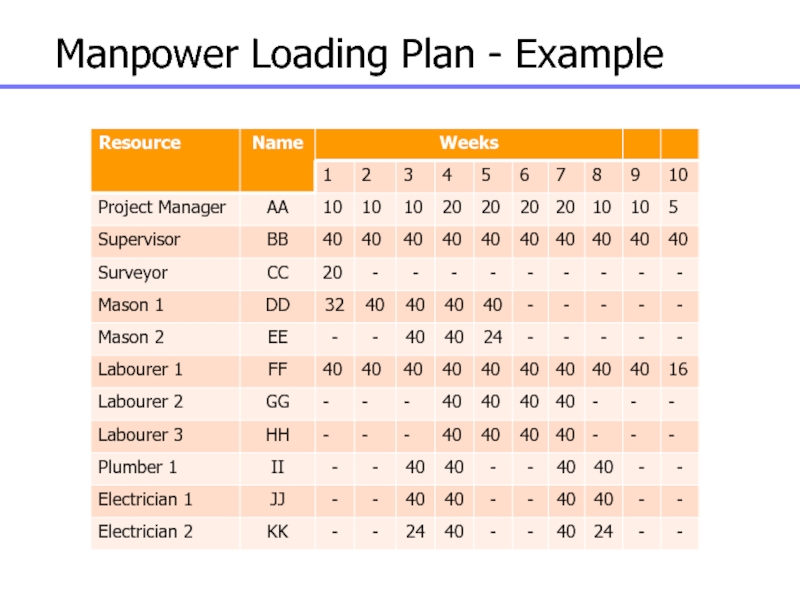
Слайд 104Manpower Loading Plan - Example
Task 1
Task 2
Task 3
Task 4
Слайд 105Cost Estimating
Developing an approximation of the costs of the resources
needed to complete project activities
Слайд 106What to include in your estimates
Materials could include
Hardware
Software
Suppliers
Facilities
Tools
Travel
Special equipment
Shipping
Human
Resources could include
Customer resources
Business partner
Supplier
Technical support
Consultants
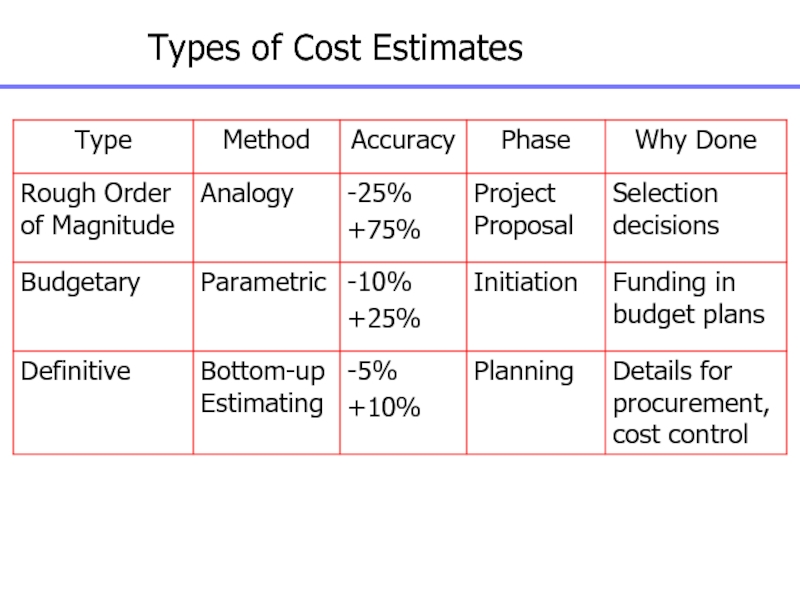
Слайд 107Cost Estimating Methodologies
Analogous
Parametric
Detailed (Bottom-up)
Vendor Quotes
Слайд 109Cost Estimating: Terminology
Contingency
Management reserve
Dayworks
Prime cost sum
Provisional sum
Attendance
Слайд 110Project Risk
An uncertain event or condition that, if it
occurs, has a positive or negative impact on project objectives
(time, cost, quality/scope)
A risk has a cause and if it occurs, an effect
Project risks include threats and opportunities
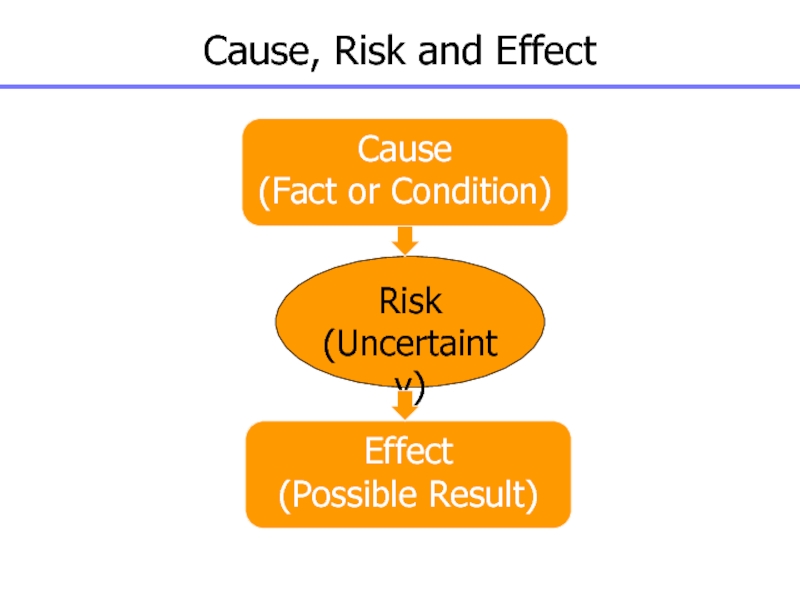
Слайд 111Cause, Risk and Effect
Cause
(Fact or Condition)
Effect
(Possible Result)
Risk
(Uncertainty)
Слайд 112Risk Factors
All project risks are characterised by the following three
risk factors:
Risk Event – precisely what might happen to the
detriment or advantage to the project
Risk Probability – how likely the event is to occur
Risk Impact or Amount at Stake – the severity of the consequence if the Risk Event occurs
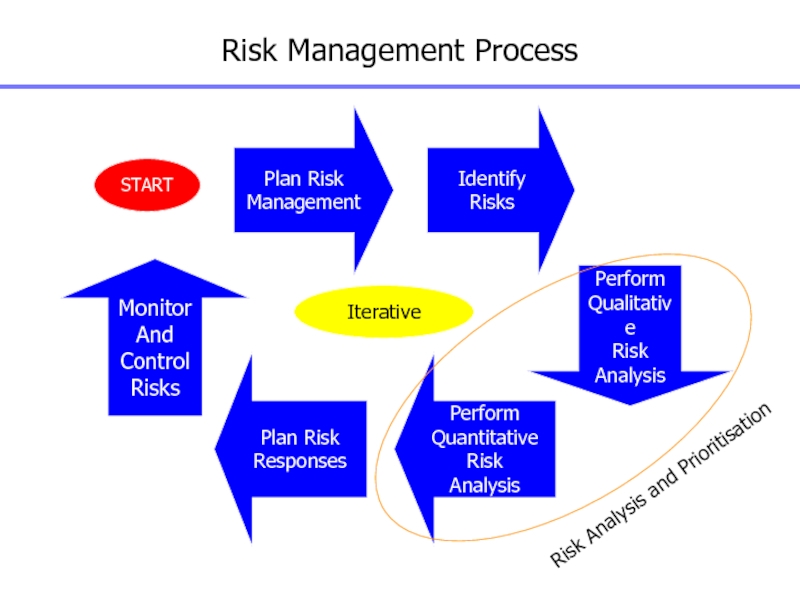
Слайд 113Risk Management Process
Plan Risk
Management
Identify Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk
Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk
Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor
And
Control
Risks
START
Iterative
Risk Analysis and Prioritisation
Слайд 114Plan Risk Management
The process of deciding how to conduct risk
management activities for a project
To ensure that the level, type
and visibility of risk management are commensurate with both the risk and importance of the project to the organisation:
To provide sufficient resources and time for risk management activities
To establish an agreed-upon basis for evaluating risks
Should begin as a project is conceived and should be completed early during project planning
Слайд 115Identify Risks
Determining which risks might affect the project and documenting
their characteristics
An iterative process as new risks may evolve or
become known as the project progresses
Team (and external experts as required) activity
Identify both negative (threats) and positive (opportunity) risks
Слайд 116Identify Risks: Tools & Techniques
Documentation Review
Present Project
Previous Projects, Lessons Learnt
Database
Information Gathering Techniques
Brainstorming
Nominal Group Technique
Delphi Technique
Interviewing
Root Cause Analysis
Checklist Analysis
Assumptions Analysis
Diagramming
Techniques
Cause and Effect Diagrams
System or Process Flow Charts
Influence Diagrams
SWOT Analysis
Expert Judgement
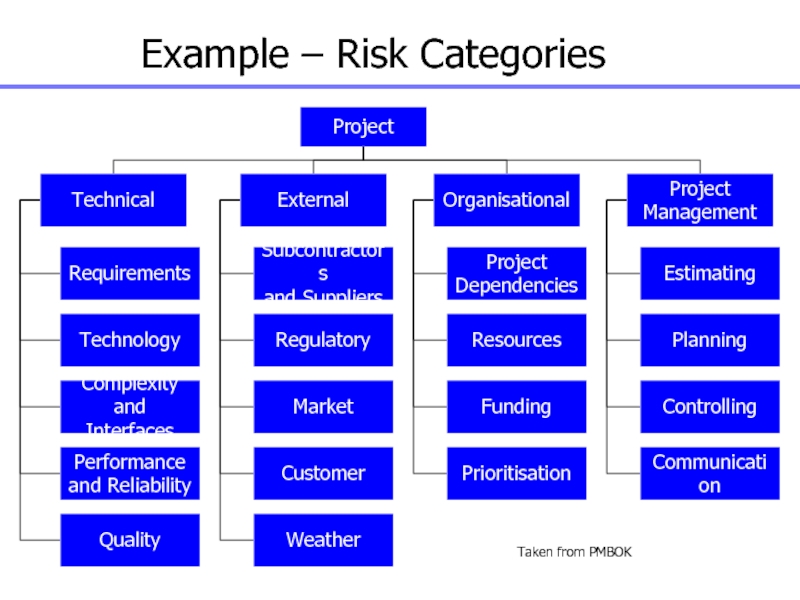
Слайд 117Example – Risk Categories
Project
Technical
External
Requirements
Technology
Complexity and
Interfaces
Performance
and Reliability
Quality
Subcontractors
and Suppliers
Regulatory
Market
Customer
Weather
Organisational
Project
Dependencies
Resources
Funding
Prioritisation
Project
Management
Estimating
Planning
Controlling
Communication
Taken from PMBOK
Слайд 118Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
Process for prioritising the identified risks for
further analysis or action by assessing and combining their probability
of occurrence and impact
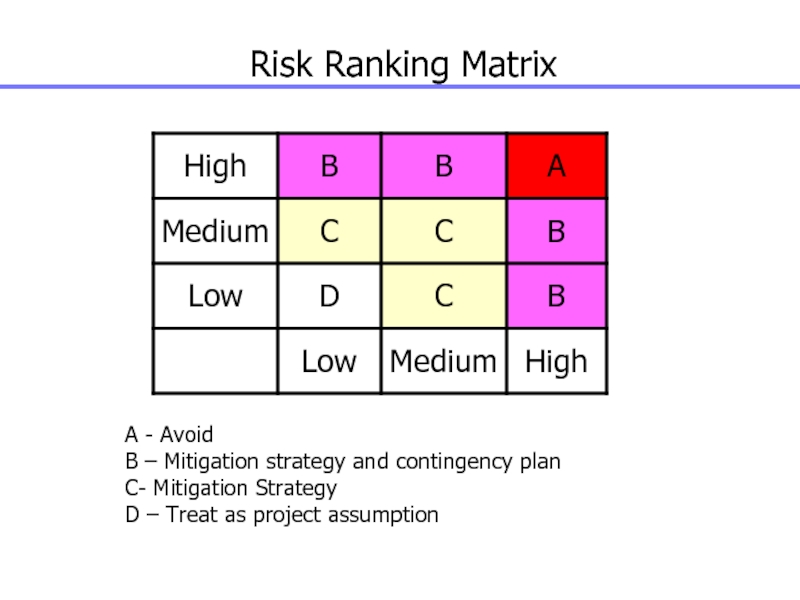
Takes into account other factors such as time frame for response and organisation’s risk tolerance associated with project objectives of scope, cost, schedule and quality
Слайд 119Risk Ranking Matrix
A - Avoid
B – Mitigation strategy and contingency
plan
C- Mitigation Strategy
D – Treat as project assumption
Слайд 120Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
Provides a numerical estimate of the overall
effect of risk on the objectives of the project, based
on current plans and information, when considering risks simultaneously
Results can be used to evaluate the likelihood of success in achieving project objectives and to estimate contingency reserves, usually for time and cost that are appropriate to both the risks and the risk tolerance of project stakeholders
Presents a quantitative approach to making decisions in the presence of uncertainty
Слайд 121Plan Risk Responses
The process of developing options and determining actions
to enhance opportunities and reduce threats to project’s objectives
Includes the
identification and assignment of one person to take responsibility for each agreed-to and funded risk response
Addresses risks by their priority, inserting resources and activities into the budget, schedule and project management plan, as needed
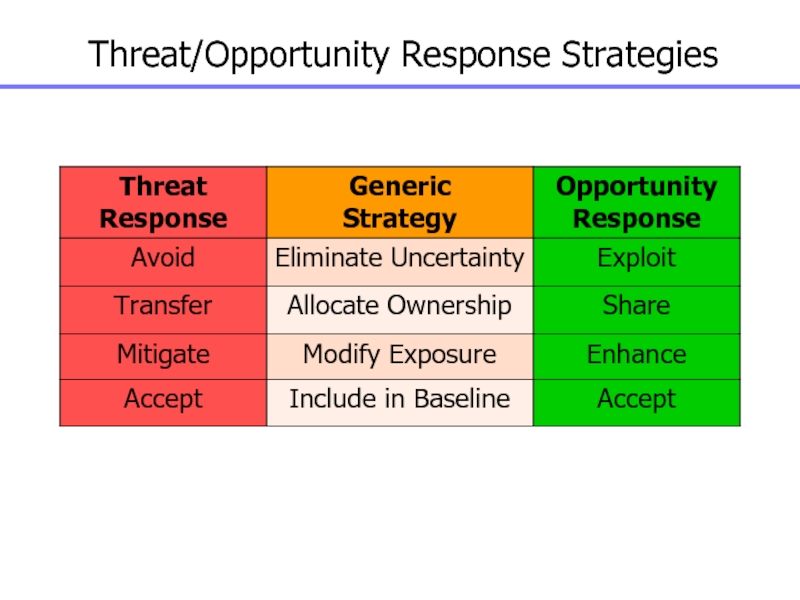
Слайд 122Strategies for Negative Risks
Risk Avoidance: eliminate the risk or the
condition that causes the risk
Risk Transfer: shifting some or
all of the negative impact of a threat, along with ownership of the response, to third party
Risk Mitigation: aims at reducing the probability and/or impact of a risk to within an acceptable threshold
Risk Acceptance
Слайд 123Strategies for Positive Risks (1 of 2)
Exploit: seeks to eliminate
the uncertainty associated with a particular upside risk by ensuring
the opportunity definitely happens. Examples:
Assigning an organisation’s most talented resources to the project to reduce the time for completion or to provide lower cost than originally planned
Share: allocating some or all of the ownership of the opportunity to a third party who is best able to capture the opportunity for the benefit of the project. Example:
Forming risk-sharing partnerships, teams, special-purpose companies, or joint ventures, for the express purpose of taking advantage of the opportunity so that all parties gain from their actions
Слайд 124Strategies for Positive Risks (2 of 2)
Enhance: increase the probability
and/or the positive impacts of an opportunity. Identifying and maximising
key drivers of these positive-impact risks may increase the probability of their occurrence. Examples include adding more resources to an activity to finish early
Accept: being willing/prepared to take advantage of an opportunity if it comes along
Слайд 125Threat/Opportunity Response Strategies
Слайд 126Monitor and Control Risks
Process of implementing risk response plans, tracking
identified risks, monitoring residual risks, identifying new risks, and evaluating
risk process effectiveness throughout the life of the project
Risk reassessment:
Periodic review to ensure that information remains current
Occurrence of major or unexpected risk
Need to analyse a complex change request
Phase end review
Project re-planning or major plan elaboration
An ongoing process for the life of the project
Слайд 128Exercise 7: Project Risk Management
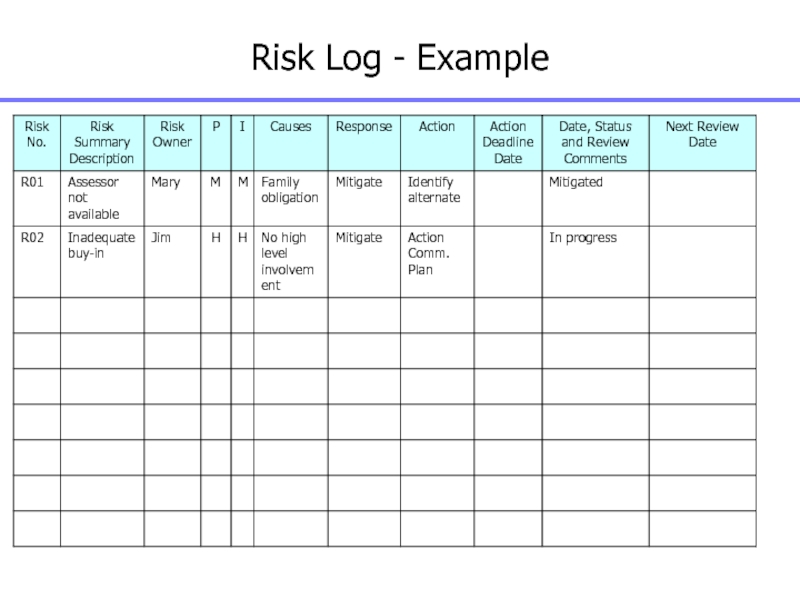
Identify your top ten (10) risk
events for the project and create a risk log detailing
the risk management strategy and relevant actions to manage the risks
Слайд 129Compliance with HSE Policy and Plan
Have an HSE kick-off meeting
Get
commitment from all team members
Track statistics & use trends for
predictive purposes
Implement measures to reduce risk of HSE accidents/ incidents during project
HSE Management Plan
Слайд 130Project Quality Management
Plan Quality: The process of identifying quality
requirements and/or standards for the project and product and documenting
how the project will demonstrate compliance
Perform Quality Assurance: The process of auditing the quality requirements and the results from quality control measurements to ensure appropriate quality standards and operational definitions are used
Perform Quality Control: The process of monitoring and recording results of executing the quality activities to assess performance and recommend necessary changes
Compliance with Contract ITP (Inspection and Test Plan)!!
Слайд 131Module 7
Execute and Control Project Plan
Слайд 132Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
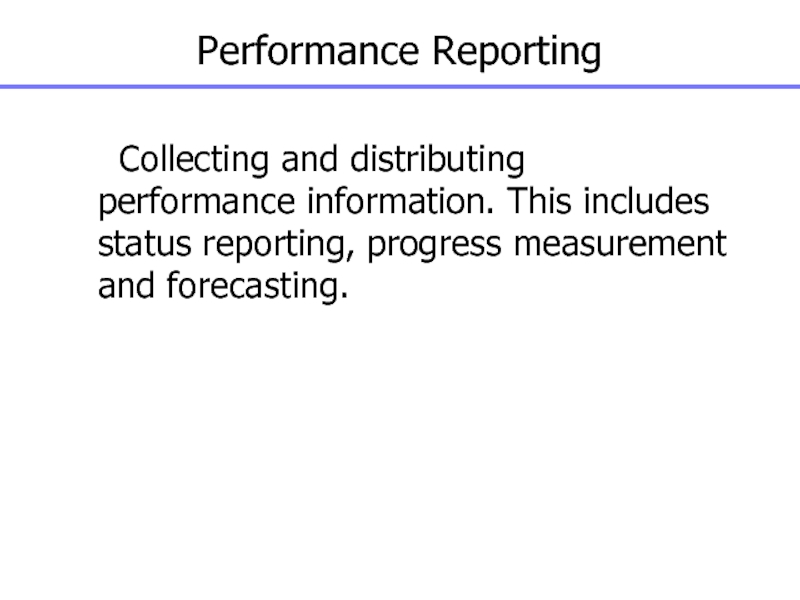
Слайд 134Performance Reporting
Collecting and distributing performance information. This includes status
reporting, progress measurement and forecasting.
Слайд 135Performance Reporting
Status reporting – describing where the project now stands
Progress
reporting – describing what the project team has accomplished (e.g.
percent complete to date, percent complete to schedule, what is completed vs what is in process)
Forecasting – predicting future project status and progress
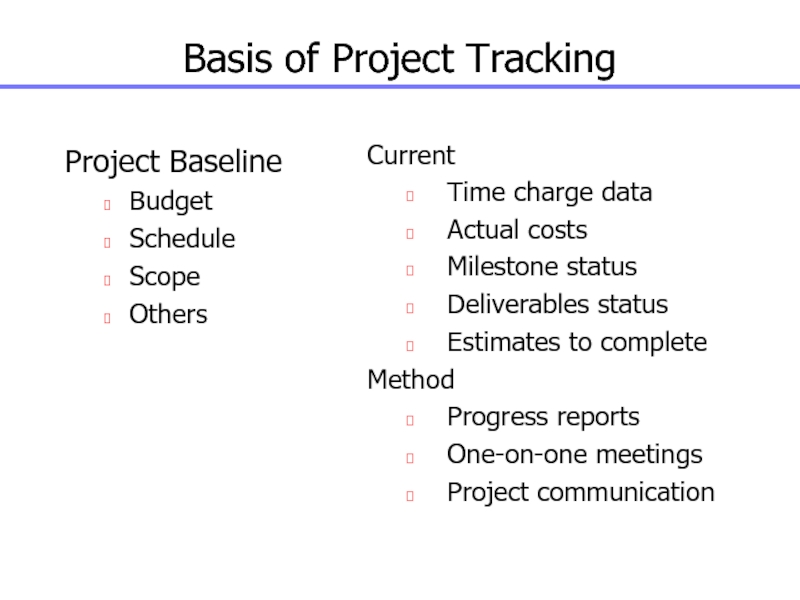
Слайд 136Basis of Project Tracking
Project Baseline
Budget
Schedule
Scope
Others
Current
Time charge data
Actual costs
Milestone status
Deliverables status
Estimates
to complete
Method
Progress reports
One-on-one meetings
Project communication
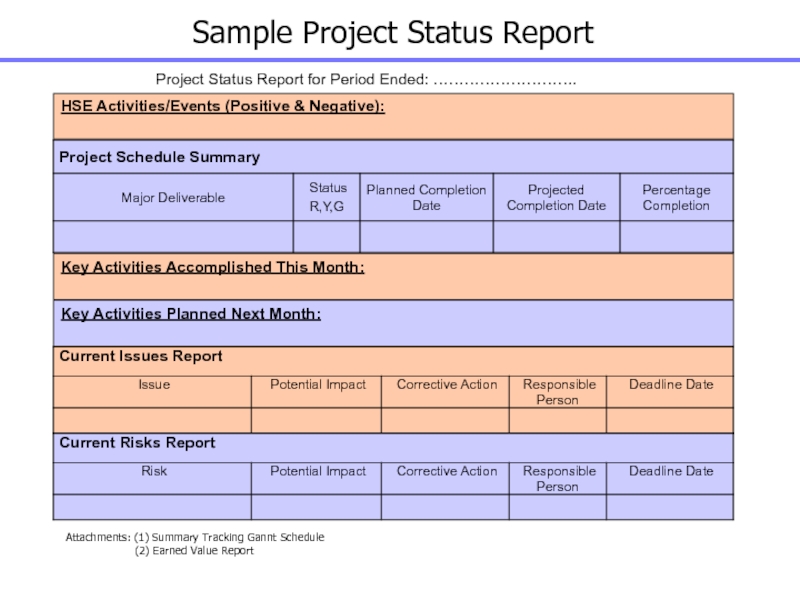
Слайд 138Sample Project Status Report
Project Status Report for Period Ended: ……………………….
HSE
Activities/Events (Positive & Negative):
Key Activities Accomplished This Month:
Key Activities Planned
Next Month:
Attachments: (1) Summary Tracking Gannt Schedule
(2) Earned Value Report
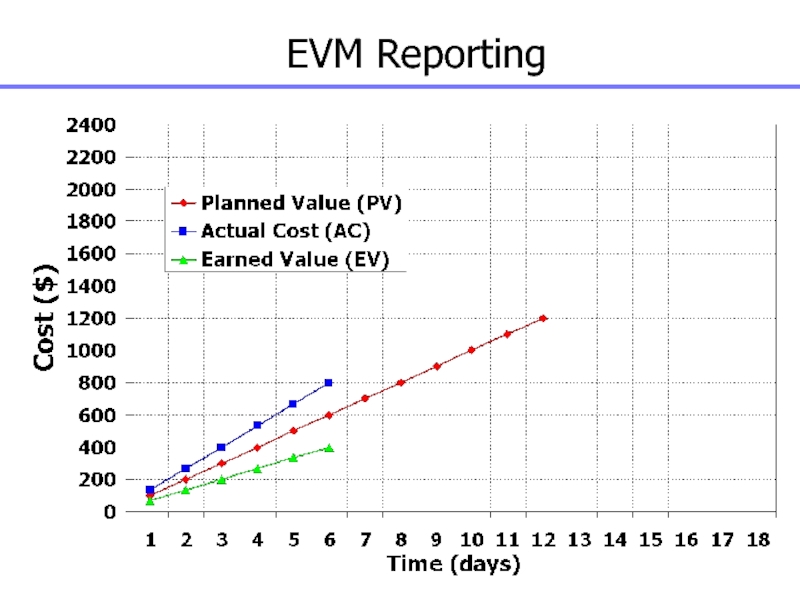
Слайд 139Earned Value Management
A method of integrating scope, schedule and
resources (cost), and for measuring project performance. It compares the
amount work that was planned with what was actually earned with what was actually spent to determine if cost and schedule are as planned
Слайд 140Value of Earned Value
Schedule Status Reporting
Cost Status Reporting
Forecasting
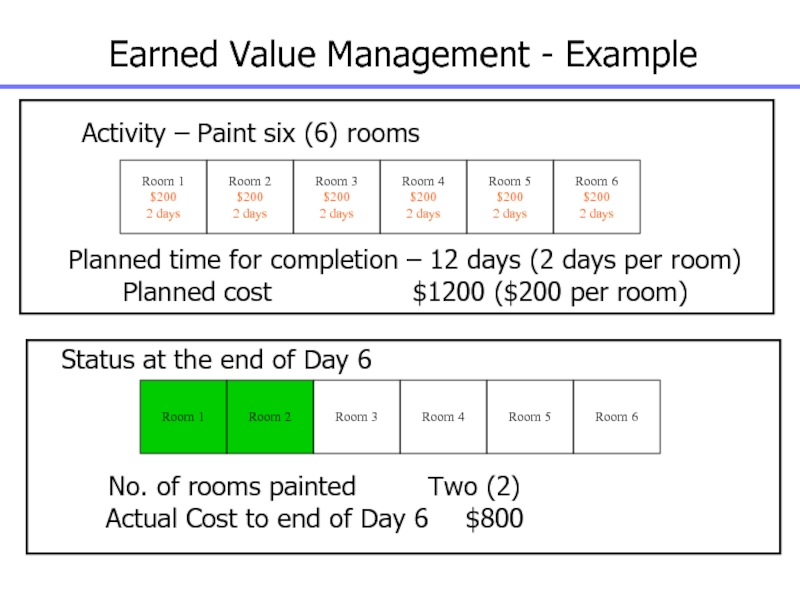
Слайд 141Earned Value Management - Example
Activity – Paint six (6) rooms
Planned
time for completion – 12 days (2 days per room)
Planned
cost $1200 ($200 per room)
Room 1
Room 2
Room 3
Room 4
Room 5
Room 6
No. of rooms painted Two (2)
Actual Cost to end of Day 6 $800
Status at the end of Day 6
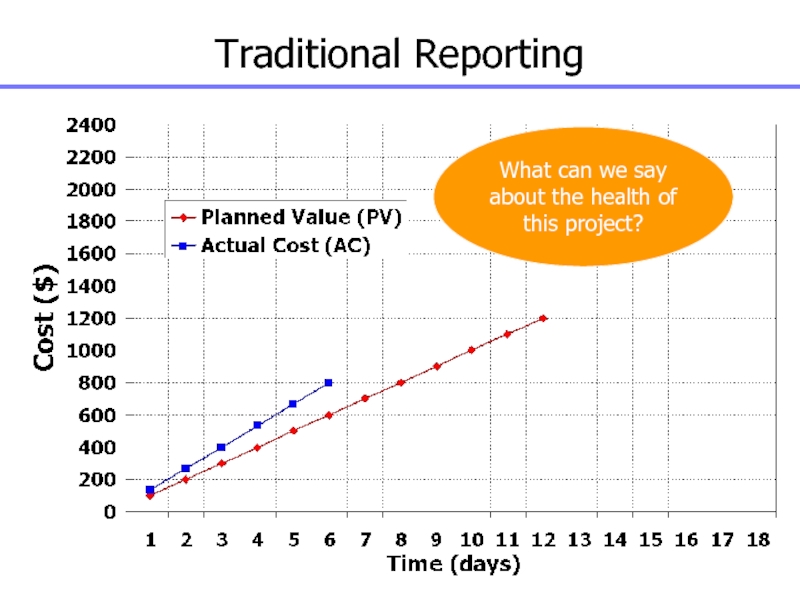
Слайд 142Traditional Reporting
What can we say about the health of this
project?
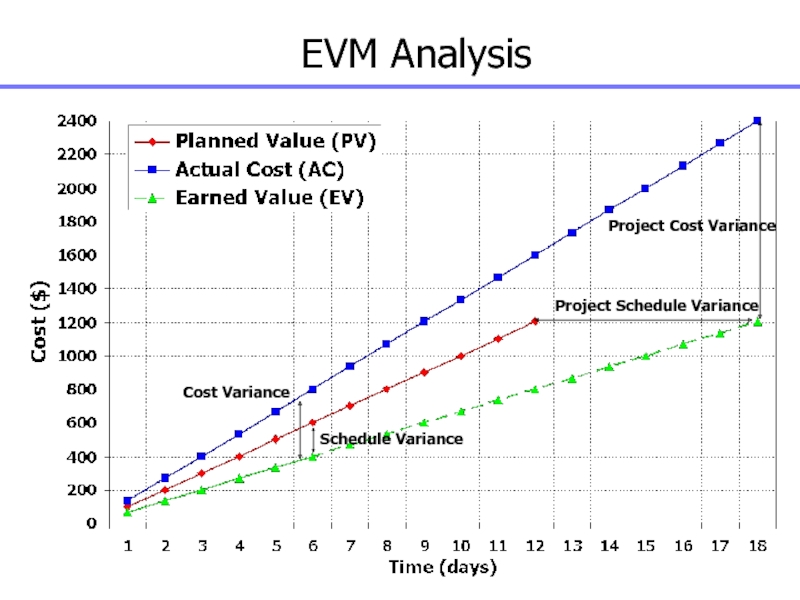
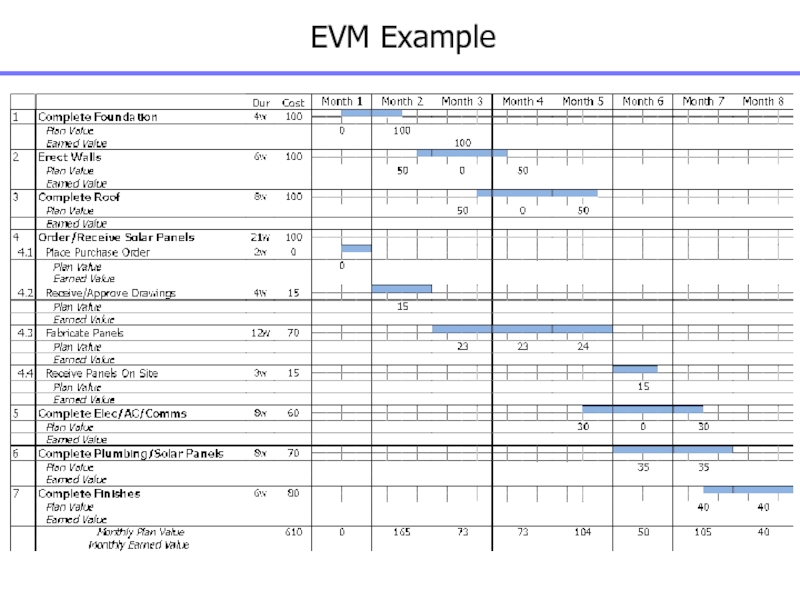
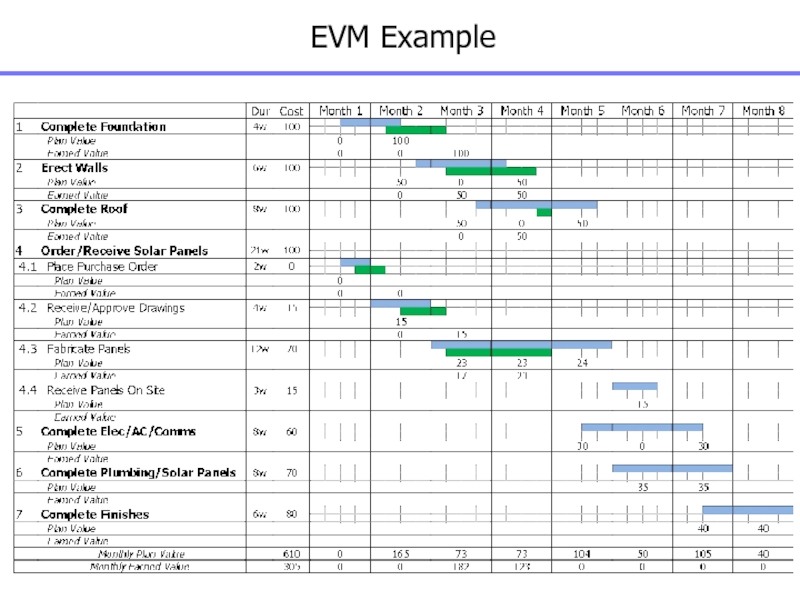
Слайд 144EVM Analysis
Schedule Variance
Cost Variance
Project Schedule Variance
Project Cost Variance
Слайд 145EV Methods – Fixed Formula Example
0/100 Method
Nothing is earned when
activity starts but 100% of budget is earned when completed
Usually
used for work packages less than 1 month in length
50/50 Method
50% is earned when activity starts and 100% of budget is earned when completed
Usually used for work packages less than 2 months in length
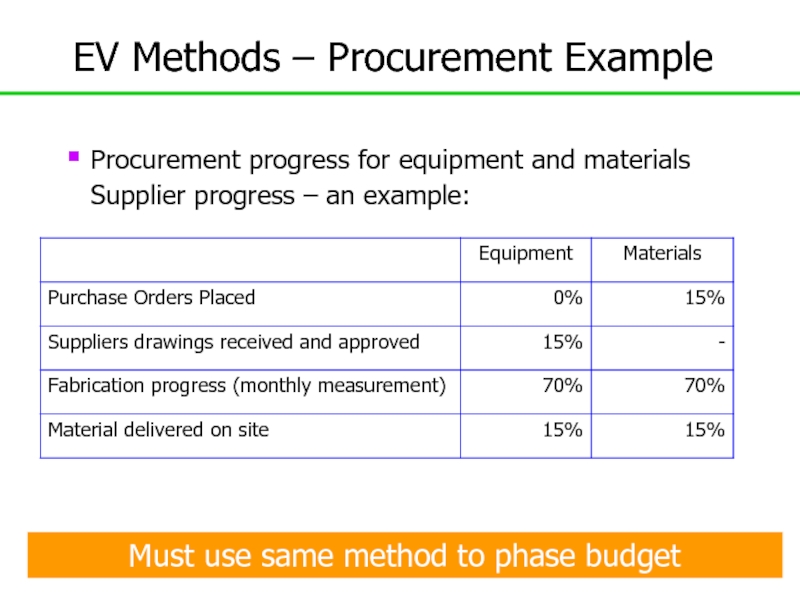
Слайд 146EV Methods – Procurement Example
Procurement progress for equipment and materials
Supplier progress – an example:
Must use same method to phase
budget
Слайд 149Change Control Management
Define how changes to the project scope will
be executed
Scope Change
Schedule changes
Technical Specification Changes
All changes require collaboration and
buy in via the project sponsor’s signature
prior to implementation of the changes
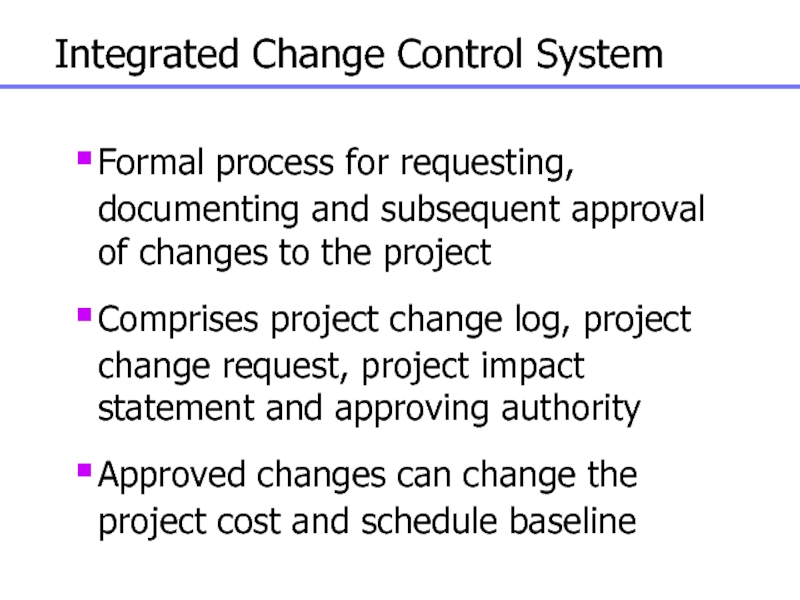
Слайд 150Integrated Change Control System
Formal process for requesting, documenting and
subsequent approval of changes to the project
Comprises project change log,
project change request, project impact statement and approving authority
Approved changes can change the project cost and schedule baseline
Слайд 151Integrated Change Control System
Coordinates changes across the entire project
Scope
change control
Schedule change control
Cost change control
Quality control
Risk change control
Contract administration
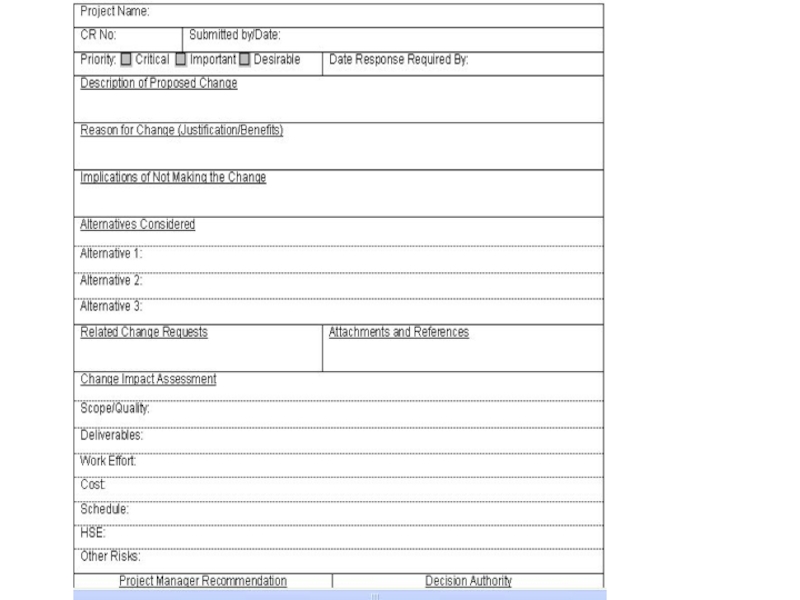
Слайд 152Change Control Form
Includes:
Type of change (scope, schedule, cost, performance)
Description
and justification
Impact if change is not carried out
Additional risk management
results
Effect on schedule, cost, performance (quality), scope
List of required approvals
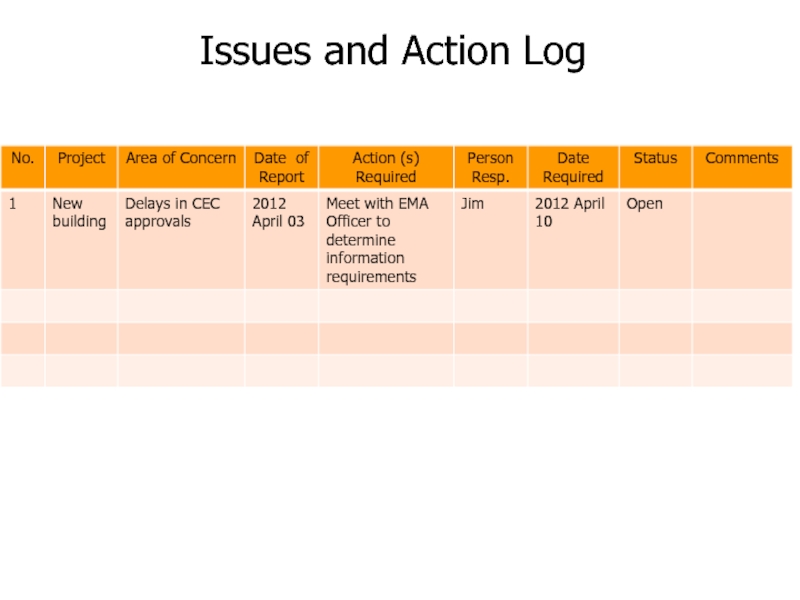
Слайд 154Issue Management
Issues are restraints to accomplishing the deliverables of the
project.
Typically identified throughout the project and logged and tracked
through resolution.
Rope not thick enough?
Issue… already impacting the cost, time or quality
Слайд 156Project Charter
Responsibility Matrix
Team Charter
Stakeholder Analysis
Communication Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Schedule Baseline
Cost
Baseline
Risk Response Plan
HSE Plan
QA/QC Plan
Interface Management Plan
Key Resources Plan/Schedule
Earned Value
Reporting
Project Status Reporting
Change Control Process
Variance Analysis
Issue and Risks Action Logs
Close out checklists
Lessons Learnt Report
Project deliverables/ results
Procurement Strategy/Plan
PROJECT PLAN
Deliverable
Слайд 157Close-Out
The last major phase of a project's life cycle is
the close-out. The key activity in project closeout is gathering
project records and disseminating information to formalize acceptance of the product, service or project as well as to perform project closure.
Слайд 158Close Project
Comprises:
Product verification
Integrated activities to collect project records
Analyse project
success or failure
Gather lessons learned
Archiving and disseminating such information for
future use
Слайд 159Summary - Closing the Project
Get client acceptance of deliverables
Ensure
that deliverables are installed
Ensure that documentation is in place
Get client
sign-off on final report
Conduct post implementation audit
Celebrate success
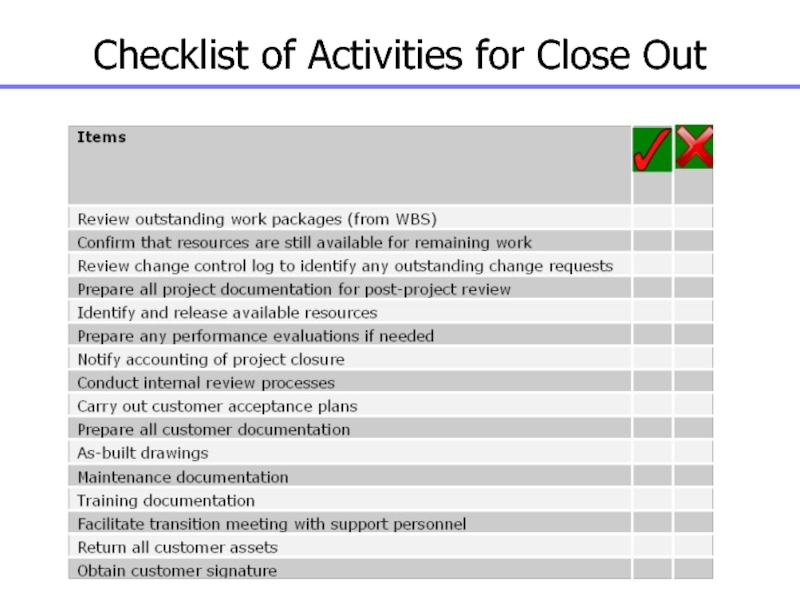
Слайд 160Checklist of Activities for Close Out
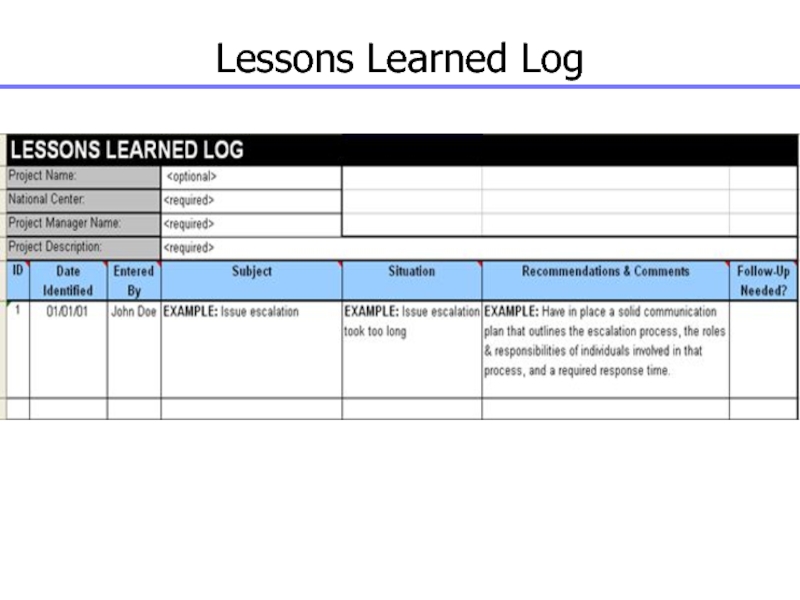
Слайд 161Lessons Learned
Lessons learned are used to document the successes and
failures of the project. The Lessons Learned Report records the
problems and corrective actions for problems that may have applicability to all projects. It is a source of information to solve project problems.
It can be searched to see if other projects have experienced similar problems and what the corrective action resolved the problem.