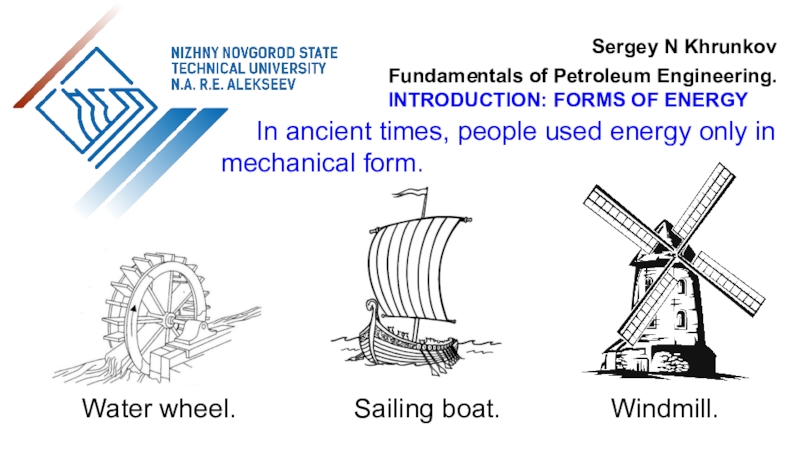
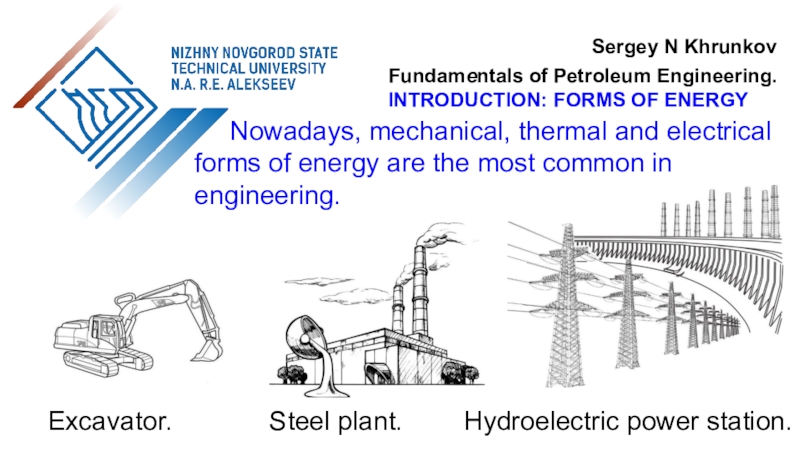
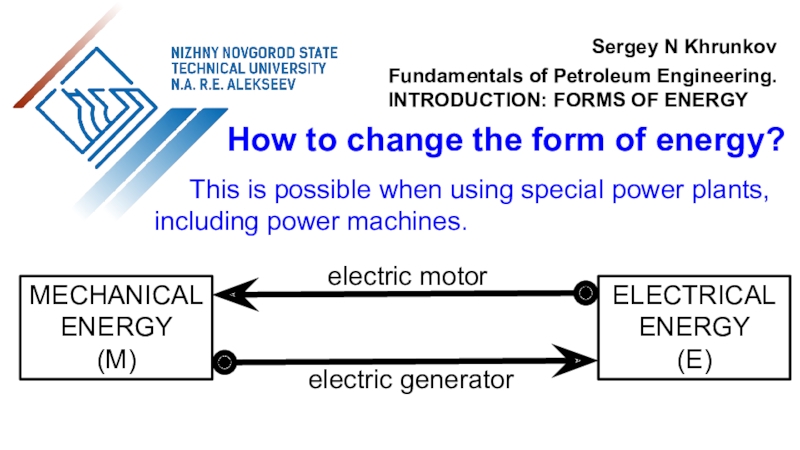
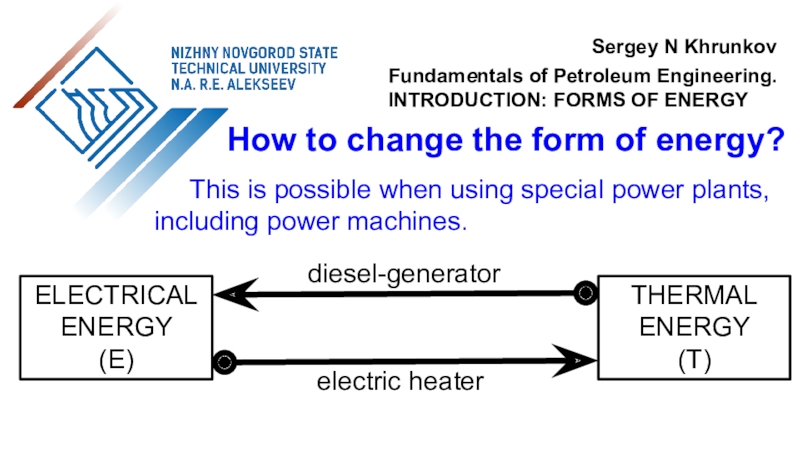
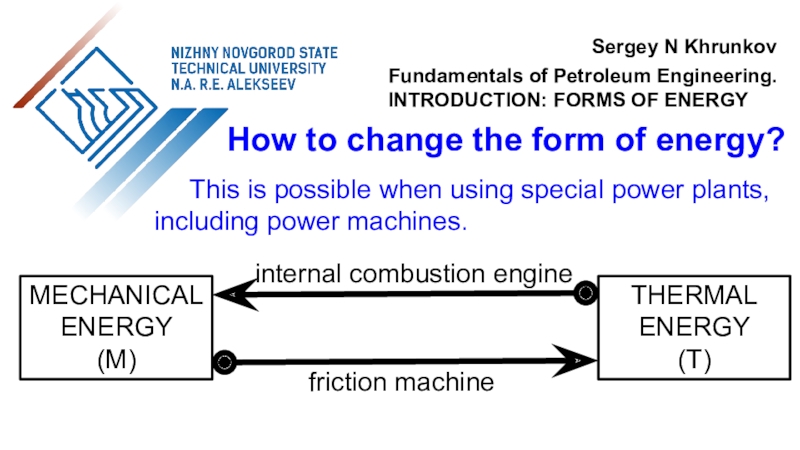
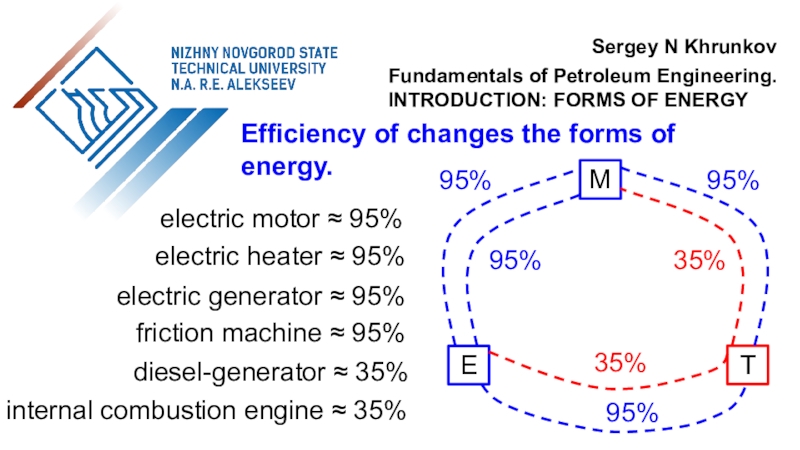
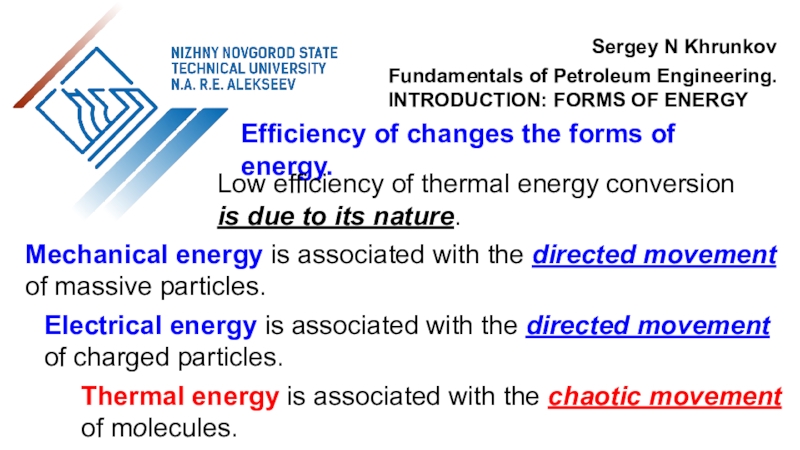
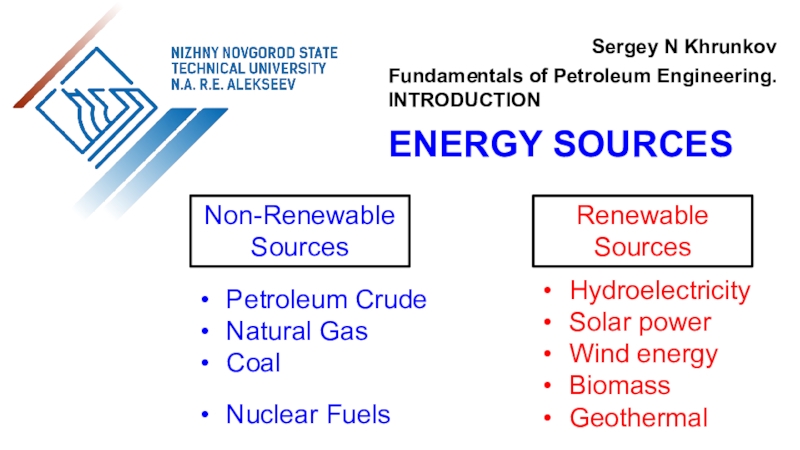
the use of air flow through wind turbines to provide
the mechanical power. Air flow can be used to run wind turbines. Modern utility-scale wind turbines range from around 100 W to 9 MW of rated power.
Renewable Sources: wind energy
Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering. INTRODUCTION: ENERGY SOURCES
The power available from the wind is a function of the cube of the wind speed, so as wind speed increases, power output increases up to the maximum output for the particular turbine. The use of wind power plants has many technical difficulties. The wind blows at different speeds and in different directions. The main thing is that the wind does not always blow.
Areas where winds are stronger and more constant, such as offshore and high-altitude sites, are preferred locations for wind farms. Typically, full load hours of wind turbines vary between 16 and 57 percent annually, but might be higher in particularly favorable offshore sites.