Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Strategic Management
Содержание
- 1. Strategic Management
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall8–Exhibit 8–1 The Strategic Management Process
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall8–Exhibit 8–2 Components of a Mission Statement
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall8–Exhibit 8–3 Types of Organizational Strategies
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall8–Exhibit 8–4 The BCG Matrix
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 32. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 33. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 34. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 35. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 36. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 37. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.8.1 Strategic Management
Define strategic management, strategy, and business model.
Give three reasons why strategic management is important.
8.2 The Strategic Management Process
Describe the six steps in the strategic management process.
Define SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats).
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Learning
Outcomes
8.3 Corporate Strategies
Describe the three major types of corporate strategies.
Explain
how the BCG matrix and how it’s used to manage corporate strategies.8.4 Competitive Strategies
Describe the role of competitive advantage.
Explain Porter’s five forces model.
Describe Porter’s three competitive strategies.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Learning
Outcomes
8.5 Current Strategic Management Issues
Explain why strategic flexibility is important.
Describe
e-business strategies.Discuss what strategies organizations might use to become more customer oriented and to be more innovative.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategic
Management
What managers do to develop an organization’s strategies
Strategies
The decisions and
actions that determine the long-run performance of an organization. Business Model
Is a strategic design for how a company intends to profit from its strategies, work processes, and work activities.
Focuses on two things:
Whether customers will value what the company is providing.
Whether the company can make any money doing that.
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Why
Is Strategic Management Important?
It results in higher organizational performance.
It requires
that managers examine and adapt to business environment changes.It coordinates diverse organizational units, helping them focus on organizational goals.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
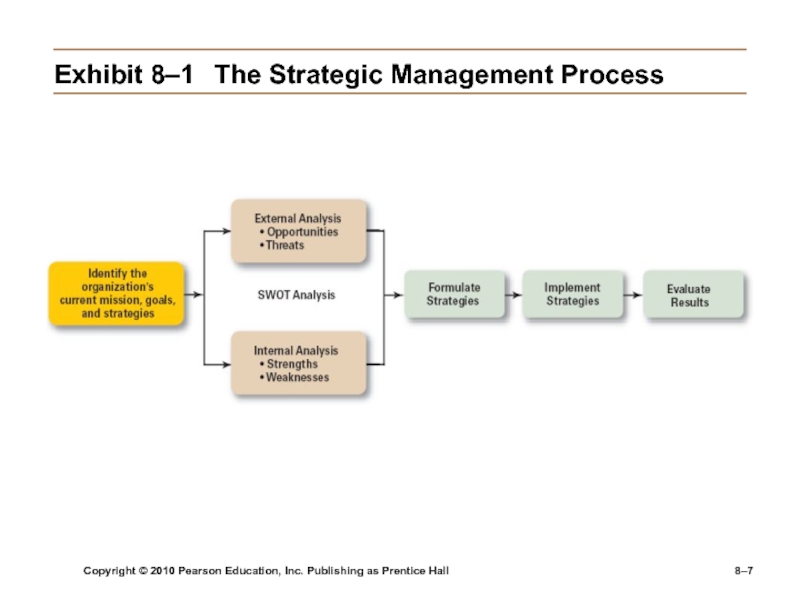
Exhibit
8–1 The Strategic Management Process
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategic
Management Process
Step 1: Identifying the organization’s current mission, goals, and
strategiesMission: a statement of the purpose of an organization
The scope of its products and services
Goals: the foundation for further planning
Measurable performance targets
Step 2: Doing an external analysis
The environmental scanning of specific and general environments
Focuses on identifying opportunities and threats
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Exhibit
8–2 Components of a Mission Statement
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategic
Management Process
Step 3: Doing an internal analysis
Assessing organizational resources,
capabilities, and activities:Strengths create value for the customer and strengthen the competitive position of the firm.
Weaknesses can place the firm at a competitive disadvantage.
Analyzing financial and physical assets is fairly easy, but assessing intangible assets (employee’s skills, culture, corporate reputation, and so forth) isn’t as easy.
Steps 2 and 3 combined are called a SWOT analysis. (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats)
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategic
Management Process
Step 4: Formulating strategies
Develop and evaluate strategic alternatives
Select
appropriate strategies for all levels in the organization that provide relative advantage over competitorsMatch organizational strengths to environmental opportunities
Correct weaknesses and guard against threats
Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategic
Management Process
Step 5: Implementing strategies
Implementation: effectively fitting organizational structure
and activities to the environment.The environment dictates the chosen strategy; effective strategy implementation requires an organizational structure matched to its requirements.
Step 6: Evaluating results
How effective have strategies been?
What adjustments, if any, are necessary?
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
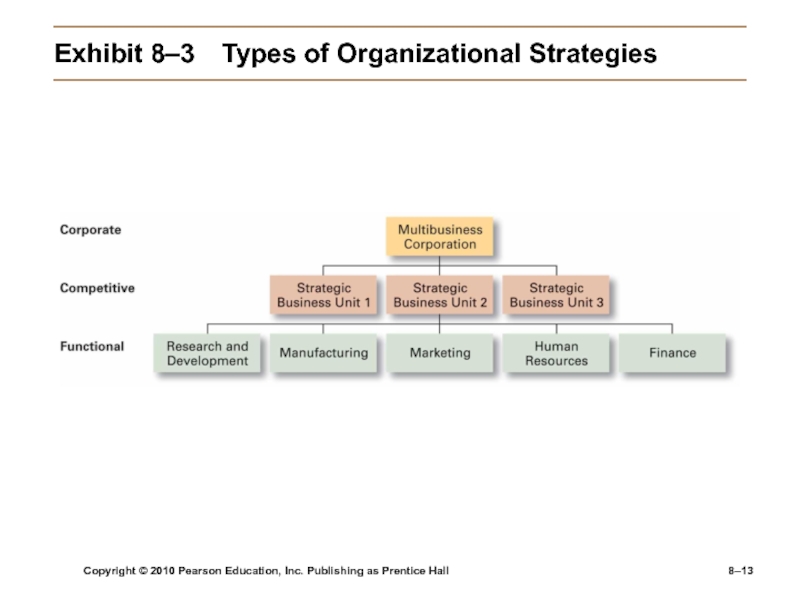
Exhibit
8–3 Types of Organizational Strategies
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Types
of Organizational Strategies
Corporate Strategies
Top management’s overall plan for the entire
organization and its strategic business unitsTypes of Corporate Strategies
Growth: expansion into new products and markets
Stability: maintenance of the status quo
Renewal: examination of organizational weaknesses that are leading to performance declines
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Corporate
Strategies
Growth Strategy
Seeking to increase the organization’s business by expansion into
new products and markets.Types of Growth Strategies
Concentration
Vertical integration
Horizontal integration
Diversification
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Corporate
Strategies
Concentration
Focusing on a primary line of business and increasing the
number of products offered or markets served.Vertical Integration
Backward vertical integration: attempting to gain control of inputs (become a self-supplier).
Forward vertical integration: attempting to gain control of output through control of the distribution channel or provide customer service activities (eliminating intermediaries).
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Corporate
Strategies
Horizontal Integration
Combining operations with another competitor in the same
industry to increase competitive strengths and lower competition among industry rivals.Related Diversification
Expanding by combining with firms in different, but related industries that are “strategic fits.”
Unrelated Diversification
Growing by combining with firms in unrelated industries where higher financial returns are possible.
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Corporate
Strategies
Stability Strategy
A strategy that seeks to maintain the status
quo to deal with the uncertainty of a dynamic environment, when the industry is experiencing slow- or no-growth conditions, or if the owners of the firm elect not to grow for personal reasons.Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Corporate
Strategies
Renewal Strategies
Developing strategies to counter organization weaknesses that are
leading to performance declines.Retrenchment: focusing of eliminating non-critical weaknesses and restoring strengths to overcome current performance problems.
Turnaround: addressing critical long-term performance problems through the use of strong cost elimination measures and large-scale organizational restructuring solutions.
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Corporate
Portfolio Analysis
Managers manage portfolio (or collection) of businesses using a
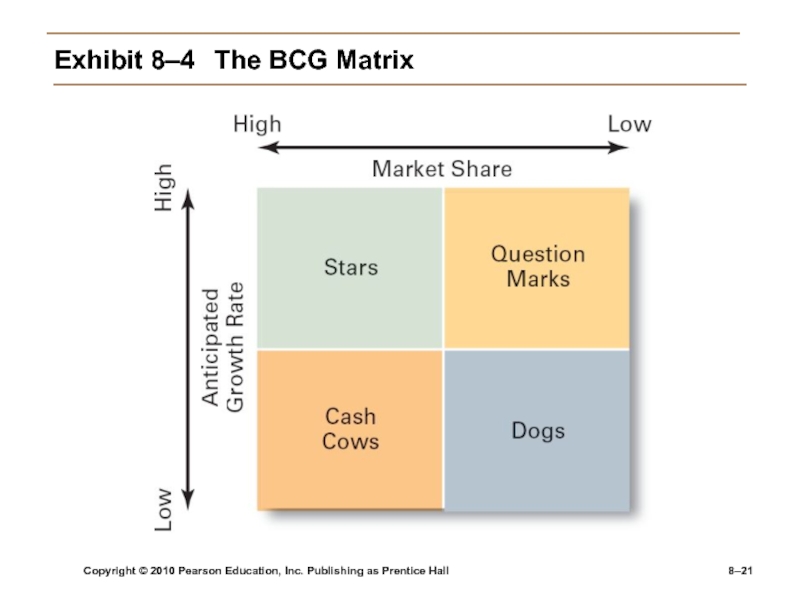
corporate portfolio matrix such as the BCG Matrix.BCG Matrix
Developed by the Boston Consulting Group
Considers market share and industry growth rate
Classifies firms as:
Cash cows: low growth rate, high market share
Stars: high growth rate, high market share
Question marks: high growth rate, low market share
Dogs: low growth rate, low market share
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Exhibit
8–4 The BCG Matrix
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Competitive
Strategies
Competitive Strategy
A strategy focused on how an organization will compete
in each of its SBUs (strategic business units).Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
The
Role of Competitive Advantage
Competitive Advantage
An organization’s distinctive competitive edge.
Quality as
a Competitive AdvantageDifferentiates the firm from its competitors.
Can create a sustainable competitive advantage.
Represents the company’s focus on quality management to achieve continuous improvement and meet customers’ demand for quality.
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
The
Role of Competitive Advantage (cont’d)
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Continuing over time to
effectively exploit resources and develop core competencies that enable an organization to keep its edge over its industry competitors.Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Exhibit
8–5 Five Forces Model
Source: Based on M.E. Porter, Competitive Strategy: Techniques
for Analyzing Industries and Competitors (New York: The Free Press, 1980).Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Five
Competitive Forces
Threat of New Entrants
The ease or difficulty with which
new competitors can enter an industry.Threat of Substitutes
The extent to which switching costs and brand loyalty affect the likelihood of customers adopting substitutes products and services.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The degree to which buyers have the market strength to hold sway over and influence competitors in an industry.
Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Five
Competitive Forces
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The relative number of buyers to
suppliers and threats from substitutes and new entrants affect the buyer-supplier relationship.Current Rivalry
Intensity among rivals increases when industry growth rates slow, demand falls, and product prices descend.
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Types
of Competitive Strategies
Cost Leadership Strategy
Seeking to attain the lowest total
overall costs relative to other industry competitors.Differentiation Strategy
Attempting to create a unique and distinctive product or service for which customers will pay a premium.
Focus Strategy
Using a cost or differentiation advantage to exploit a particular market segment rather a larger market.
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategic
Management Today
Strategic Flexibility
New Directions in Organizational Strategies
e-business
customer service
innovation
Слайд 30Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Exhibit
8–6 Creating Strategic Flexibility
Know what’s happening with strategies currently being used
by monitoring and measuring results.Encourage employees to be open about disclosing and sharing negative information.
Get new ideas and perspectives from outside the organization.
Have multiple alternatives when making strategic decisions.
Learn from mistakes.
Source: Based on K. Shimizu and M. A. Hitt, “Strategic Flexibility: Organizational Preparedness to Reverse Ineffective Strategic Decisions,” Academy of Management Executive, November 2004, pp. 44–59.
Слайд 31Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Strategies
for Applying
e-Business Techniques
Cost Leadership
On-line activities: bidding, order processing, inventory
control, recruitment and hiringDifferentiation
Internet-based knowledge systems, online ordering and customer support
Focus
Chat rooms and discussion boards, targeted Web sites
Слайд 32Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Customer
Service Strategies
Giving the customers what they want.
Communicating effectively with them.
Providing
employees with customer service training.Слайд 33Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Innovation
Strategies
Possible Events
Radical breakthroughs in products.
Application of existing technology to new
uses.Strategic Decisions about Innovation
Basic research
Product development
Process innovation
First Mover
An organization that brings a product innovation to market or use a new process innovations
Слайд 34Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
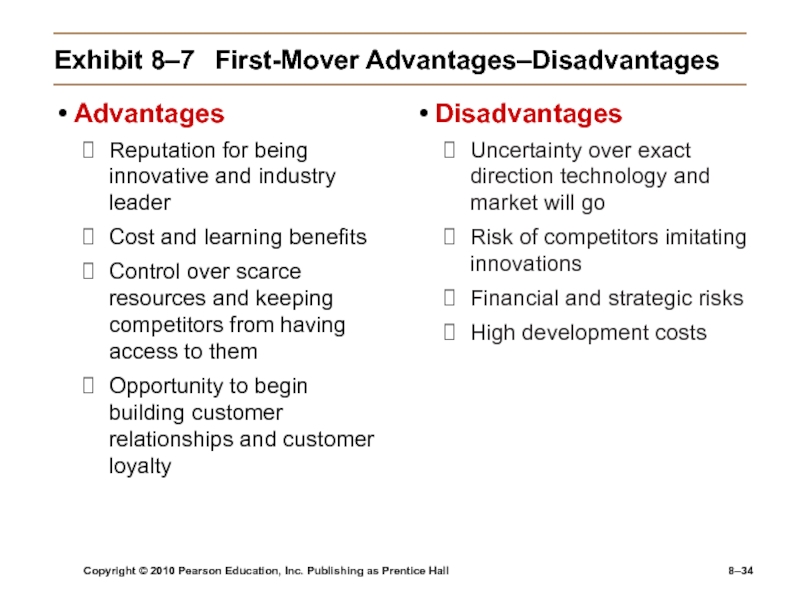
Exhibit
8–7 First-Mover Advantages–Disadvantages
Advantages
Reputation for being innovative and industry leader
Cost and learning
benefitsControl over scarce resources and keeping competitors from having access to them
Opportunity to begin building customer relationships and customer loyalty
Disadvantages
Uncertainty over exact direction technology and market will go
Risk of competitors imitating innovations
Financial and strategic risks
High development costs
Слайд 35Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
8–
Terms
to Know
strategic management
strategies
business model
strategic management process
mission
opportunities
threats
resources
capabilities
core competencies
strengths
weaknesses
SWOT analysis
corporate strategy
growth strategy
stability
strategyrenewal strategy
BCG matrix
competitive strategy
strategic business units
competitive advantage
functional strategies
strategic flexibility
first mover