Слайд 1Stylistic analysis
Setting
Plot
Theme
Narration
Characters
Слайд 2Stylistic analysis
1. Summarize the plot (a one-sentence description)
2. Identify
the message
3. Setting
4. Type of narration
5. Description of the author's
style
6. Description of characters through their language
7. Stylistic devices and their functions in the text
Слайд 3
Setting
the time in which the action takes place
The specific characteristics
of location - building, room, etc.
The geographical location, including
Слайд 4Setting
can help in the portrayal of characters.
“I write this sitting
in the kitchen sink. That is, my feet are in
it; the rest of me is on the draining-board."
“I capture the Castle”
by Dodie Smith
Слайд 5Setting
can establish the atmosphere of a work.
“It was a dark
and stormy night… .”
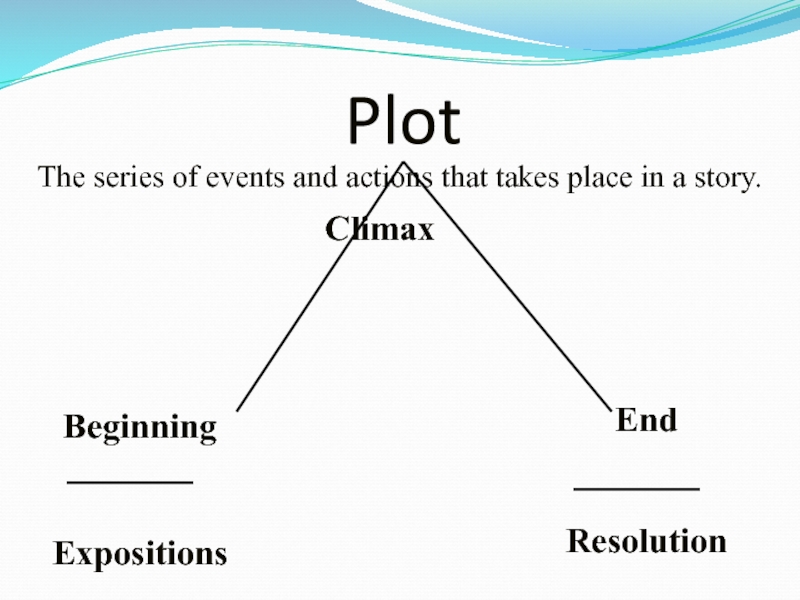
Слайд 6Plot
The series of events and actions that takes place in
a story.
Beginning
Expositions
Climax
End
Resolution
Слайд 7Elements of Plot
Conflict
Man VS Man
Man VS Nature
Man VS Society
Man VS
Himself
Слайд 8The Theme / Message
.
is the central idea, the purpose of
a work
some insight into the human nature or society
•
the moral lesson (perhaps)
•stands clear only through the overall analysis
Слайд 9Narration
Author’s narrative: omniscient (= all-knowing) point of view
Entrusted narrative:
a) the story is told from the point
of view of one of the characters who uses the 1st person pronoun “I.”
b) the story is told from the point of view of one of the characters who uses the 3d person.
Слайд 10Free direct speech
The young woman added hastily:
“What style would you
like – something modish?”
“No. Simple.”
“What figure would the young lady
be?”
“I don’t know; about two inches shorter than you.”
Слайд 11Free indirect speech
“Julie got up. She looked determined. She would
go to Brighton after all.”
Слайд 12Fiction Elements
Dialogue (speech characteristics)
Interior monologue
Stream-of-consciousness
Author’s remarks
Слайд 13Fiction Elements: Structure
Foreshadowing: early clues about what will happen later
in a piece of fiction
Chronological: starts at the beginning and
moves through time.
Flashback: starts in the present and then goes back to the past.
Circular or Anticipatory: starts in the present, flashes back to the past, and returns to the present at the conclusion.
Panel: same story told from different viewpoints.
Слайд 14Style: Level of Complexity
mostly simple sentence structure or varies the
sentence structures (simple, compound, complex sentences);
simple vocabulary or higher-level word
choices
dialogue
figurative language (similes, metaphors, onomatopoeia, personification, symbolism)
level of detail (detailed or schematic)
descriptive / too wordy / too flowery / too confusing or “convoluted”
means to visualize the images, to understand the concepts, to build suspense
Слайд 15TONE
is the author’s attitude toward the subject.
can be recognized
by the language/word choices the author uses.
Слайд 16
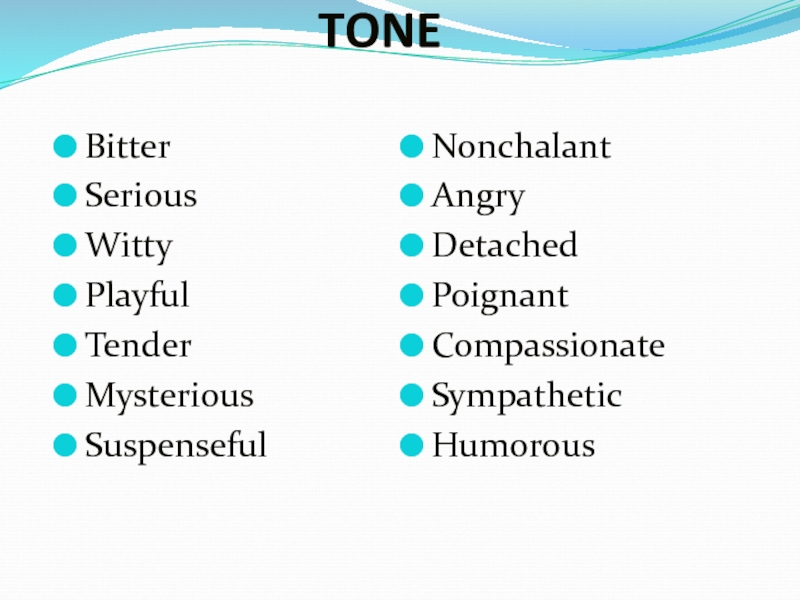
TONE
Bitter
Serious
Witty
Playful
Tender
Mysterious
Suspenseful
Nonchalant
Angry
Detached
Poignant
Compassionate
Sympathetic
Humorous
Слайд 17Tone : “A Gift in His Shoes”
Donovan and Larry were
early for baseball practice. They decided to run up and
down the bleachers to exercise before the rest of the team arrived. Larry was first to the top. He whispered to Donovan, “Look over there.” He pointed to a man sleeping on the highest, narrow bench of the bleachers. His pants and shirt were faded, worn, and too large for his thin frame. One big toe stuck out of a huge hole in his sock. His scraped-up shoes sat a few feet away. Donovan whispered, “We should help him out. Let’s hide something good in his shoes. Then, when he wakes up, he will have a nice surprise.”
Слайд 18Tone: “A Gift in His Shoes”
How would you describe the
tone of this passage?
Angry
Detached
Sympathetic
Evidence: help him out, something good, a
nice surprise
Слайд 19MOOD
MOOD is the overall feelings or emotions that are created
IN THE READER.
Authors “move” their readers’ moods through their
choice of words and level of detail.
Слайд 20MOOD
Cheerful
Relieved
Gloomy
Bleak
Uncertain
Bittersweet
Relaxed
Confused
Hopeless
Tense
Слайд 21MOOD EXAMPLE
During the holidays, my mother's house glittered with decorations
and hummed with preparations. We ate cookies and drank cider
while we helped her wrap bright packages and trim the tree. We felt warm and excited, listening to Christmas carols and even singing along sometimes. We would tease each other about our terrible voices and then sing even louder.
Mood: content, happy ("warm, excited, glittered”)
Слайд 22MOOD EXAMPLE
After New Year's the time came to put all
the decorations away and settle in for the long, cold
winter. The house seemed to sigh as we boxed up its finery. The tree was dry and brittle, and now waited forlornly by the side of the road to be picked up.
Mood: dreary, depressed. ("cold, sigh, brittle, forlornly“)
Слайд 23Types of Characters
Round Character: convincing, true to life and have
many character traits.
Dynamic Character: undergoes some type of change in
story because of something that happens to them.
Flat Character: stereotyped, shallow, often symbolic. They have one or two personality traits.
Static Character: does not change in the course of the story
Слайд 24Characters
Protagonist -the main character in a literary work (usually positive).
Antagonist
- the character who opposes the protagonist.
Слайд 25Methods of Characterization
direct - “he was an old man…”
characters’ thoughts, words, and actions
reactions/comments of other characters
character’s
physical appearance
characters’ thoughts
Слайд 26Symbolism
A symbol represents an idea, quality, or concept larger than
itself.
A Journey can symbolize life.
Black can represent evil or death.
Water
may represent a new beginning.
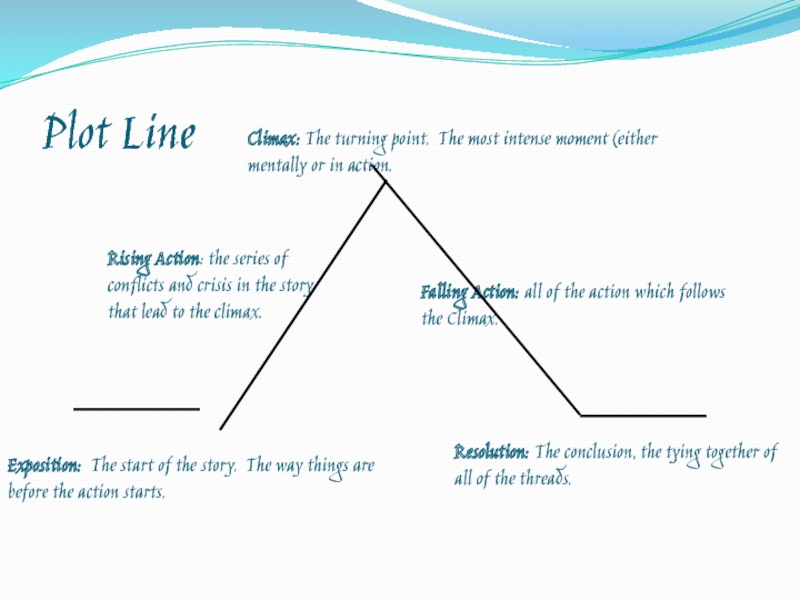
Слайд 27Plot Line
Exposition: The start of the story. The way things
are before the action starts.
Rising Action: the series of conflicts
and crisis in the story that lead to the climax.
Climax: The turning point. The most intense moment (either mentally or in action.
Falling Action: all of the action which follows the Climax.
Resolution: The conclusion, the tying together of all of the threads.