Слайд 1Subject: " The VND types, the doctrine of Nominative of
Pavlov about I and II alarm systems".
1. The doctrine of
Nominative of Pavlov about a conditioned reflex.
2 . Characteristic of conditioned reflexes.
3 . Technique of development of conditioned reflexes.
4 . Difference of conditioned reflexes from the unconditional.
5 . Types of conditioned reflexes, dynamic stereotype.
6 . Temporary communication – a basis of a conditioned reflex,
education mechanisms.
7 . Analitiko-sintetichesky activity of bark
brain.
Слайд 2Doctors, the scientists who are simply conceiving of people always
features of behavior of the person interested.
Now there is
a large number of classifications of types of nervous activity at the heart of which the various principles lie.
We will stop on main of them. It should be noted that it is possible to define the VND type of any person only in the most general terms.
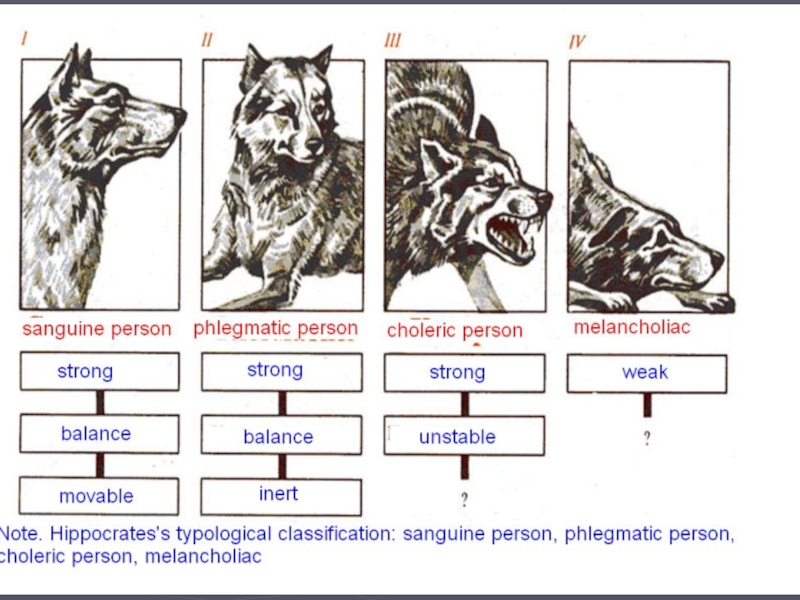
Слайд 3Modern ideas of the VND types are substantially identified with
four types of human temperament allocated still with Ancient Greek
doctor Hippocrates (ІV in B.C.) on the basis of supervision over behavior of people.
The choleric;
The melancholic;
The Flegmatichesky;
The sanguine.
Слайд 4Nominative Pavlov, studying development and fixing of conditioned reflexes at
dogs, I defined that an important role in formation like
nervous activity is played by properties of cortical processes: FORCE, STEADINESS, MOBILITY.
Force is degree of expressiveness of processes of excitement and braking.
Steadiness – a ratio of processes of excitement and braking in total amount of biological reactions.
Mobility – the speed of emergence and speed of change of processes of excitement and braking.
Taking into account these properties of Nominative Pavlov allocated four VND types.
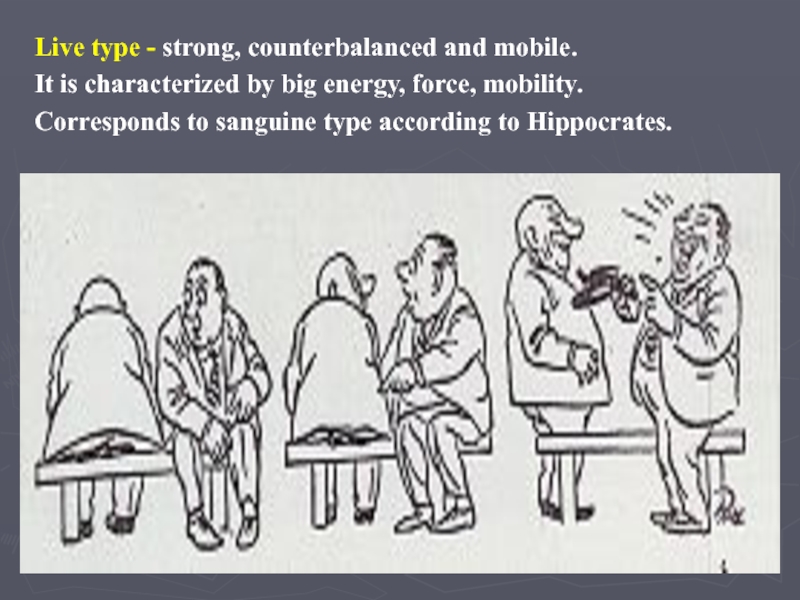
Слайд 6Live type - strong, counterbalanced and mobile.
It is characterized by
big energy, force, mobility.
Corresponds to sanguine type according to Hippocrates.
Слайд 7The quiet – strong, counterbalanced, inactive.
It is characterized by
the sufficient force of processes of excitement and braking, their
rather low mobility.
Corresponds to flegmatichesky type according to Hippocrates.
Слайд 8The impetuous – strong, unbalanced, mobile,
with prevalence of processes
of excitement.
Corresponds to choleric type according to Hippocrates.
Слайд 9Weak (inert) – unbalanced, inactive with prevalence of brake process
over exciting.
Corresponds to melancholic type according to Hippocrates.
Слайд 10The VND types are formed on a basis as genotype,
and phenotype, i.e. on genetically put features of nervous system
all variety of influences of education, conditions of environment, situations in which there is an organism is imposed.
Слайд 11Nominative Pavlov created the doctrine about the first and second
alarm systems.
The first alarm system is visual, acoustical
and other sensual signals which proceed from world around and the internal environment of an organism. It is the general for the person and animals.
The second alarm system – verbal, inherent only to the person. As its signals words said, heard, read serve. By means of the word transition from a sensual image of the first alarm system to representations of the second alarm system is carried out.
Слайд 12At children by first year of life opportunity to react
to words which replace various signals intensively develops.
The word
becomes ekivalenty the signals perceived by sense organs.
The word becomes a signal of signals.
Слайд 13The word does the person by the member of society.
The person becomes a being social.
The word played a
huge role in development of labor activity, accumulation of experience and knowledge in process of human society.
Слайд 14In temporal shares there is a touch center of speech
(the center to Vernika). At destruction of this zone of
people hears, but doesn't understand value of that hears.
In a frontal lobe of the left hemisphere is the motor center (Brock), at his destruction of people loses ability to speak, but understands when to it address orally or in writing.
Слайд 15
Pavlov allocated with nominative the VND specific types inherent in
the person in connection with existence of speech (ІІ-y alarm
system), its cogitative and creative activity.
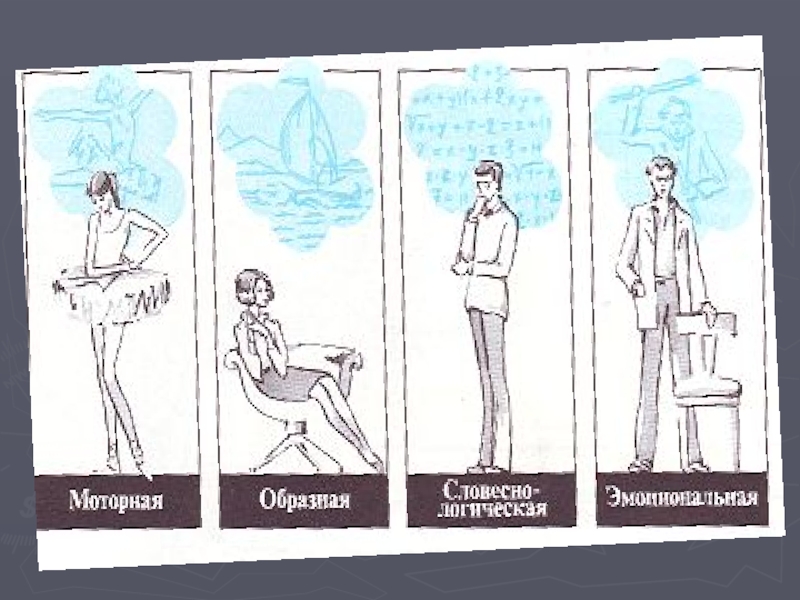
Слайд 16The first type – art.
People with a pronounced visual
and acoustical susceptibility of environment, i.e. prevalence І - oh
alarm system, the concrete, figurative thinking (in the most part it is artists and musicians) is expressed.
Слайд 17
The second type – cogitative. Differs tendency to logical and
abstaktny thinking, prevalence ІІ-oh alarm system (scientists, philosophers, mathematics).
Слайд 18
The third type - mixed.
Properties of perception of environment
and thinking are expressed to the same extent.
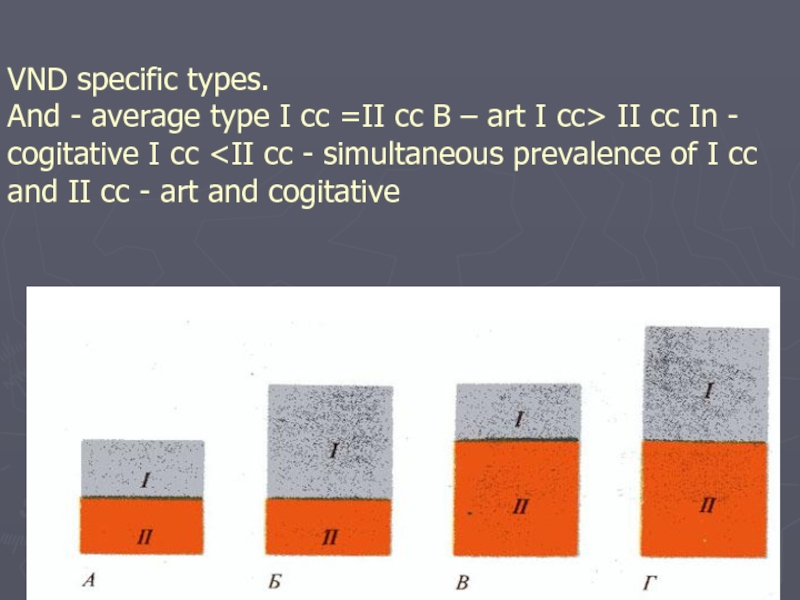
Слайд 19VND specific types.
And - average type I сс =II
сс B – art I сс> II сс In -
cogitative I сс
Слайд 20
To speak about the special mental abilities connected with the
VND separate types it isn't necessary since talented people meet
manifestation of characteristics of all VND types.
On the other hand, it is possible to speak about individual predisposition of each person to one of the VND types.
Слайд 21The left and right hemispheres are responsible for different functions,
i.e. there is a mezhpolusharny asymmetry.
The left hemisphere (partially dominating):
Verbal perception (verbal);
Temporary relations;
Analysis of incentives;
Consecutive perception;
Abstract thinking;
Right hemisphere:
-Nonverbal perception (visual);
-Spatial relations;
-Synthetic activity.
-Simultaneous perception;
- Concrete thinking.
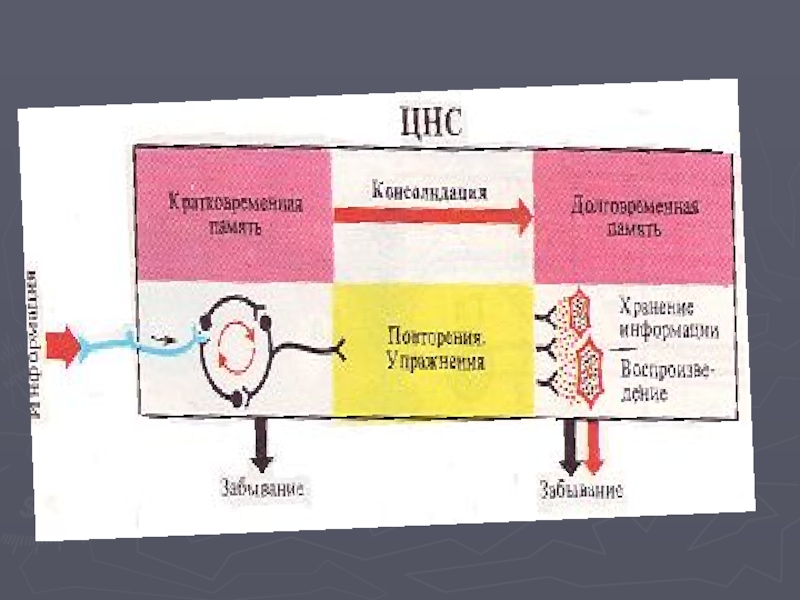
Слайд 22Memory – accumulation, storage, processing and vosprozvedeny information.
1. Types of
memory:
2. The specific;
3. The individual.
4. The short-term;
5. The long-term;
6. The
mechanical;
7. The logical;
8. The touch;
The emotional.
Memory consists of 3 processes:
1. Storing;
2. Preservation;
3. Reproduction.
Memory levels:
1. The reproducing – the highest level;
2. The identifying;
3. The facilitating.
Слайд 24Memory theories
1 . Conditioned-reflex;
2 . Theory neural models;
3 . Associative;
4
. Chemical;
Слайд 26Subject: " Dream, dreams. Emotions. Motivations".
Plan:
1 . Dream, types of
a dream.
2 . Dream mechanisms.
3 . Emotions. Classification of emotions.
4
. Theories of emotions.
5 . Motivations.
6 . Architecture of the complete behavioural act.
Слайд 27Dream – a condition of an organism which is characterized
by considerable decrease in all functions of an organism, partial
shutdown of consciousness.
Types of a dream:
1 . Physiological dream:
- polyphase dream at children;
- monophase dream at adults;
- seasonal dream;
2 . Hypnotic dream.
3 . Pathological dream:
- narcotic dream;
- somnambolizm (sleepwalking);
- lethargical sleep.
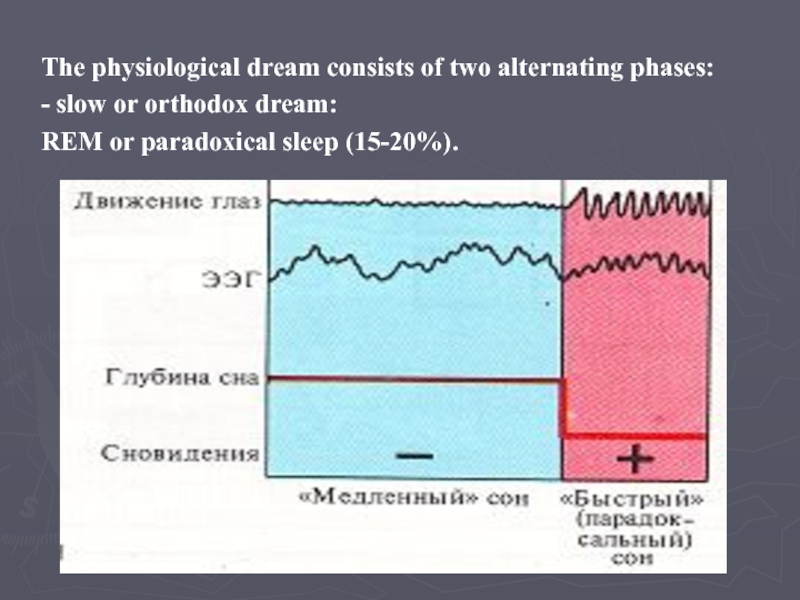
Слайд 28The physiological dream consists of two alternating phases:
- slow or
orthodox dream:
REM or paradoxical sleep (15-20%).
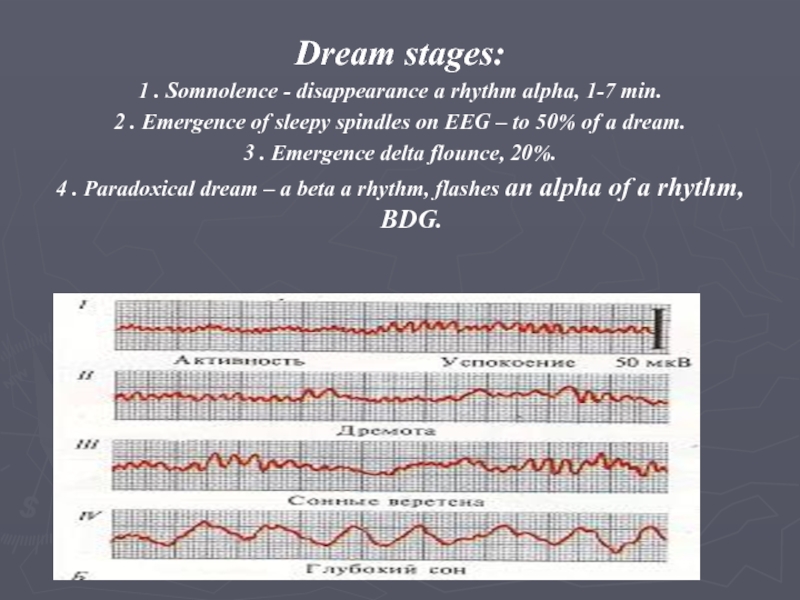
Слайд 29Dream stages:
1 . Somnolence - disappearance a rhythm alpha, 1-7
min.
2 . Emergence of sleepy spindles on EEG – to
50% of a dream.
3 . Emergence delta flounce, 20%.
4 . Paradoxical dream – a beta a rhythm, flashes an alpha of a rhythm, BDG.
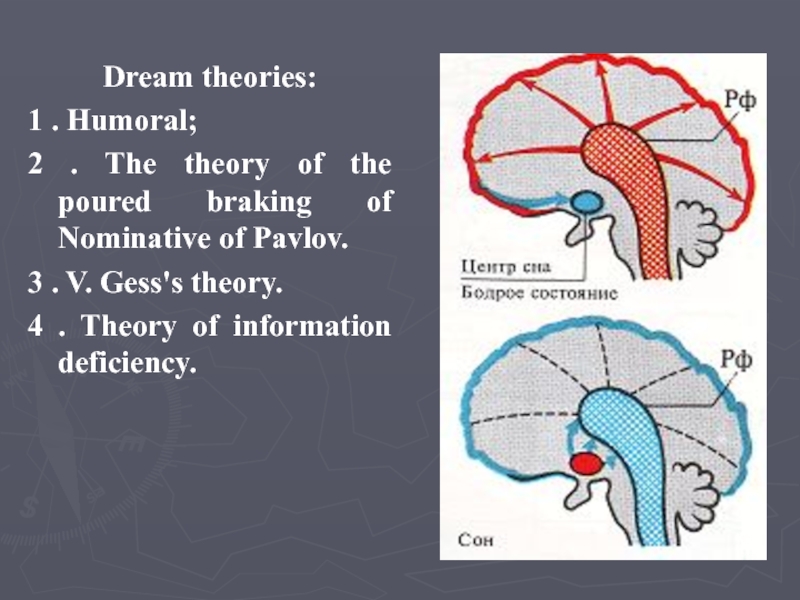
Слайд 30Dream theories:
1 . Humoral;
2 . The theory of the poured
braking of Nominative of Pavlov.
3 . V. Gess's theory.
4 .
Theory of information deficiency.
Слайд 31
Dreams – always accompany a dream and are more often
connected with a phase of a paradoxical dream.
I.M.Setchenov characterized them
as "unknown combinations of skilled impressions".
Слайд 32Emotion (I induce, I excite) – a physiological condition having
in pronounced subjective coloring, is a component of motivations.
Distinguish concepts:
1
. Emotional stress.
2 . Affect.
3 . Mood.
Classification of emotions:
1 . Positive, negative;
2 . The highest, the lowest.
3 . Sthenic, asthenic.
Слайд 33Emotion theories:
1 . C.Darvina's theory (instinctive action);
2 . P.K.Anokhin's biological
theory.
3 . P. V. Simonov's information theory.
Э
= П (requirement) x (Ying – Is);
Ying – necessary information,
Ис – existing information.
4 . G.I.Kositskogo's theory.
Э = C (Ying En Vn – Is Es Vs)
Ying En Vn – necessary information, energy, time
Is Es Vs – existing information, energy, time.
5 . Central theory.
6 . Korkovo – the subcrustal theory.
Слайд 36Motivations are the emotionally painted aspirations of the person and
animals to satisfaction of leading requirements.
Motivations leads to purposeful search
behavior.
Interests – emotional manifestation of informative need of the person.
Types of motivations:
1 . The lowest (biological, vitalny).
2 . The highest:
- the social.
- the ideal.
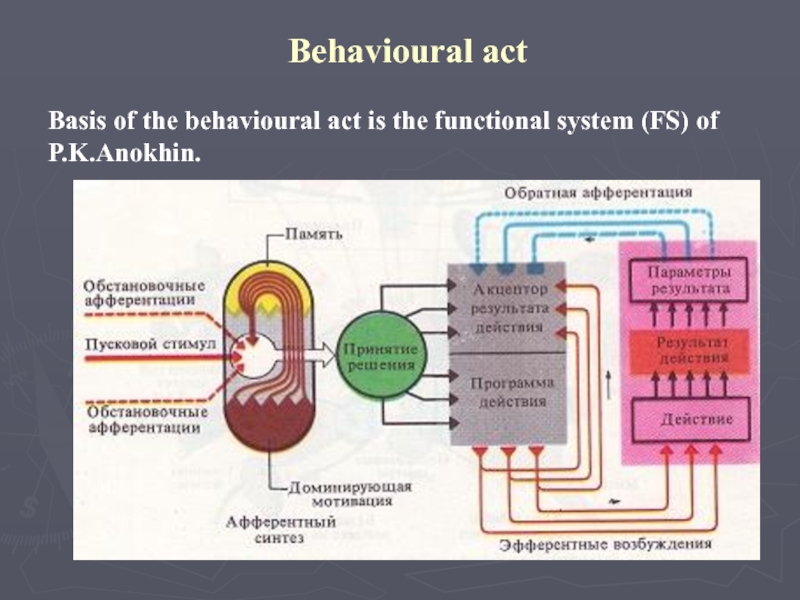
Слайд 37Behavioural act
Basis of the behavioural act is the functional system
(FS) of P.K.Anokhin.
Слайд 38The behavioural act includes:
1 . Afferentny synthesis;
2 . Decision;
3 .
Program of action and action acceptor;
4 . Efferent synthesis (action,
result of action, result parameters - the return afferentation).