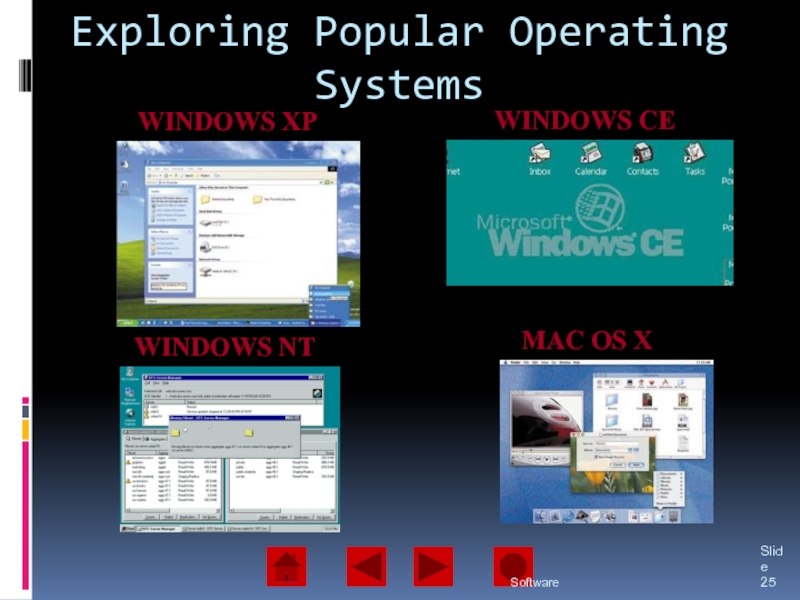
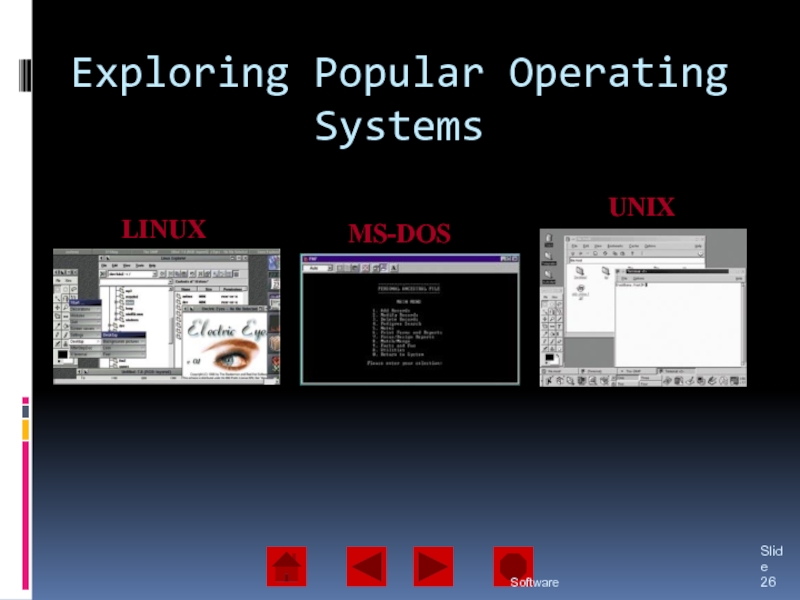
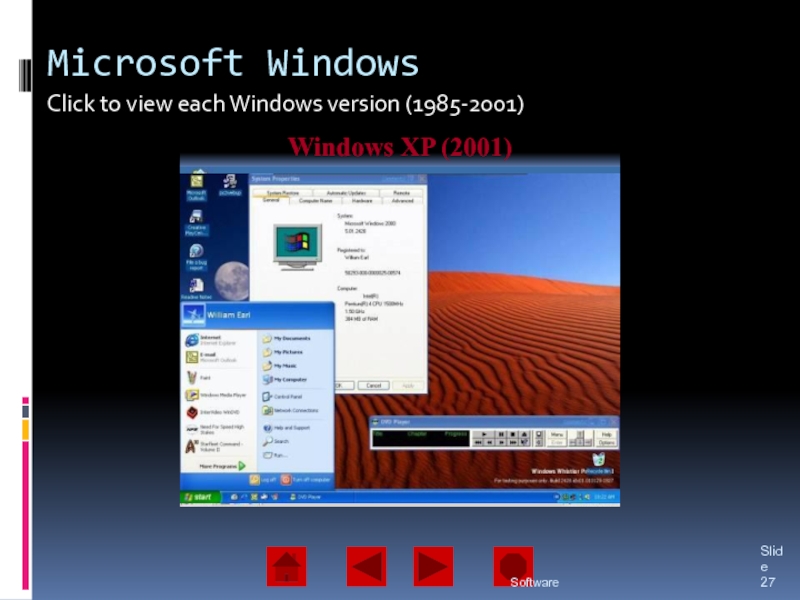
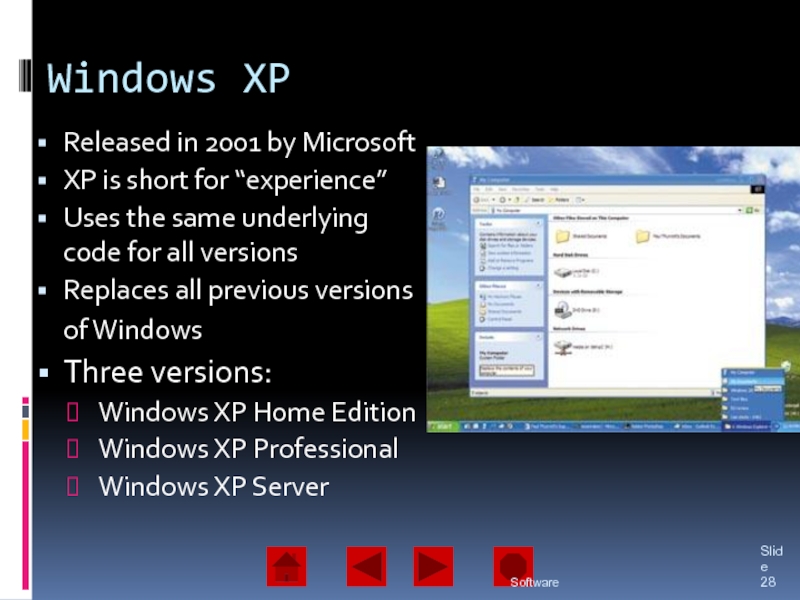
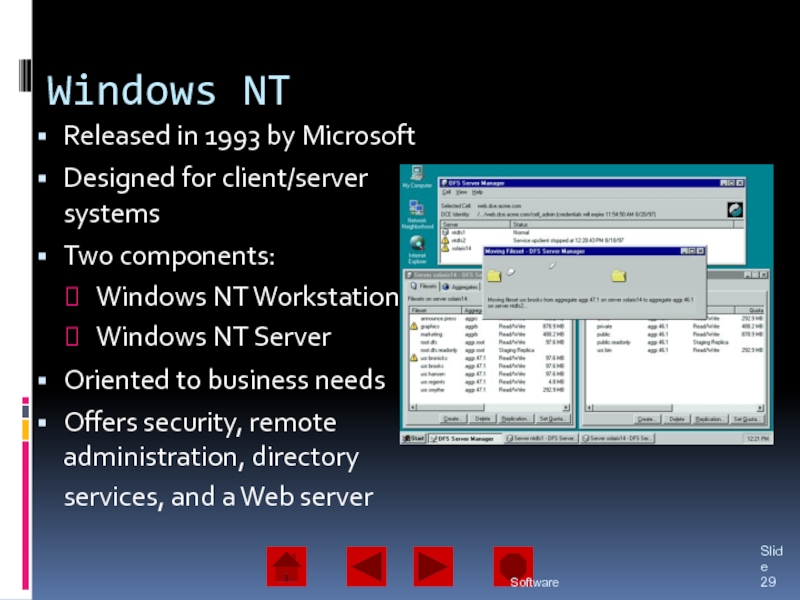
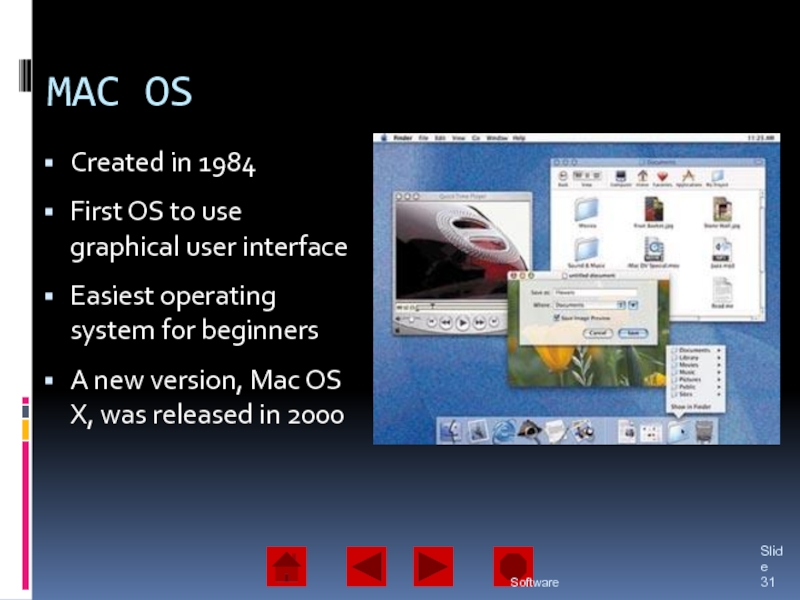
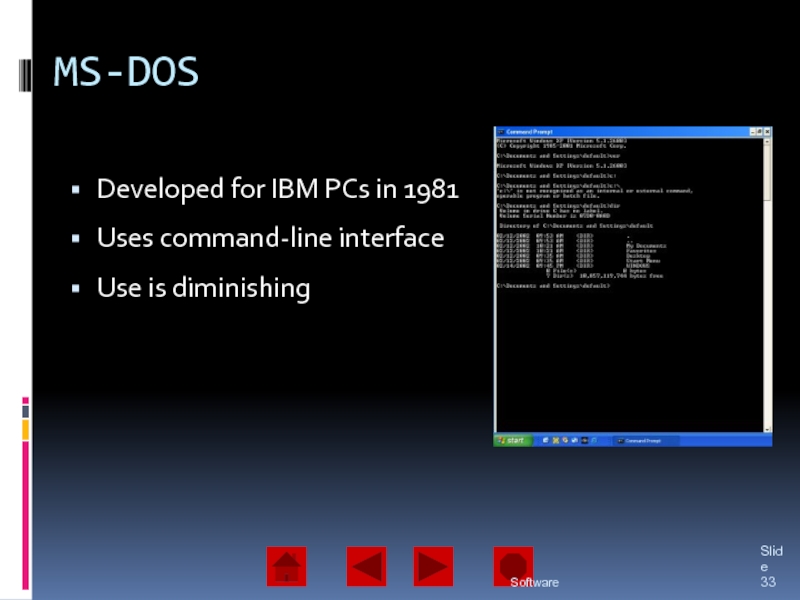
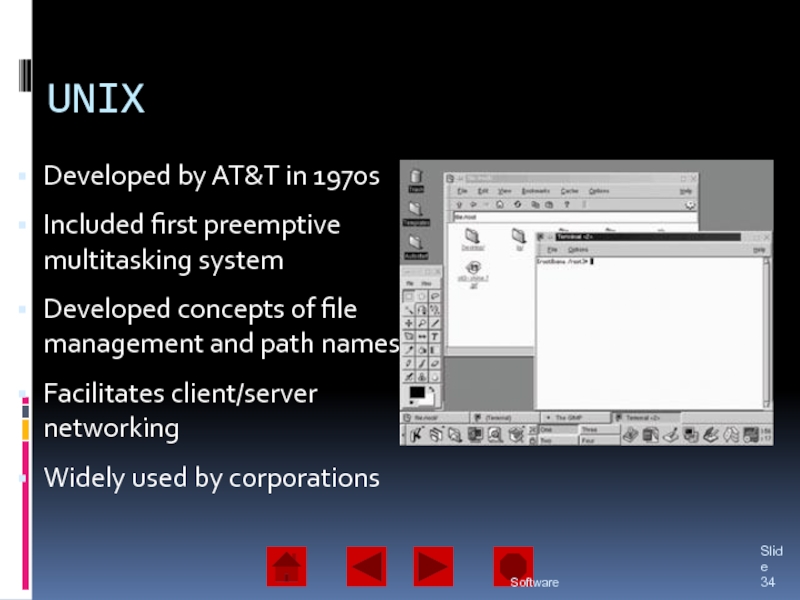
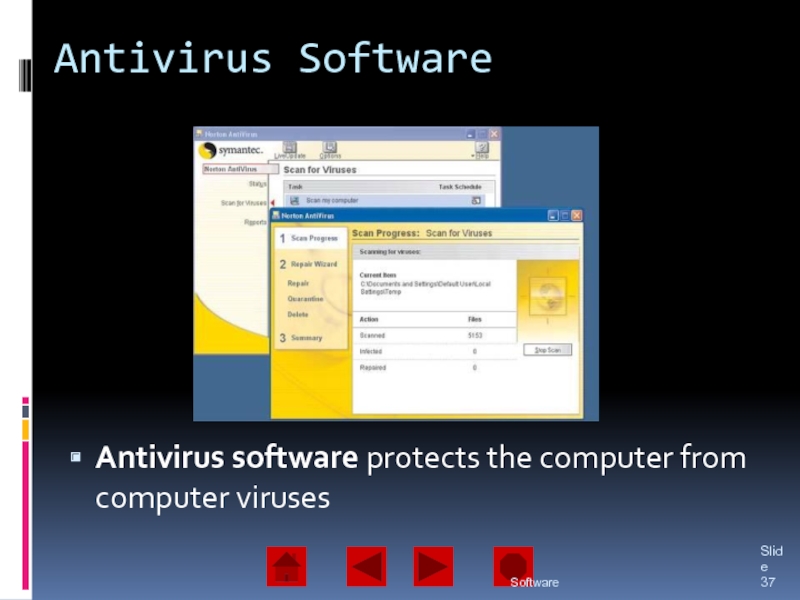
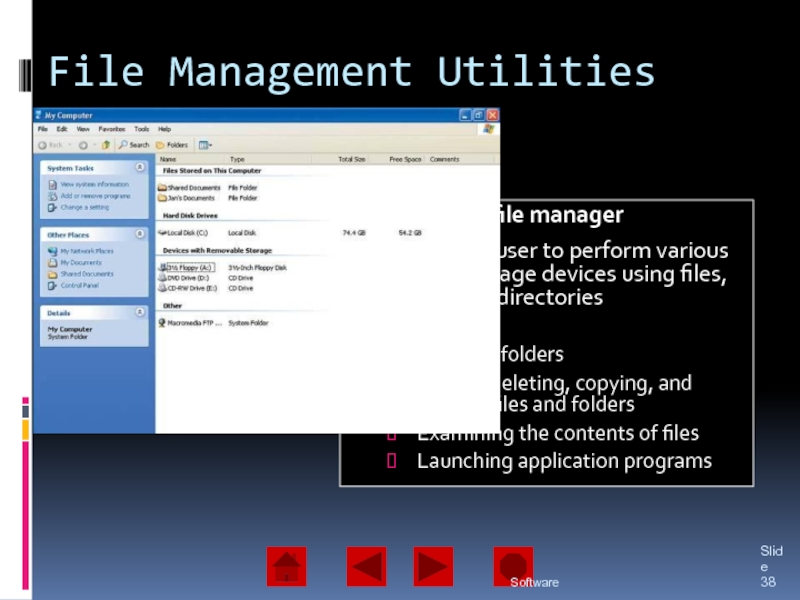
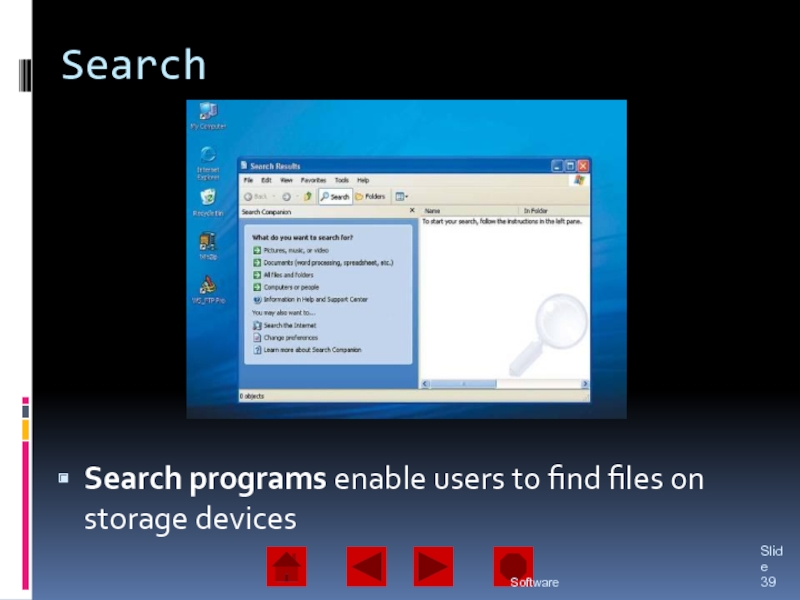
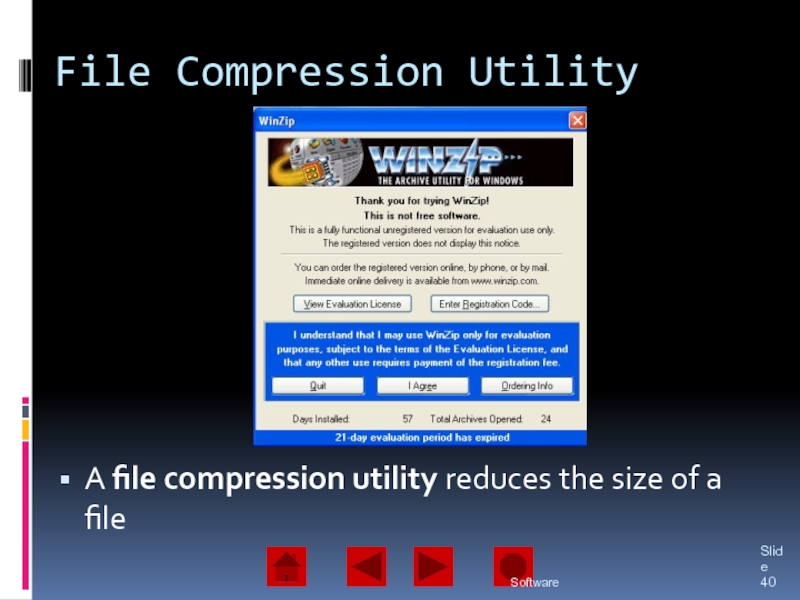
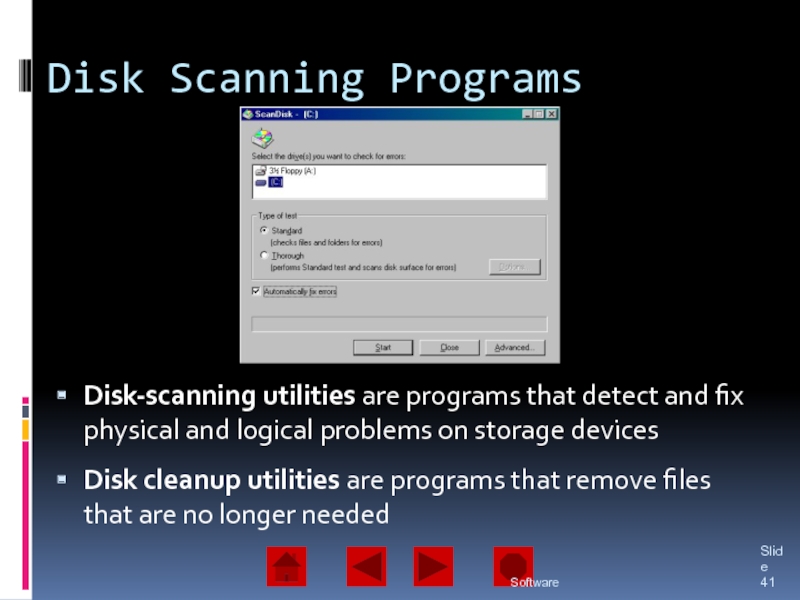
of operating system software
Why a computer isn’t useful without an
operating systemThe five basic functions of an operating system
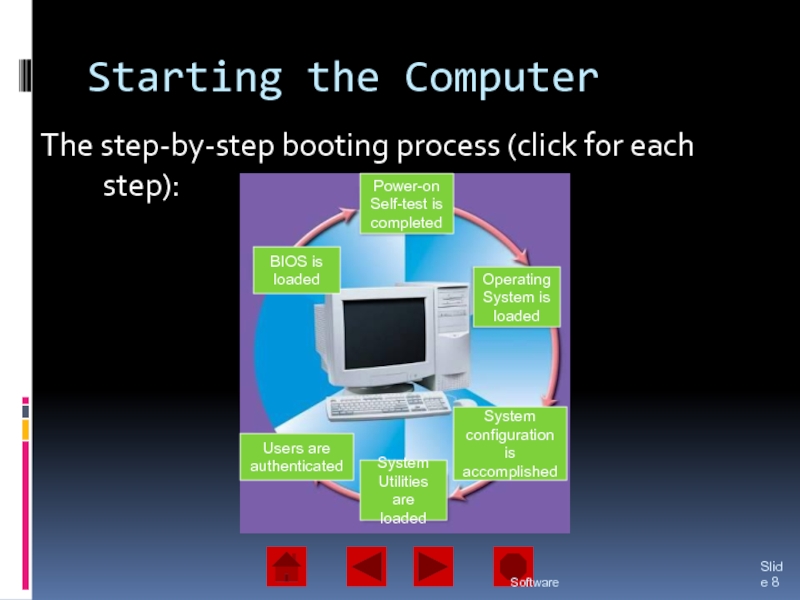
What happens when you turn on a computer
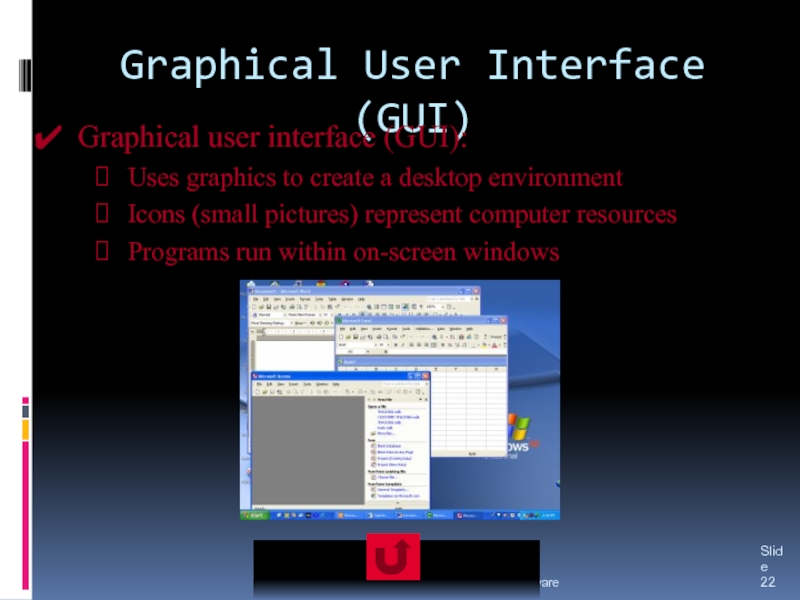
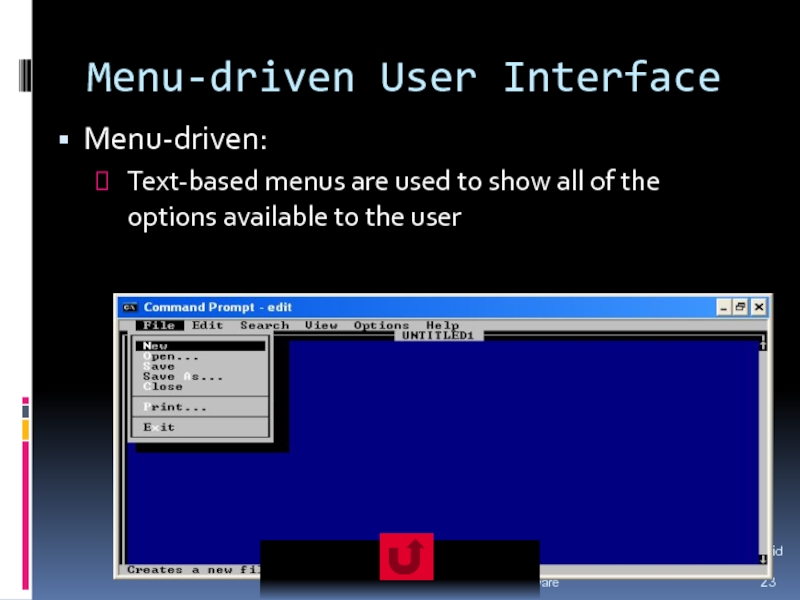
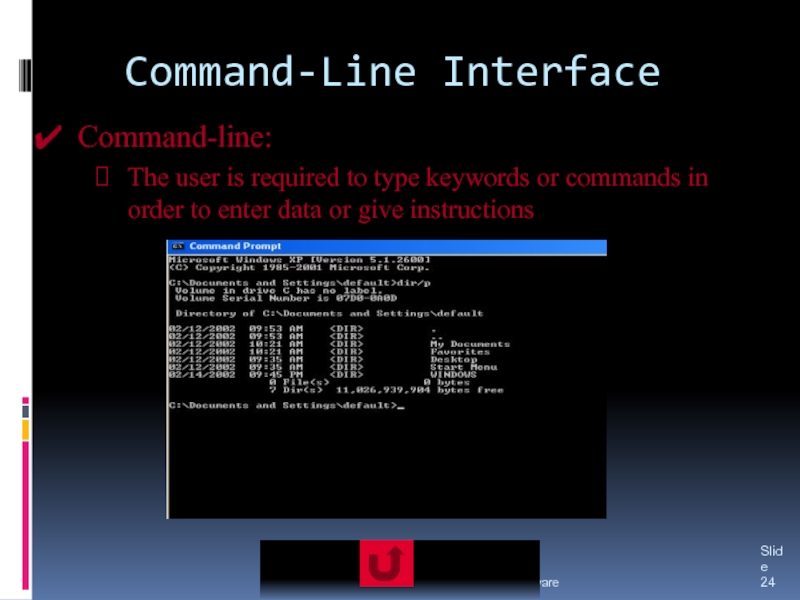
The three major types of user interfaces
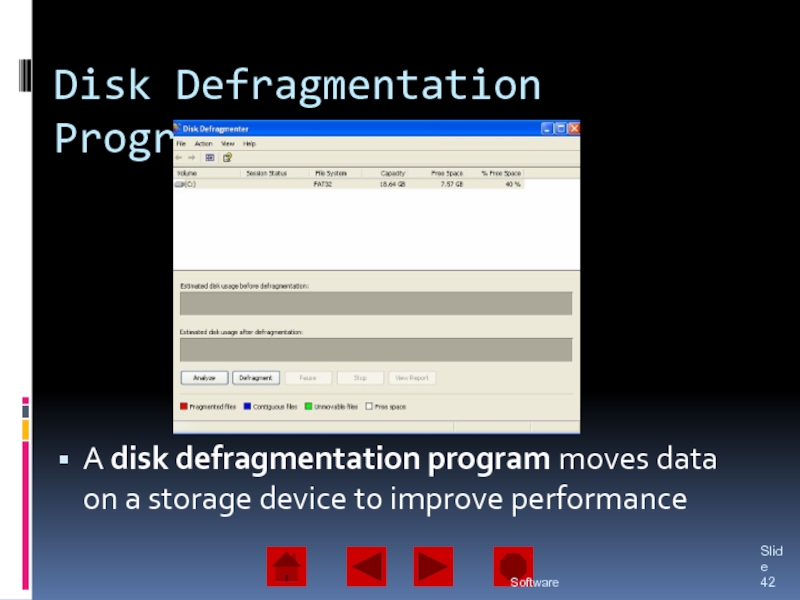
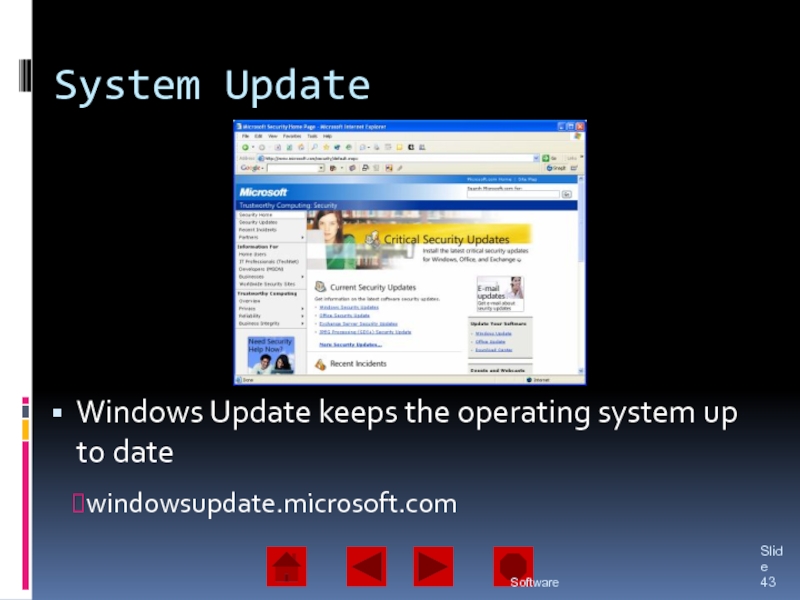
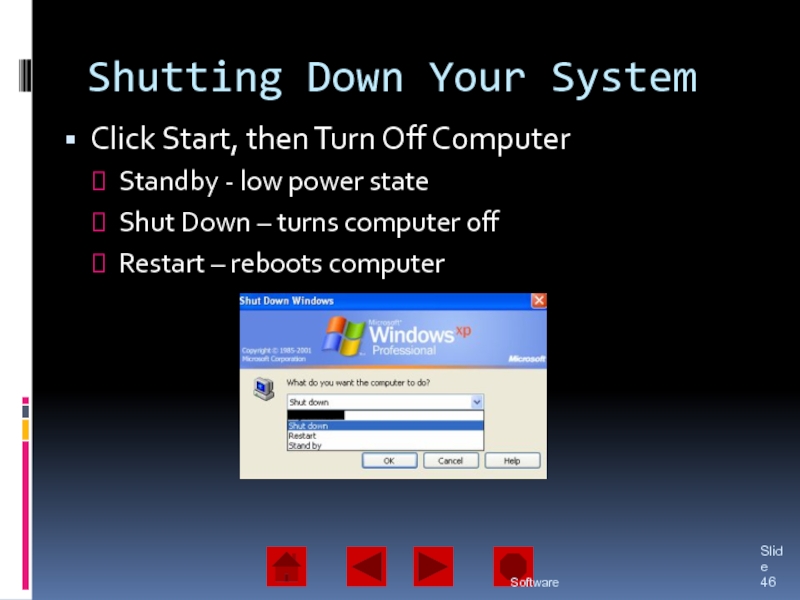
Software
Slide