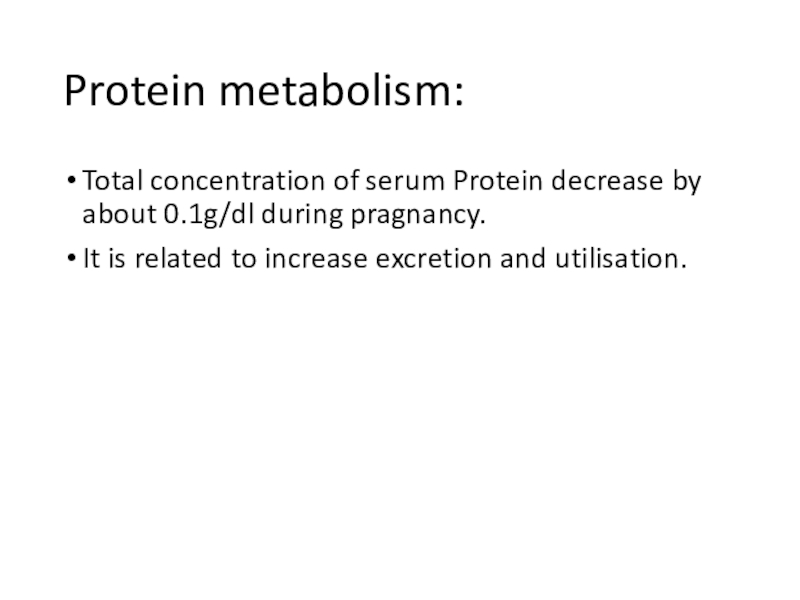Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
T o p i c : M e t a b olic changes in pregnancy
Содержание
- 1. T o p i c : M e t a b olic changes in pregnancy
- 2. Metabolic changes in pregnancy:Total metabolism is increasing
- 3. Carbohydrates metabolism:Glucose is much needed from mother
- 4. Insulin : secretion also favors.During maternal fasting
- 5. Iron metabolism:Total iron requirment during pregnancy is
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Absence of iron supplements can cause drop
- 8. Protein metabolism:Total concentration of serum Protein decrease
- 9. Fat metabolism:Average 3-4kg of fat is stored during pregnancy.Mostly in abdominal wall, breast ,hips and thighs.
- 10. Lipid metabolism:HDL levels increase by 15% LDL is utilised for placental steroids synthesis.
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Metabolic adaptation during pregnancy:It have 2 phase
- 14. Keton bodies: embryonic brain development and neurophysiologic
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Скачать презентанцию
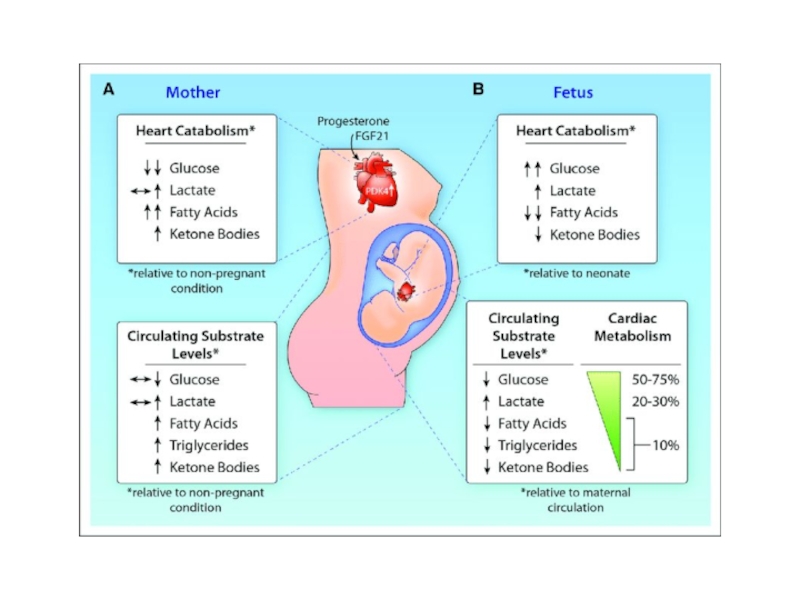
Metabolic changes in pregnancy:Total metabolism is increasing due to the needs of the growing fetus and the uterus.It increases to the extent of 30% higher than that of the average for
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Metabolic changes in pregnancy:
Total metabolism is increasing due to the
needs of the growing fetus and the uterus.
the extent of 30% higher than that of the average for the non-pragnant women .Слайд 3Carbohydrates metabolism:
Glucose is much needed from mother to fetus throughout
pragnancy .
Insulin secretion is increasing the hyperplasia and hypertrophy of
beta cells of pancreas .And sensitivity to insulin is deceased.
So, the plsma insulin is increasing thus ensure continuous supply of glucose to fetus .
Слайд 4Insulin : secretion also favors.
During maternal fasting :there is hypoglycemia,hypoinsulinemia
and hyperlipidemia.
Lipolysis takes action and generate fatty acids for gluconeogenesis
and fuel supply.Слайд 5Iron metabolism:
Total iron requirment during pregnancy is estimated 1000mg.
The amount
of iron absorbed from the diet and that mobilized from
the store is inadequate to meet the demand.Absorption through the gutis enhanced during pregnancy
Слайд 7Absence of iron supplements can cause drop in hemoglobin,serum iron
and serum ferritin concentration.
However, placenta transfer adequate iron to the
fetus , despite sever maternal iron deficiency.Слайд 8Protein metabolism:
Total concentration of serum Protein decrease by about 0.1g/dl
during pragnancy.
It is related to increase excretion and utilisation.
Слайд 9Fat metabolism:
Average 3-4kg of fat is stored during pregnancy.
Mostly in
abdominal wall, breast ,hips and thighs.
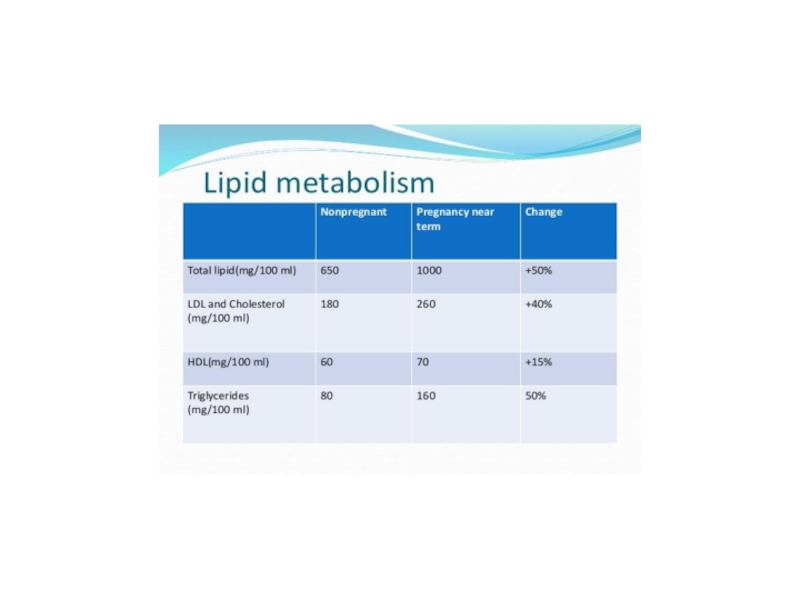
Слайд 10Lipid metabolism:
HDL levels increase by 15% LDL is utilised for
placental steroids synthesis.
Слайд 13Metabolic adaptation during pregnancy:
It have 2 phase : catabolic and
anabolic.
In anabolic adaptation : fatty acids :: key energy sources
,organogenesis.Cholesterol : cell membrane. Development, fluidity regulator , cell proliferation , differentiation as well as cell to cell communication.