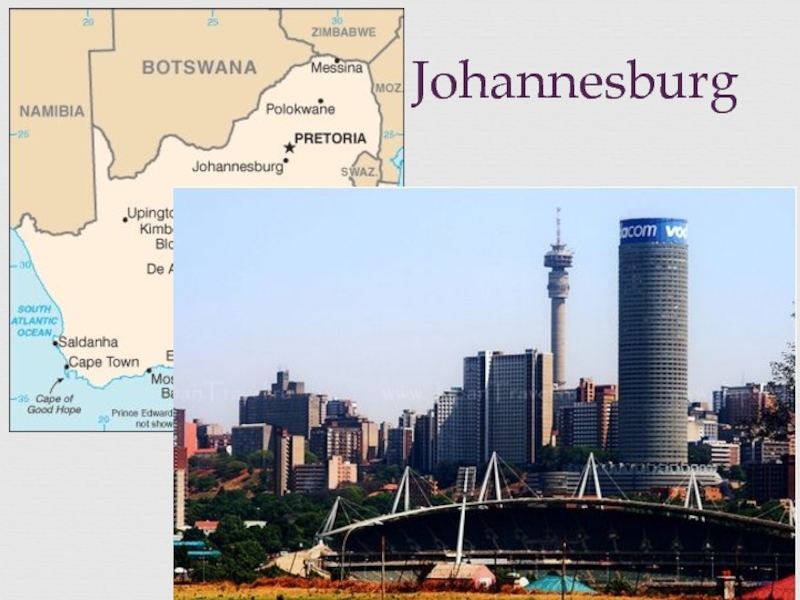
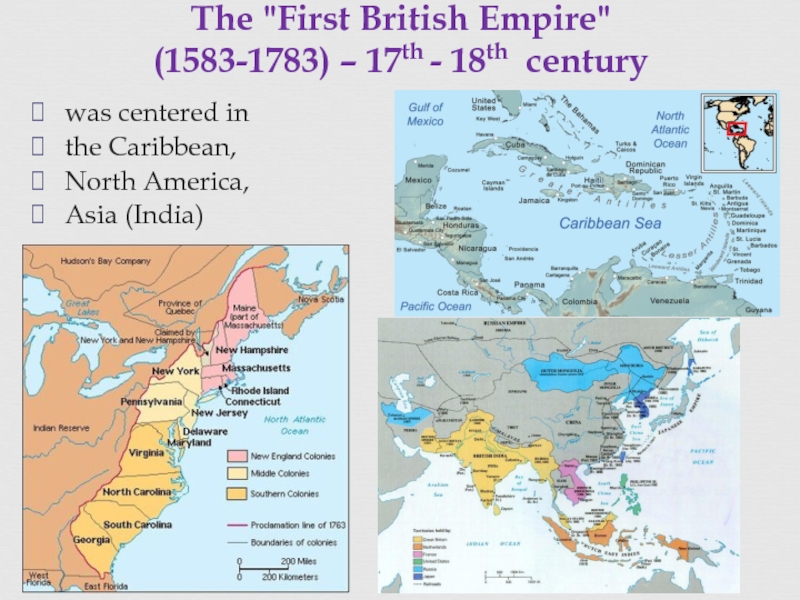
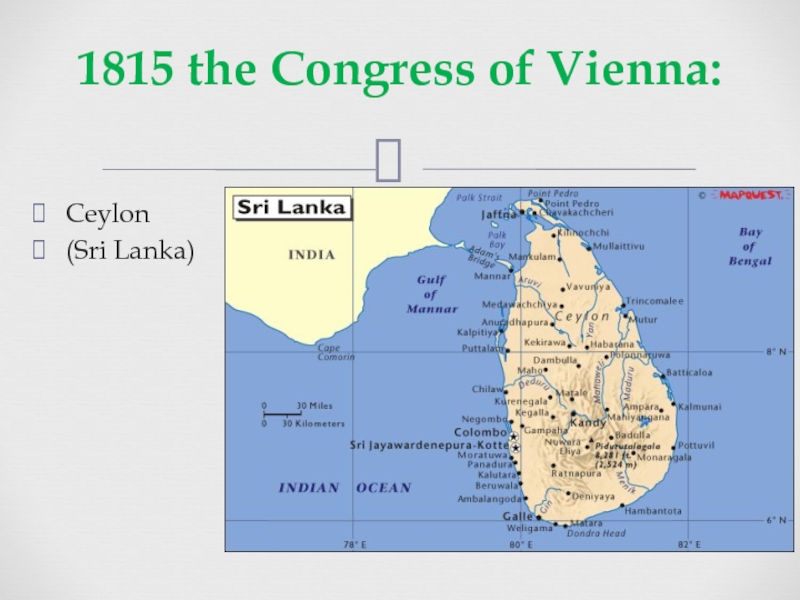
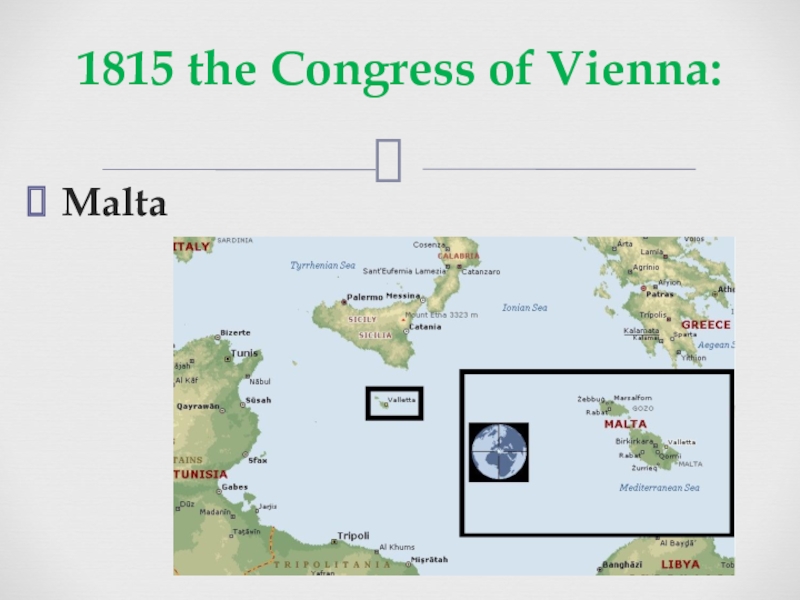
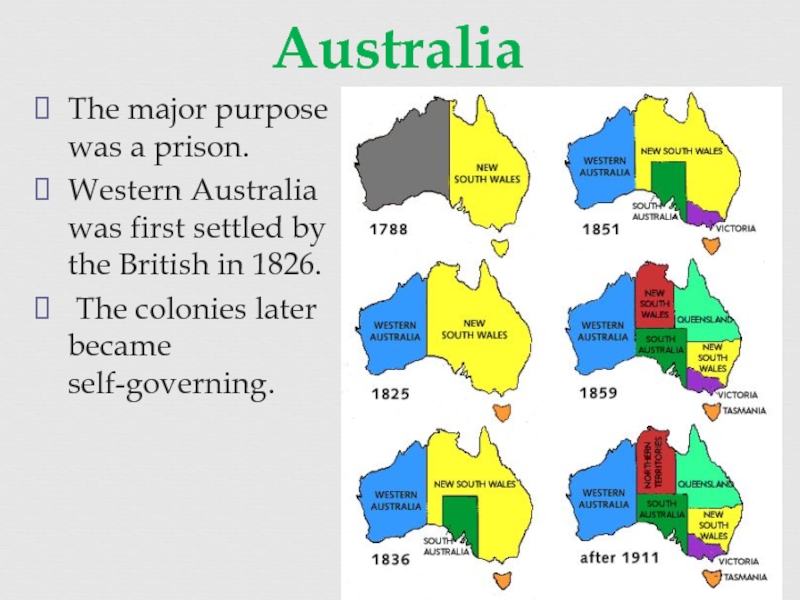
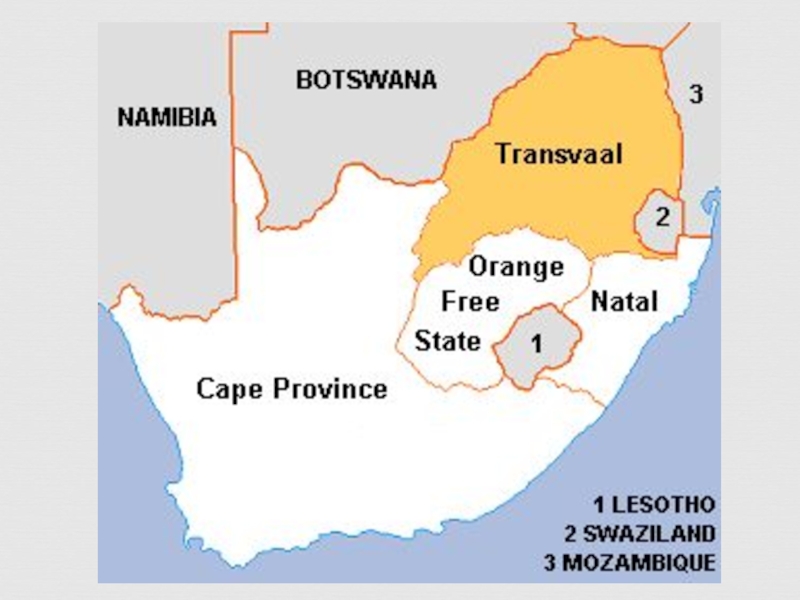
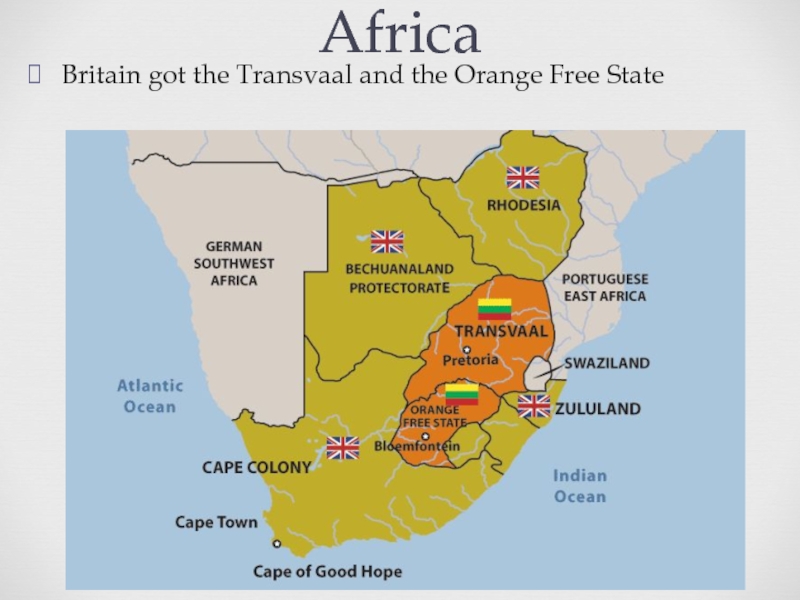
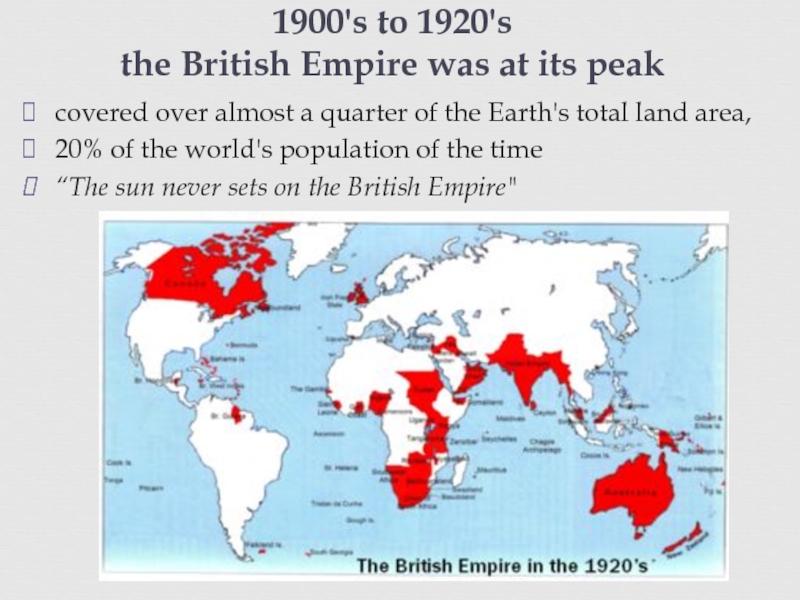
of some three centuries
was brought under the sovereignty of
the crown of GB and the administration of the British government.
Colonies, protectorates, dominions, mandates and other territories.
The British Empire