Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The word classes or parts of speech in English
Содержание
- 1. The word classes or parts of speech in English
- 2. Lecture outlineParts of speech: a historical perspectiveTraditional approaches based on various criteriaDebatable issues
- 3. The wordA meaningful, expressive, nominative unit of
- 4. Groups of words in lexicologySemantic classification of
- 5. Classes of words in grammar Grammar organizes
- 6. Lexical and grammatical properties of the wordA
- 7. The grammatical meaningThe grammatical meaning is a
- 8. The historical perspective Prescriptive grammars
- 9. The historical perspective Non-structural descriptive grammarsHenry Sweet:
- 10. The historical perspective Non-structural descriptive grammarsOtto Jespersen
- 11. The historical perspective Structural Descriptive GrammariansCharles Fries
- 12. Modern traditional approaches The criteria:semantic (generalized meaning)
- 13. Modern traditional approaches (1) Notional
- 14. Modern traditional approaches The Nounmeaning:
- 15. The Noun (function)Subject: The boy is very
- 16. Functional wordsThe preposition expresses the dependencies and
- 17. Subclasses: the nounProper and common (the Danube
- 18. Modern traditional approaches (2)A part of speech
- 19. Modern traditional approaches (2)lexico-grammatical meaning: nouns ‘substance’,
- 20. Modern traditional approaches (2)combinability (the power of
- 21. Modern traditional approaches (2) Nouns, adjective, pronouns,
- 22. Semi-notional parts of speech very general
- 23. The latest approach (form and function)“A Comprehensive
- 24. The latest approachClosed classed (only exceptionally extended
- 25. The latest approachClosed classes: preposition – of,
- 26. Disputable points in the parts of
- 27. The theory of field structure of
- 28. ConclusionParts of speech are lexico-grammatical classes of
- 29. Скачать презентанцию
Lecture outlineParts of speech: a historical perspectiveTraditional approaches based on various criteriaDebatable issues
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Lecture outline
Parts of speech: a historical perspective
Traditional approaches based on
various criteria
Слайд 3The word
A meaningful, expressive, nominative unit of language;
Belongs to a
particular language level;
Consists of form and meaning (signified and signifier).
Слайд 4Groups of words in lexicology
Semantic classification of words: synonyms and
antonyms;
etymologically: words of native origin and borrowing;
stylistically: neutral or stylistically
marked;frequency: active and passive, etc.
Слайд 5Classes of words in grammar
Grammar organizes the words into
a comparatively small number of classes:
grammatically relevant classes;
traditionally – parts
of speech (from Ancient Greece, rather confusing);the system of the parts of speech is historically variable.
Слайд 6Lexical and grammatical properties of the word
A word has a
certain lexical meaning: the individual meaning of the word (chair
– a definite piece of furniture);it also possesses a more general and abstract meaning – grammatical meaning, the meaning of the whole class or subclass of words (thingness, countableness of ‘chair’).
Слайд 7The grammatical meaning
The grammatical meaning is a generalized, abstract meaning,
which unites big sets or classes of words and is
expressed with the help of characteristic formal markers or their absence.Слайд 8
The historical perspective
Prescriptive grammars
Latin grammars;
declinables (nouns, adjectives, pronouns,
verbs, participles) and indeclinables (adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, articles);
the number
of parts of speech varied from author to author: for instance, nouns and adjectives formed one part of speech. Слайд 9The historical perspective
Non-structural descriptive grammars
Henry Sweet: declinables and indiclinables (based
on form, meaning, and function):
Declinables:
noun-words (noun, noun-pronoun, noun-numeral, infinitive,
gerund), adjective-words (adjective, adjective-pronoun, adjective-numeral, participle),
verb (finite verb),
verbals (infinitive, gerund, participle).
Indeclinables:
adverb,
preposition,
conjunction,
interjection.
Слайд 10The historical perspective
Non-structural descriptive grammars
Otto Jespersen (form and function)
substantives,
adjectives,
pronouns,
verbs,
and particles (adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections).
Otto Jespersen
(function in a sentence):primary, secondary, tertiary word.
A happily laughing child
(3) (2) (1)
Слайд 11The historical perspective Structural Descriptive Grammarians
Charles Fries , syntactic and
distributional analysis
(the combinability tested by substitution)
Words that exhibit the
same distribution (which is the set of contexts, i.e. immediate linguistic environments, in which a word can appear) belong to the same class. Frame A: The concert was good.
Frame B: The clerk remembered the tax.
Frame C: The team went there.
Class 1 words (all words that can take the position of the words ‘concert, clerk, tax, team.
Class 2 words (was, remembered and went).
Class 3 words (good).
Class 4 words (there).
15 groups of function words: Group A (determiners), Group B (modal verbs, Group C (the negative particle ‘not’), etc.
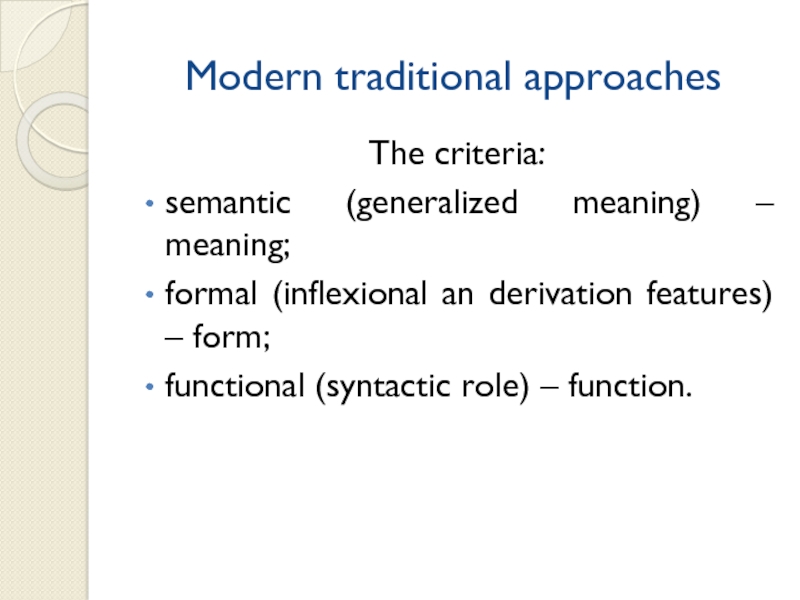
Слайд 12Modern traditional approaches
The criteria:
semantic (generalized meaning) – meaning;
formal (inflexional
an derivation features) – form;
functional (syntactic role) – function.
Слайд 13
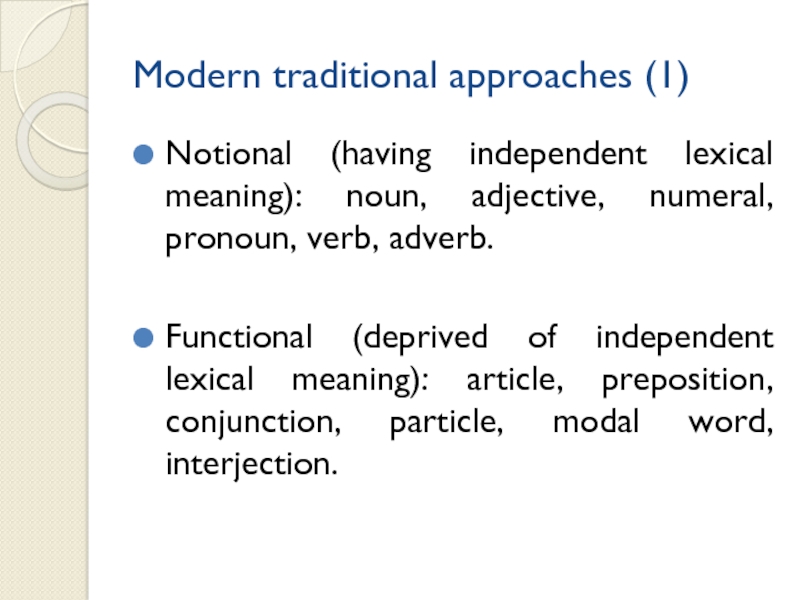
Modern traditional approaches (1)
Notional (having independent lexical meaning): noun,
adjective, numeral, pronoun, verb, adverb.
Functional (deprived of independent lexical meaning):
article, preposition, conjunction, particle, modal word, interjection.Слайд 14
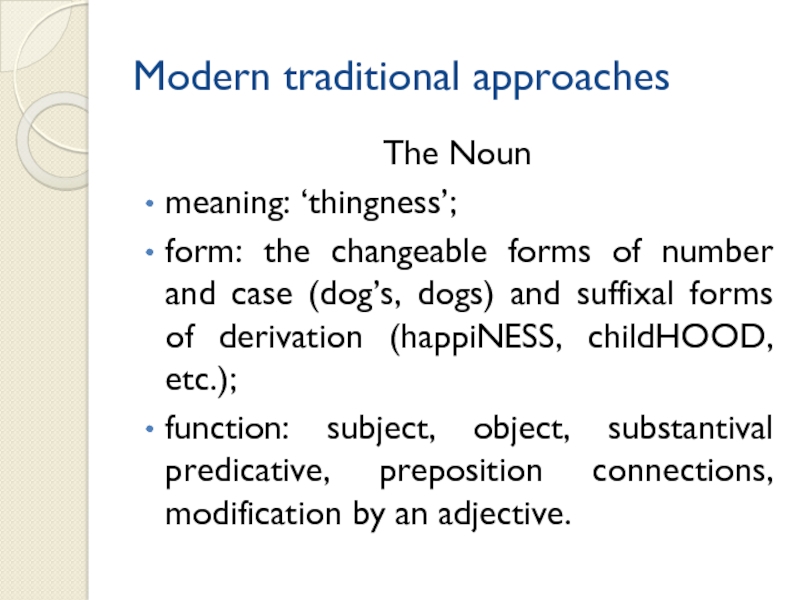
Modern traditional approaches
The Noun
meaning: ‘thingness’;
form: the changeable forms of
number and case (dog’s, dogs) and suffixal forms of derivation
(happiNESS, childHOOD, etc.);function: subject, object, substantival predicative, preposition connections, modification by an adjective.
Слайд 15The Noun (function)
Subject: The boy is very happy.
Object: She saw
the boy.
Substantival predicative: This is a boy.
Prepositional connections: He came
up to the boy.Modification by an adjective: He was a clever boy.
Слайд 16Functional words
The preposition expresses the dependencies and interdependencies of referents.
The
article expresses the specific limitation of the substantive function.
Слайд 17Subclasses:
the noun
Proper and common (the Danube vs. a girl;
Animate and
inanimate (a man vs. a chair);
Countable and uncountable ( a
dog vs. information).Слайд 18Modern traditional approaches (2)
A part of speech is a class
of words characterized by:
Its lexico-grammatical meaning;
Its lexico-grammatical morphemes;
Its grammatical categories
or its paradigms;Its combinability;
Its function in a sentence.
Слайд 19Modern traditional approaches (2)
lexico-grammatical meaning: nouns ‘substance’, verbs ‘action’, etc.;
lexico-grammatical
morphemes: -ness, -ist, -ism; -ize, -ify; -ful, -less,
-ish, etc.;grammatical categories of paradigms: case and number for nouns (dog vs. dog’s, dog vs. dogs); tense, mood, voice, etc, for verbs (walk, walked, is walking, has walked, etc.).
Слайд 20Modern traditional approaches (2)
combinability (the power of words to form
combinations of definite patterns with word of certain classes): nouns+
prepositions, but * preposition+ adverb (*for loudly);function in a sentence.
The words often lack one or more features.
Слайд 21Modern traditional approaches (2)
Nouns, adjective, pronouns, numerals, verbs, adverbs,
adlinks (the category of state: seem, look), modal words, prepositions,
conjunctions, particles, interjections, articles, response words (yes, no);notional vs. semi-notional.
Слайд 22
Semi-notional parts of speech
very general and comparatively weak lexical meaning
(rare or no substitutes);
unilateral or bilateral combinability (1) articles; 2)
preposition);the functions of linking or specifying.
Слайд 23The latest approach
(form and function)
“A Comprehensive Grammar of the English
Language”;
word classes are the most general categories to which lexical
items can be appropriately assigned (state further subclassification). Слайд 24The latest approach
Closed classed (only exceptionally extended by the creation
of additional members);
Open classes (indefinitely extendable);
Numerals (between open-class and closed-class
items);interjections (a closed class – fully institutionalized and few in number, but are grammatically peripheral);
a small number of words of unique function.
Слайд 25The latest approach
Closed classes: preposition – of, at, in, without,
in spite of; pronoun – he, they, anybody, one, which;
determiner – the, a, that, every, some; conjunction –and, that, when, although; modal verb – can, must, will, could; primary verb – be, have, do);Open classes: noun – John, room, answer, play, adjective – happy, steady, new, large, round, full verb – search, grow, play, adverb – steadily, completely, really;
Numerals – two, three; first, second, third;
Interjections – oh, ah, wow etc;
words of unique function – the negative particle not and the infinitive marker to.
Слайд 26
Disputable points in the parts of speech classification
Nouns, verbs and
their properties are agreed upon by most scientists vs. particles,
modal word are more problematic;Adverbs (a dustbin (F.Palmer), мусорная куча (V.Vinogradov): perfectly vs, again; after all, anyway, actually, etc.
Слайд 27 The theory of field structure of the parts of speech
(V. Admoni)
Each part of speech has units (words) possessing all
the features typical of that parts of speech – the centre of the field;there are unit which have some features only (periphery).
Слайд 28Conclusion
Parts of speech are lexico-grammatical classes of words.
The classification can
be based on various criteria: formal, semantic, functional, or all
of them together.Part of speech are historical variable.
There are problematic points which require solving.