Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The Mordovian female grave of XIIIth century at the Staroselsky cemetery
Содержание
- 1. The Mordovian female grave of XIIIth century at the Staroselsky cemetery
- 2. The Staroselsky cemetery is located within the
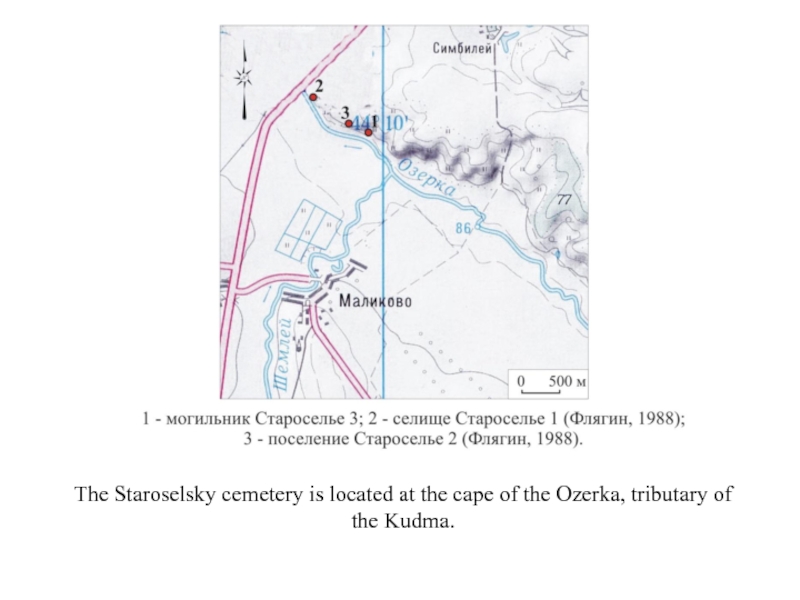
- 3. The Staroselsky cemetery is located at the cape of the Ozerka, tributary of the Kudma.
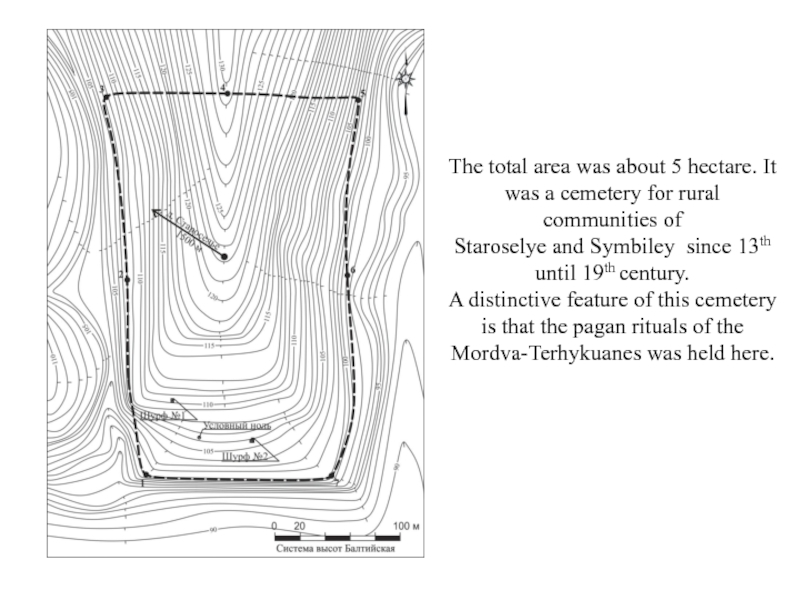
- 4. The total area was about 5 hectare.
- 5. The general viewof the cemetery Scientific studies
- 6. The burial does not have any external
- 7. This Mordovian female grave was found as
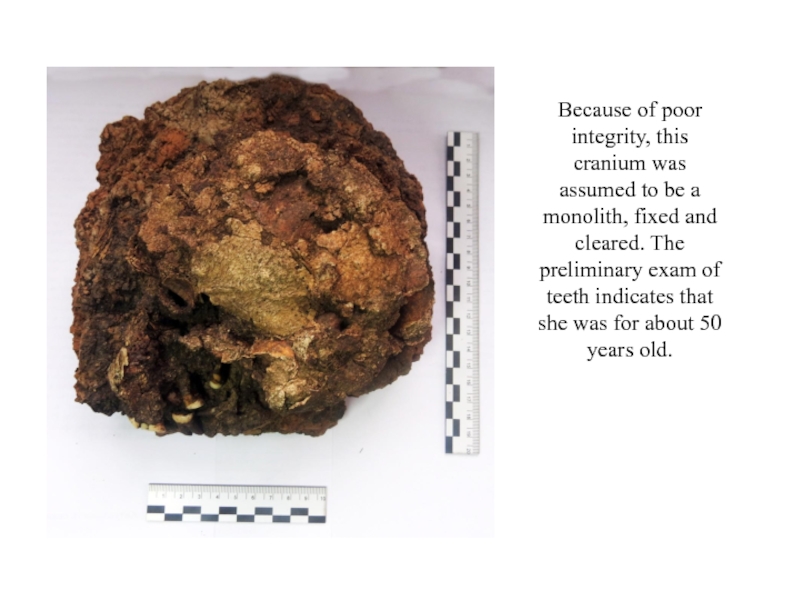
- 8. Because of poor integrity, this cranium was
- 9. The features (body position, ritual implements and
- 10. In the described grave there was fabric
- 11. Analogies in form of such concentration of
- 12. Interpretation of band can be proved by
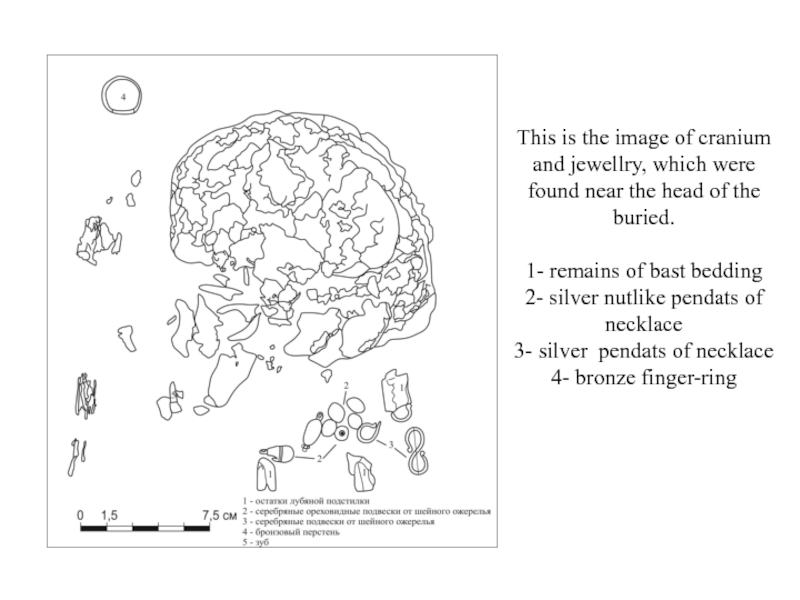
- 13. This is the image of cranium and
- 14. 1 - It’s important to point out
- 15. Quadrifolium silver finger-ring with blackened engraving, decorated by floral-geometric ornament.
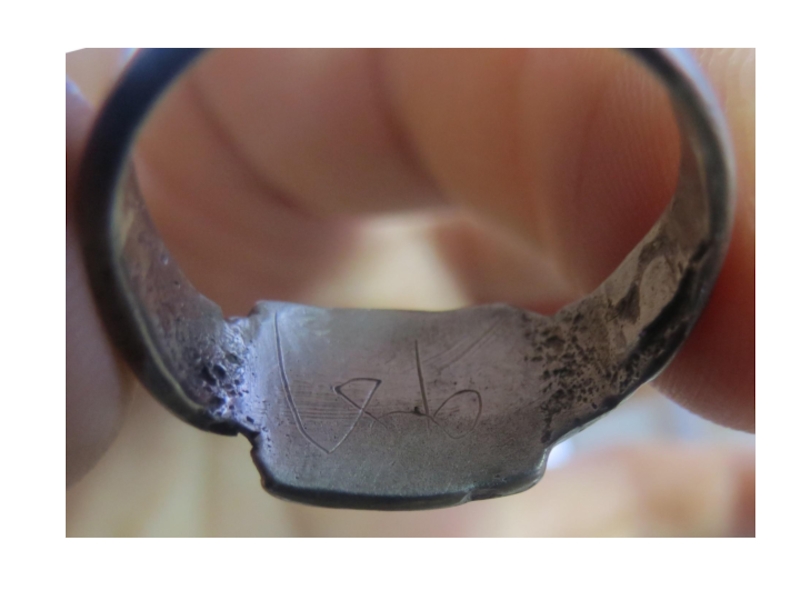
- 16. On the back of this finger-ring there
- 17. On the back of the second silver finger-ring with solar ornament there is a Tamga engraving.
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. The word «tamga» is polysemantic. On the
- 20. The tamga was widespread in 13th-15th. It
- 21. Besides the named artifacts in the grave,
- 22. Thank you for your attention
- 23. Скачать презентанцию
The Staroselsky cemetery is located within the borders of modern Dalnekonstantinovsky municipality in Nizhny Novgorod region, In medieval times, this territory had a dense population of the Mordva-Terhykuan tribe.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2The Staroselsky cemetery is located within the borders of modern
Dalnekonstantinovsky municipality in Nizhny Novgorod region, In medieval times, this
territory had a dense population of the Mordva-Terhykuan tribe.Слайд 4The total area was about 5 hectare. It was a
cemetery for rural communities of
Staroselye and Symbiley since 13th
until 19th century. A distinctive featurе of this cemetery is that the pagan rituals of the Mordva-Terhykuanes was held here.
Слайд 5The general view
of the cemetery
Scientific studies of this archeological
site started in 2016 by an expedition of the Dalnekonstantinovsky
museum of E.V. Chetvertakov.Слайд 6The burial does not have any external characteristics of the
embankment or pits. It was exhumed 90 cm below daylight
surface. The burial was made ritually by inhumation. Poor preservation quality did not let us to reconstruct the height of this woman.Слайд 7This Mordovian female grave was found as a result of
archaeological research at the Staroselsky cemetery in 2017.
It was dated
13th century by the presence of objects there.
Слайд 8Because of poor integrity, this cranium was assumed to be
a monolith, fixed and cleared. The preliminary exam of teeth
indicates that she was for about 50 years old.Слайд 9The features (body position, ritual implements and the orientation of
the head to the north- west) of the burial shown
us that it was a woman. The buried woman lies on the right side in a crooked position with bent knees and hands tied to the face so that her wrists were at the level of the orbits.Слайд 10In the described grave there was fabric used as a
band with successive bronze and silver fibulas.
Color of fiber fabrics
is light brown, the thickness of the threads are 0,5 – 0,6 mm, fibers are smooth, twist of thread - type ZZ.Слайд 11Analogies in form of such concentration of fibulas can be
found in other Mordovian cemeteries, for example, Korinsky cemetery –
Schatkovsky district, Nizhegorodskiy region.Слайд 12Interpretation of band can be proved by the presence of
this element in this 19th century Teryukhan’ female dress, in
which instead of fibulas there were coins.One of the fabric fragments with bronze and silver fibulas.
Слайд 13
This is the image of cranium and jewellry, which were
found near the head of the buried.
1- remains of
bast bedding 2- silver nutlike pendats of necklace
3- silver pendats of necklace
4- bronze finger-ring
Слайд 141 - It’s important to point out nutlike silver pendants
among detected artifacts, decorated with granulation, filigree. Analogies of such
pendants could be found in Volga Bulgar in 12th-13th centuries. 2 – bronze pendant in the shape eight is with remains of the threads, on which it was attached.Слайд 15Quadrifolium silver finger-ring with blackened engraving, decorated by floral-geometric ornament.
Слайд 16On the back of this finger-ring there are remains of
a scratched inscription, which is unreadable and hence not understood.
Слайд 17On the back of the second silver finger-ring with solar
ornament there is a Tamga engraving.
Слайд 19The word «tamga» is polysemantic. On the one hand, it
means tax to the owner of tamga. On the other
hand, tamga is a mark of ownership.Слайд 20The tamga was widespread in 13th-15th. It could be used
for collecting taxes from the local population.
But on the coins
of Bulgar it is also found in combination « the main tamga». The time of coinage of these coins is the first years of Mengu- Timur`s rule- Khan ulus Juchi (Golden Hord)1266-1282. During his reign, the collection of tribute went to the local sovereigns including Mordovian. It is interesting that a gold pendant with a tamga image was found in a female grave 58 in the Saratov region of a Mordovian cemetery dated 13th-14th century on the southern edge of Atkarsk.