Слайд 1Unit 3
Organizations & Behavior
London School of Business and Finance
HND
Слайд 2On successful completion of LO 1 a learner MUST be
able to:
Compare and contrast different organizational structures and culture (AC
1.1)
Explain how the relationship between an organization's structure and culture can impact on the performance of the business ( AC 1.2)
Factors which influences individual behaviour at work( AC.1.3)
Слайд 4Organisations can effective achieve their goals when the following are
in place
Structure
Processes
Procedures
Structure follows strategies
Structure must be flexible
Yahoo failed to make
changes to their organizational structure.
Jerry Young ousted in 2008.
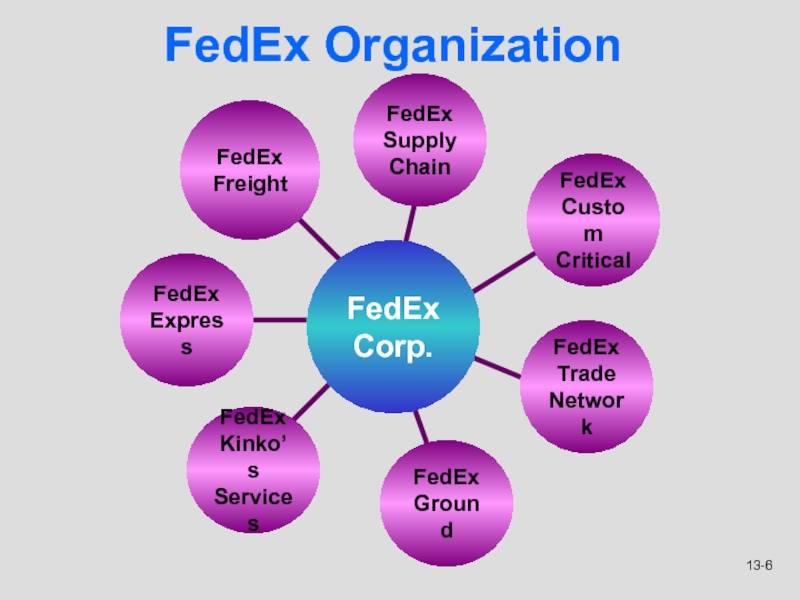
Слайд 5Integrated Portfolio at FedEx
With all the acquisitions by FedEx, there
was a need to change their structure.
It adopted a
multi-divisional structure. Significant authority has been delegated to the divisions. Each division manages its own specialized network of services.
Do you know of other companies that operate in a similar fashion?
Is this a good model for organizations to follow as they grow and develop?
Слайд 6FedEx
Freight
FedEx
Supply
Chain
FedEx
Kinko’s
Services
FedEx
Express
FedEx
Corp.
FedEx
Custom
Critical
FedEx
Trade
Network
FedEx
Ground
FedEx Organization
Слайд 7Types of Organisational structures
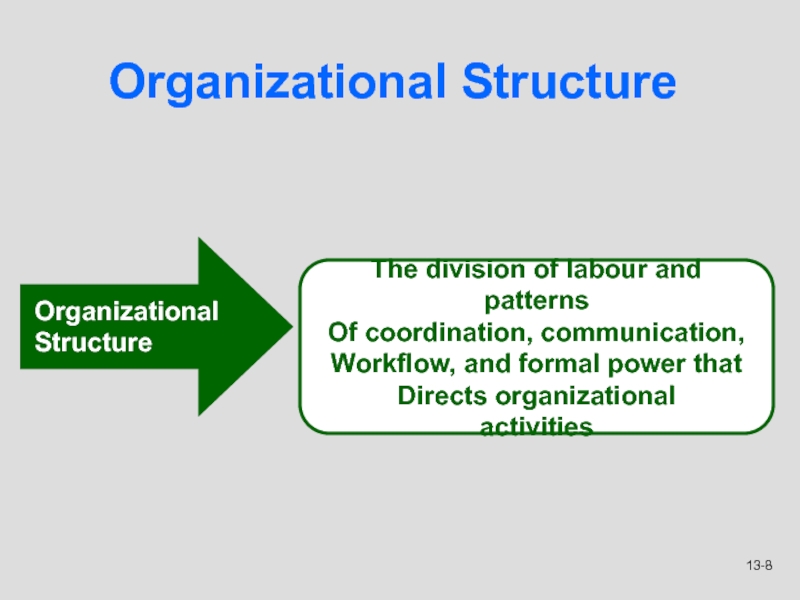
Слайд 8Organizational Structure
The division of labour and patterns
Of coordination,
communication,
Workflow, and formal power that
Directs organizational
activities
Слайд 9
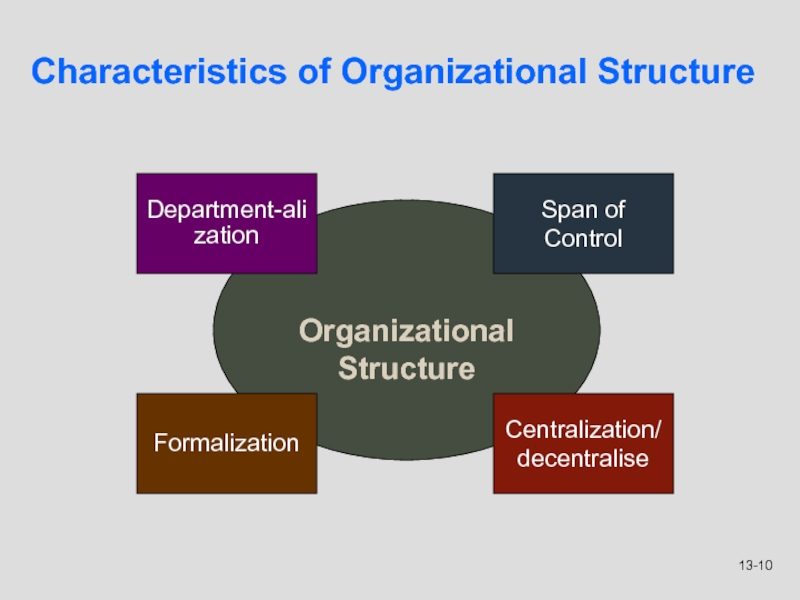
1. The division of tasks ( departmentalisation)
2. The depth of
the hierarchy (span of control);
3. The extent of authority delegation
(how much decentralization or centralisation?)
Formalisation
Four key features of organizational structure:
Слайд 10
Organizational
Structure
Span of Control
Centralization/decentralise
Department-alization
Formalization
Characteristics of Organizational Structure
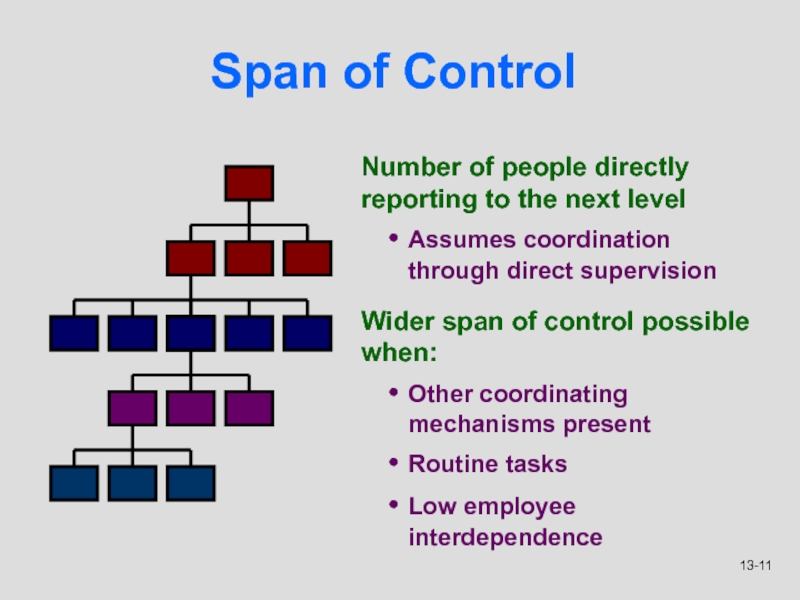
Слайд 11Span of Control
Number of people directly reporting to the next
level
Assumes coordination through direct supervision
Wider span of control possible when:
Other
coordinating mechanisms present
Routine tasks
Low employee interdependence
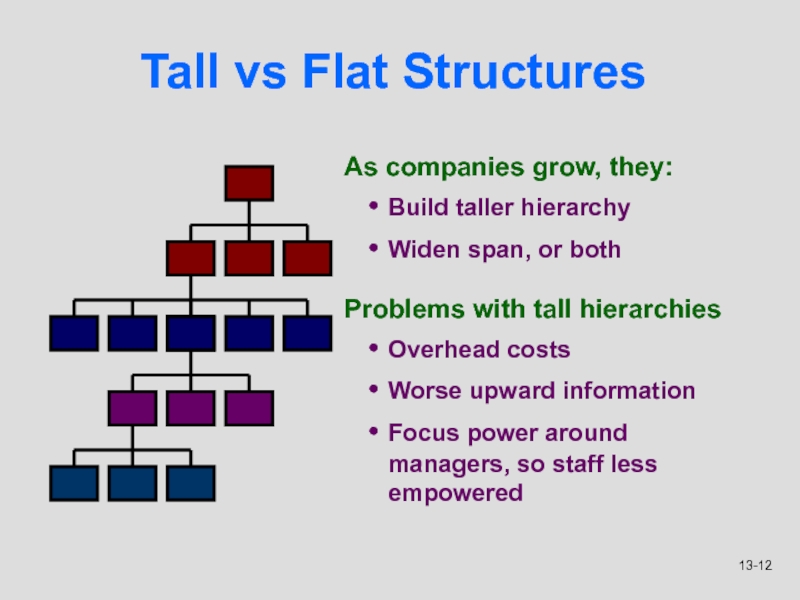
Слайд 12Tall vs Flat Structures
As companies grow, they:
Build taller hierarchy
Widen span,
or both
Problems with tall hierarchies
Overhead costs
Worse upward information
Focus power around
managers, so staff less empowered
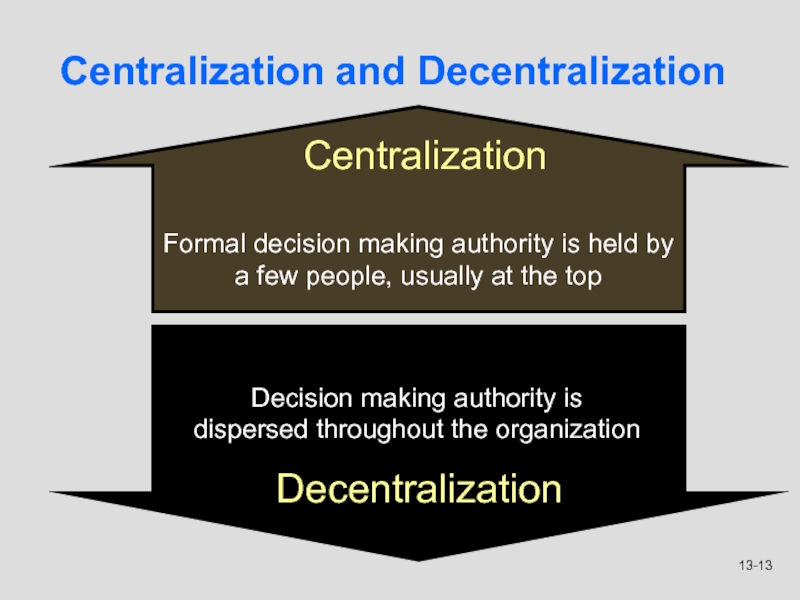
Слайд 13Centralization and Decentralization
Слайд 14Formalization
The degree to which organizations standardize behavior through rules, procedures,
formal training, and related mechanisms.
Formalization increases as firms get older,
larger, and more regulated
Problems with formalization
Reduces organizational flexibility
Discourages organizational learning/creativity
Reduces work efficiency
Increases job dissatisfaction and work stress
Слайд 15Departmentalization
Specifies how employees and their activities are grouped together
Three functions
of departmentalization
Establishes chain of command
Creates common mental models, measures of
performance, etc
Encourages coordination through informal communication
Слайд 16Types of Organizational Structure
Networking Structure
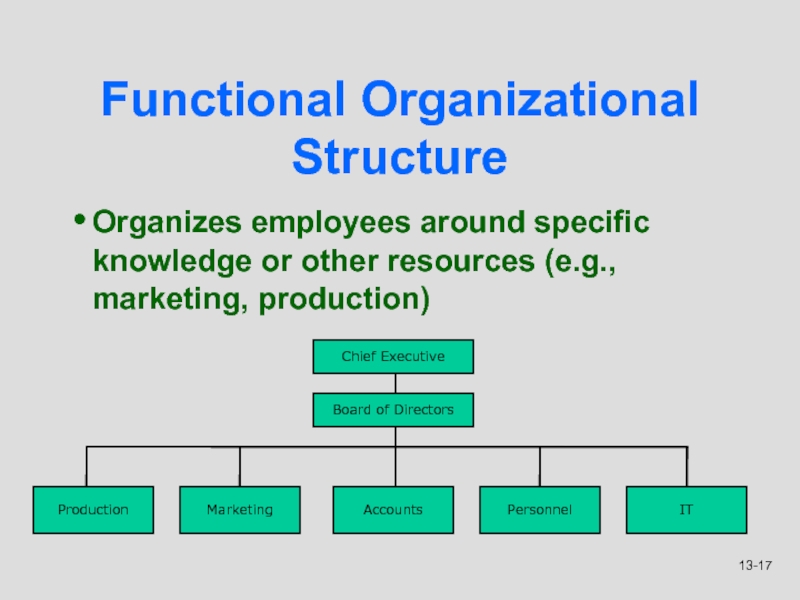
Слайд 17Functional Organizational Structure
Organizes employees around specific knowledge or other resources
(e.g., marketing, production)
Production
Marketing
Accounts
Personnel
IT
Board of Directors
Chief Executive
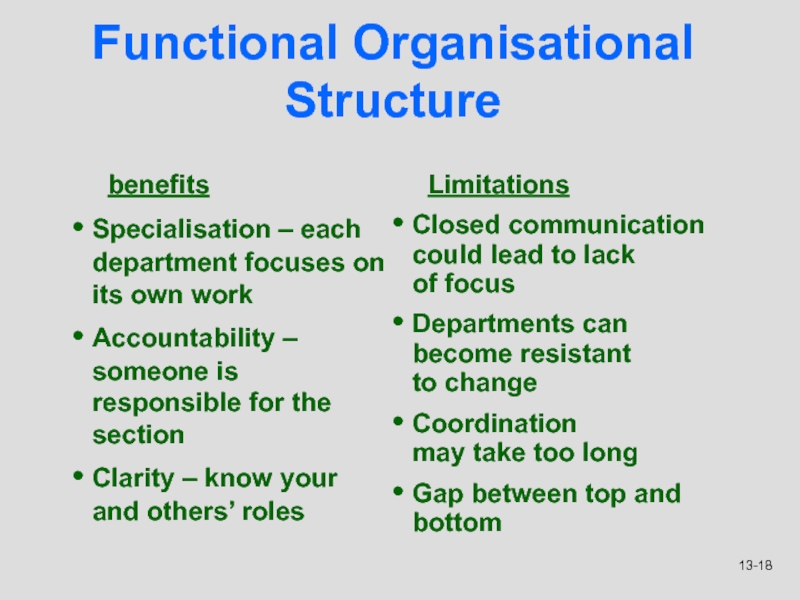
Слайд 18Functional Organisational Structure
benefits
Specialisation – each department focuses on its own
work
Accountability – someone is responsible for the section
Clarity – know
your and others’ roles
Limitations
Closed communication could lead to lack
of focus
Departments can become resistant
to change
Coordination
may take too long
Gap between top and bottom
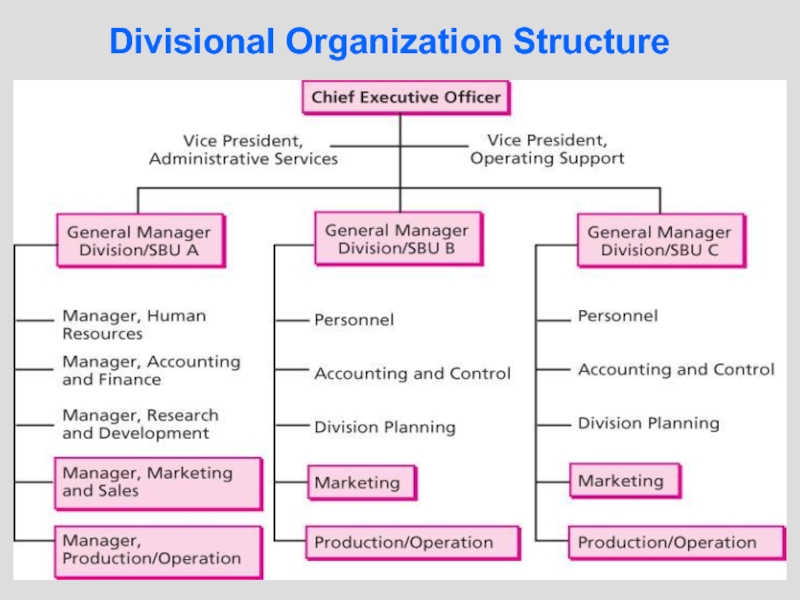
Слайд 19Divisional Organization Structure
Слайд 20Divisional Based Organisational Structures
Benefits
Building block structure -- accommodates growth
Focuses on
markets/products/clients
Limitations
Duplication, inefficient use of resources
Specializations are dispersed--silos of knowledge
Politics/conflict
when two forms of equal value
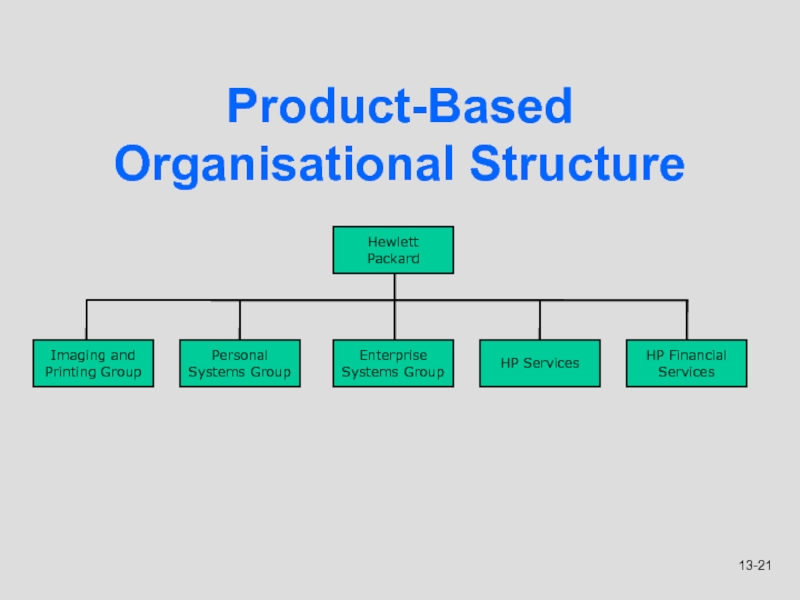
Слайд 21Product-Based Organisational Structure
Imaging and
Printing Group
Personal
Systems Group
Enterprise
Systems Group
HP Services
HP Financial
Services
Hewlett Packard
Слайд 22Product-Based Organisational Structure
Benefits
Clear focus on market segment helps meet customers’
needs
Positive competition between divisions
Better control as each division can act
as separate profit centre
Limitations
Duplication of functions (e.g. different sales force for each division)
Negative effects of competition
Lack of central control over each separate division
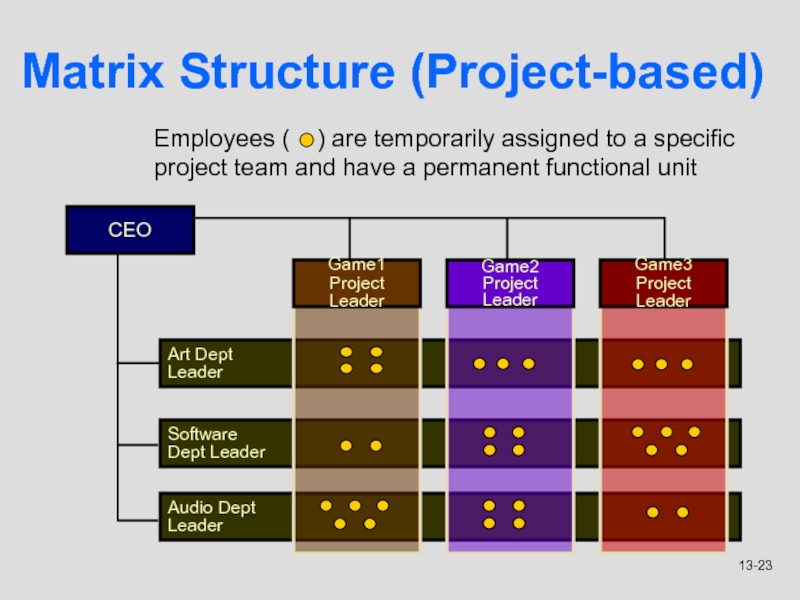
Слайд 23Audio Dept
Leader
Software
Dept Leader
Art Dept
Leader
Matrix Structure (Project-based)
CEO
Слайд 24Matrix Organisational Structures
Benefits
Uses resources and expertise effectively
Improves communication, flexibility, innovation
Focuses specialists on clients and products
Supports knowledge sharing within specialty
Solution
when two divisions have equal importance
Limitations
Increases goal conflict and ambiguity
Two bosses dilutes accountability
More conflict, organizational politics, and stress
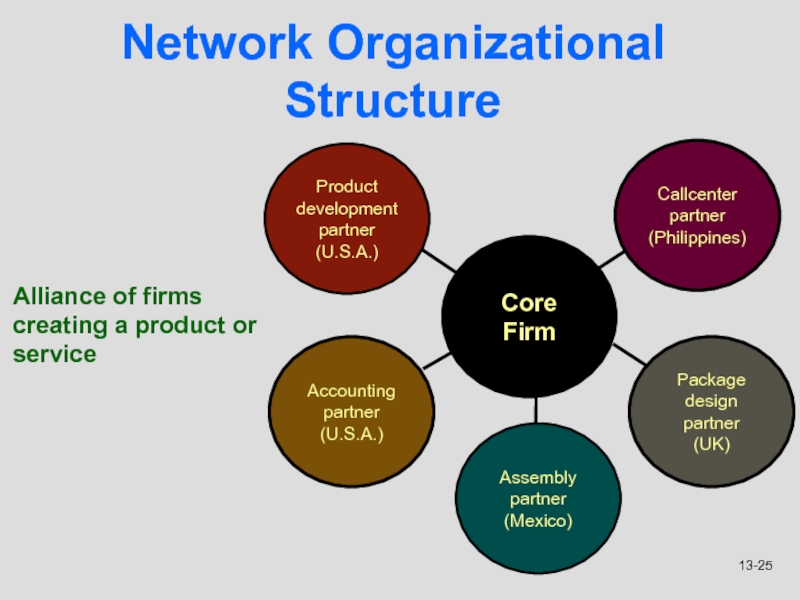
Слайд 25Core
Firm
Product
development partner
(U.S.A.)
Callcenter
partner
(Philippines)
Accounting partner
(U.S.A.)
Package design partner
(UK)
Assembly partner
(Mexico)
Network Organizational Structure
Alliance of firms
creating a product or service
Слайд 26Network organisational Structures
Benefits
Highly flexible
Potentially better use of skills and technology
Not
saddled with same resources for all products
Limitations
Exposed to market forces
Less
control over subcontractors than in-house
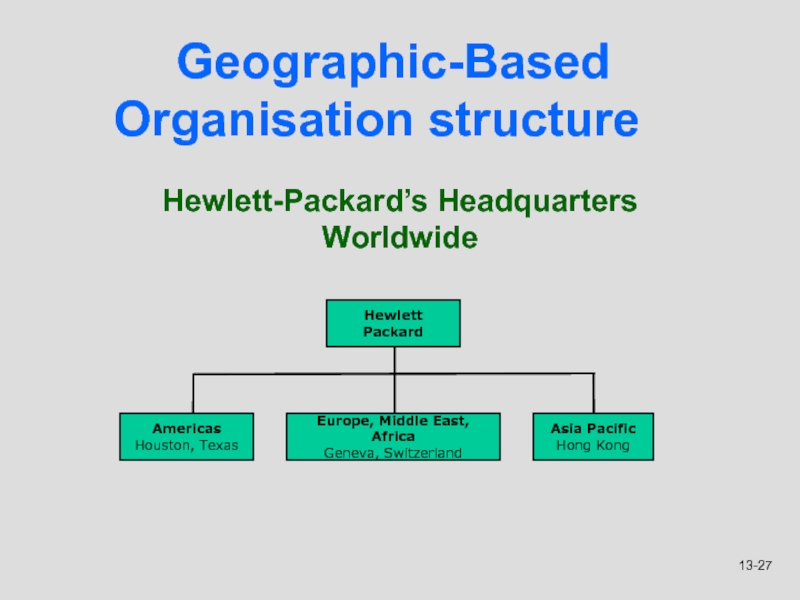
Слайд 27Geographic-Based Organisation structure
Hewlett-Packard’s Headquarters Worldwide
Americas
Houston, Texas
Europe, Middle East, Africa
Geneva, Switzerland
Asia
Pacific
Hong Kong
Hewlett Packard
Слайд 28Geographic-Based Organisation structure
Advantages
Serve local needs better
Positive competition
More effective
communication between firm and local customers
Disadvantages
Conflict between local and
central management
Duplication of resources and functions
Слайд 29Group Activity 1
In your small groups, brainstorm on what factors
could cause an organisation to change it structure or to
adopt a totally different structure? ( 20min)
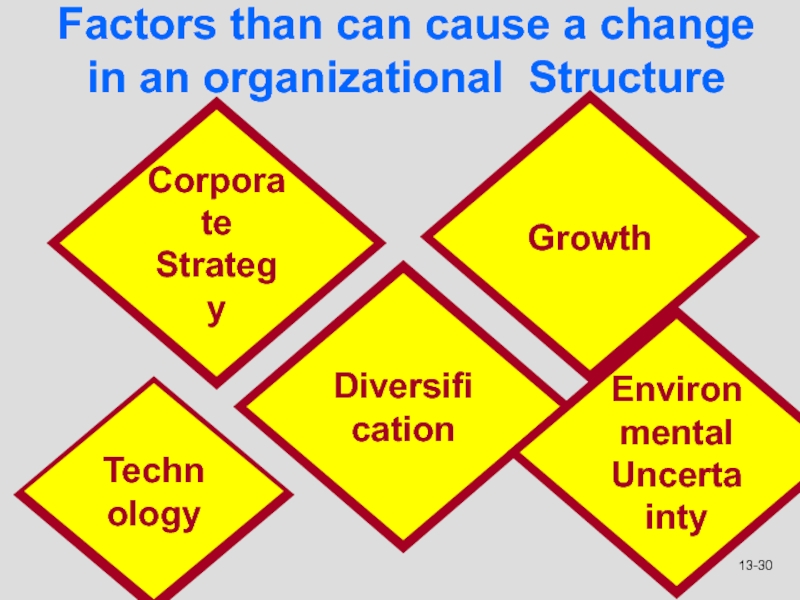
Слайд 30Factors than can cause a change in an organizational Structure
Слайд 31Would the following cause a structural change within an organisation?
A
change in the key individuals
A failure to meet goals
An inability
to get things done
An increase in overseas customer complaints
Personality clash in same department
Слайд 32How structure and culture impacts on business performance
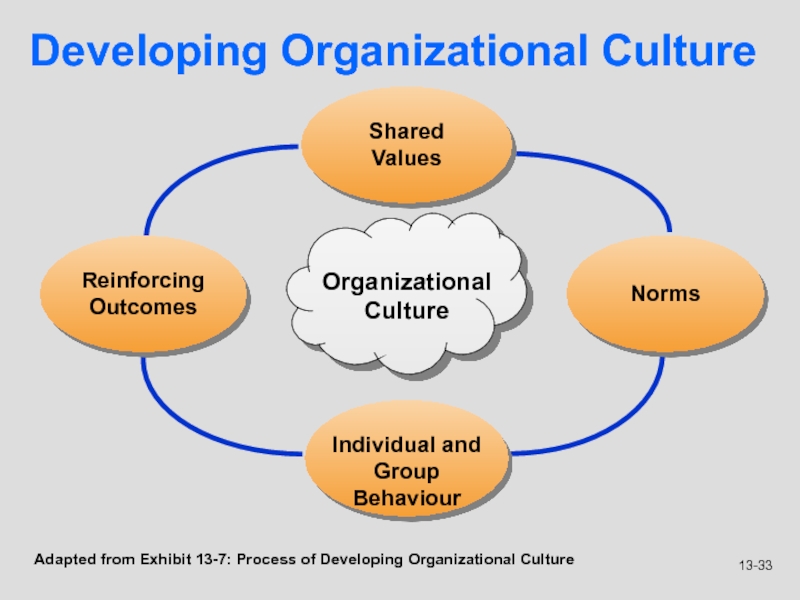
Слайд 33Developing Organizational Culture
Adapted from Exhibit 13-7: Process of Developing Organizational
Culture
Слайд 34Where Do Organizational Cultures Come From?
Founder imprinting
Founders defined and shaped
the culture
Apple (Steve Jobs)
Disney (Walt Disney)
Microsoft (Bill Gates)
Wal-mart’s “low cost”
culture by Sam Walton
Recruit people that fit the culture
Zappos vs. Genentech
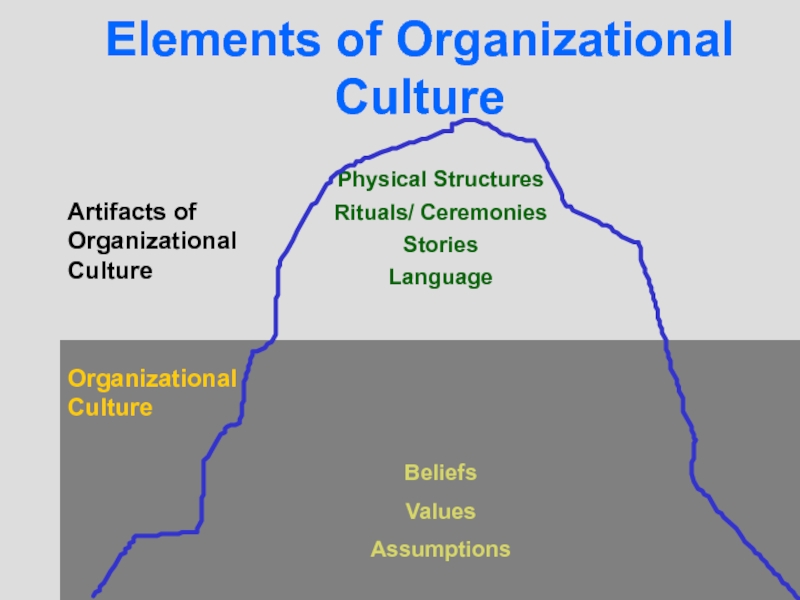
Слайд 35Physical Structures
Rituals/ Ceremonies
Stories
Language
Beliefs
Values
Assumptions
Artifacts of
Organizational
Culture
Organizational
Culture
Elements of Organizational Culture
Слайд 36Courtesy of Oakley, Inc.
Artifacts: Physical Structures/Space
Courtesy of Oakley, Inc.
Слайд 37Courtesy of Oakley, Inc.
Artifacts: Physical Structures/Space
Courtesy of Oakley, Inc.
Слайд 38Organizational Culture Defined
The basic pattern of shared assumptions, values, and
beliefs considered to be the correct way of thinking about
and acting on problems and opportunities facing the organization.
© Reuters/New media, Inc./ CORBIS
Слайд 39Williams, Dobson and Walters
Williams et al (1989) redefined the four
categories listed by Harrison and Handy as follows:
Power orientation
Role orientation
Task
orientation
People orientation
Слайд 40Power orientation
Power culture is when one person has control over
everything that goes on within the organisation.
There are central
powerful figure, very few rules and systems in, fast decisions, and personal communications.
An example of this would be Sir Alan Sugar’s organisation, where he is the central powerful figure, and he does not relinquish and control. He makes all of the decisions, like employees’ wages, how much time employees are allowed for their holidays, who gets employed, who is made redundant and what products are sold.
Слайд 41Role Orientation
Role culture is based on structure, with more rules
to abide by and bureaucracy.
Work is decided via rules
and regulations.
Power is a based on level in a hierarchy, i.e. your job position. For example a manager would have more power than a supervisor.
People work to a job description. This means that not just one person has control over the whole business, but a number of people who have important job positions will also have important decisions to make depending on their job role.
Слайд 42Task orientation
Task culture is all about teamworking, when people come
together to form a team in order to work on
a project.
This means that people in the teams will have different skills to use in the project.
No one has greater position over anyone in this type of culture as people will have different skills to use together in order to get the project completed.
The task is key, rather than the individual or rules
London 2012 Olympics adapt task culture as a lot of people are working together in order to get the project completed. After the task is over, they will probably never work together again.
Слайд 43Person orientation
Person culture is the individual person is the focus
of the business, and has the authority to make all
decisions regarding specific tasks and or activities.
The person will be using their own expertise to complete he task. There is no hierarchy, and the organisation only exists to serve the interests of those within it.
Examples include barristers, architects, doctors and surgeons. A doctor is his own boss and completes the work at his own pace, without being told what to do.
Слайд 44Activity 1- FedEx Culture Attracts
High-Quality Associates
Do you think FedEx
would have enjoyed its success had a different type of
culture been introduced?
Suggest any organization that could benefit with a similar culture?
As FedEx continues to grow, will the culture survive or will it possibly be replaced by a more traditional culture?
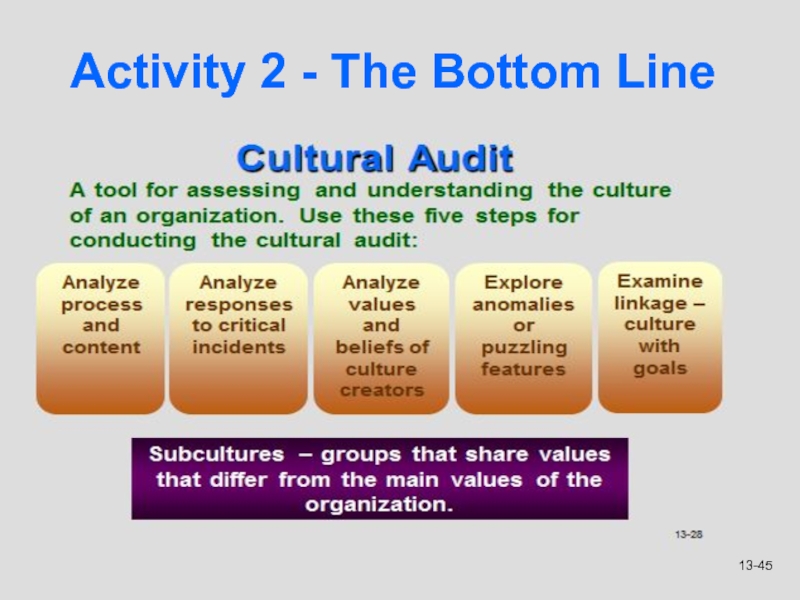
Слайд 46Relationship between Structure and Culture
Read case study article
Make individual comments
(20 min class reading and sharing comments)
Слайд 47Organizational Culture and impact on business
Cultural impact on employee behavior
Motivates
employees by appealing to their ideas
Strengthen employee commitment, engagement, and
effort
Culture is vital to an organization
Stronger founder imprinting leads to higher performance
Effective alignment allows development and refines organizational core competency
Слайд 48Organisational structure and impact on performance of the business
Specialization -
higher productivity & less satisfaction
-But: Individual differences &
differences in types of task!
-The higher educated, the less satisfaction from specialized job
No supported relationship between span of control and performance
-Some people like to work alone
-Some people prefer security of boss available
-Manager s satisfaction increases with number of subordinates
Слайд 49Links of Structures With Employee
Performance & Satisfaction
Performance & Satisfaction
Centralization
linked with job satisfaction
-Less centralized organizations - more
participatory decision making - more satisfaction
Again dependent on individual characteristics
Слайд 50Factors which influences individual behaviour at work( AC.1.3)
Слайд 51Some factors impacting on human behaviour…..
Personality traits
Self-awareness
Self-esteem
Skills & Knowledge
Experience
Ambition
Passion
Trust
Cultural background
Social
background
Views & attitudes
Personal Values
Confidence &Self-worth
Position Power
Response to pressure
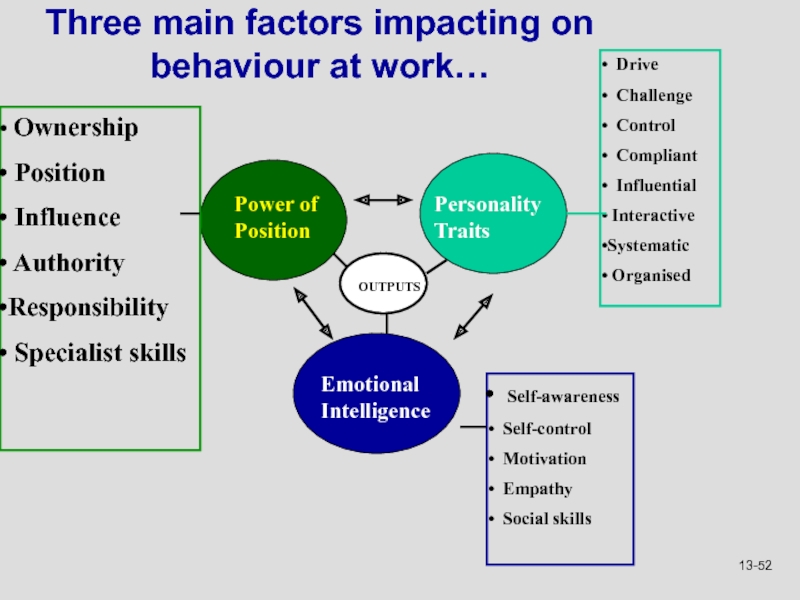
Слайд 52Three main factors impacting on behaviour at work…
OUTPUTS
Power of
Position
Personality Traits
Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness
Self-control
Motivation
Empathy
Social skills
Drive
Challenge
Control
Compliant
Influential
Interactive
Systematic
Organised
Ownership
Position
Influence
Authority
Responsibility
Specialist skills
Слайд 53Case study 1
This case involved a personality clash between two
senior employees who were working under a partnership arrangement. Both
had joint responsibility for managing a team made up from practitioners from each organisation. The conflict between them was beginning to threaten the success of the partnership.
Question: what personality traits could be inhibiting their working together?
Слайд 54Case study 2
Both Jessica and Alan have been working alongside
one another for many years at the local newspaper. As
their existing manager leaves the company, Alan is promoted, but still shares an office with the team, of which he used to be a member. Tensions arise when Alan decides to introduce a new policy, which makes little sense to the rest of the team and is likely to increase their already heavy workload.
What could have ignited the disagreement?
Слайд 55 I’m Not Crazy….
I’m Just Not You!!
Слайд 56Welcome to Myers-Briggs Personality Type
Every students is expected to use
either a computer in the library,
personal internet on smart
phones to conduct the Myers Briggs
personality test and bring their results to class in 20mins.
Type Myers Briggs Test in Google.
Слайд 58Activity 1 –
What is YOUR Myers Briggs Type ??
In small groups discuss how your personality types influences your
work-life outcomes