Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Южный Федеральный Университет Инженерно-технологическая академия Институт
Содержание
- 1. Южный Федеральный Университет Инженерно-технологическая академия Институт
- 2. ContentsGlossaryTechnology in BriefMethodologyState-of-the-Art and Open IssuesIndustry Leaders & StartupsBibliography
- 3. GlossaryThe following are the must-know terms regarding
- 4. Technology in brief3D printing, also known as
- 5. Technology in briefA time-lapse of a gripper
- 6. MethodologyStereolithography is a 3D-printing technique that uses
- 7. State-of-the-Art and Open Issues 4D printing is a
- 8. Industry Leaders & StartupsSince 4D printing is
- 9. Bibliographyhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Four-dimensional_printinghttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_printinghttps://all3dp.com/1/4d-printing/Al-Rodhan, N. “Design Within Reach: Preparing for the 4D-Printing Revolution” – 2014
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Скачать презентанцию
ContentsGlossaryTechnology in BriefMethodologyState-of-the-Art and Open IssuesIndustry Leaders & StartupsBibliography
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Южный Федеральный Университет
Инженерно-технологическая академия
Институт Компьютерных технологий
и информационной безопасности
Кафедра Вычислительной
техники
Слайд 2Contents
Glossary
Technology in Brief
Methodology
State-of-the-Art and Open Issues
Industry Leaders & Startups
Bibliography
Слайд 3Glossary
The following are the must-know terms regarding 4D-Printing:
3D-printing – any
of various processes in which material is joined or solidified
under computer control to create a three-dimensional object, with material being added together;4D-Printing – mostly same as 3D-printing, with an additional 4th dimension being transformation over time;
Programmable matter – special materials that have the ability to change their physical properties (shape, density, moduli, conductivity, optical properties, etc.) in a programmable fashion, based upon user input or autonomous sensing.
Слайд 4Technology in brief
3D printing, also known as “Additive Manufacturing”, turns
digital blueprints to physical objects by building them layer by
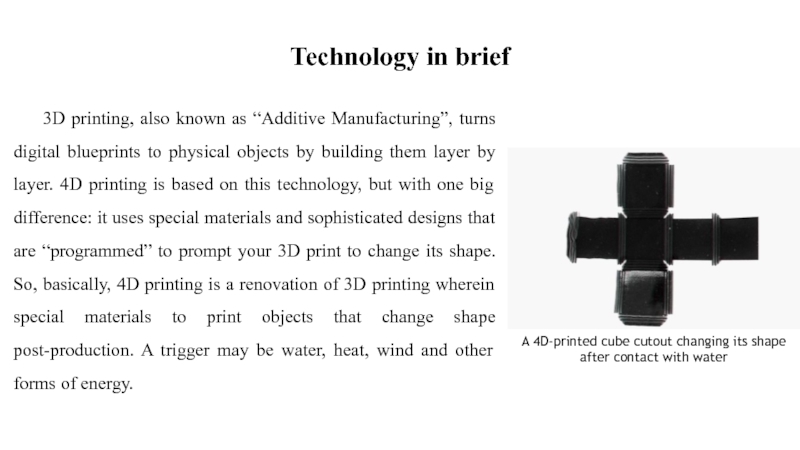
layer. 4D printing is based on this technology, but with one big difference: it uses special materials and sophisticated designs that are “programmed” to prompt your 3D print to change its shape. So, basically, 4D printing is a renovation of 3D printing wherein special materials to print objects that change shape post-production. A trigger may be water, heat, wind and other forms of energy.A 4D-printed cube cutout changing its shape after contact with water
Слайд 5Technology in brief
A time-lapse of a gripper developed for grabbing
and releasing an object.
The ability to change shape arises from
the near infinite configurations at a micrometer resolution, creating solids with engineered molecular spatial distributions and thus allowing unprecedented multifunctional performance. 4D printing is a relatively new advance in biofabrication technology, rapidly emerging as a new paradigm in disciplines such as bioengineering, materials science, chemistry, and computer sciencesСлайд 6Methodology
Stereolithography is a 3D-printing technique that uses photopolymerization to bind
substrate that has been laid layer upon layer, creating a
polymeric network. As opposed to fused-deposition modeling, where the extruded material hardens immediately to form layers, 4D printing is fundamentally based in stereolithography, where in most cases ultraviolet light is used to cure the layered materials after the printing process has completed. Anisotropy is vital in engineering the direction and magnitude of transformations under a given condition, by arranging the micromaterials in a way so that there is an embedded directionality to the finished print.Слайд 7State-of-the-Art and Open Issues
4D printing is a relatively new advancement
in technology. As of now, it is most commonly applied
in architecture and biomedical studies.There are, however, some existing techniques/technologies that could potentially be applied and adjusted for 4D printing. They include Cell Traction Force, Electrical and Magnetic Smart Materials, as well as Commerce and transportation.
Слайд 8Industry Leaders & Startups
Since 4D printing is a relatively new
advancement in technology, it’s not fully commercial yet.
At the
moment, the industry leaders mostly are colleges such as MIT and University of Bayreuth.Research teams are still developing new approaches and methods of using 4D-printing.