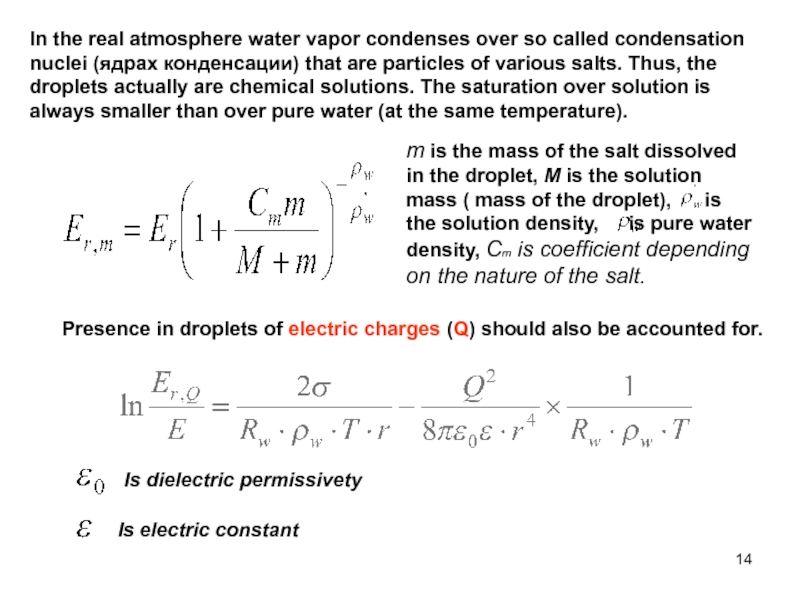
there is one particular one the people call “TSAREVNA’S TEARS”.
That is the rain which can not be named by any other name but this.The drops of this rain look larger than usual raindrops, They seem to fall slower from a small cloud. The Sun shinning from a side and reflecting from the drops makes them as if they are made with gold. Being transparent, they bear blue color from that part of the sky which is not covered with clouds.
Gold and blue combination makes them so beautiful that the name “ tsarevna’s tears” seems to be the most appropriate name for this rain.