Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Software Engineering
Содержание
- 1. Software Engineering
- 2. Model of the software life cycleMajor software
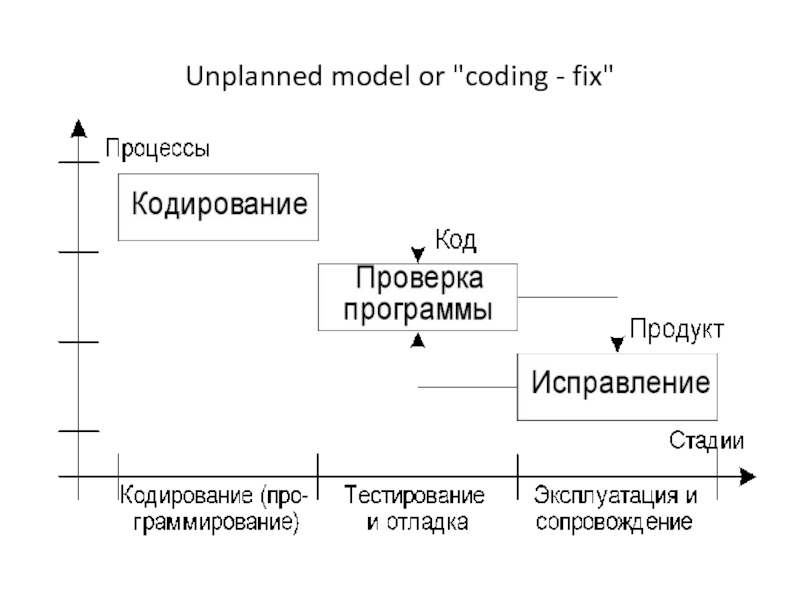
- 3. Unplanned model or "coding - fix"
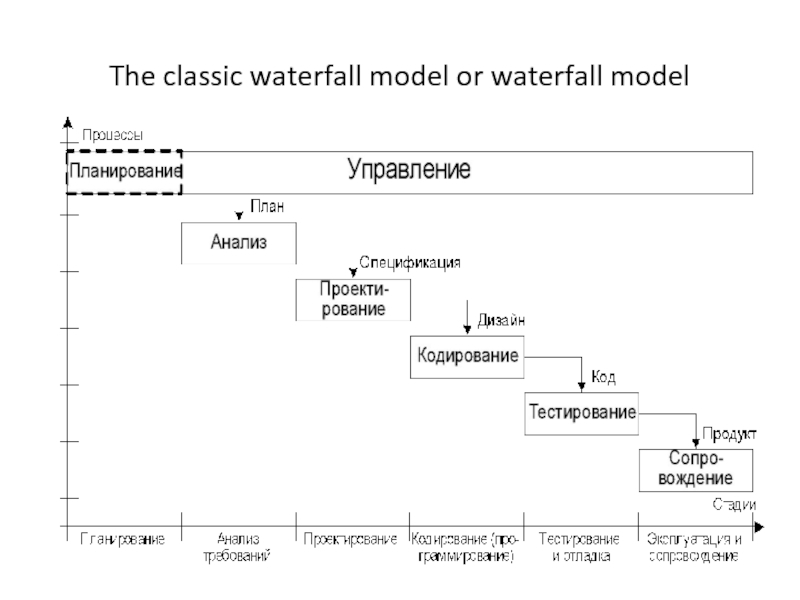
- 4. The classic waterfall model or waterfall modelThe
- 5. The classic waterfall model or waterfall model
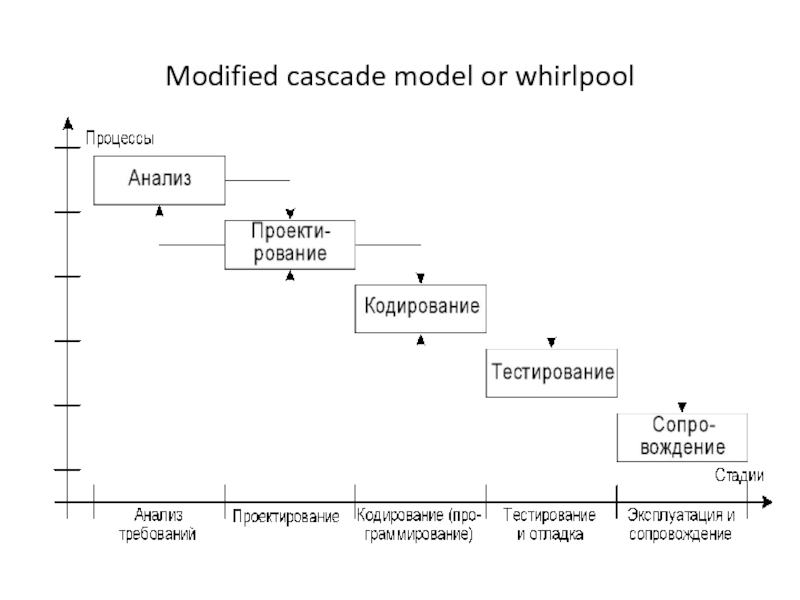
- 6. Modified cascade model or whirlpoolIn practice, the
- 7. Modified cascade model or whirlpool
- 8. Prototipiruemaya model or prototypePrototipiruemaya model or prototype
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Скачать презентанцию
Model of the software life cycleMajor software life cycle models are: The cascade model, Iterative incremental model The evolutionary model Spiral Model. Unplanned model or "coding -