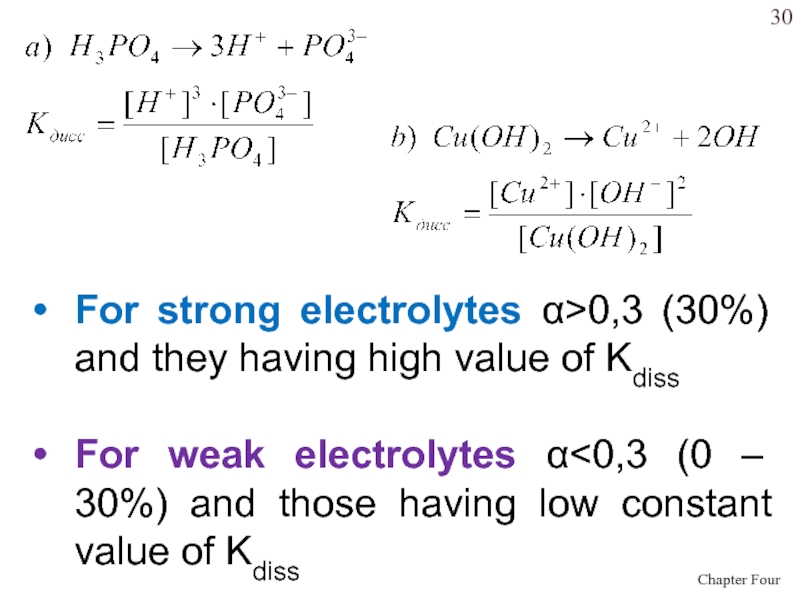Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Aqueous Solutions of Electrolytes
Содержание
- 1. Aqueous Solutions of Electrolytes
- 2. LESSON OBJECTIVES:Concept of electrolytesDefine electrolyte, electrolytic solution,
- 3. Electrolytes Substances which on dissolution, even at
- 4. In the world of chemistry, an electrolyte
- 5. Pure water does not conduct an electric
- 6. Unlike charges (+ and –) attract
- 7. Electric current is a movement or flow
- 8. Ions are atoms (or groups of atoms)
- 9. Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions
- 10. Electrical Conductivity of Ionic Solutions
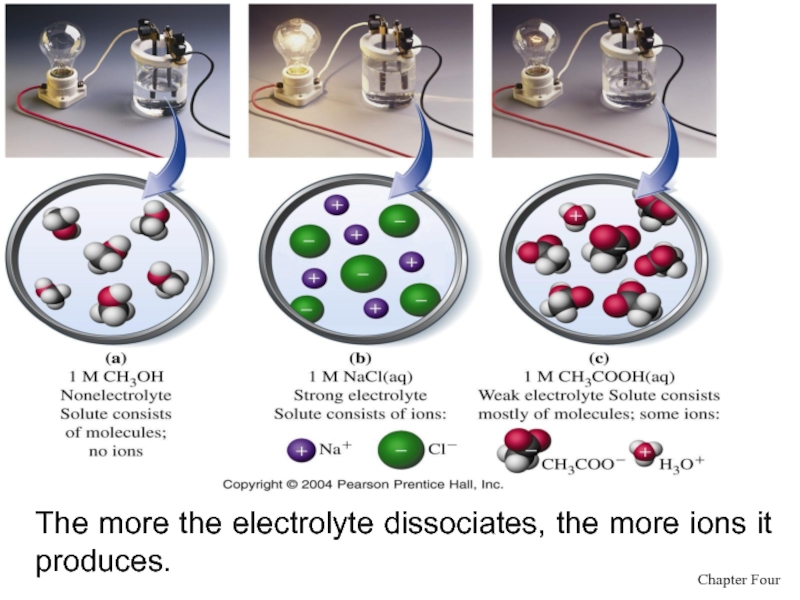
- 11. The more the electrolyte dissociates, the more ions it produces.
- 12. TYPES OF ELECTROLYTES A weak electrolyte dissociates partially.Weak
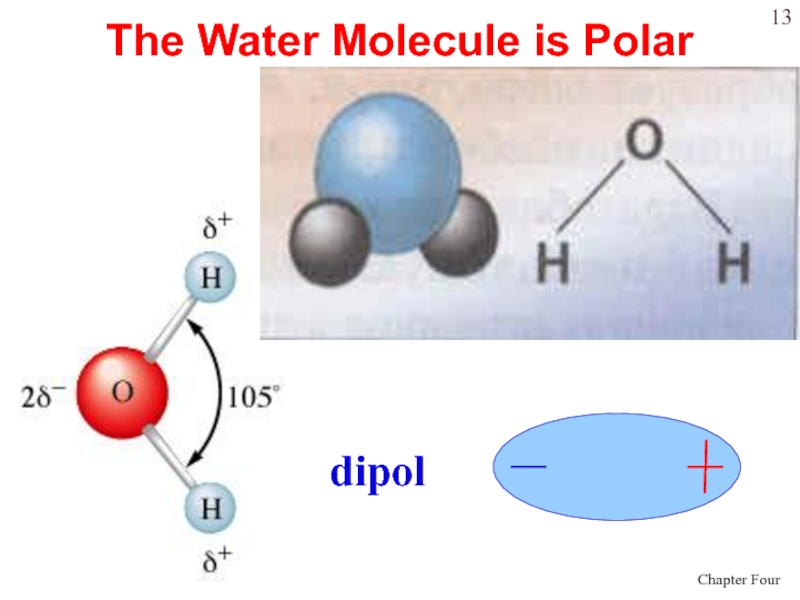
- 13. The Water Molecule is Polardipol
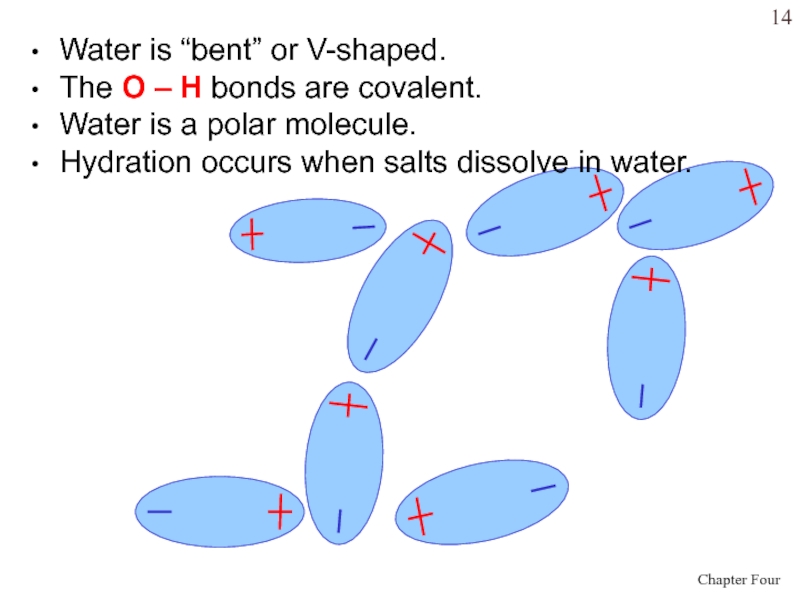
- 14. Water is “bent” or V-shaped.The O –
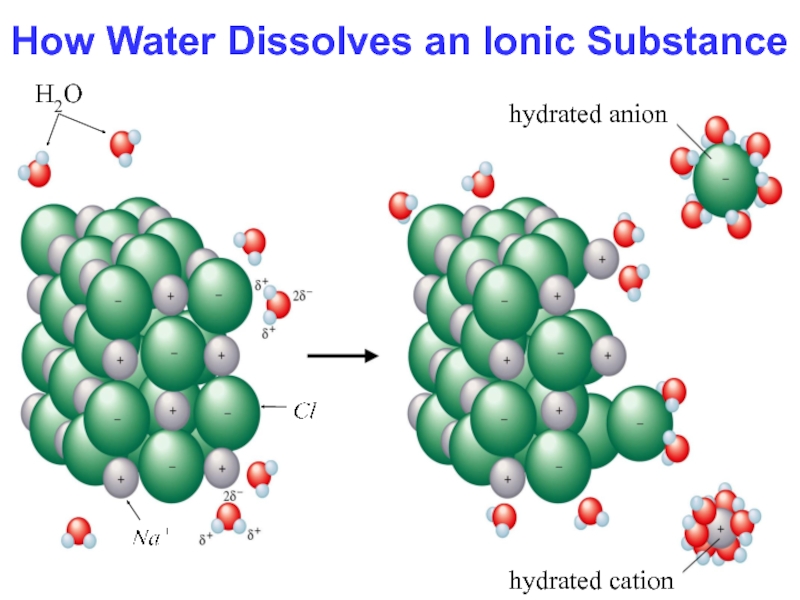
- 15. How Water Dissolves an Ionic SubstanceH2Ohydrated cationhydrated anion
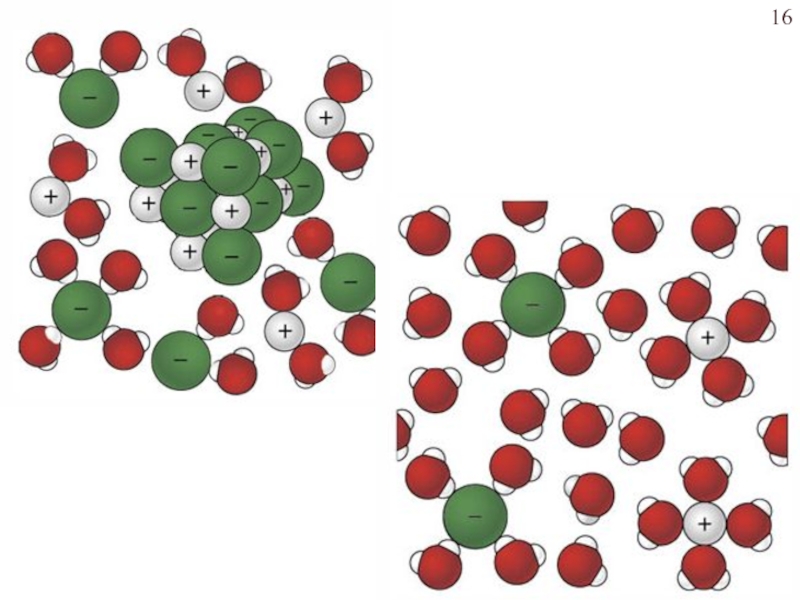
- 16. Слайд 16
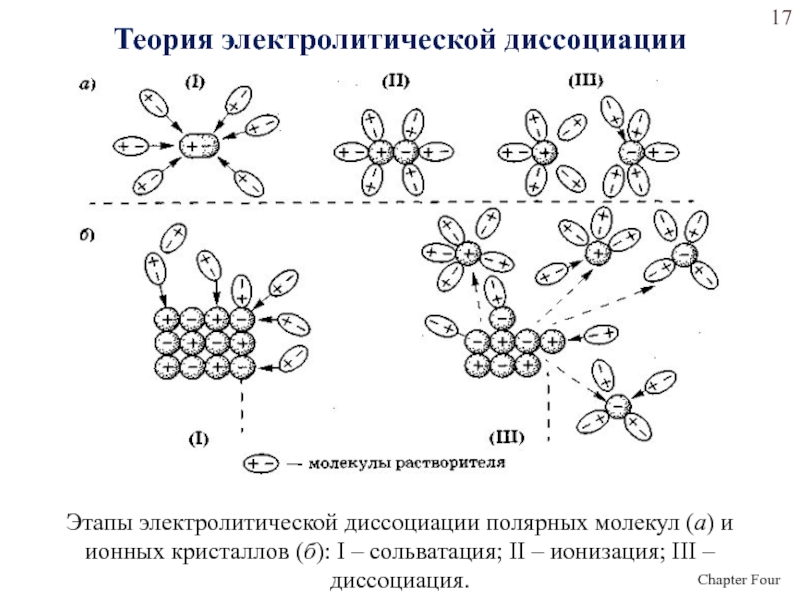
- 17. Этапы электролитической диссоциации полярных молекул (а) и
- 18. In order to explain the properties of
- 19. THE MAIN POINTS OF THE THEORY ARE:An
- 20. The properties of electrolytes in solution are
- 21. An acid is a substance that increase
- 22. Strong acids are strong electrolytes; completely ionized
- 23. A base is a substance that increase
- 24. Strong bases: Most are ionic hydroxides (Group
- 25. Common Strong Acids and Strong BasesA pragmatic
- 26. Strength and properties of the electrolyte are
- 27. Values of the degree of dissociation (ex)depends
- 28. When temperature is increased, degree of ionization
- 29. Dissociation is reversible process. Ions present in
- 30. For strong electrolytes >0,3 (30%) and they having high value of Kdiss For weak electrolytes
- 31. OSTWALD'S DILUTION LAWFor strong electrolytes:where K is
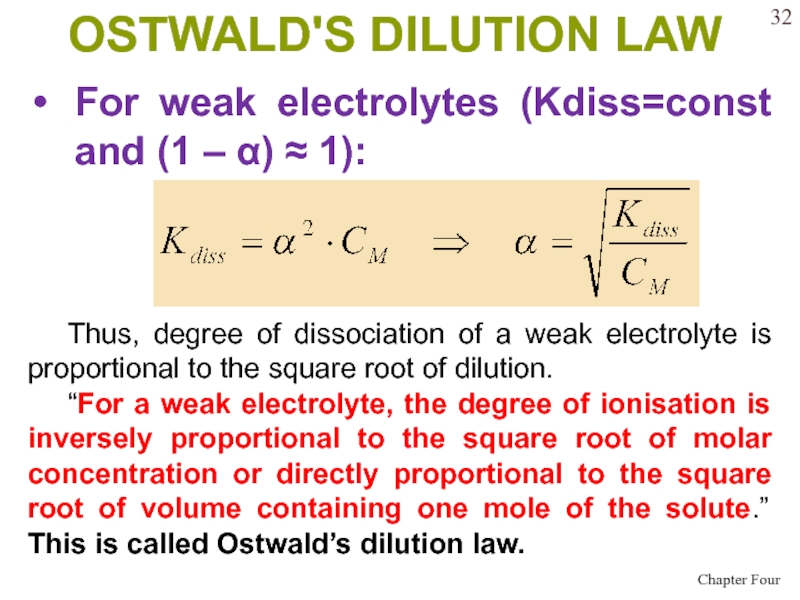
- 32. OSTWALD'S DILUTION LAWFor weak electrolytes (Kdiss=const and
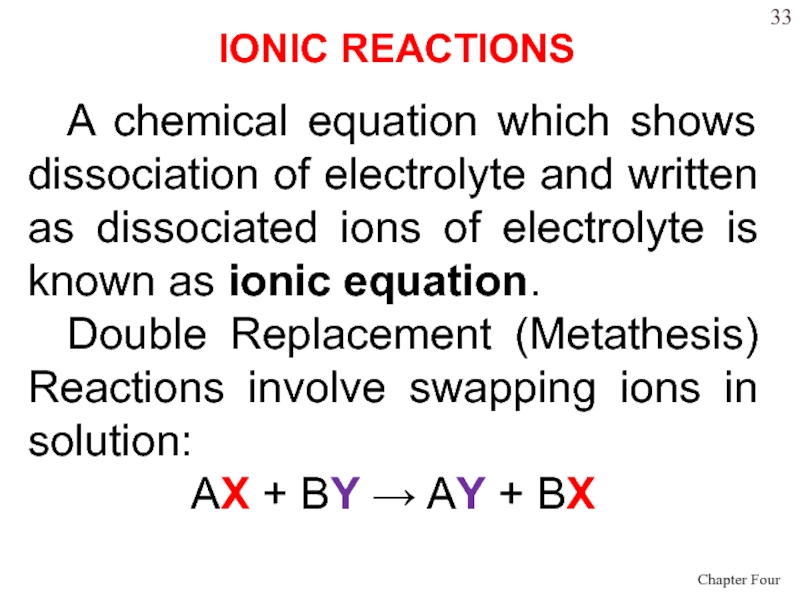
- 33. A chemical equation which shows dissociation of
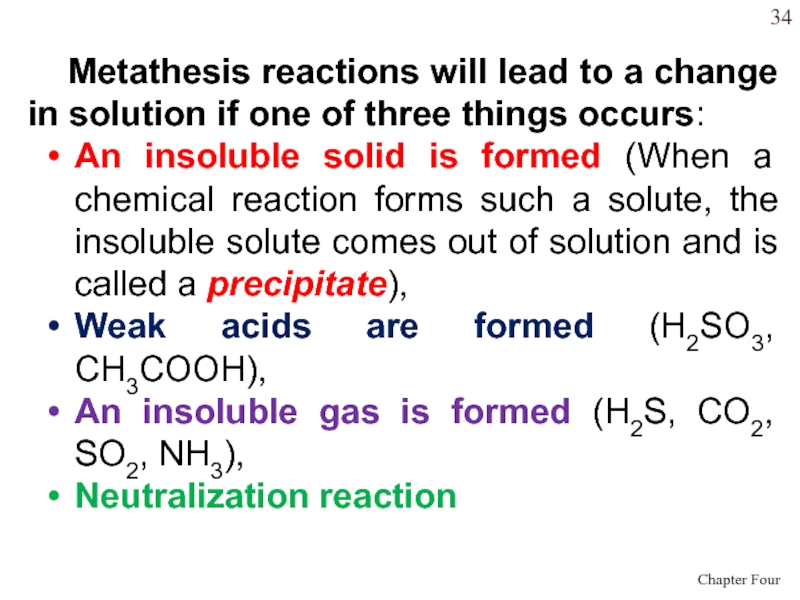
- 34. Metathesis reactions will lead to a change
- 35. Irreversible reactionPrecipitate(↓)BaCl2 + Na2SO4 = BaSO4 ↓
- 36. Neutralization is the (usually complete) reaction of
- 37. In the reaction above, the HCl, NaOH,
- 38. There are limits to the amount of
- 39. Silver Iodide PrecipitationA solution containing silver ions
- 40. With these guidelines we can predict precipitation
- 41. Слайд 41
- 42. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2LESSON OBJECTIVES:
Concept of electrolytes
Define electrolyte, electrolytic solution, ion, cation, anion
Arrhenius
theory of electrolytic dissociation
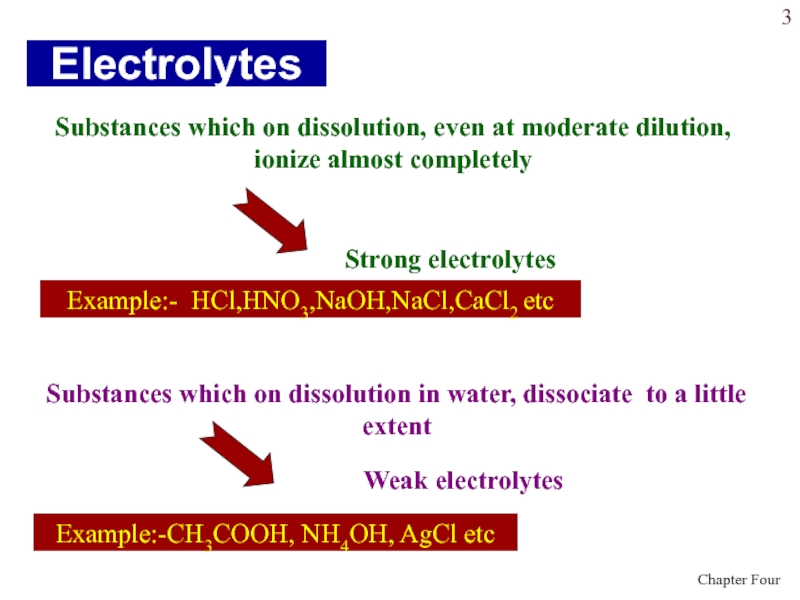
electrolyte solutionsСлайд 3Electrolytes
Substances which on dissolution, even at moderate dilution, ionize
almost completely
Substances which on dissolution in water, dissociate to a
little extentStrong electrolytes
Example:- HCl,HNO3,NaOH,NaCl,CaCl2 etc
Weak electrolytes
Example:-CH3COOH, NH4OH, AgCl etc
Слайд 4 In the world of chemistry, an electrolyte is a substance
having the free ions so that the substance is electrical
conductor. We can say that any substance, which furnishes ions in the solution, is called the electrolyte.Due to the presence of free ions some of the solutions can pass electricity through them. As we can say that the pure distilled water is not an electrolyte but if we add some table salt, it becomes an electrolyte and the electric current pass through it.
The electrolyte is an ionic solution but the electrolytes can also be in molten and in the solid state.
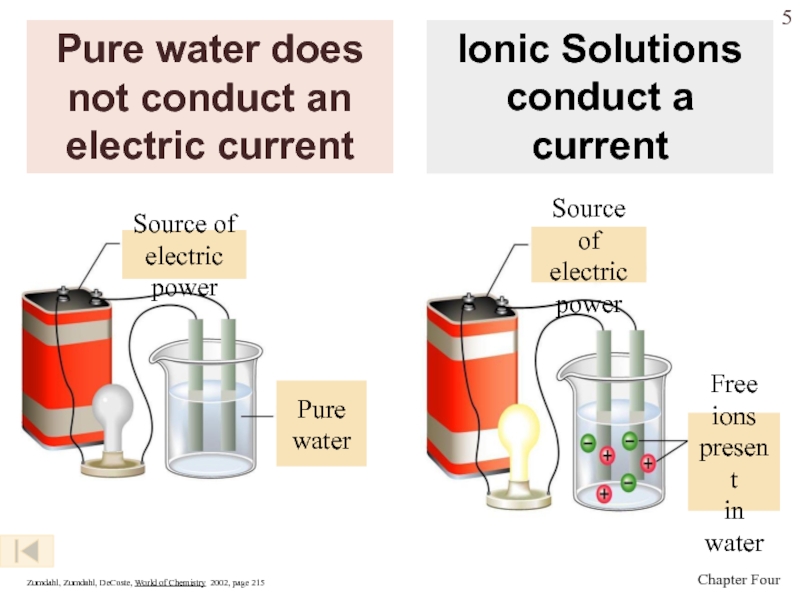
Слайд 5Pure water does not conduct an electric current
Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste,
World of Chemistry 2002, page 215
Ionic Solutions conduct a current
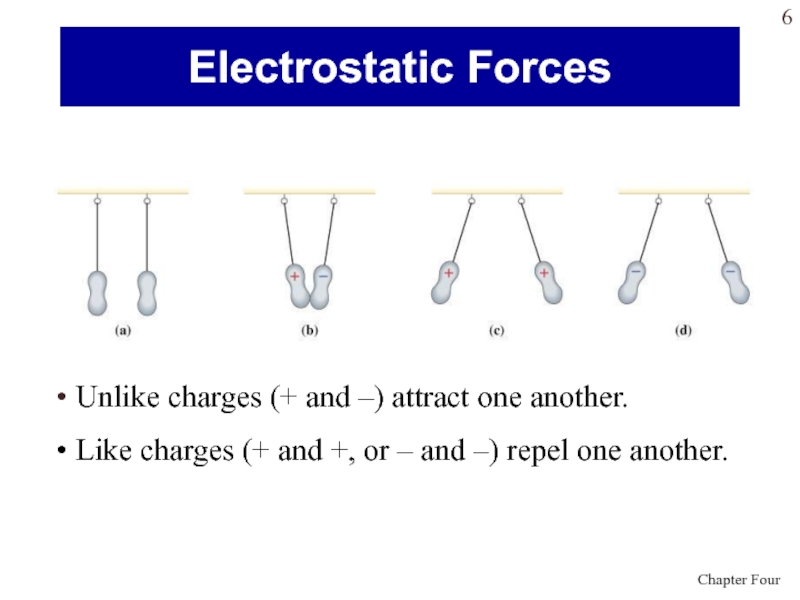
Слайд 6 Unlike charges (+ and –) attract one another.
Like
charges (+ and +, or – and –) repel one
another.Electrostatic Forces
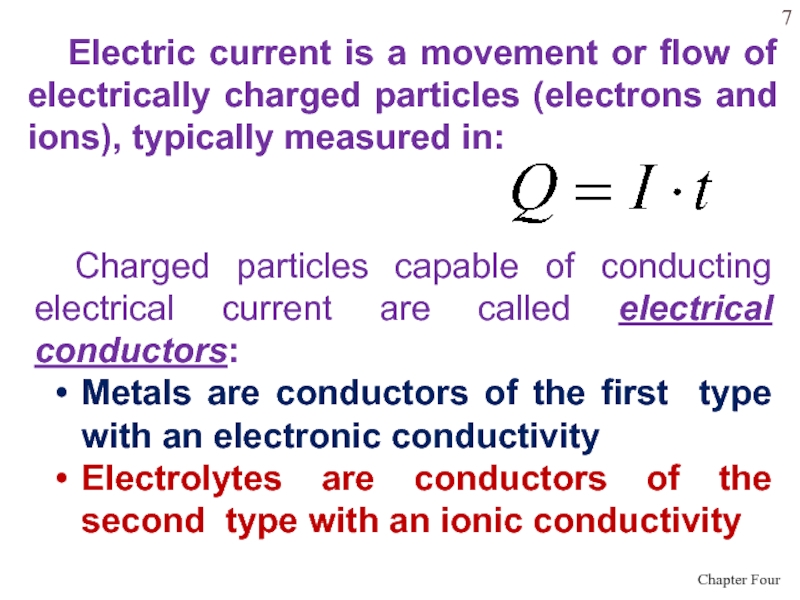
Слайд 7 Electric current is a movement or flow of electrically charged
particles (electrons and ions), typically measured in:
Charged particles capable of
conducting electrical current are called electrical conductors:Metals are conductors of the first type with an electronic conductivity
Electrolytes are conductors of the second type with an ionic conductivity
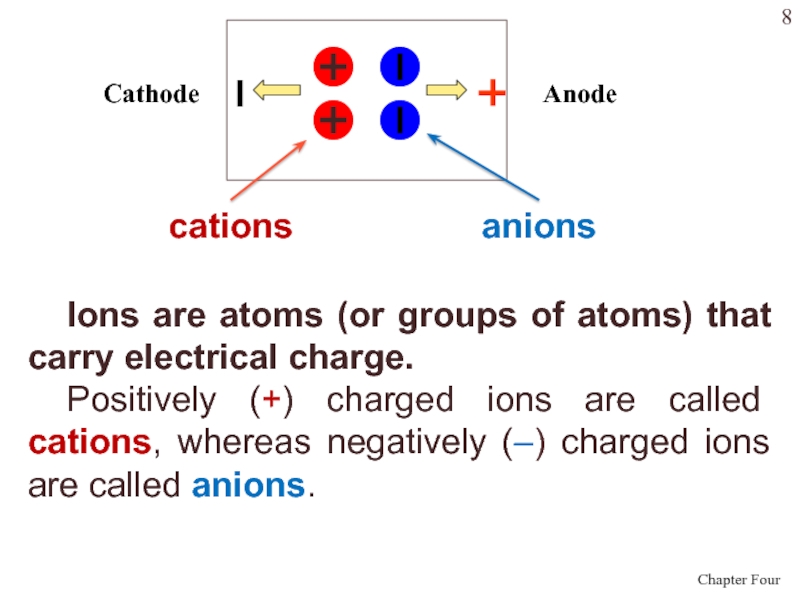
Слайд 8Ions are atoms (or groups of atoms) that carry electrical
charge.
Positively (+) charged ions are called cations, whereas negatively
(–) charged ions are called anions. cations
anions
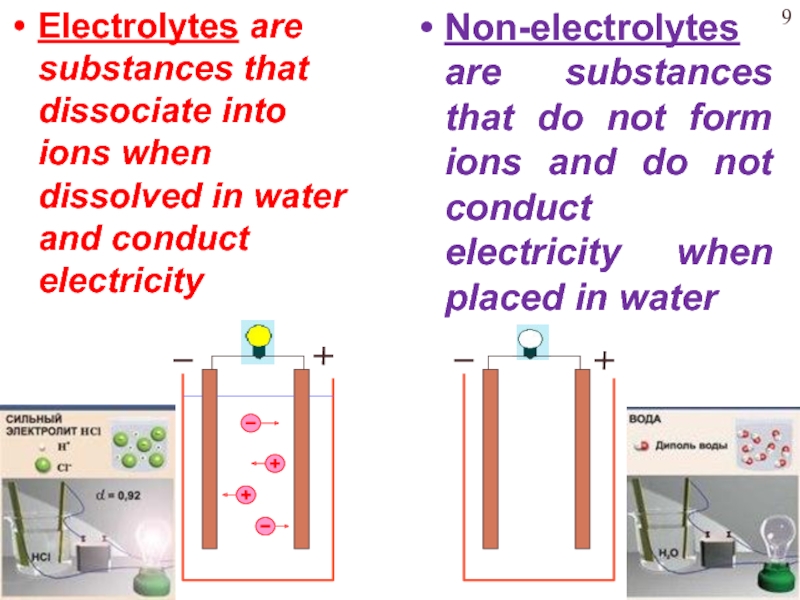
Слайд 9Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in
water and conduct electricity
Non-electrolytes are substances that do not form
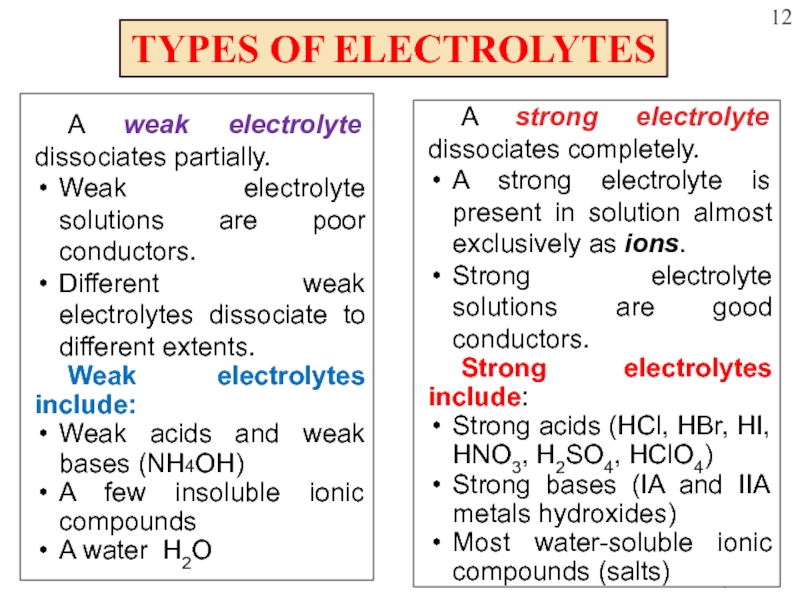
ions and do not conduct electricity when placed in waterСлайд 12TYPES OF ELECTROLYTES
A weak electrolyte dissociates partially.
Weak electrolyte solutions are
poor conductors.
Different weak electrolytes dissociate to different extents.
Weak electrolytes include:
Weak
acids and weak bases (NH4OH)A few insoluble ionic compounds
A water H2O
A strong electrolyte dissociates completely.
A strong electrolyte is present in solution almost exclusively as ions.
Strong electrolyte solutions are good conductors.
Strong electrolytes include:
Strong acids (HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4)
Strong bases (IA and IIA metals hydroxides)
Most water-soluble ionic compounds (salts)
Слайд 14Water is “bent” or V-shaped.
The O – H bonds are
covalent.
Water is a polar molecule.
Hydration occurs when salts dissolve in
water.Слайд 17Этапы электролитической диссоциации полярных молекул (а) и ионных кристаллов (б):
I – сольватация; II – ионизация; III – диссоциация.
Теория электролитической
диссоциацииСлайд 18 In order to explain the properties of electrolytic solutions, Arrhenius
put forth, in 1884, a comprehensive theory which is known
as theory of electrolytic dissociation or ionic theory.ARRHENIUS THEORY OF ELECTROLYTIC DISSOCIATION
Svante Arrhenius,
Swedish chemist and
Nobel laureate,
1859-1927.
Слайд 19THE MAIN POINTS OF THE THEORY ARE:
An electrolyte, when dissolved
in water, breaks up into two types of charged particles.
These charged particles are called ions.When an electric current is passed through the electrolytic solution, the positive ions (cations) move towards cathode and the negative ions (anions) move towards anode and get discharged, i.e., electrolysis occurs.
The process of splitting of the electrolytes molecules into ions under the influence of polar molecules of solvent is called ionization (dissociation):
cation
anion
Слайд 20The properties of electrolytes in solution are the properties of
ions present in solution. For example, acidic solution always contains
H+ ions while basic solution contains OH- ions and characteristic properties of solutions are those of H- ions and OH- ions respectively.The ions act like molecules towards depressing the freezing point, elevating the boiling point, lowering the vapour pressure and establishing the osmotic pressure.
The conductively of the electrolytic solution depends on the nature and number of ions as the current is carried through solution by the movement of ions.
Слайд 21 An acid is a substance that increase H+ when dissolved
in water:
Some acids have more than one ionizable hydrogen
atom. They ionize in “steps”:H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4–
HSO4– → H+ + SO42–
hydrogen sulfate ion
sulfate ion
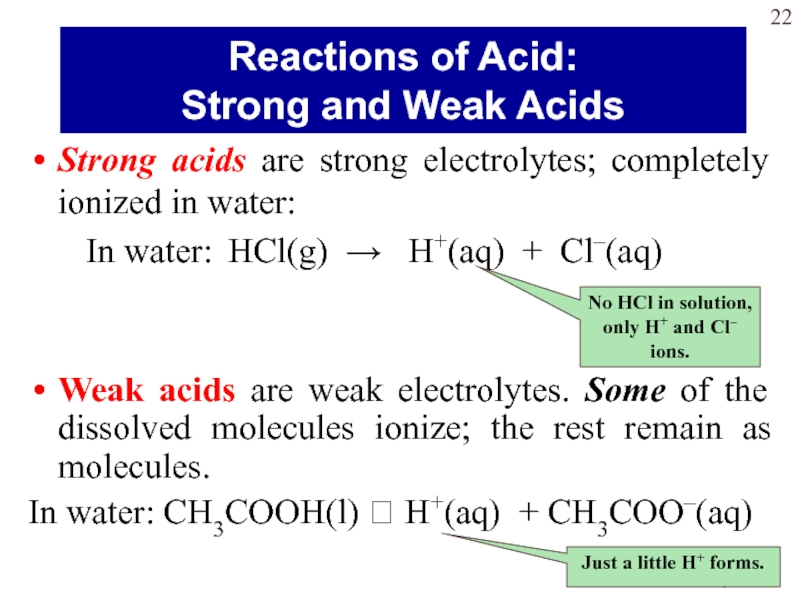
Слайд 22Strong acids are strong electrolytes; completely ionized in water:
In
water: HCl(g) → H+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
Weak acids are weak electrolytes.
Some of the dissolved molecules ionize; the rest remain as molecules.In water: CH3COOH(l) H+(aq) + CH3COO–(aq)
No HCl in solution, only H+ and Cl– ions.
Just a little H+ forms.
Reactions of Acid:
Strong and Weak Acids
Слайд 23 A base is a substance that increase OH- when dissolved
in water:
An ampholyte is a substance dissolving in water
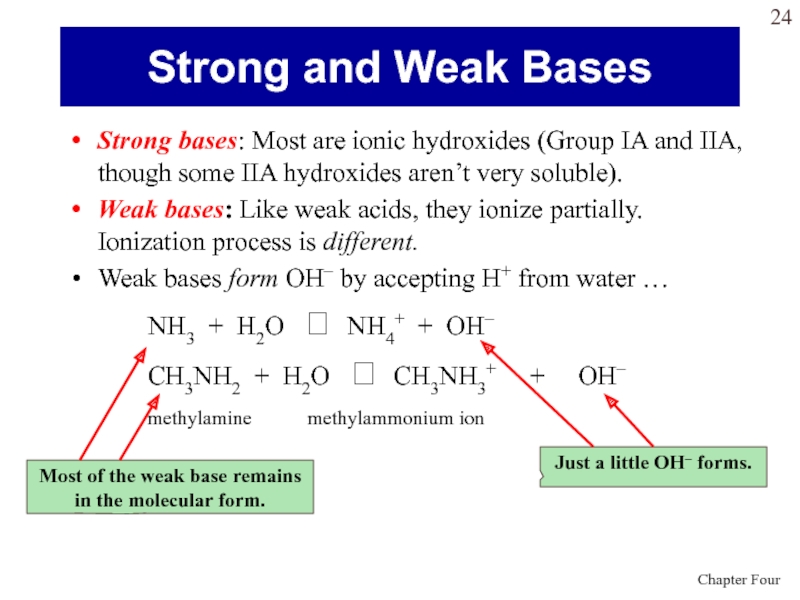
to OH- and H+ ions: Слайд 24Strong bases: Most are ionic hydroxides (Group IA and IIA,
though some IIA hydroxides aren’t very soluble).
Weak bases: Like
weak acids, they ionize partially. Ionization process is different.Weak bases form OH– by accepting H+ from water …
NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH–
CH3NH2 + H2O CH3NH3+ + OH–
methylamine methylammonium ion
Strong and Weak Bases
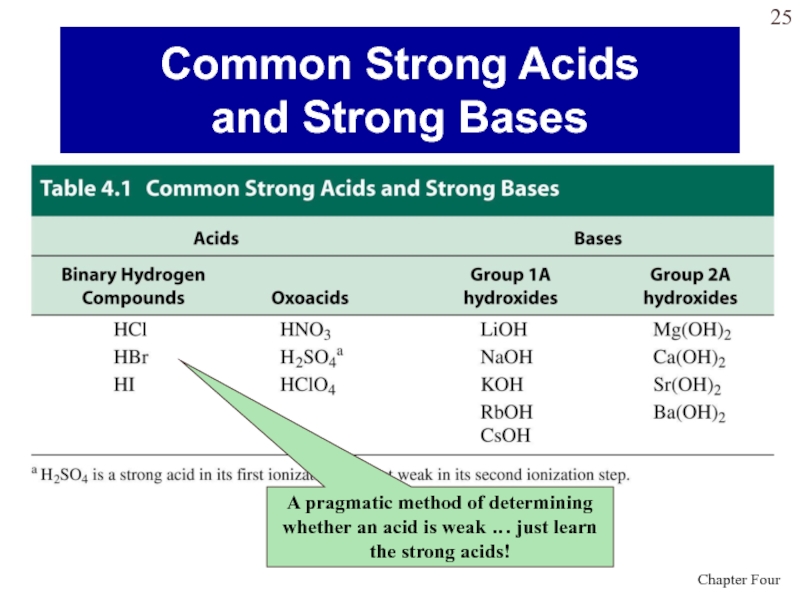
Слайд 25Common Strong Acids
and Strong Bases
A pragmatic method of determining whether
an acid is weak … just learn the strong acids!
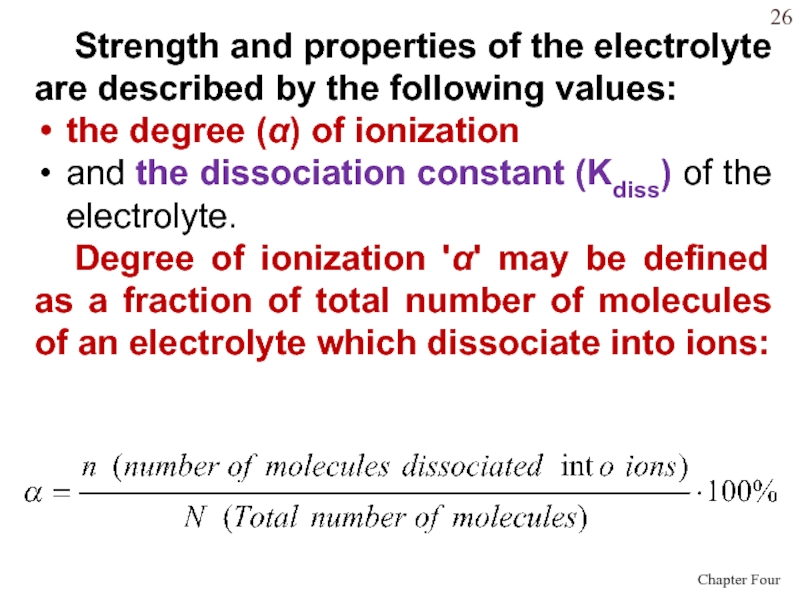
Слайд 26 Strength and properties of the electrolyte are described by the
following values:
the degree () of ionization
and the dissociation
constant (Kdiss) of the electrolyte. Degree of ionization '' may be defined as a fraction of total number of molecules of an electrolyte which dissociate into ions:
Слайд 27Values of the degree of dissociation (ex)depends upon the following
factors
nature of solute
2. nature of solvent
3. concentration
4. temperature
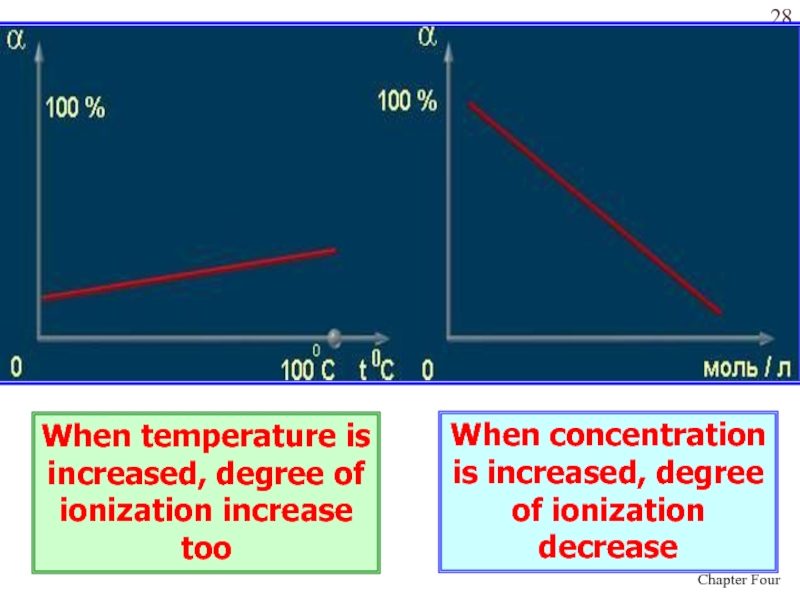
Слайд 28When temperature is increased, degree of ionization increase too
When
concentration is increased, degree of ionization decrease
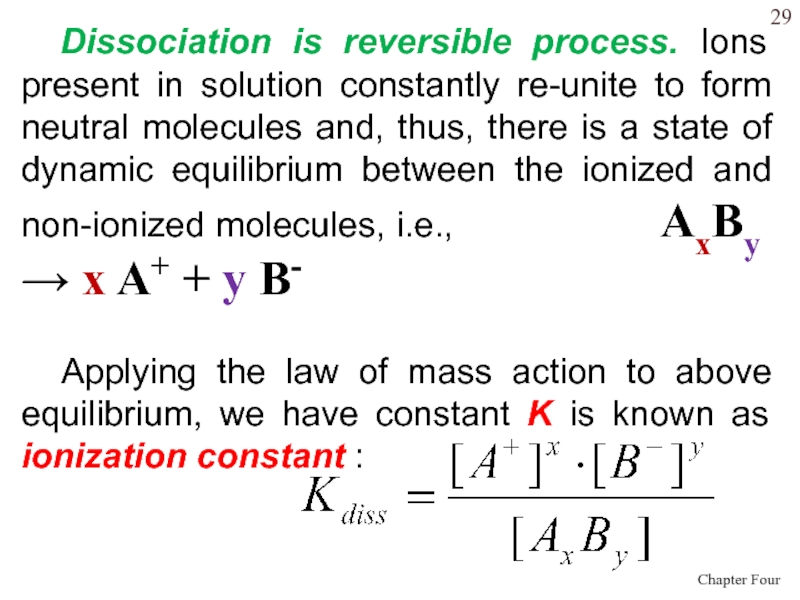
Слайд 29Dissociation is reversible process. Ions present in solution constantly re-unite
to form neutral molecules and, thus, there is a state
of dynamic equilibrium between the ionized and non-ionized molecules, i.e., AxBy x A+ + y B-Applying the law of mass action to above equilibrium, we have constant K is known as ionization constant :
Слайд 30For strong electrolytes >0,3 (30%) and they having high value of
Kdiss
For weak electrolytes
having low constant value of KdissСлайд 31OSTWALD'S DILUTION LAW
For strong electrolytes:
where K is dissociation constant and
C is molar concentration of the solution.
This law is based
on the fact that only a portion of the electrolyte is dissociated into ions at ordinary dilution and completely at infinite dilution. Strong electrolytes are almost completely ionized at all dilutions and /∞ does not give an accurate value of 'α'.When the concentration of ions is very high, the presence of charges on the ions appreciably affects the equilibrium. Hence, law of mass action cannot be strictly applied in the case of strong electrolytes.
Слайд 32OSTWALD'S DILUTION LAW
For weak electrolytes (Kdiss=const and (1 – )
1):
Thus, degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is
proportional to the square root of dilution.“For a weak electrolyte, the degree of ionisation is inversely proportional to the square root of molar concentration or directly proportional to the square root of volume containing one mole of the solute.” This is called Ostwald’s dilution law.
Слайд 33A chemical equation which shows dissociation of electrolyte and written
as dissociated ions of electrolyte is known as ionic equation.
Double
Replacement (Metathesis) Reactions involve swapping ions in solution:AX + BY AY + BX
IONIC REACTIONS
Слайд 34 Metathesis reactions will lead to a change in solution if
one of three things occurs:
An insoluble solid is formed (When
a chemical reaction forms such a solute, the insoluble solute comes out of solution and is called a precipitate),Weak acids are formed (H2SO3, CH3COOH),
An insoluble gas is formed (H2S, CO2, SO2, NH3),
Neutralization reaction
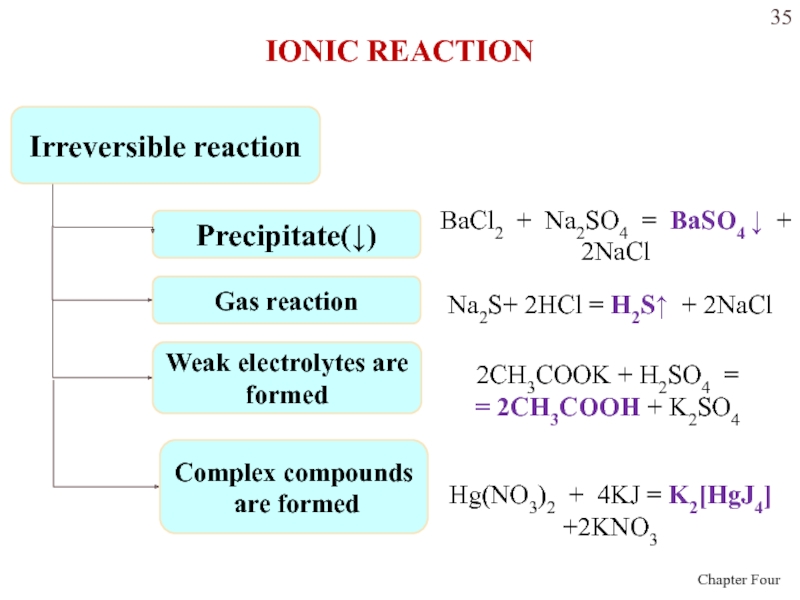
Слайд 35Irreversible reaction
Precipitate(↓)
BaCl2 + Na2SO4 = BaSO4 ↓ + 2NaCl
Gas
reaction
Na2S+ 2HCl = H2S↑ + 2NaCl
Weak electrolytes are
formed
2CH3COOK
+ H2SO4 = = 2CH3COOH + K2SO4
Complex compounds
are formed
Hg(NO3)2 + 4KJ = K2[HgJ4] +2KNO3
IONIC REACTION
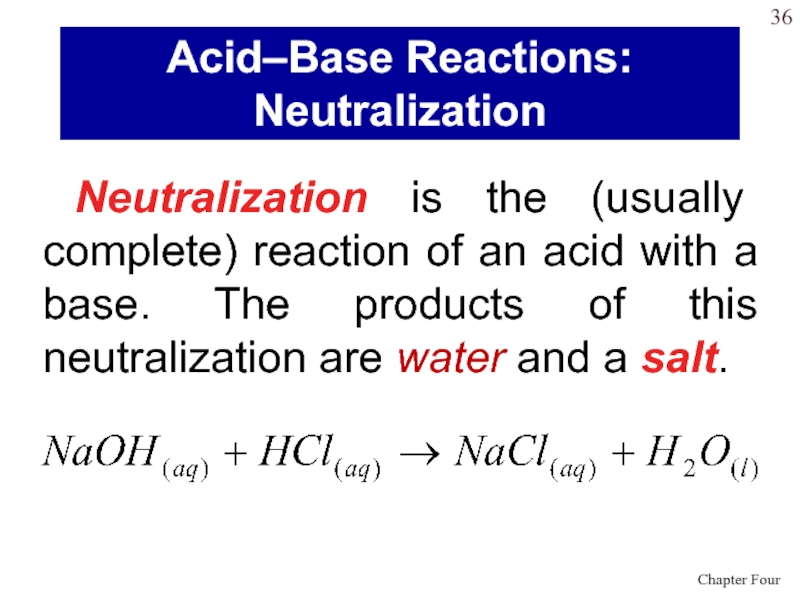
Слайд 36 Neutralization is the (usually complete) reaction of an acid with
a base. The products of this neutralization are water and
a salt.Acid–Base Reactions:
Neutralization
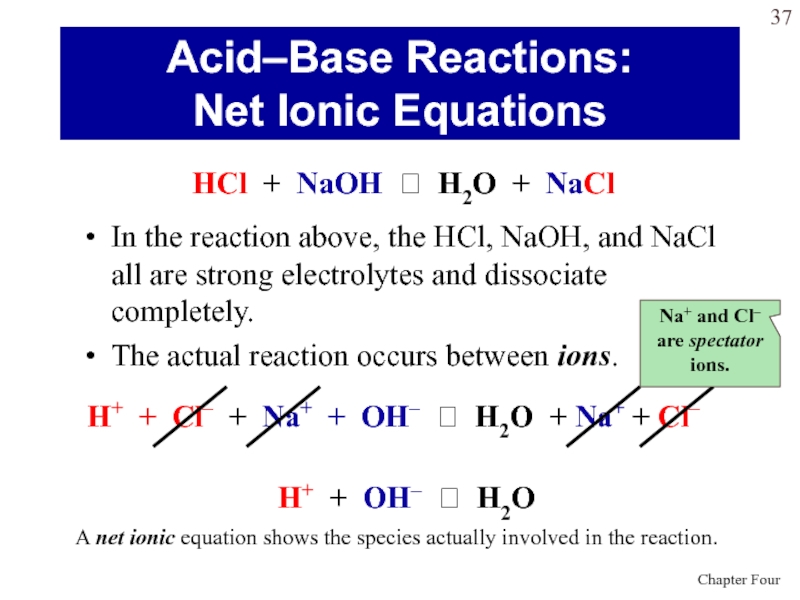
Слайд 37In the reaction above, the HCl, NaOH, and NaCl all
are strong electrolytes and dissociate completely.
The actual reaction occurs between
ions.Acid–Base Reactions:
Net Ionic Equations
HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl
H+ + Cl– + Na+ + OH– H2O + Na+ + Cl–
H+ + OH– H2O
A net ionic equation shows the species actually involved in the reaction.
Na+ and Cl– are spectator ions.
Слайд 38There are limits to the amount of a solute that
will dissolve in a given amount of water.
If the maximum
concentration of solute is less than about 0.01 M, we refer to the solute as insoluble in water.When a chemical reaction forms such a solute, the insoluble solute comes out of solution and is called a precipitate.
Reactions that Form Precipitates
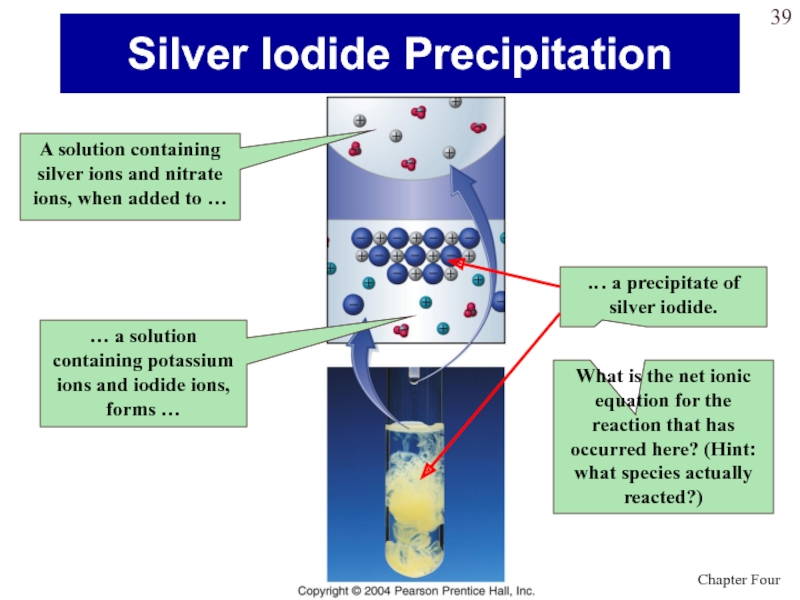
Слайд 39Silver Iodide Precipitation
A solution containing silver ions and nitrate ions,
when added to …
… a solution containing potassium ions and
iodide ions, forms …What is the net ionic equation for the reaction that has occurred here? (Hint: what species actually reacted?)
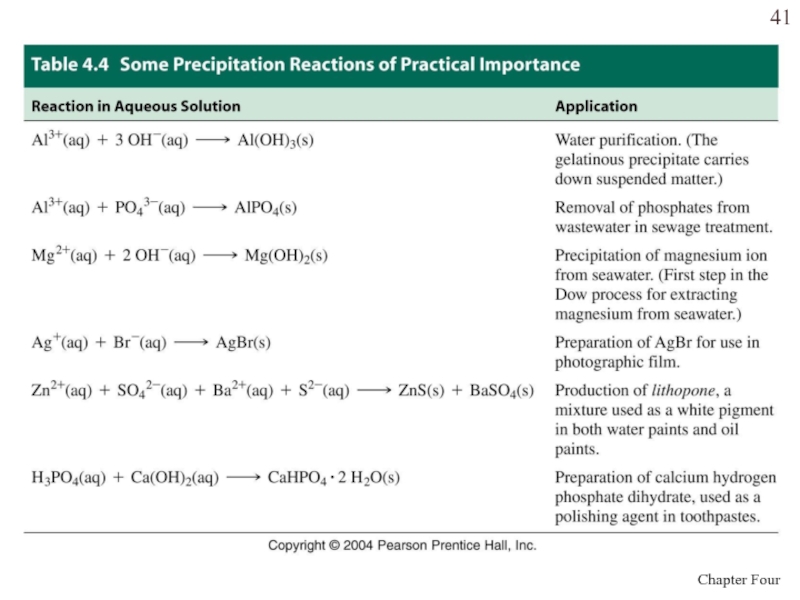
Слайд 40With these guidelines we can predict precipitation reactions.
When solutions of
sodium carbonate and iron (III) nitrate are mixed, a precipitate
will form.When solutions of lead acetate and calcium chloride are mixed, a precipitate will form.