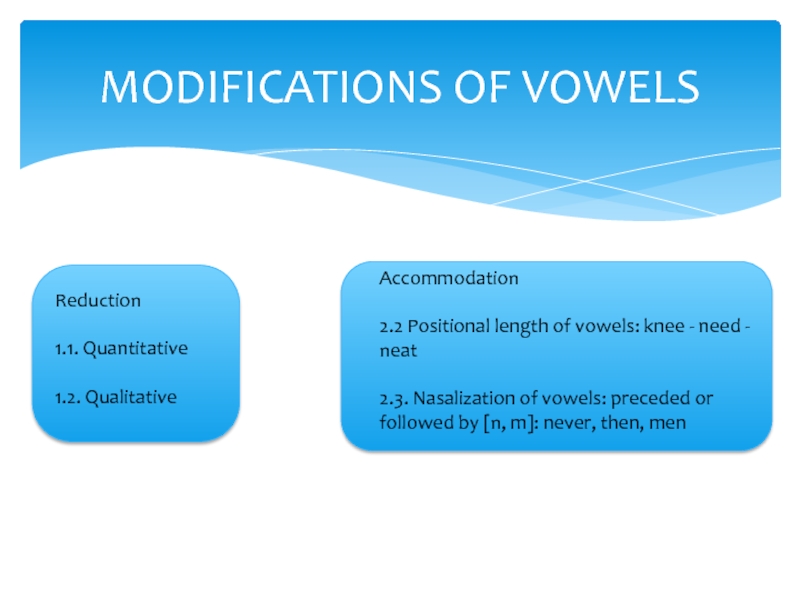
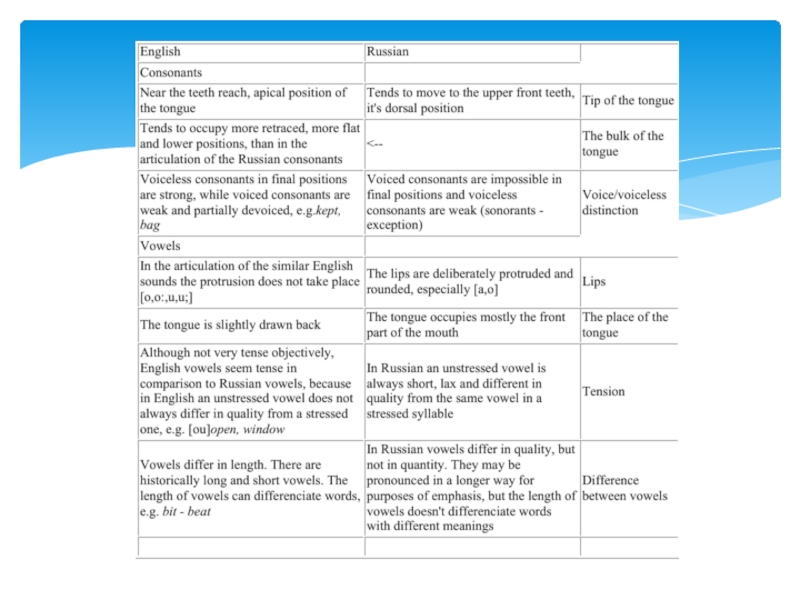
θ]: eighth, at the, said that
• t, d > post-alveolar
before [r]: tree, true, dream, the third room
• s, z > post-alveolar before [∫]: this shop, does she
• t, d > affricates before [j]: graduate, could you
• m > labio-dental before [f]: symphony
Loss of [h] in personal and possessive pronouns and the forms of the auxiliary verb have.
[l] lends to be lost when preceded by [o:]: always, already, all right
In cluster of consonants: next day, just one. mashed potatoes
Lip position
• consonant + back vowel: pool, rude, who (rounded)
• consonant + front vowel: tea, sit, keep (spread)
Linking [r] (potential pronunciation of [r]): car owner
Intrusive [r]: [r] is pronounced where no r is seen in the spelling china and glass: it is not recommended to foreign learners.
Assimilation
Accommodation
Elision
Inserting of sounds




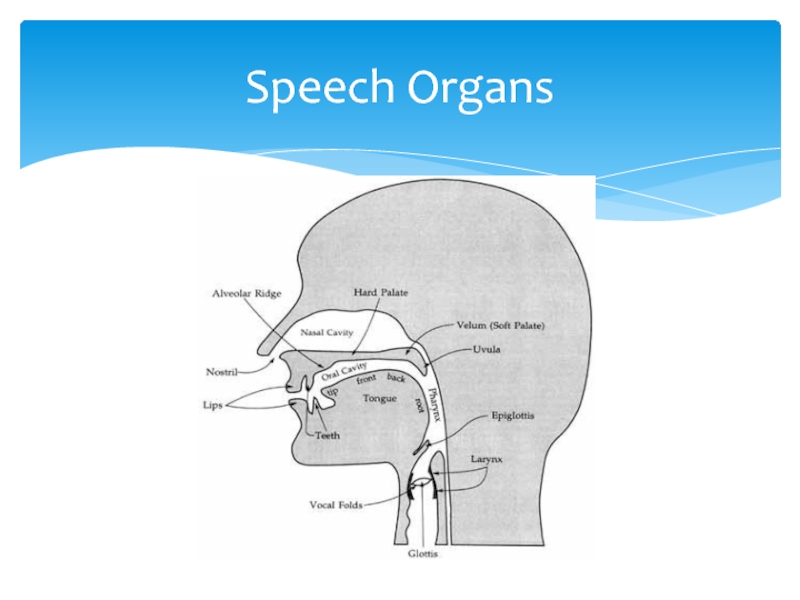
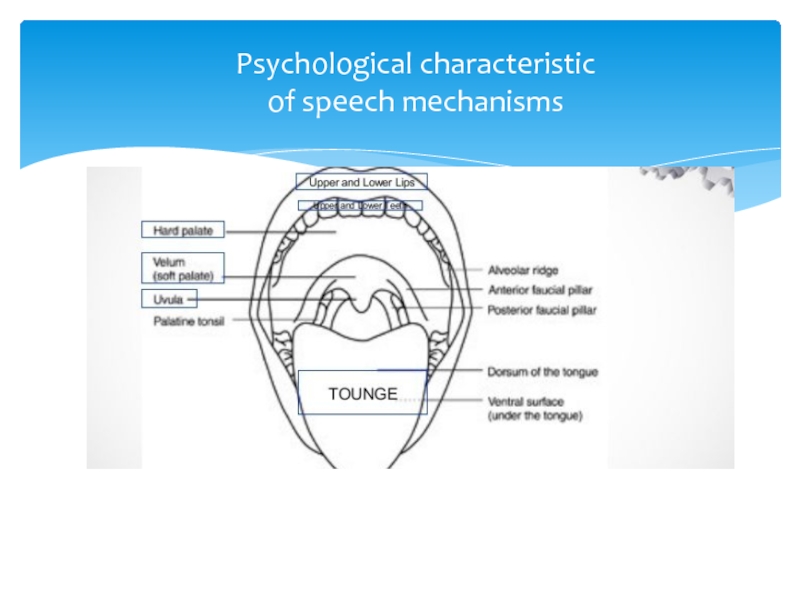








![Articulatory Aspect of speech sound MODIFICATIONS OF CONSONANTS • t, , d > dental before [ð, MODIFICATIONS OF CONSONANTS • t, , d > dental before [ð, θ]: eighth, at the, said that•](/img/thumbs/177be2f619ff3b3b5f37b5d780e86192-800x.jpg)