Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
BRANDING A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Richard Gilbert, Ph.D., H.E., OIA
Содержание
- 1. BRANDING A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Richard Gilbert, Ph.D., H.E., OIA
- 2. Brands are all about trust …The reason
- 3. Brand is an experience A brand is essentially
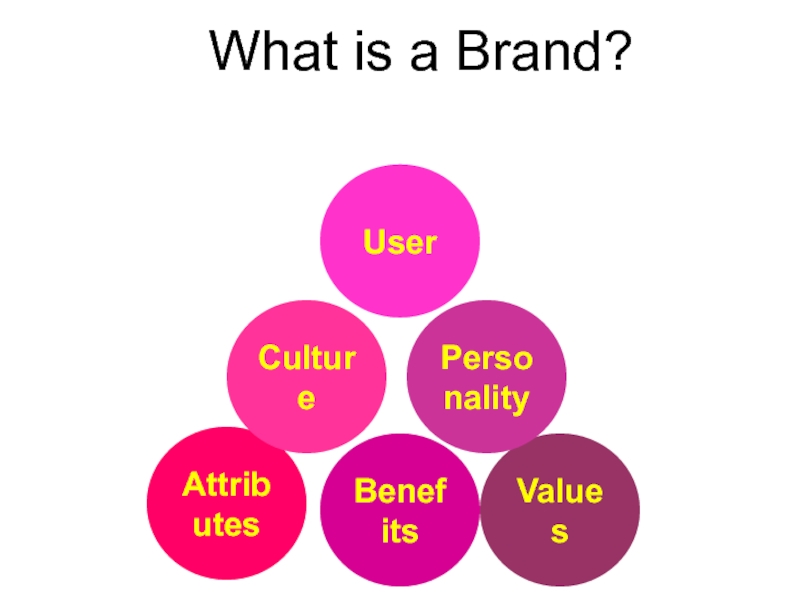
- 4. What is a Brand?AttributesBenefitsValuesCultureUserPersonality
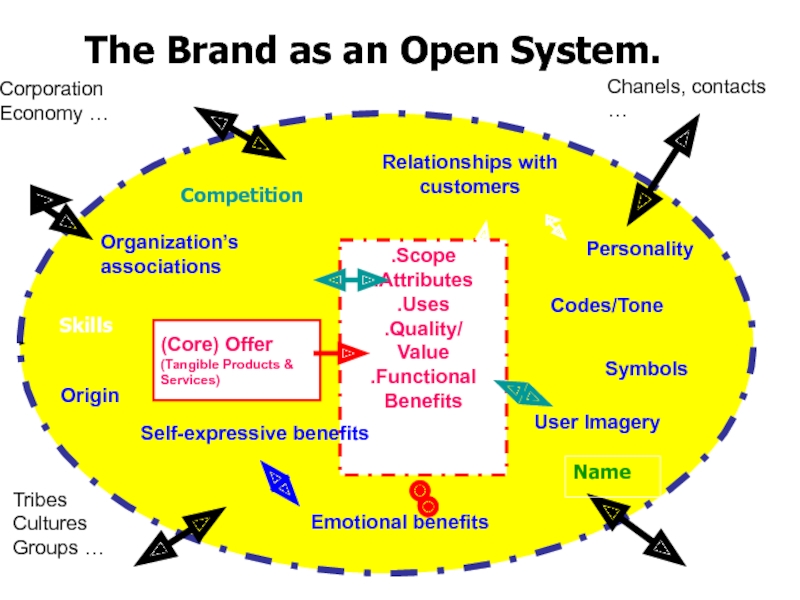
- 5. The Brand as an Open System. .Scope.Attributes.Uses.Quality/Value.FunctionalBenefitsOrganization’s
- 6. This Brand System interacts AS ...1) ..
- 7. THE BRAND AS A SOCIO-ECONOMIC AGENT PART
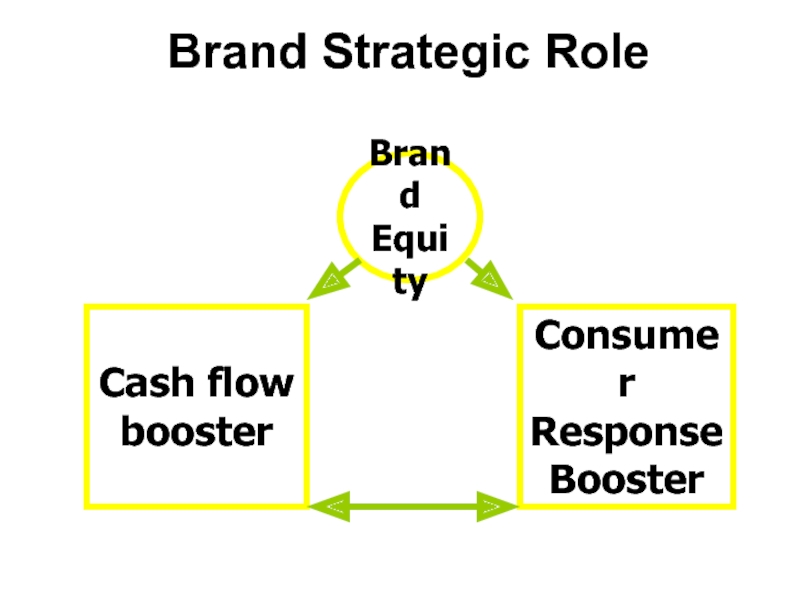
- 8. Brand Strategic Role Brand EquityCash flowboosterConsumerResponseBooster
- 9. THE BRAND AS A CORPORATE ASSETA PROTECTED
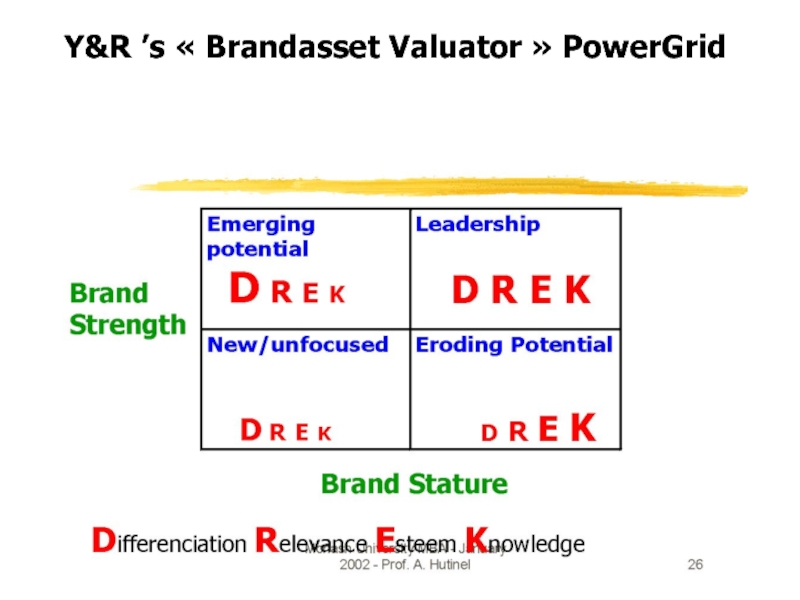
- 10. Y&R ’s « Brandasset Valuator » PowerGrid
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Building Brand EquityBrand Equity(Name & Symbol)Value To
- 13. THE BRAND AS A COMMUNICATION & SELLING
- 14. A modern brand is A « persona » that
- 15. From Traditional to Experiential BrandingFromBrands as identifiersNames,
- 16. Implications on Higher Education
- 17. New Demands on Higher EducationChanging landscape of
- 18. THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE OF COMPETITION IN HIGHER
- 19. THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE OF COMPETITION IN HIGHER
- 20. THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE OF COMPETITION IN HIGHER
- 21. CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATIONImplications for urban
- 22. CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATIONImplications for urban
- 23. CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATIONHOW DOES THIS
- 24. CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATIONWhat kinds of
- 25. CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATIONWhat kinds of
- 26. CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATIONKey strategic problem:
- 27. CAMPUS MICRO-ECONOMY AS NODAL LEVER FOR ACCESSING
- 28. TWO MODELS: DO-It-ALL or DO-it-Different and Do-it-WellThe
- 29. DO-It-ALL or DO-it-Different and Do-it-WellThe traditional model:
- 30. DO-it-Different & Do-it-WellAmerican universities never like this.Expansion
- 31. Do-it-Different & Do-it-WellSmall – always struggled to ‘do it all’Traded on difference (e.g. Agricultural vs. Business)
- 32. Do-it-Different & Do-it-WellVulnerability:Small campus university, rural location.Too
- 33. Do-it-Different & Do-it-WellOpportunity:Already primed by history &
- 34. BRANDING: A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGEFramework tying
- 35. A= Interdisciplinary research focusB= Interdisciplinary focus on
- 36. BRANDING: A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGEInterdisciplinary research:
- 37. BRANDING: A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGEInterdisciplinary research:Teaching: Collegiality, learning culture, participation, engagement
- 38. Campus community and social lifeLiveabilty – food
- 39. Campus community and social lifeEconomy – Keep the money on campus: short courses, training
- 40. Thank You
- 41. Скачать презентанцию
Brands are all about trust …The reason consumers flock to some brands and ignore others is that behind the brand stands an unspoken promise of value. That is why brands are
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1BRANDING A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Richard Gilbert, Ph.D., H.E., OIA American
University of Health Science
Слайд 2Brands are all about trust …
The reason consumers flock to
some brands and ignore others is that behind the brand
stands an unspoken promise of value.That is why brands are becoming even more important drivers of growth.
Слайд 3Brand is an experience
A brand is essentially a container for
a custumer’s complete experience with the offer and the company.
(Sergio Zyman)
Слайд 5The Brand as an Open System.
.Scope
.Attributes
.Uses
.Quality/
Value
.Functional
Benefits
Organization’s associations
Personality
Symbols
Origin
User Imagery
Relationships with
customers
Self-expressive
benefits
Emotional benefits
(Core) Offer
(Tangible Products &
Services)
Codes/Tone
Competition
Skills
Name
Corporation
Economy …
Chanels, contacts
…
Tribes
Cultures
Groups …
Слайд 6This Brand System interacts AS ...
1) .. A SOCIO-ECONOMIC AGENT
2)
.. A CORPORATE ASSET
3) .. A STRATEGIC MARKETING TOOL
4) ..
A COMMUNICATION & SELLING AGENTСлайд 7THE BRAND AS A SOCIO-ECONOMIC AGENT
PART OF EACH INDIVIDUAL’S
AND SOCIETAL GROUPS ’ SET OF REFERENCES
A POWERFUL
SOCIAL DRIVERA GLOBAL CEMENT
A VALUE ADDING ECONOMIC AGENT
Слайд 9THE BRAND AS A CORPORATE ASSET
A PROTECTED PROPERTY (owner's right
to use)
BOOK VALUE, GOODWILL. - ASSET that can be
sold and bought MARKETING « NON TANGIBLE » ASSET precisely measurable and valuable (when brand is on sale) :
STRENGTH , LEADERSHIP & EQUITY, ie capacity to justify price.
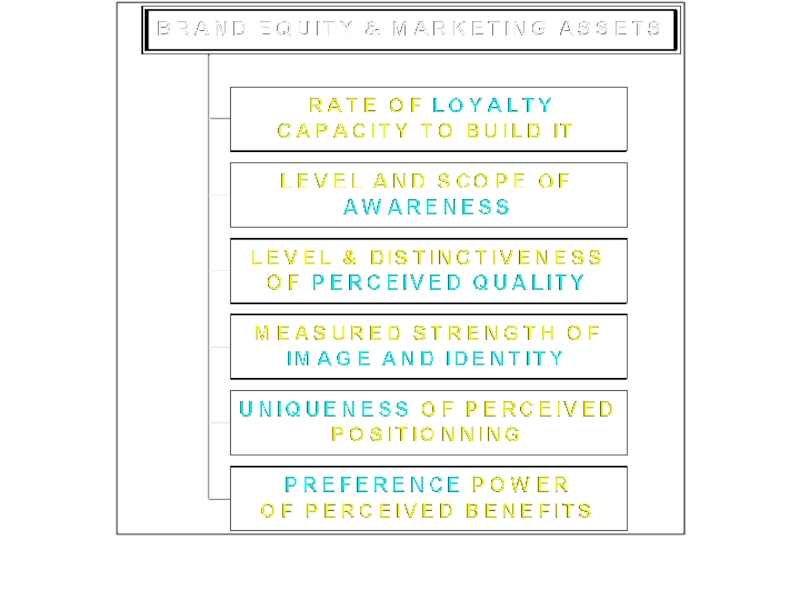
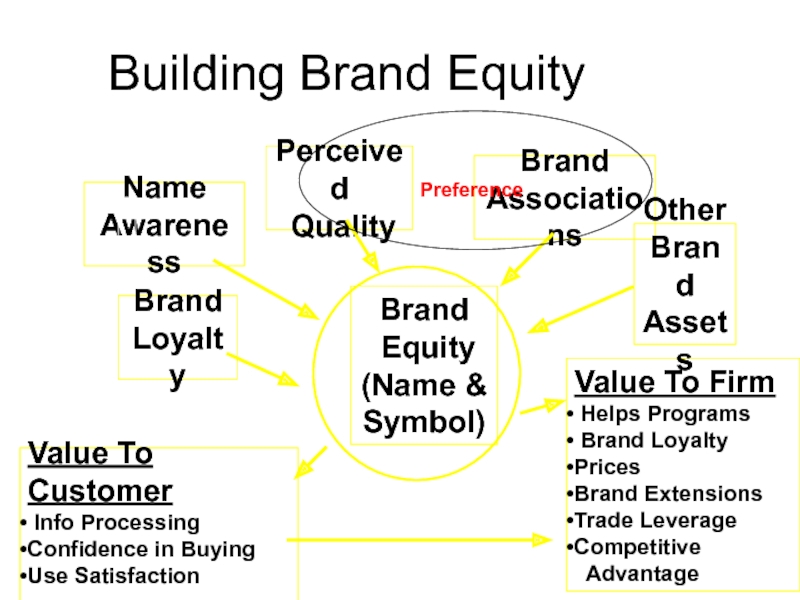
Слайд 12Building Brand Equity
Brand
Equity
(Name &
Symbol)
Value To Customer
Info Processing
Confidence
in Buying
Use Satisfaction
Value To Firm
Helps Programs
Brand Loyalty
Prices
Brand Extensions
Trade
LeverageCompetitive
Advantage
Name
Awareness
Perceived
Quality
Brand
Associations
Other
Brand
Assets
Brand
Loyalty
Preference
Слайд 13THE BRAND AS A COMMUNICATION
& SELLING AGENT
* A
RELATIONSHIP ACTOR/BUILDER
* AN INFLUENCER
* IT GIVES MEANINGS TO PRODUCTS/SERVICES ...
* ... AND A CREATOR OF « NEW » WORLDS
Слайд 14A modern brand is
A « persona » that overlays and includes
the physical products/services
the sum of fundamental values and attributes ascribed
to it by peoplethe entity that the consumers construct from the products’ meanings, symbols and images that they perceive as defining the brand.
Слайд 15From Traditional to Experiential Branding
From
Brands as identifiers
Names, logos, slogans build
awareness and image
TO
Brands as experience providers
Names, logos, slogans, events, customer
contacts which build sensory, affective, creative relations and ways of being (lifestyles) with the brandsСлайд 17New Demands on Higher Education
Changing landscape of competition in HE
Two
university models: Do-it-All versus
Do-it Different & Well
Branding as a
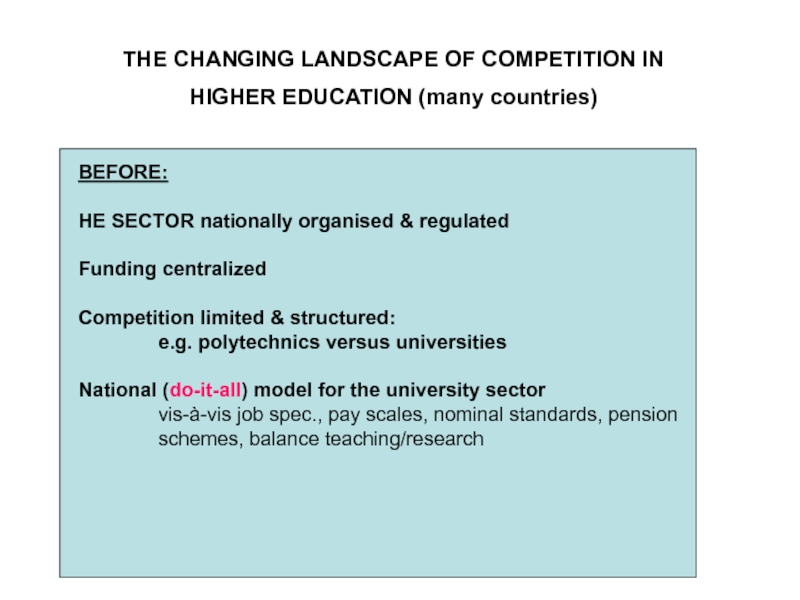
vehicle for competitive niche marketing.Слайд 18THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE OF COMPETITION IN
HIGHER EDUCATION (many countries)
BEFORE:
HE
SECTOR nationally organised & regulated
Funding centralized
Competition limited & structured:
e.g. polytechnics
versus universitiesNational (do-it-all) model for the university sector
vis-à-vis job spec., pay scales, nominal standards, pension
schemes, balance teaching/research
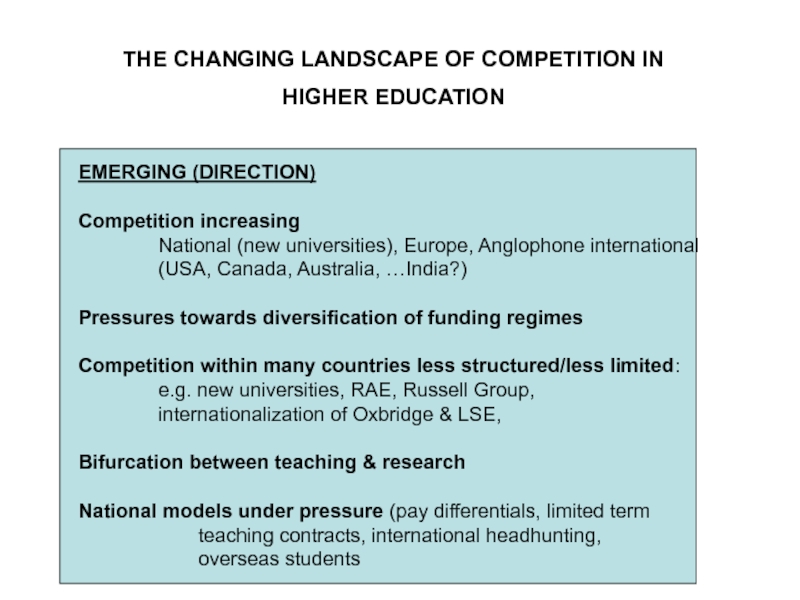
Слайд 19THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE OF COMPETITION IN
HIGHER EDUCATION
EMERGING (DIRECTION)
Competition increasing
National
(new universities), Europe, Anglophone international
(USA, Canada, Australia, …India?)
Pressures towards
diversification of funding regimesCompetition within many countries less structured/less limited:
e.g. new universities, RAE, Russell Group,
internationalization of Oxbridge & LSE,
Bifurcation between teaching & research
National models under pressure (pay differentials, limited term
teaching contracts, international headhunting,
overseas students
Слайд 20THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE OF COMPETITION IN
HIGHER EDUCATION
CHARACTERIZATION:
Place versus space:
plight of cities in a global economy
Place bound cities can’t
move and follow mobile capitalIMPERATIVE:
To divert capital flows through particular cities
To embed economic activity
To develop economic activity less vulnerable to the vagaries of capital flight
Слайд 21CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATION
Implications for urban economic strategy?
Higher value-added
activities less vulnerable
Headquarter & R&D functions less prone to relocation
LESSON:
Do not produce high-volume, low value products.
Go for higher value, lower volume knowledge intensive,
products.
Слайд 22CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATION
Implications for urban economic strategy?
Importance
of place-branding and place-marketing –
image /liveability
Imperative:
Need to attract
mobile, metropolitan middle classesImportance of good living environment, good food, good schools, liberal metropolitan activities and values
Слайд 23CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATION
HOW DOES THIS APPLY TO UNIVERSITIES?
Place-bound
communities (like cities)
Need to divert capital & embed economic activity
Слайд 24CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATION
What kinds of capital?
HUMAN CAPITAL:
Better undergraduate
students
Better post-graduate students
More international students
Better academic staff
Слайд 25CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATION
What kinds of capital?
FINANCE CAPITAL
Capital investment
(block funding, private sector)
Discretionary research funding (research councils)
Ancillary revenue streams
Short courses,
Commercial management of estates
Commercial management of other assets [merchandising?]
IPR/patenting/commercialisation of research
Private benefactors (alumni schemes etc)
Слайд 26CHANGING COMPETITION IN HIGHER EDUCATION
Key strategic problem:
How to divert
flows and attract these different forms of capital?
Solution
SENSE OF PLACE
/COMMUNITY (PLACE-MARKETING, IMAGE, LIVEABILITY, AUTHENTICITY)
HIGHER VALUE-ADDED NICHE PRODUCT, LESS VULNERABLE
TO COMPETITIVE PRESSURES.
Do something other universities don’t and preferably can not do.
Do-it-Different and Do-it-Well
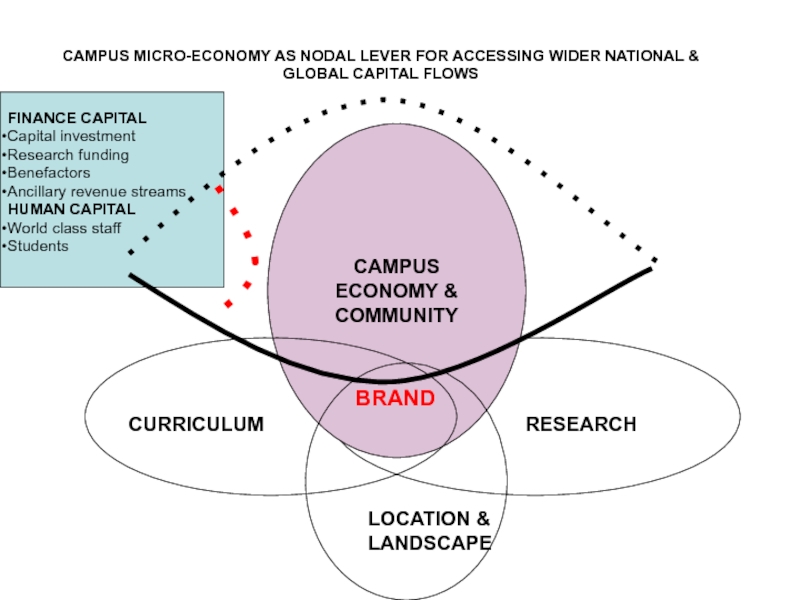
Слайд 27CAMPUS MICRO-ECONOMY AS NODAL LEVER FOR ACCESSING WIDER NATIONAL &
GLOBAL CAPITAL FLOWS
CAMPUS ECONOMY &
COMMUNITY
CURRICULUM
RESEARCH
LOCATION &
LANDSCAPE
BRAND
FINANCE CAPITAL
Capital investment
Research
fundingBenefactors
Ancillary revenue streams
HUMAN CAPITAL
World class staff
Students
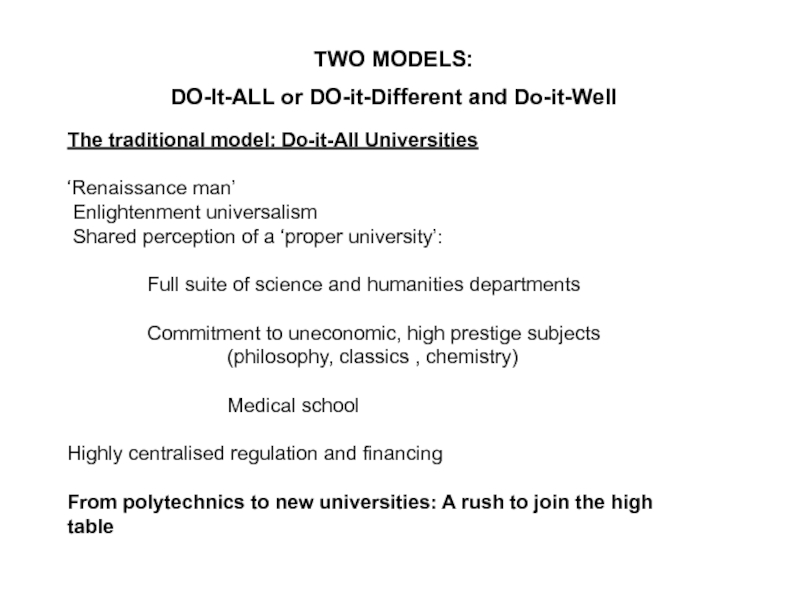
Слайд 28TWO MODELS:
DO-It-ALL or DO-it-Different and Do-it-Well
The traditional model: Do-it-All
Universities
‘Renaissance man’
Enlightenment universalism
Shared perception of a ‘proper university’:
Full
suite of science and humanities departmentsCommitment to uneconomic, high prestige subjects
(philosophy, classics , chemistry)
Medical school
Highly centralised regulation and financing
From polytechnics to new universities: A rush to join the high table
Слайд 29DO-It-ALL or DO-it-Different and Do-it-Well
The traditional model: Do-it-All Universities
ACHIEVEMENTS:
“
British Education” as international brand/benchmark
Standardized level of provision and quality
Слайд 30DO-it-Different & Do-it-Well
American universities never like this.
Expansion of mass higher
education + globalizing competition brings new pressures for market differentiation
Слайд 31Do-it-Different & Do-it-Well
Small – always struggled to ‘do it all’
Traded
on difference (e.g. Agricultural vs. Business)
Слайд 32Do-it-Different & Do-it-Well
Vulnerability:
Small campus university, rural location.
Too small to compete
head-to-head
Lacks large urban ‘home’ market
Increasing competition from new universities
Lacks access
to exciting metropolitan lifeDANGER:
Being pushed down, pushed mainstream
Слайд 33Do-it-Different & Do-it-Well
Opportunity:
Already primed by history & tradition + location
for Do-it-Different & Well
Possibility of creating a market niche for
a higher value, low volume, and more locally embedded product.
Possibility of deciding how and against which institutions to compete
(or better still side-step competition)
RESPONSE:
Aggressive & concerted niche marketing and lateral competition
Слайд 34BRANDING: A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Framework tying together:
Place-marketing & liveability
Higher
value added product
Specifically:
Research
Teaching
Physical infrastructure and operations
Sense of place &
communityСлайд 35A= Interdisciplinary research focus
B= Interdisciplinary focus on teaching, including
innovative links with NGOs and industry.
C= Liveability and ‘sense
of place’(e.g. cinema, cafes, live music,
music festivals, quality of retail outlets,
second hand bookshop etc)
D = Architecture, localisation of
food, energy, and material inputs
BRANDING: A VEHICLE FOR COMPETITION ADVANTAGE