Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
CARDIOMYOPATHY
Содержание
- 1. CARDIOMYOPATHY
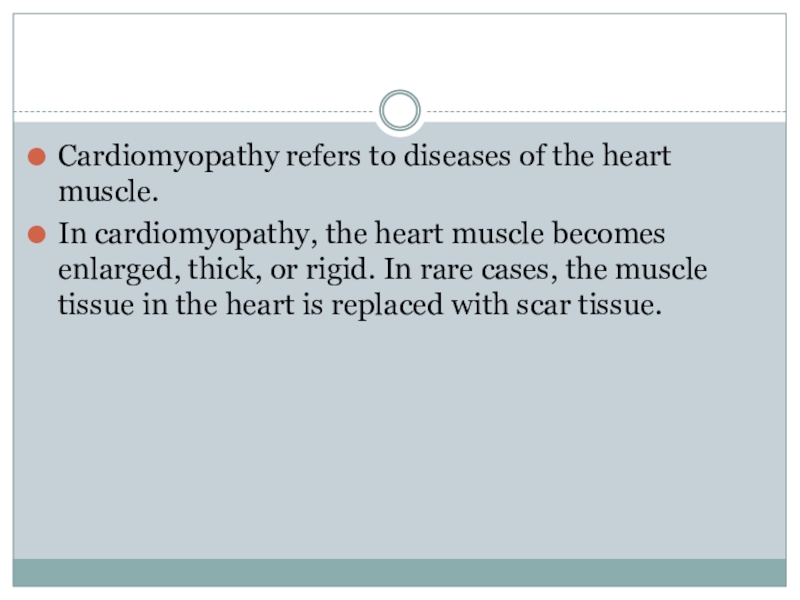
- 2. Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart
- 3. CLASSIFICATION According to the WHO types of cardiomyopathy are:Hypertrophic cardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathyRestrictive cardiomyopathyArrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasiaUnclassified cardiomyopathy
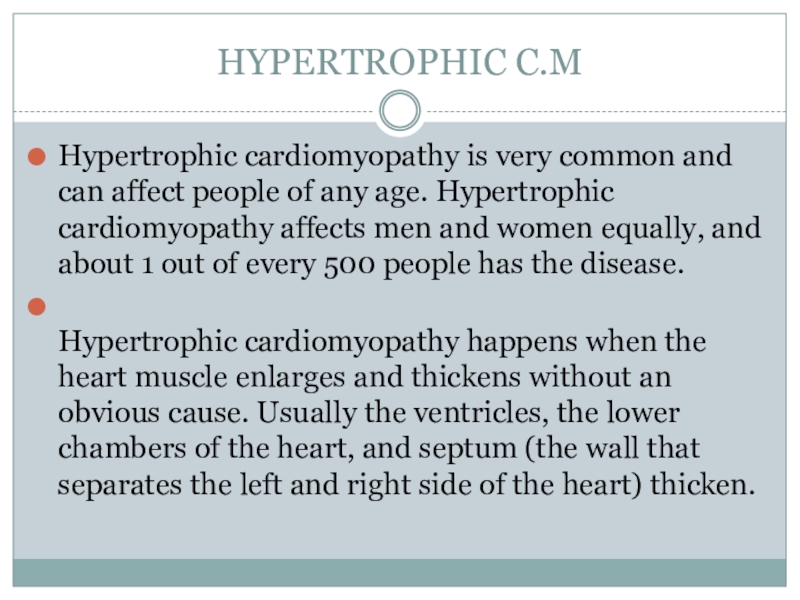
- 4. HYPERTROPHIC C.MHypertrophic cardiomyopathy is very common and
- 5. Слайд 5
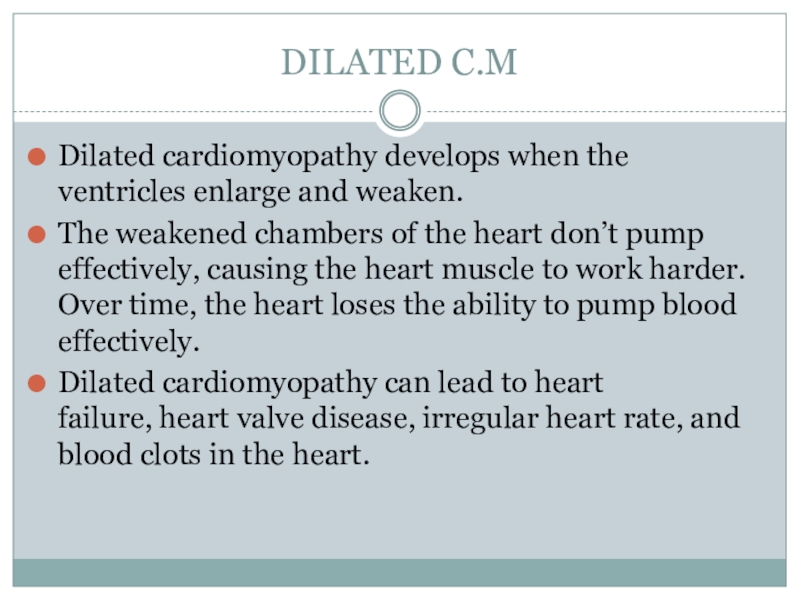
- 6. DILATED C.MDilated cardiomyopathy develops when the ventricles
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. RESTRICTIVE C.MRestrictive cardiomyopathy develops when the ventricles
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. ARRHYTHMOGENIC RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSPLASIAArrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. UNCLASSIFIED C.MLeft ventricular noncompaction happens when the
- 14. FETAL CM
- 15. HCM CAUSESHypertrophic cardiomyopathy usually is inherited. It’s
- 16. DCM CAUSESAlcohol, especially if you also have
- 17. RCM CAUSESAmyloidosisConnective tissue disordersHemochromatosisSarcoidosisSome cancer treatments, such as radiation and chemotherapy.
- 18. MAJOR RISK FACTORSA family history of cardiomyopathy, heart
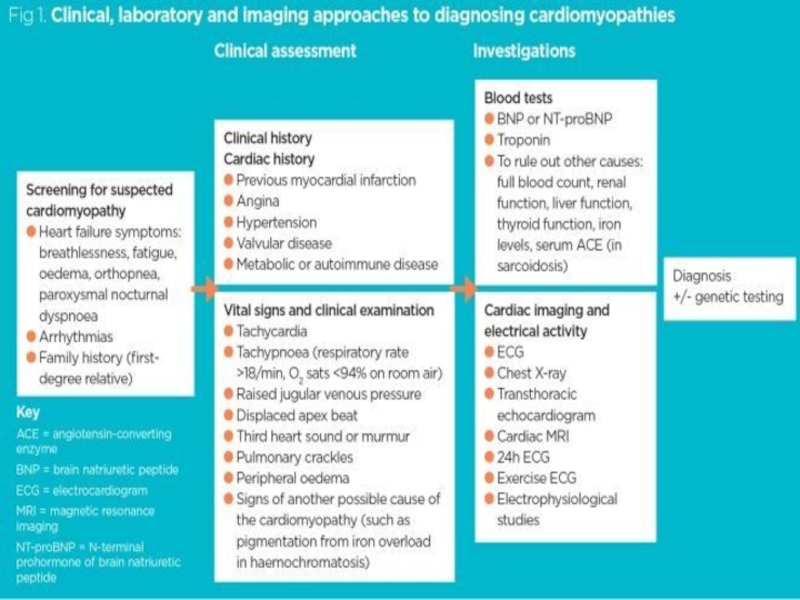
- 19. DIAGNOSTIC SIGNS
- 20. It’s important to identify those who may
- 21. If people without symptoms recognize their heightened
- 22. Signs and symptoms of cardiomyopathy include:Shortness of
- 23. 5. Lightheadedness6. Fainting during physical activity7. Arrhythmias
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. DIAGNOSTIC TESTS / PROCEDURES
- 26. DIAGNOSTIC TESTSBlood testsChest X-rayElectrocardiogram (EKG or ECG):
- 27. Holter and event monitors: A Holter monitor
- 28. Echocardiogram (Echo): It shows how well your
- 29. Stress test: In a stress test, the
- 30. DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURESCardiac catheterizationCoronary angiography Myocardial biopsyGenetic testing
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
- 33. Aortic StenosisGenetics of Fabry DiseaseHypertensive Heart DiseasePaediatric Supravalvar Aortic StenosisType II Glycogen Storage Disease (Pompe Disease)
- 34. MyocarditisAcute PericarditisCardiac TamponadeAcute Coronary SyndromeConstrictive PericarditisHyperthyroidism Heavy Metal Toxicity
- 35. Скачать презентанцию
Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart muscle.In cardiomyopathy, the heart muscle becomes enlarged, thick, or rigid. In rare cases, the muscle tissue in the heart is replaced with scar tissue.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3CLASSIFICATION
According to the WHO types of cardiomyopathy are:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Restrictive
cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
Unclassified cardiomyopathy
Слайд 4HYPERTROPHIC C.M
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is very common and can affect people
of any age. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy affects men and women equally,
and about 1 out of every 500 people has the disease.Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy happens when the heart muscle enlarges and thickens without an obvious cause. Usually the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, and septum (the wall that separates the left and right side of the heart) thicken.
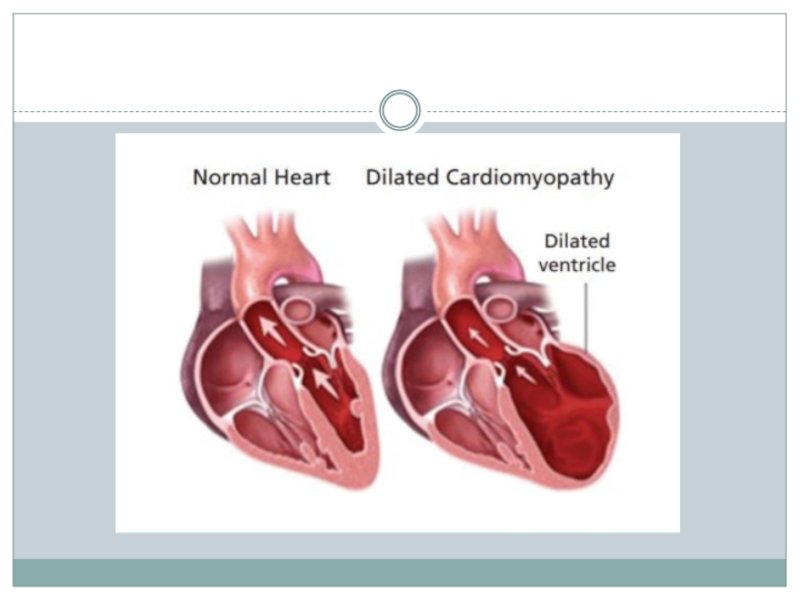
Слайд 6DILATED C.M
Dilated cardiomyopathy develops when the ventricles enlarge and weaken.
The weakened chambers of the heart don’t pump effectively, causing
the heart muscle to work harder. Over time, the heart loses the ability to pump blood effectively. Dilated cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure, heart valve disease, irregular heart rate, and blood clots in the heart.
Слайд 8RESTRICTIVE C.M
Restrictive cardiomyopathy develops when the ventricles become stiff and
rigid but the walls of the heart do not thicken.
As a result, the ventricles do not relax and don’t fill with the normal blood volume. As the disease progresses, the ventricles do not pump as well and the heart muscle weakens. Слайд 10ARRHYTHMOGENIC RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSPLASIA
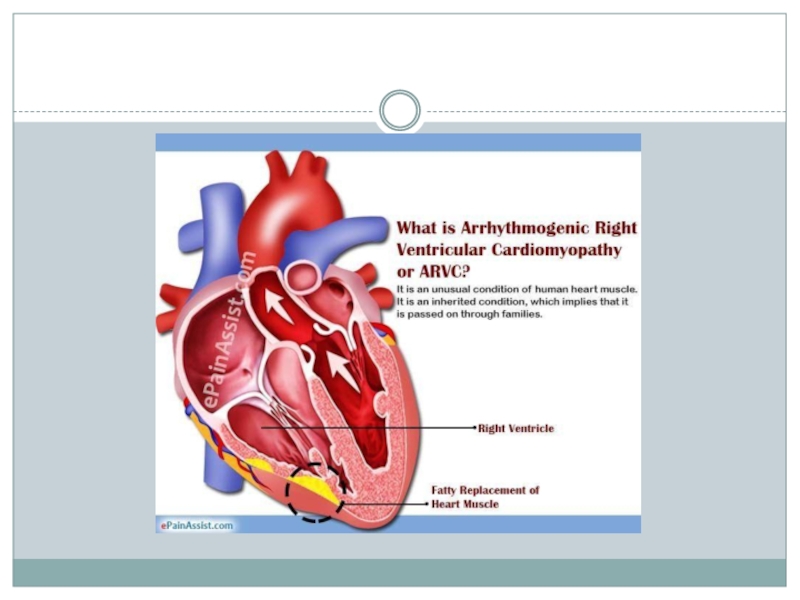
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia is a rare
type of cardiomyopathy that occurs when the muscle tissue in
the right ventricle is replaced with fatty or fibrous tissue.This can lead to disruptions in the heart’s electrical signals and causes arrhythmias.
Слайд 13UNCLASSIFIED C.M
Left ventricular noncompaction happens when the left ventricle has
trabeculations, projections of muscle inside the ventricle.
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, or broken
heart syndrome, happens when extreme stress leads to heart muscle failure. Though rare, this condition is more common in post-menopausal women.Слайд 15HCM CAUSES
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy usually is inherited. It’s caused by a
mutation or change in some of the genes in heart
muscle proteins.Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy also can develop over time because of high blood pressure, aging, or other diseases, such as diabetes or thyroid disease.
Слайд 16DCM CAUSES
Alcohol, especially if you also have a poor diet
Certain
toxins, such as poisons and heavy metals
Complications during the last
months of pregnancyIschemic heart disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, diabetes, thyroid disease, viral hepatitis, and HIV
Illegal drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, and some medicines used to treat cancer
Infections, especially viral infections that inflame the heart muscle
Слайд 17RCM CAUSES
Amyloidosis
Connective tissue disorders
Hemochromatosis
Sarcoidosis
Some cancer treatments, such as radiation and
chemotherapy.
Слайд 18MAJOR RISK FACTORS
A family history of cardiomyopathy, heart failure, or sudden cardiac
arrest (SCA).
A disease or condition that can lead to cardiomyopathy, such
as ischemic heart disease, heart attack, or a viral infection that inflames the heart muscle.Diabetes or other metabolic diseases, or severe obesity
Diseases that can damage the heart, such as hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis, or amyloidosis.
Long-term alcoholism.
Long-term high blood pressure.
Слайд 20It’s important to identify those who may be at high
risk for cardiomyopathy.
After all, some people with cardiomyopathy never have
signs or symptoms. Others don’t have signs or symptoms in the early stages of the disease.
Слайд 21If people without symptoms recognize their heightened risk for cardiomyopathy,
there’s a better chance of diagnosing it early, when treatment
may be most effective.Signs and symptoms of heart failure usually occur in the later stages of cardiomyopathy, as the heart weakens.
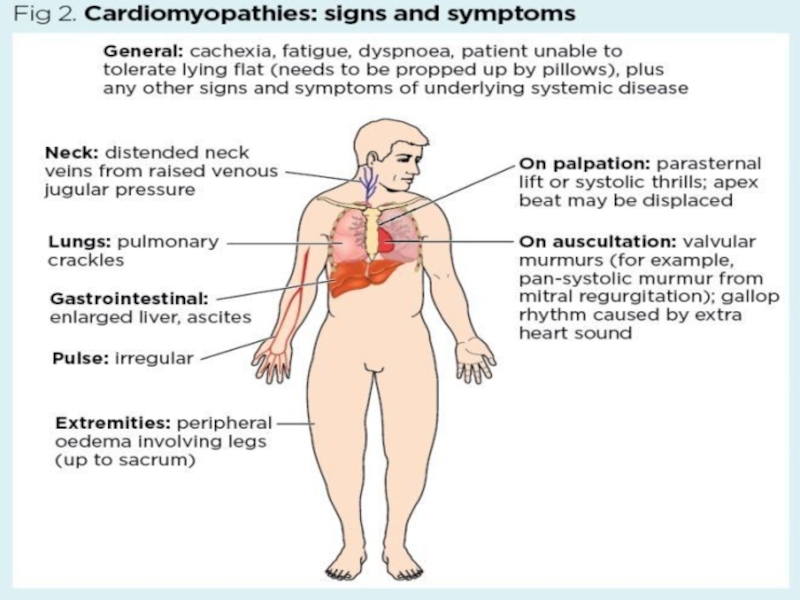
Слайд 22Signs and symptoms of cardiomyopathy include:
Shortness of breath or trouble
breathing, especially with physical exertion
Fatigue
Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs,
abdomen and veins in the neckDizziness