Слайд 1Chapter 15
Mutual Funds: An Easy
Way to Diversify
Слайд 2Learning Objectives
Weigh the advantages and disadvantages of investing in mutual
funds.
Differentiate between types of mutual funds, ETFs, and investment trusts.
Classify
mutual funds according to objectives.
Select a mutual fund that is right for you.
Calculate mutual fund returns.
Слайд 3Mutual Funds
Pool investors’ money, investing in stocks, bonds, and various
short-term securities.
Professional managers tend to the investments.
Allow investors to diversify,
even with a small investment.
Слайд 4Why Invest in Mutual Funds?
Advantages of mutual funds:
Professional management
Access
to the best research to evaluate investment alternatives.
Minimal transaction costs
Low commissions because of volume, which may translate into higher returns.
Liquidity
Easy to buy and sell on phone or online.
Слайд 5Why Invest in Mutual Funds?
Advantages of mutual funds:
Flexibility –
over 8,000 funds to choose from, covering many objectives and
risk levels.
Service – provide bookkeeping, checking accounts, automatic additions or withdrawals.
Avoidance of bad brokers – avoid potentially bad advice, high sales commissions, and churning.
Слайд 6Why Invest in Mutual Funds?
Disadvantages of mutual funds:
Lower than
market performance – mutual funds underperform the market on average.
Costs
– sales fee or load can be as high as 8.5% in addition to annual expense ratio at 3%.
Risks – not all mutual funds are safe; specialized funds may lack diversification outside a specific industry.
Слайд 7Why Invest in Mutual Funds?
Disadvantages of mutual funds:
Systematic risk
- mutual funds do not diversify away systematic risk. Even
mutual funds will suffer in a crash.
Taxes – mutual funds trade frequently, so investors may pay taxes on capital gains. You cannot defer taxes.
Слайд 8Mutual Fund-Amentals
A mutual fund pools money from investors with similar
financial goals.
You are investing in a diversified portfolio that’s professionally
managed according to set goals.
Investment objectives are clearly stated.
Слайд 9Mutual Fund-Amentals
Make money 3 ways in a mutual fund:
As the
value of the securities in the fund increases, the value
of each mutual fund share also rises.
Most pay dividends or interest to shareholders.
Shareholders receive a capital gains distribution when the fund sells a security for more than originally paid.
Слайд 10Mutual Fund-Amentals
Organization of a mutual fund:
Fund is set up as
a corporation or trust, owned by shareholders.
Shareholders elect a board
of directors.
Fund is run by a management company.
Each individual fund hires an investment advisor to oversee the fund.
Contracts with a custodian, a transfer agent, and an underwriter.
Слайд 11Investment Companies
A firm that invests the pooled money of a
number of investors in return for
a fee.
Types of investment companies:
Open-End
Investment Companies
Closed-End Investment Companies
Unit Investment Trusts
Real Estate Investment Trusts
Слайд 12Open-End Investment Companies
These mutual funds are the most popular form
of investment companies.
Open-end means the investment company can issue an
unlimited number of ownership shares.
Shares do not trade in the secondary market, must buy or sell through the fund.
Price based on net asset value (NAV).
Слайд 13Closed-End Investment Companies
Has a fixed number of shares, cannot issue
new shares.
Shares sold initially by investment company, afterwards they trade
like a common stock.
Price based on demand, not NAV.
Слайд 14Unit Investment Trusts
A fixed pool of securities with each unit
representing a proportionate ownership in the pool.
They are not managed.
Fund
purchases a fixed amount of bonds, holds them until maturity, then the trust dissolves.
Слайд 15Real Estate Investment Trusts
Like a mutual fund specializing in real
estate.
Has a professional manager.
Uses pooled funds.
Is actively managed.
Must collect
75% of its income from real estate and distribute 95% of that income in the form of dividends.
Слайд 16Real Estate Investment Trusts
Types of REITs:
Equity – buys property directly
and manages it. Investors look for appreciation in value.
Mortgage –
investment is limited to mortgages. Investors receive interest payments only.
Hybrid – a combination of the two. Invests in both property and mortgages, receiving both interest and capital appreciation.
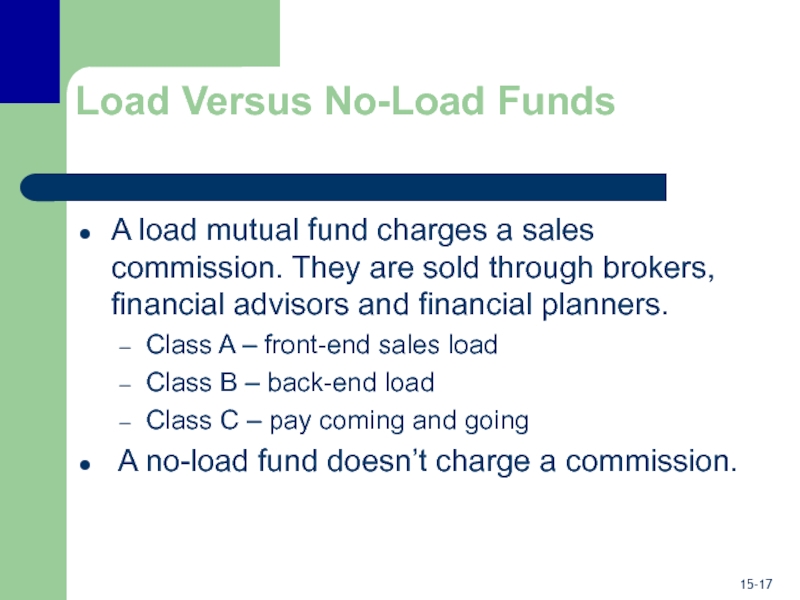
Слайд 17Load Versus No-Load Funds
A load mutual fund charges a sales
commission. They are sold through brokers, financial advisors and financial
planners.
Class A – front-end sales load
Class B – back-end load
Class C – pay coming and going
A no-load fund doesn’t charge a commission.
Слайд 18Management Fees and Expenses
Invest in a fund with a low
expense ratio
Ratio compares funds expenses to total assets.
Look at
the turnover rate
Measures the level of the fund’s trading activity.
12b-1 Fees
Marketing expenses for advertising and sales promotion.
Слайд 19Money Market Mutual Funds
Invest in Treasury bills, CDs, and other
short-term investments, less than 30 days.
Regarded as practically risk-free.
Carry no
loads, trade at a constant $1 NAV, and have minimal expenses.
Tax-exempt money market fund invests only in short-term municipal debt.
Слайд 20Stock Mutual Funds
Aggressive Growth Funds – maximize capital appreciation while
ignoring income. Have wider price swings than other funds.
Small-Company Growth
Funds – similar to aggressive growth funds but limited to investments in small companies. Look to uncover and invest in undiscovered companies with unlimited growth potential.
Слайд 21Stock Mutual Funds
Growth and Income Funds – provide a steady
stream of income with the potential for increasing value. Less
risky, stable dividends, less price movement.
Sector Funds – specialized mutual fund investing 65% of its assets in securities from a specific industry. Less risky than an individual stock, but more risky than a traditional mutual fund.
Слайд 22Stock Mutual Funds
Index Funds – try to track a market
index, such as the S&P 500, by buying stocks in
that index. Provide diversification at a low cost.
International Funds – concentrate on securities from other countries, may have political and currency risks.
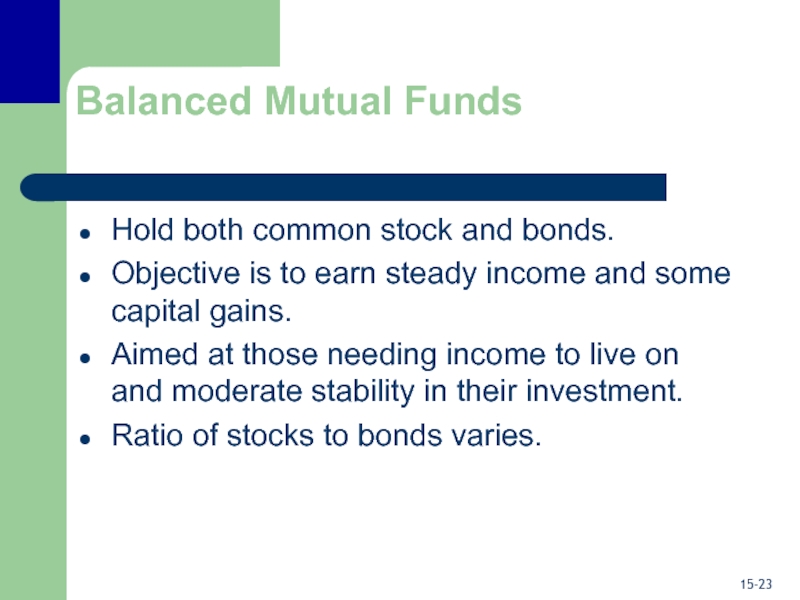
Слайд 23Balanced Mutual Funds
Hold both common stock and bonds.
Objective is to
earn steady income and some capital gains.
Aimed at those needing
income to live on and moderate stability in their investment.
Ratio of stocks to bonds varies.
Слайд 24Asset Allocation Funds
Similar to a balanced fund, invest in stocks,
bonds, and money market securities.
Differ in that they move money
between stocks and bonds to outperform the market.
It is a balanced fund practicing market timing.
Слайд 25Life Cycle and Target
Retirement Funds
Life cycle is the newest type
of funds. An asset allocation fund that tailors holdings to
investor’s characteristics, such as age and risk tolerance.
Target retirement funds are managed based on when you plan to retire.
Слайд 26Bond Funds
Bond Funds
$1000 investment buys a diversified portfolio.
More liquidity
Professional
management
Have automatic reinvestment
Individual Bonds
Save mutual fund expenses
Bond funds do
not mature, individual bonds do
Слайд 27
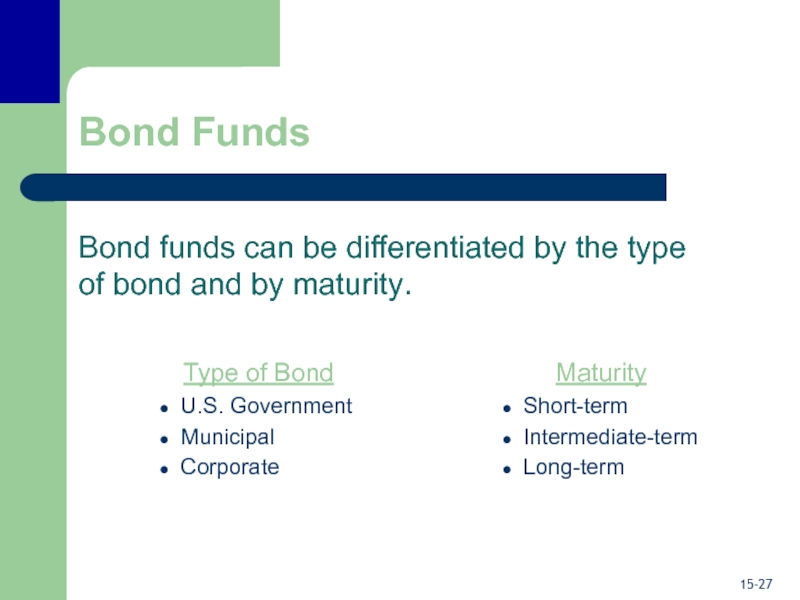
Bond Funds
Bond funds can be differentiated by the type of
bond and by maturity.
Type of Bond
U.S. Government
Municipal
Corporate
Maturity
Short-term
Intermediate-term
Long-term
Слайд 28Bond Funds
U.S. Government Bond Funds
or GNMA Funds
U.S. Treasury Bond Funds
Specialize in Treasury securities.
No default risk, but will fluctuate with
changes in interest rates.
GNMA Funds
Specialize in mortgage-backed securities.
Carry interest rate risk
and prepayment risk.
Слайд 29Bond Funds
Municipal Bond Funds – interest is generally tax-exempt from
federal taxes.
Aimed at those looking to avoid taxes.
Corporate Bond Funds
– invest in various types of corporate bonds, including high quality and junk bonds.
As interest rates rise, NAV goes down.
Слайд 30Bond Funds
Bond funds and their maturities:
Short-term – 1-5 years in
maturity
Intermediate-term – 5-10 years in maturity
Long-term – 10-30 years in
maturity
As interest rates change, long-term bonds fluctuate more than short-term.
Слайд 31ETFs or Exchange Traded Funds
First issued in 1993, these are
hybrids between a mutual fund and an individual stock or
bond.
Trade on an exchange and can be bought or sold throughout the day.
QQQ tracks the NASDAQ 100 Index.
SPDRS tracks the S&P 500.
Слайд 32ETFs or Exchange Traded Funds
Advantages of ETFs:
Trade on an exchange
and can be bought and sold throughout the day.
Can be
sold short or bought on margin.
Allow an instant position in a sector or country.
Low annual expenses.
More tax efficient than mutual funds.
Слайд 33ETFs or Exchange Traded Funds
Disadvantages of ETFs:
Pay a commission because
they trade like stocks.
Don’t necessarily trade at NAV.
Bid-ask spread because
buying from another investor.
Expensive for those who trade often, incur brokerage costs.
Слайд 34Mutual Fund Services
Automatic investment and withdrawal plans
Automatic reinvestment of
interest, dividends, and capital gains
Wiring and funds express options
Phone switching
Easy
establishment of retirement plans
Check writing
Bookkeeping and help with taxes
Слайд 35Buying a Mutual Fund
Step 1: Determining Your Goals
Buying a
mutual fund involves determining your investment goals and time horizon.
Understand
why you are investing:
To receive additional income
Supplement your retirement income
Save for a child’s education
Слайд 36Buying a Mutual Fund
Step 2: Meeting Your Objectives
Identify the
fund’s objectives by looking at objective classifications.
Don’t assume the fund’s
name reflects the strategy or objectives.
Morningstar provides an investment style box to understand the investment style.
Слайд 37Buying a Mutual Fund
Step 2: Meeting Your Objectives
Look in
the prospectus for:
Fund’s goals and investment strategy
Fund manager’s past experience
Any
investment limitations the fund may have
Tax considerations of importance to investors
Redemption and investment process
Services provided
Performance over past 10 years
Fund fees and expenses
Fund’s annual turnover rate
Слайд 38Buying a Mutual Fund
Step 3: Evaluating the Fund
Look closely
at past performance and scrutinize their costs.
Past performance does not
predict future results, but it does give insight.
Limit comparisons to funds with similar objectives.
Investigate how the fund did during upturns and downturns.
Слайд 39Buying a Mutual Fund
Step 3: Evaluating the Fund
Sources of
Information:
Wall Street Journal
Forbes – annual mutual fund survey
Kiplinger’s Personal Finance
magazine
Morningstar www.morningstar.com
Слайд 40Buying a Mutual Fund
Making the Purchase:
Buy direct – use
phone or internet.
Buy through a mutual fund supermarket – such
as Fidelity or Schwab.