Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Complex coMPOUNDS
Содержание
- 1. Complex coMPOUNDS
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Слайд 3
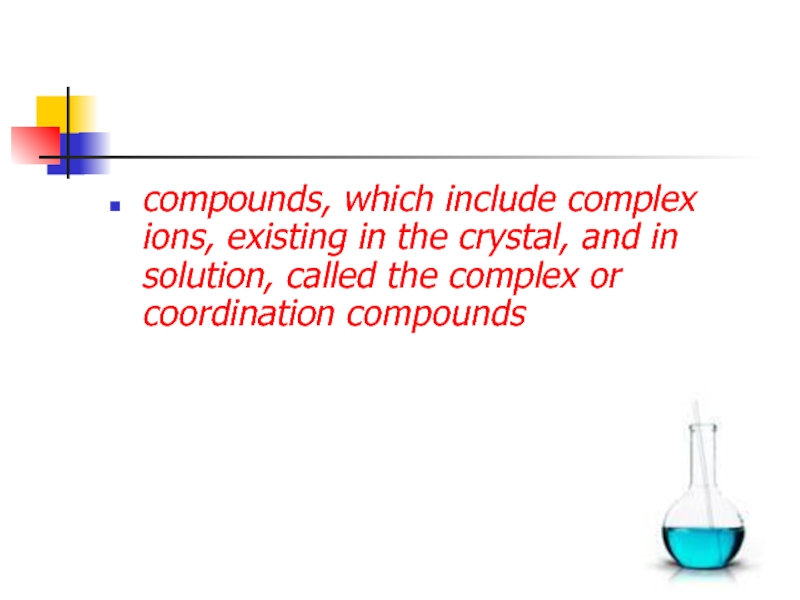
- 4. compounds, which include complex ions, existing in
- 5. Structure of complex compounds In
- 6. Oppositely charged ions or neutral molecules called ligands are coordinated around the central ion.
- 7. The complexing agent and ligands form inner
- 8. The total number of coordinate bonds formed
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Nomenclature of complex compoundsNames of complex compounds
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. [Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 – tetraammine copper(II) chloride; K2 [Cu(OH)4] – potassium tetrahydroxocupprate(II); [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] – trichloro triammine chromium(III).
- 13. Слайд 13
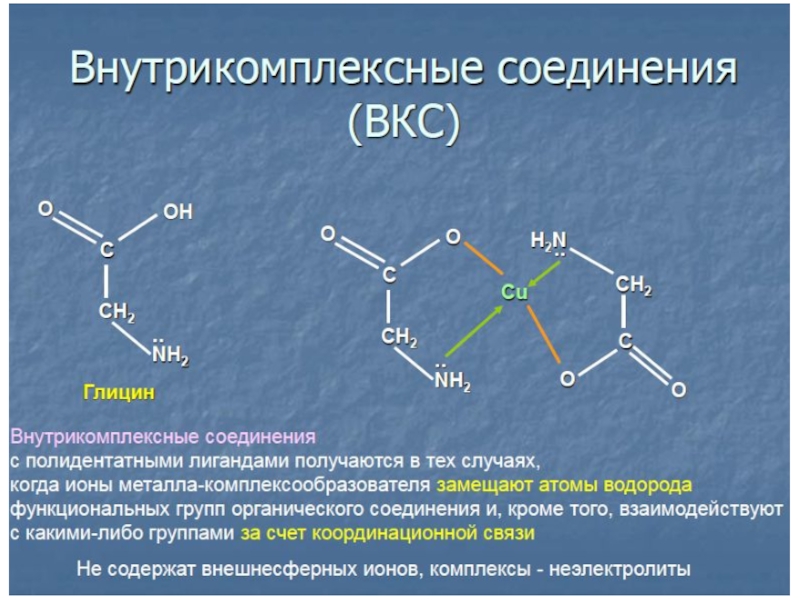
- 14. Classification of complex compoundsThere are several types of classification of complex compounds.
- 15. Classification of complex compounds1. Depending upon a charge
- 16. 22) Depending upon the type of the ligand:(i) Aqua-complexes
- 17. б)Гидроксокомплексы – это комплексные анионы, в которых лигандами
- 18. Depending upon the nature of a central ion: complexes of copper, silver, iron, chrome etc.
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
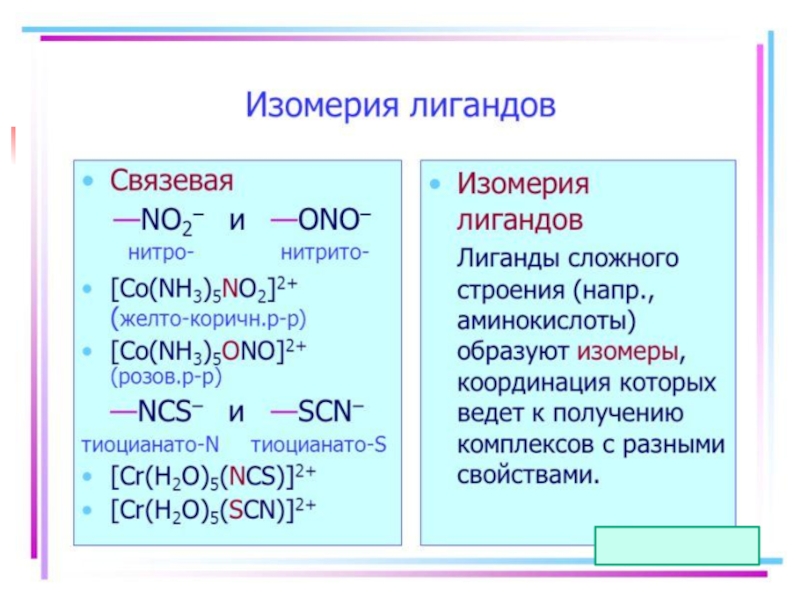
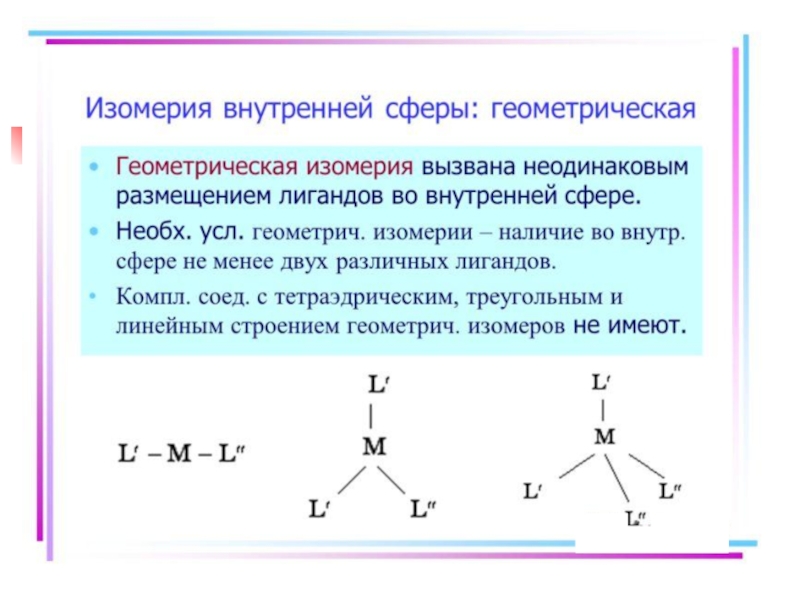
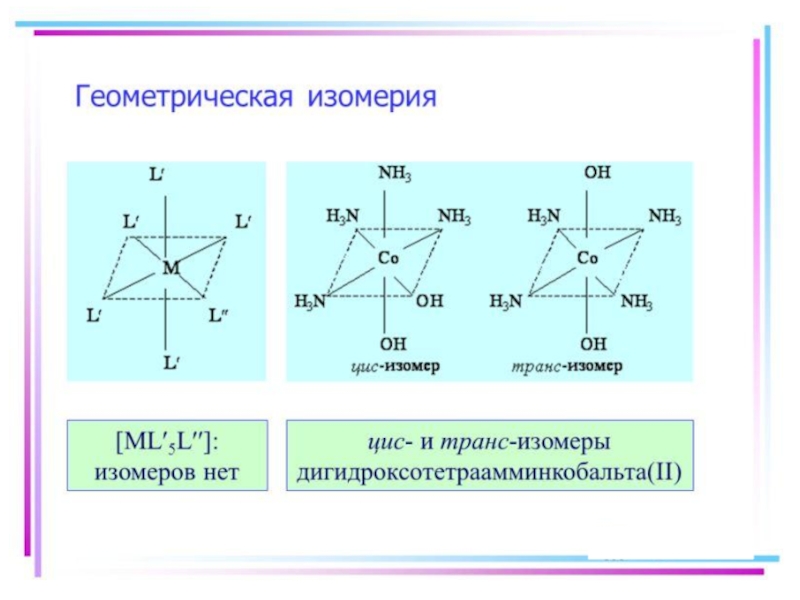
- 21. Isomerism
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Electronic structure of
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. Слайд 32
- 33. Слайд 33
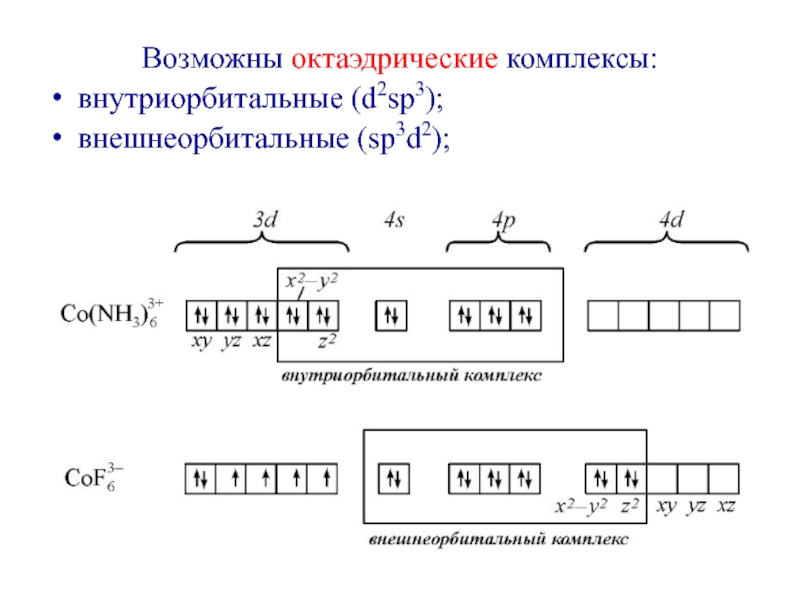
- 34. Возможны октаэдрические комплексы:внутриорбитальные (d2sp3);внешнеорбитальные (sp3d2);
- 35. Электронное строения атома кобальта:
- 36. Entering of lone electronic pairs
- 37. Слайд 37
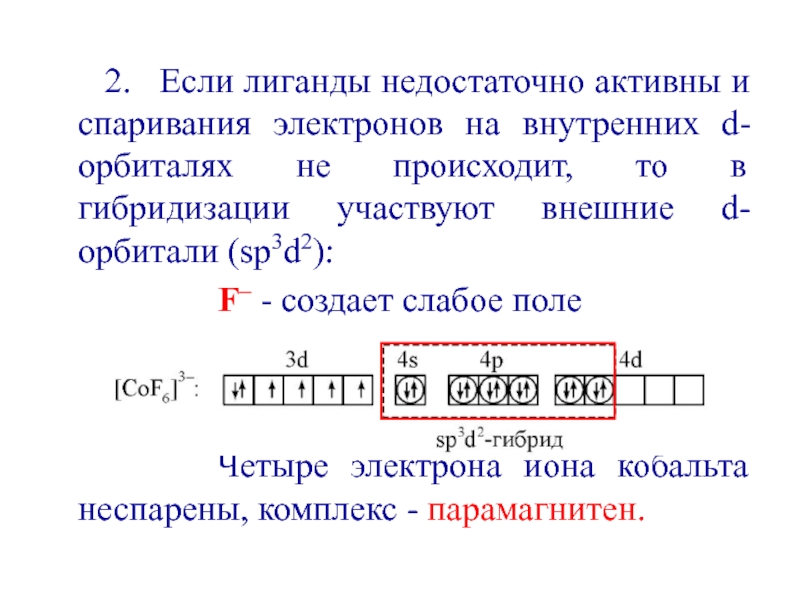
- 38. 2. Если лиганды
- 39. Слайд 39
- 40. Слайд 40
- 41. Скачать презентанцию
compounds, which include complex ions, existing in the crystal, and in solution, called the complex or coordination compounds
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4compounds, which include complex ions, existing in the crystal, and
in solution, called the complex or coordination compounds
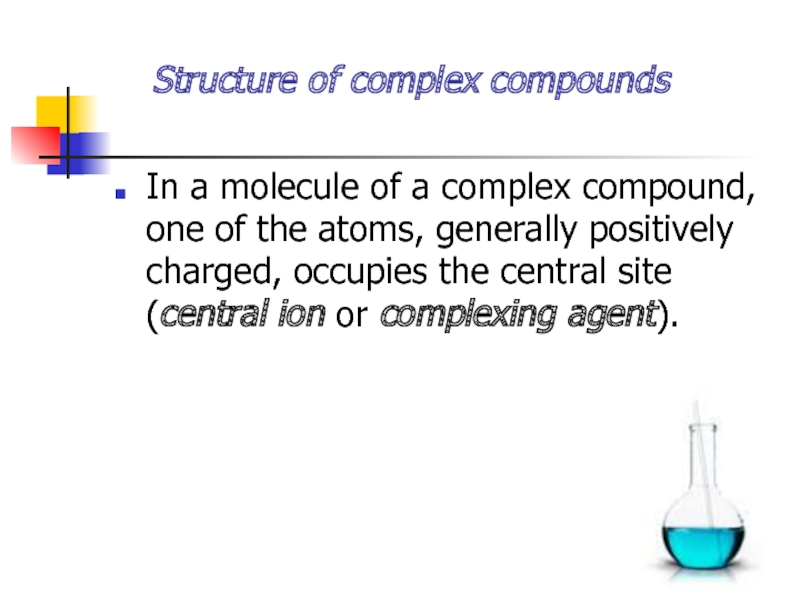
Слайд 5 Structure of complex compounds
In a molecule of a
complex compound, one of the atoms, generally positively charged, occupies
the central site (central ion or complexing agent).Слайд 6Oppositely charged ions or neutral molecules called ligands are coordinated
around the central ion.
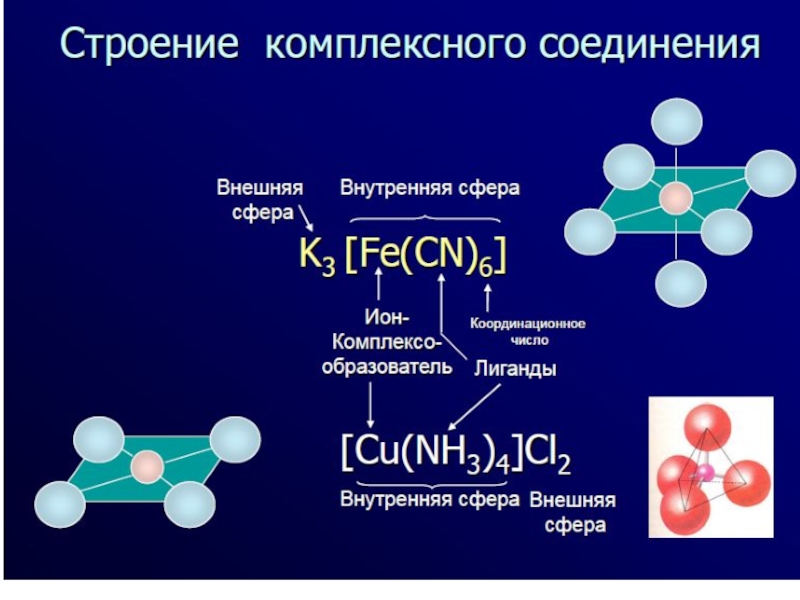
Слайд 7The complexing agent and ligands form inner sphere of a
complex compound. It is characterized by coordinate bonds which are
formed while overlapping of empty p- and d-orbitals of a central ion and orbitals containing lone electron pairs of ligands. The ions in the outer sphere are mainly bonded to the complex ions by forces of electrostatic interaction (ionic bonds).Слайд 8The total number of coordinate bonds formed by the complexing
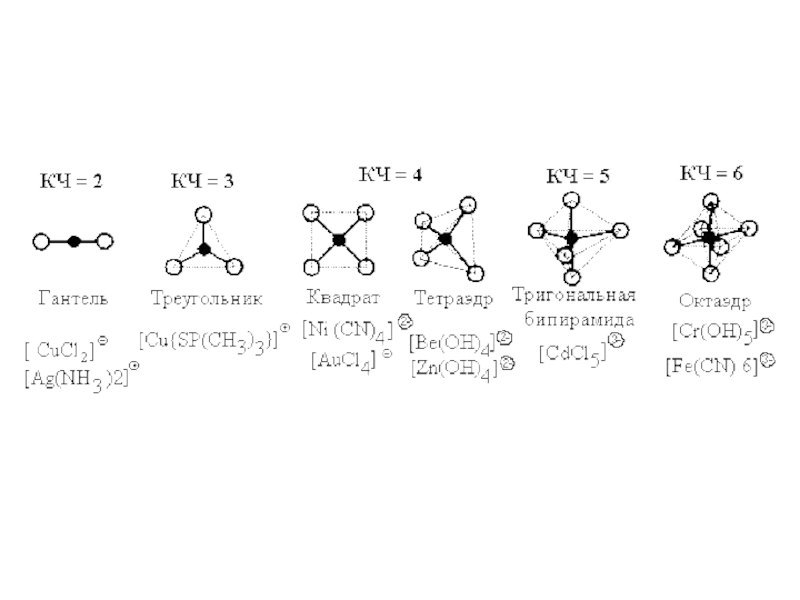
agent is known as coordination number of the central ion.
It mainly depends upon the charge of the complexing agent (for monocharged ions it usually equals 1, for discharged ions – 4 or 6, for tricharged – 6 and above), and the size of an ion (the larger the central ion, the greater its coordination number is, for lanthanides and actinides it can reach to 12).Слайд 10Nomenclature of complex compounds
Names of complex compounds are similar to
the names of simple salts. The order of naiming particles
in a complex ion is the following: anionic ligands – neutral ligands – central ion. Number of ligands is designated with the help of greek numeralsСлайд 12[Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 – tetraammine copper(II) chloride;
K2 [Cu(OH)4] – potassium tetrahydroxocupprate(II);
[Cr(NH3)3Cl3] – trichloro triammine chromium(III).
Слайд 14Classification of complex compounds
There are several types of classification of
complex compounds.
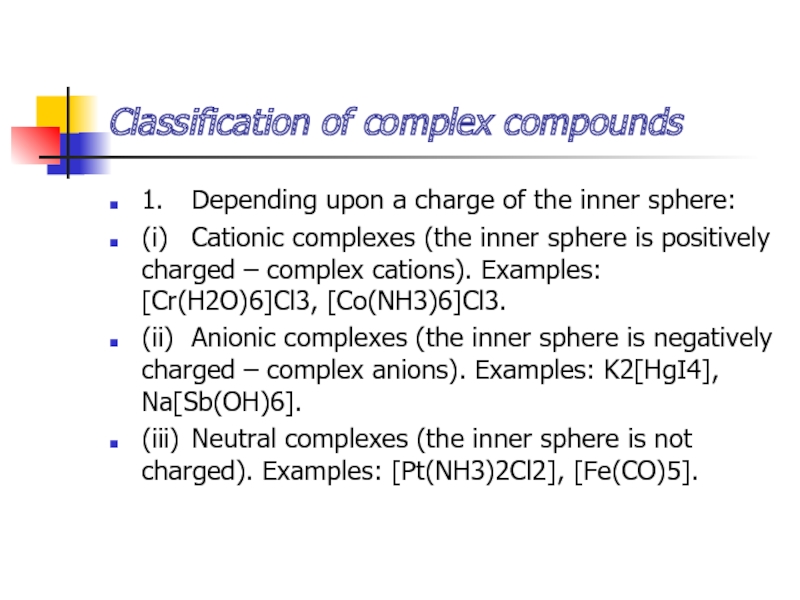
Слайд 15Classification of complex compounds
1. Depending upon a charge of the inner
sphere:
(i) Cationic complexes (the inner sphere is positively charged – complex
cations). Examples: [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3, [Co(NH3)6]Cl3.(ii) Anionic complexes (the inner sphere is negatively charged – complex anions). Examples: K2[HgI4], Na[Sb(OH)6].
(iii) Neutral complexes (the inner sphere is not charged). Examples: [Pt(NH3)2Cl2], [Fe(CO)5].
Слайд 1622) Depending upon the type of the ligand:
(i) Aqua-complexes (ligands are water
molecules – [Cu(H2O)5]SO4).
(ii) Ammino-complexes (ligands are molecules of ammonia or organic
ammines – [Ag(NH3)2]Cl).(iii) Hydroxy-complexes (ligands are OH– anions – Na2[Sn(OH)4]).
(iv) Carbonyl-complexes (ligands are molecules of carbon monoxide – [Fe(CO)5]).
(v) Acido-complexes (ligands are anions of inorganic acids). Examples: chlorocomplexes K2[HgCl4], fluorocomplexes K3[FeF6], cyanocomplexes KFe[Fe(CN)6], thiocyanocomplexes K3[Fe(SCN)6], sulphitocomplexes K[Ag(SO3)], etc.
Слайд 17б)Гидроксокомплексы – это комплексные анионы, в которых лигандами являются гидроксид-ионы OH–.
Комплексообразователями являются металлы, склонные к проявлению амфотерных свойств – Be, Zn,
Al, Cr.Например: Na[Al(OH)4], Ba[Zn(OH)4].
в) Аммиакаты – это комплексные катионы, в которых лигандами являются молекулы NH3. Комплексообразователями являются d-элементы.
Например: [Cu(NH3)4]SO4, [Ag(NH3)2]Cl.
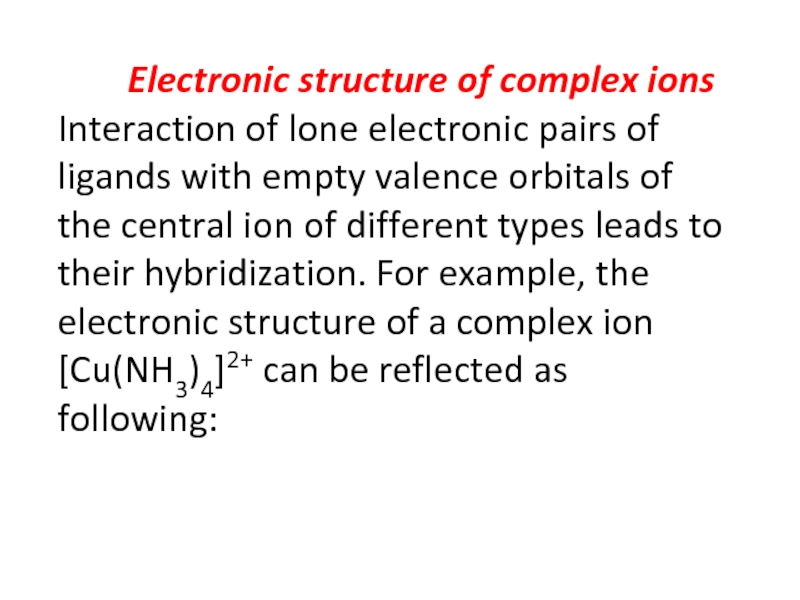
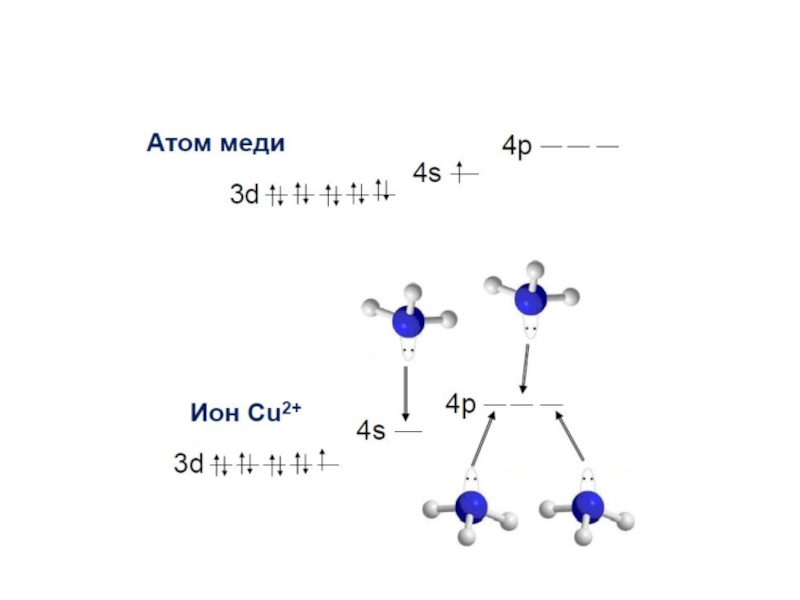
Слайд 30 Electronic structure of complex ions Interaction of
lone electronic pairs of ligands with empty valence orbitals of
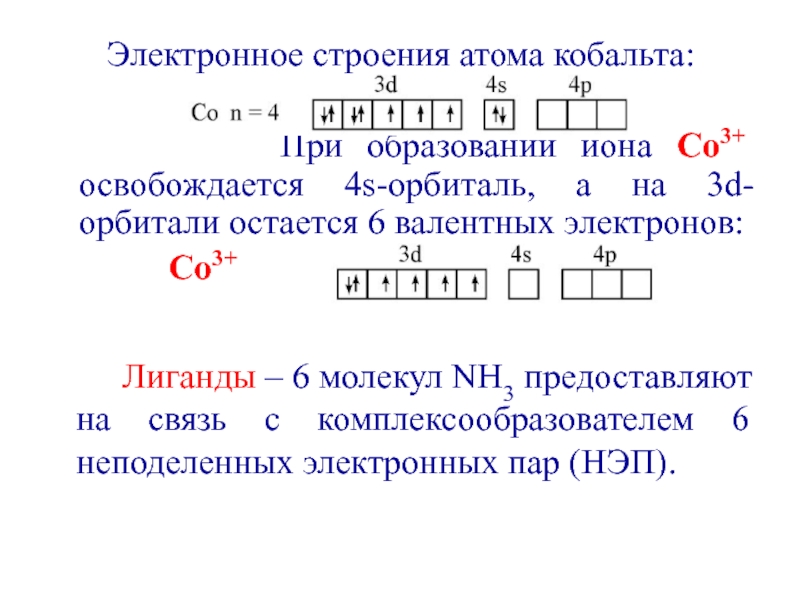
the central ion of different types leads to their hybridization. For example, the electronic structure of a complex ion [Cu(NH3)4]2+ can be reflected as following:Слайд 35Электронное строения атома кобальта:
При образовании
иона Со3+ освобождается 4s-орбиталь, а на 3d-орбитали остается 6 валентных
электронов:Со3+
Лиганды – 6 молекул NH3 предоставляют на связь с комплексообразователем 6 неподеленных электронных пар (НЭП).
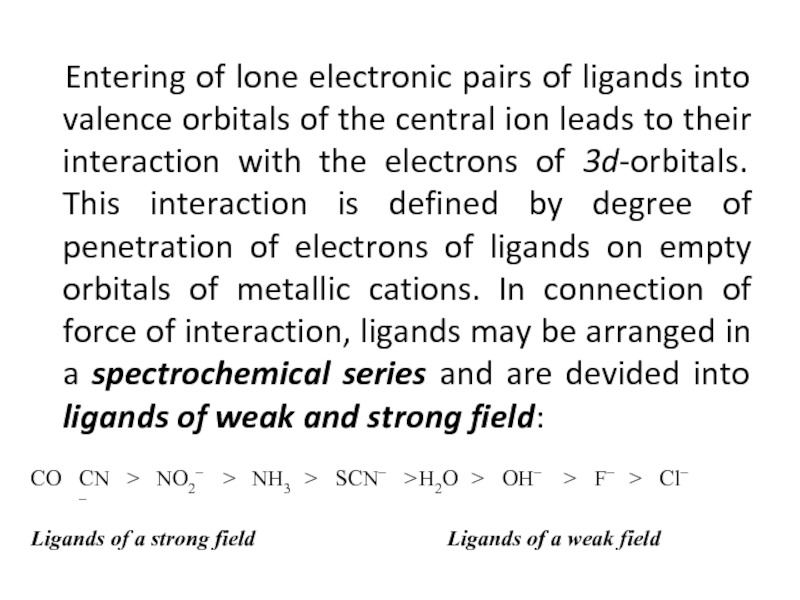
Слайд 36 Entering of lone electronic pairs of ligands into
valence orbitals of the central ion leads to their interaction
with the electrons of 3d-orbitals. This interaction is defined by degree of penetration of electrons of ligands on empty orbitals of metallic cations. In connection of force of interaction, ligands may be arranged in a spectrochemical series and are devided into ligands of weak and strong field:Слайд 37
Все валентные
электроны спарены. Комплекс [Co(NH3)6]3+ - диамагнитный, что согласуется с экспериментом.
Слайд 38 2. Если лиганды недостаточно активны и
спаривания электронов на внутренних d-орбиталях не происходит, то в гибридизации
участвуют внешние d-орбитали (sp3d2):F– - создает слабое поле
Четыре электрона иона кобальта неспарены, комплекс - парамагнитен.








![Complex coMPOUNDS [Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 – tetraammine copper(II) chloride; K2 [Cu(OH)4] – potassium tetrahydroxocupprate(II); [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] – trichloro triammine chromium(III). [Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 – tetraammine copper(II) chloride; K2 [Cu(OH)4] – potassium tetrahydroxocupprate(II); [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] – trichloro triammine chromium(III).](/img/tmb/4/349380/73b70952efbea0da6f3ddb248b688012-800x.jpg)

![Complex coMPOUNDS 22) Depending upon the type of the ligand:(i) Aqua-complexes (ligands are water molecules 22) Depending upon the type of the ligand:(i) Aqua-complexes (ligands are water molecules – [Cu(H2O)5]SO4).(ii) Ammino-complexes (ligands are molecules of](/img/thumbs/23073041b5204eb0fef609061251cb04-800x.jpg)










![Complex coMPOUNDS Все валентные электроны спарены. Комплекс [Co(NH3)6]3+ - диамагнитный, что согласуется с экспериментом. Все валентные электроны спарены. Комплекс [Co(NH3)6]3+ - диамагнитный, что](/img/thumbs/fcea1e265148da2a8285d59ff2dac222-800x.jpg)