Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Foundations of Planning
Содержание
- 1. Foundations of Planning
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall7–Exhibit 7–1 Types of Plans
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall7–Exhibit 7–2 The Downside of Traditional Goal Setting
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Foundations
of Planning
Слайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.7.1 The What And Why Of Planning
Define planning.
Describe the purposes of planning.
Explain what studies have shown about the relationship between planning and performance.
7.2 Goals And Plans
Define goals and plans.
Describe the types of goals organizations might have.
Describe each of the different types of plans.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Learning
Outcomes
7.3 Setting Goals and Developing Plans
Discuss how traditional goal setting
and MBO work.Describe well written goals and explain hw to set them.
Discuss the contingency factors that affect planning.
Describe the approaches to planning.
7.4 Contemporary Issues in Planning
Explain the criticisms of planning.
Describe how managers can effectively plan in today’s dynamic environment.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
What
Is Planning?
Planning
A primary managerial activity that involves:
Defining the organization’s goals
Establishing
an overall strategy for achieving those goalsDeveloping plans for organizational work activities
Formal planning
Specific goals covering a specific time period
Written and shared with organizational members
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Why
Do Managers Plan?
Purposes of Planning
Provides direction
Reduces uncertainty
Minimizes waste and redundancy
Sets
the standards for controllingСлайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Planning
and Performance
The Relationship Between Planning and Performance
Formal planning is associated
with:Higher profits and returns on assets.
Positive financial results.
The quality of planning and implementation affects performance more than the extent of planning.
The external environment can reduce the impact of planning on performance.
Formal planning must be used for several years before planning begins to affect performance.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
How
Do Managers Plan?
Elements of Planning
Goals (also Objectives)
Desired outcomes for individuals,
groups, or entire organizationsProvide direction and evaluation performance criteria
Plans
Documents that outline how goals are to be accomplished
Describe how resources are to be allocated and establish activity schedules
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Types
of Goals
Financial Goals
Are related to the expected internal financial performance
of the organization.Strategic Goals
Are related to the performance of the firm relative to factors in its external environment (e.g., competitors).
Stated Goals versus Real Goals
Broadly-worded official statements of the organization (intended for public consumption) that may be irrelevant to its real goals (what actually goes on in the organization).
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
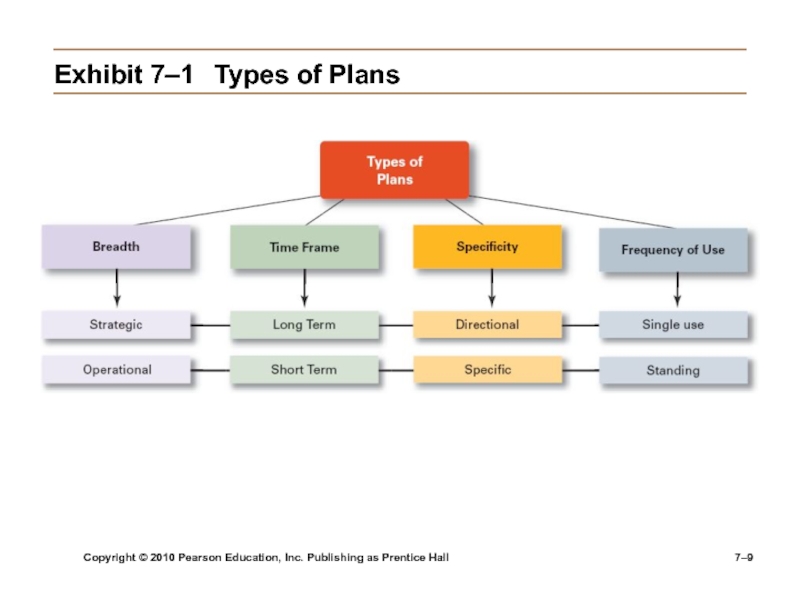
Exhibit
7–1 Types of Plans
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Types
of Plans
Strategic Plans
Apply to the entire organization.
Establish the organization’s overall
goals.Seek to position the organization in terms of its environment.
Cover extended periods of time.
Operational Plans
Specify the details of how the overall goals are to be achieved.
Cover a short time period.
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Types
of Plans
Long-Term Plans
Plans with time frames extending beyond three years
Short-Term
PlansPlans with time frames of one year or less
Specific Plans
Plans that are clearly defined and leave no room for interpretation
Directional Plans
Flexible plans that set out general guidelines and provide focus, yet allow discretion in implementation
Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Types
of Plans
Single-Use Plan
A one-time plan specifically designed to meet the
need of a unique situation.Standing Plans
Ongoing plans that provide guidance for activities performed repeatedly.
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Setting
Goals and Developing Plans
Traditional Goal Setting
Broad goals are set at
the top of the organization.Goals are then broken into sub-goals for each organizational level.
Assumes that top management knows best because they can see the “big picture.”
Goals are intended to direct, guide, and constrain from above.
Goals lose clarity and focus as lower-level managers attempt to interpret and define the goals for their areas of responsibility.
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Exhibit
7–2 The Downside of Traditional Goal Setting
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Maintaining
the Hierarchy of Goals
Means–Ends Chain
The integrated network of goals that
results from establishing a clearly-defined hierarchy of organizational goals.Achievement of lower-level goals is the means by which to reach higher-level goals (ends).
Setting Goals and Developing Plans
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Management
By Objectives (MBO)
Specific performance goals are jointly determined by employees
and managers.Progress toward accomplishing goals is periodically reviewed.
Rewards are allocated on the basis of progress towards the goals.
Key elements of MBO:
Goal specificity, participative decision making, an explicit performance/evaluation period, feedback
Setting Goals and Developing Plans
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Exhibit
7–3 Steps in a Typical MBO Program
The organization’s overall objectives
and strategies are formulated.Major objectives are allocated among divisional and departmental units.
Unit managers collaboratively set specific objectives for their units with their managers.
Specific objectives are collaboratively set with all department members.
Action plans, defining how objectives are to be achieved, are specified and agreed upon by managers and employees.
The action plans are implemented.
Progress toward objectives is periodically reviewed, and feedback is provided.
Successful achievement of objectives is reinforced by performance-based rewards.
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Does
MBO Work?
Reason for MBO Success
Top management commitment and involvement
Potential Problems
with MBO ProgramsNot as effective in dynamic environments that require constant resetting of goals.
Overemphasis on individual accomplishment may create problems with teamwork.
Allowing the MBO program to become an annual paperwork shuffle.
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Exhibit
7–4 Well-Written Goals
Written in terms of outcomes, not actions
Focuses on
the ends, not the means.Measurable and quantifiable
Specifically defines how the outcome is to be measured and how much is expected.
Clear as to time frame
How long before measuring accomplishment.
Challenging yet attainable
Low goals do not motivate.
High goals motivate if they can be achieved.
Written down
Focuses, defines, and makes goals visible.
Communicated to all necessary organizational members
Puts everybody “on the same page.”
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Steps
in Goal Setting
Review the organization’s mission statement.
Do goals reflect the
mission?Evaluate available resources.
Are resources sufficient to accomplish the mission?
Determine goals individually or with others.
Are goals specific, measurable, and timely?
Write down the goals and communicate them.
Is everybody on the same page?
Review results and whether goals are being met.
What changes are needed in mission, resources, or goals?
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Developing
Plans
Contingency Factors in a Manager’s Planning
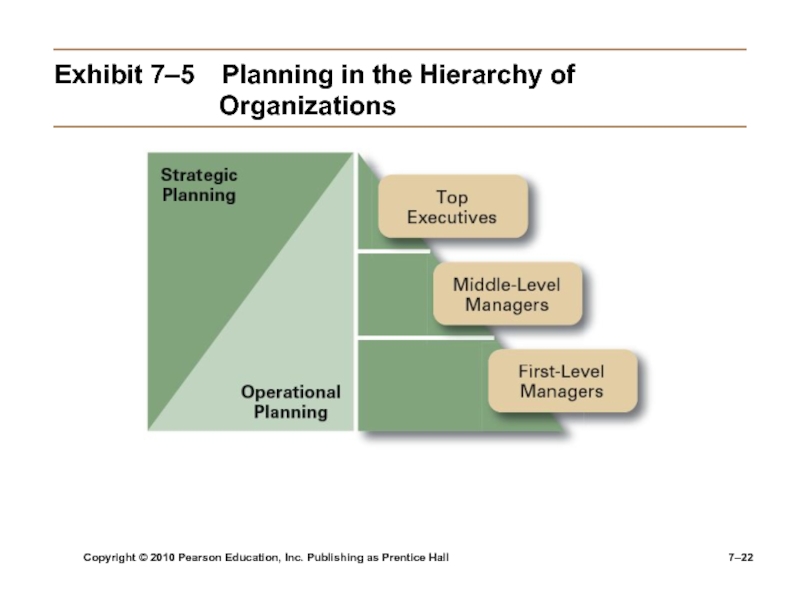
Manager’s level in the organization
Strategic
plans at higher levelsOperational plans at lower levels
Degree of environmental uncertainty
Stable environment: specific plans
Dynamic environment: specific but flexible plans
Length of future commitments
Commitment Concept: current plans affecting future commitments must be sufficiently long-term to meet those commitments.
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Exhibit
7–5 Planning in the Hierarchy of
Organizations
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Approaches
to Planning
Establishing a formal planning department
A group of planning specialists
who help managers write organizational plans.Planning is a function of management; it should never become the sole responsibility of planners.
Involving organizational members in the process
Plans are developed by members of organizational units at various levels and then coordinated with other units across the organization.
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Contemporary
Issues in Planning
Criticisms of Planning
Planning may create rigidity.
Plans cannot be
developed for dynamic environments.Formal plans cannot replace intuition and creativity.
Planning focuses managers’ attention on today’s competition not tomorrow’s survival.
Formal planning reinforces today’s success, which may lead to tomorrow’s failure.
Just planning isn’t enough.
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Contemporary
Issues in Planning (cont’d)
Effective Planning in Dynamic Environments
Develop plans that
are specific but flexible.Understand that planning is an ongoing process.
Change plans when conditions warrant.
Persistence in planning eventually pay off.
Flatten the organizational hierarchy to foster the development of planning skills at all organizational levels.
Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7–
Terms
to Know
planning
goals
plans
stated goals
real goals
framing
strategic plans
operational plans
long-term plans
short-term plans
specific plans
directional plans
single-use
planstanding plans
traditional goal setting
means-ends chain
management by objectives (MBO)
mission
commitment concept
formal planning department