Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Generations of programming language
Содержание
- 1. Generations of programming language
- 2. Assembly languageAn assembly language is a low-level
- 3. Machine codeMachine code, also known as machine
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. declarative programmingdeclarative programming is a programming
- 6. Imperative languageIn computer science, imperative programming is
- 7. Скачать презентанцию
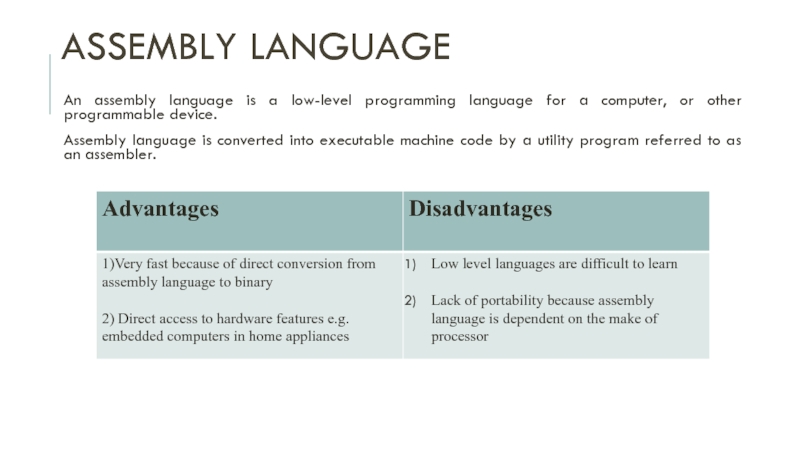
Assembly languageAn assembly language is a low-level programming language for a computer, or other programmable device. Assembly language is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Assembly language
An assembly language is a low-level programming language for
a computer, or other programmable device.
into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an assembler.Слайд 3Machine code
Machine code, also known as machine language, is the
elemental language of computers. It is read by the computer's
central processing unit (CPU), is composed of digital binary numbers and looks like a very long sequence of zeros and ones.e.g. 10001000 01010111 11000101 11110001 10100001 00010110
Each instruction performs a very specific task, such as loading a value into a register, or adding two binary numbers together.