Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Содержание
- 1. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
- 2. PLAN Definition of anemiaBlood parameters ``erythrocytes parameters``Iron metabolism
- 3. ANEMIA - DEFINITION REDUCTION OF HEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION BELOW REFERENCE VALUE
- 4. BLOOD PARAMETERSHemoglobin concentration (Hg)F: 7,2 –10; M:
- 5. Erythrocytes parametersMean corpuscular volume (MCV)N: 80-100 flRDW(Red
- 6. ReticulocytesRET: 0,5-2%ARC (absolute reticulocyte count ): 25-75x 109/lCRC (corrected reticulocyte count) RPI (reticulocyte production index)
- 7. IRON METABOLISMIron concentration (Fe)N: 50-150 g/dlTotal Iron
- 8. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIAIRON METABOLISMABSORPTION IN DUODENUMTRANSFERRIN TRANSPORTS
- 9. Most body iron is present in hemoglobin
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. IRON DEFICIENCY - STAGESPrelatent reduction in iron
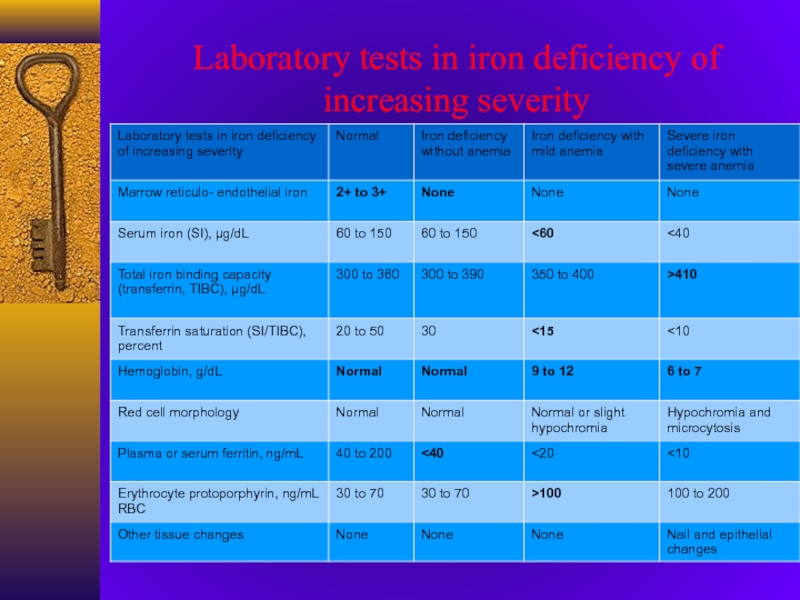
- 12. Laboratory tests in iron deficiency of increasing severity
- 13. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIAETIOLOGY:BLOOD LOSS
- 14. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIAGENERAL ANEMIA’S SYMPTOMS:FATIGABILITYDIZZINESSHEADACHESCOTOMASIRRITABILITY ROARINGPALPITATIONCHD, CHF
- 15. CHARACTERISTIC SYMPTOMSGLOSSITIS, STOMATITISDYSPHAGIA ( Plummer-Vinson syndrome)ATROPHIC GASTRITISDRY,
- 16.
- 17. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIAMCVMCH MCHC NFe TIBC and sTfRTRANSFERIN SATURATIONFERRITIN
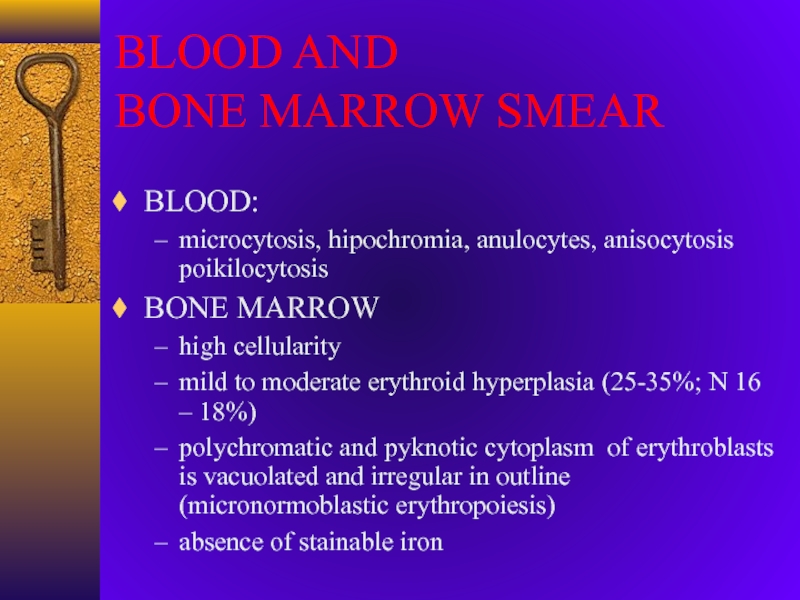
- 18. BLOOD AND BONE MARROW SMEARBLOOD:microcytosis, hipochromia,
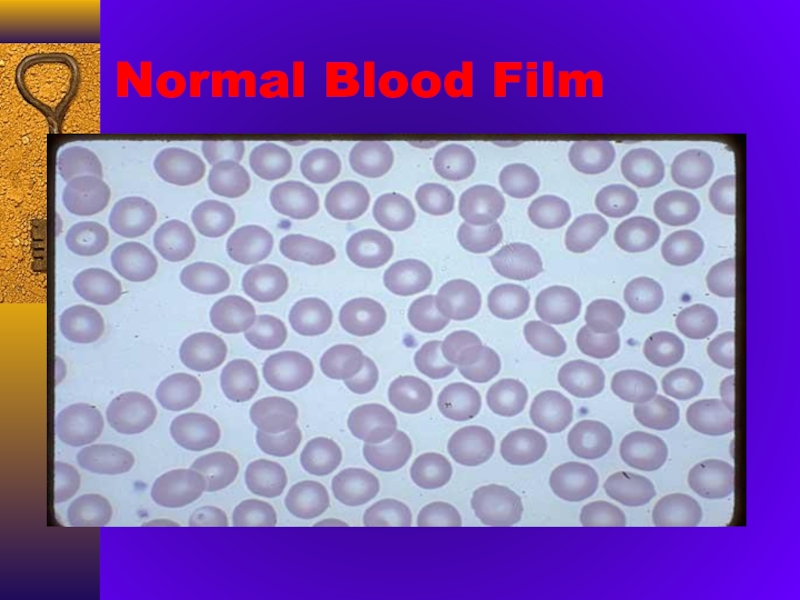
- 19. Normal Blood Film
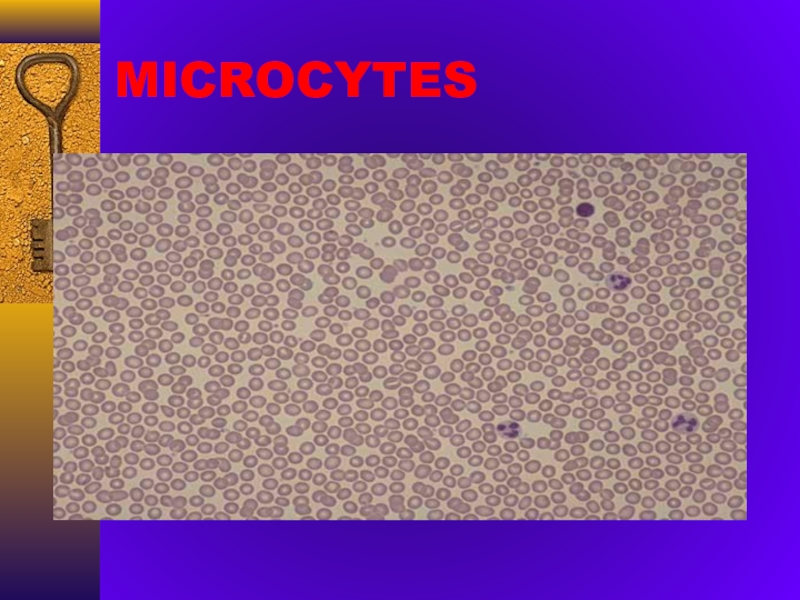
- 20. MICROCYTES
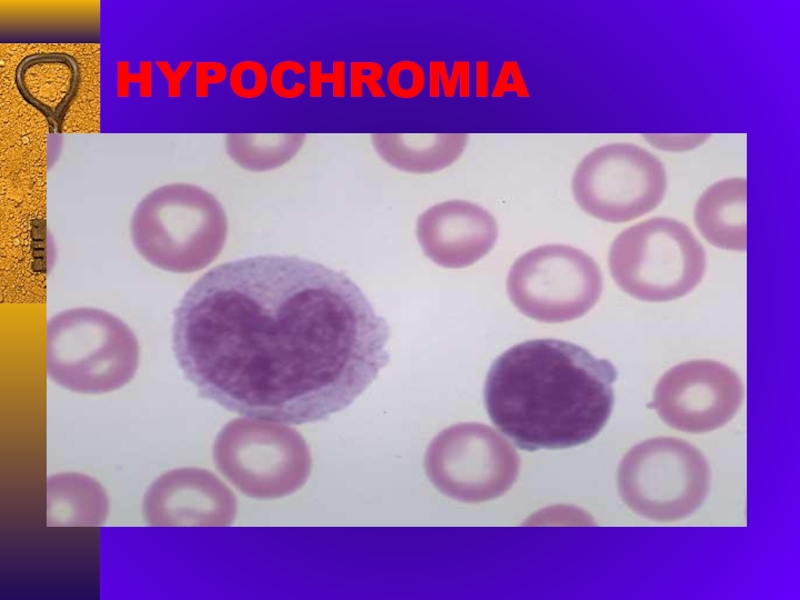
- 21. HYPOCHROMIA
- 22. ManagementHistory and physical examination is sufficient to
- 23. DIETARY IRONThere are 2 types of iron
- 24. ORAL IRON ABSORPTION TEST1. baseline serum iron
- 25. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA CUREORAL200 mg of iron
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA CUREPARENTERAL IRON SUBSTITUTIONBad oral
- 28. "NPS News 70: Iron deficiency anaemia". NPS
- 29. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENENTION!!!
- 30. Скачать презентанцию
PLAN Definition of anemiaBlood parameters ``erythrocytes parameters``Iron metabolism and iron deficiency anemiaCharacteristic symptoms of iron deficiency anemiaBlood and bone marrow smearIron deficiency anemia cure, management of anemiaUsed references
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2PLAN
Definition of anemia
Blood parameters ``erythrocytes parameters``
Iron metabolism and iron deficiency
anemia
Characteristic symptoms of iron deficiency anemia
Blood and bone marrow smear
Iron
deficiency anemia cure, management of anemiaUsed references
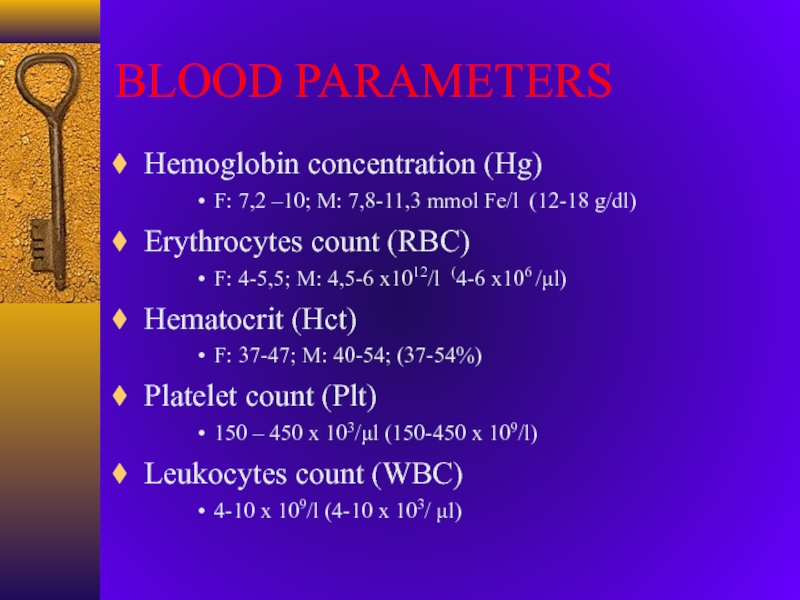
Слайд 4BLOOD PARAMETERS
Hemoglobin concentration (Hg)
F: 7,2 –10; M: 7,8-11,3 mmol Fe/l
(12-18 g/dl)
Erythrocytes count (RBC)
F: 4-5,5; M: 4,5-6 x1012/l (4-6
x106 /l)Hematocrit (Hct)
F: 37-47; M: 40-54; (37-54%)
Platelet count (Plt)
150 – 450 x 103/l (150-450 x 109/l)
Leukocytes count (WBC)
4-10 x 109/l (4-10 x 103/ l)
Слайд 5Erythrocytes parameters
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
N: 80-100 fl
RDW(Red cell Distrubution Width)
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
N: 27-34 pg
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
N:
310 – 370 g/lRBC (31-37 g/dl)Слайд 6Reticulocytes
RET: 0,5-2%
ARC (absolute reticulocyte count ):
25-75x 109/l
CRC
(corrected reticulocyte count)
RPI (reticulocyte production index)
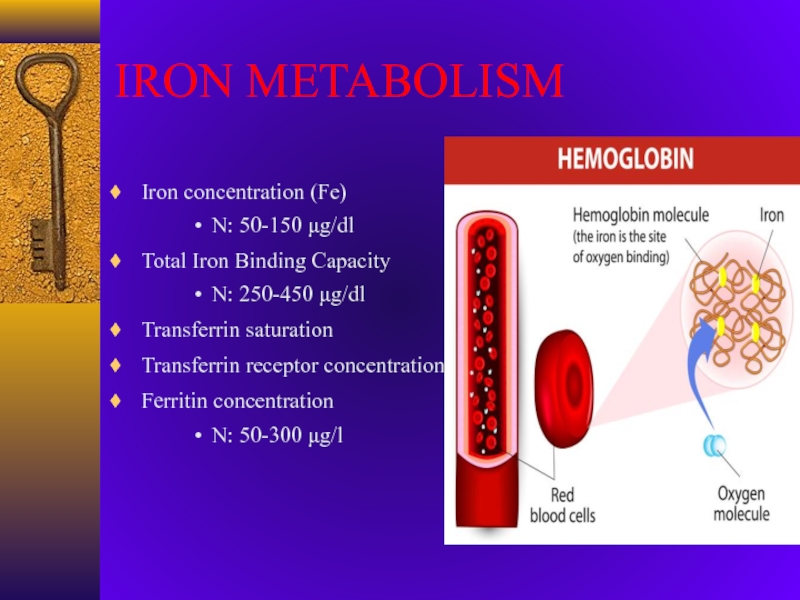
Слайд 7IRON METABOLISM
Iron concentration (Fe)
N: 50-150 g/dl
Total Iron Binding Capacity
N: 250-450
g/dl
Transferrin saturation
Transferrin receptor concentration
Ferritin concentration
N: 50-300 g/l
Слайд 8IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
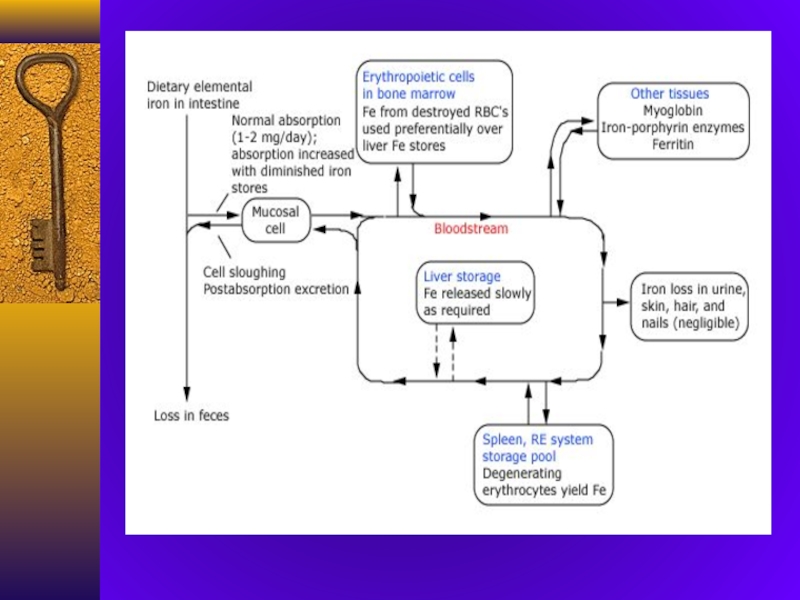
IRON METABOLISM
ABSORPTION IN DUODENUM
TRANSFERRIN TRANSPORTS IRON TO THE
CELLS
FERRITIN AND HEMOSYDERIN STORE IRON
10% of daily iron is
absorbedСлайд 9Most body iron is present in hemoglobin in circulating red
cells
The macrophages of the reticuloendotelial system store iron released from
hemoglobin as ferritin and hemosiderinSmall loss of iron each day in urine, faeces, skin and nails and in menstruating females as blood (1-2 mg daily)
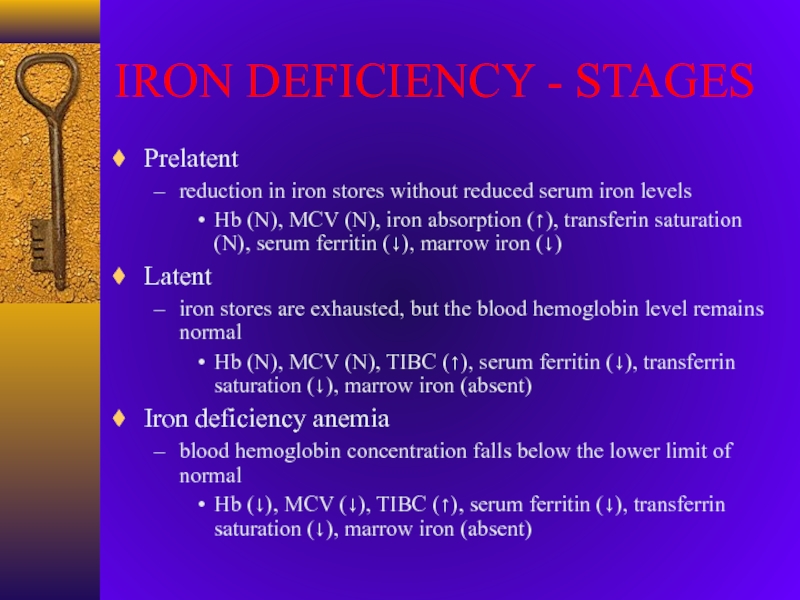
Слайд 11IRON DEFICIENCY - STAGES
Prelatent
reduction in iron stores without reduced
serum iron levels
Hb (N), MCV (N), iron absorption (), transferin
saturation (N), serum ferritin (), marrow iron ()Latent
iron stores are exhausted, but the blood hemoglobin level remains normal
Hb (N), MCV (N), TIBC (), serum ferritin (), transferrin saturation (), marrow iron (absent)
Iron deficiency anemia
blood hemoglobin concentration falls below the lower limit of normal
Hb (), MCV (), TIBC (), serum ferritin (), transferrin saturation (), marrow iron (absent)
Слайд 13IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
ETIOLOGY:
BLOOD LOSS
Chronic bleeding
MENORRHAGIA
PEPTIC ULCER
STOMACH CANCER
ULCERATIVE COLITIS
INTESTINAL CANCER
HAEMORRHOIDS
Intravascular hemolysis Pulmonary hemosiderosis
Response to erythropoietin
DECREASED IRON INTAKE
INCREASED IRON REQUIRMENT (JUVENILE AGE, PREGNANCY, LACTATION)
CONGENITAL IRON DEFICIENCY
Слайд 14IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
GENERAL ANEMIA’S SYMPTOMS:
FATIGABILITY
DIZZINESS
HEADACHE
SCOTOMAS
IRRITABILITY
ROARING
PALPITATION
CHD, CHF
Слайд 15CHARACTERISTIC SYMPTOMS
GLOSSITIS, STOMATITIS
DYSPHAGIA ( Plummer-Vinson syndrome)
ATROPHIC GASTRITIS
DRY, PALE SKIN
SPOON SHAPED
NAILS, KOILONYCHIA,
BLUE SCLERAE
HAIR LOSS
PICA (APETITE FOR NON FOOD SUBSTANCES
SUCH AS ICE, CLAY)SPLENOMEGALY (10%)
INCREASED PLATELET COUNT
Слайд 18BLOOD AND
BONE MARROW SMEAR
BLOOD:
microcytosis, hipochromia, anulocytes, anisocytosis poikilocytosis
BONE MARROW
high
cellularity
mild to moderate erythroid hyperplasia (25-35%; N 16 –
18%) polychromatic and pyknotic cytoplasm of erythroblasts is vacuolated and irregular in outline (micronormoblastic erythropoiesis)
absence of stainable iron
Слайд 22Management
History and physical examination is sufficient to exclude serious disease
(e.g pregnant or lactating women, adolescents)
- CURE
ANEMIAHistory and/or physical examination is insufficient (e.g old men, postmenopausal women)
- FIND ETIOLOGY OF ANEMIA AND CURE (CAUSAL TREATMENT)
Benzidine test
Gastroscopy
Colonoscopy
Gynaecological examination
Слайд 23DIETARY IRON
There are 2 types of iron in the diet;
haem iron and non-haem iron
Haem iron is present in Hb
containing animal food like meat, liver & spleenNon-haem iron is obtained from cereals, vegetables & beans
Milk is a poor source of iron, hence breast-fed babies need iron supplements
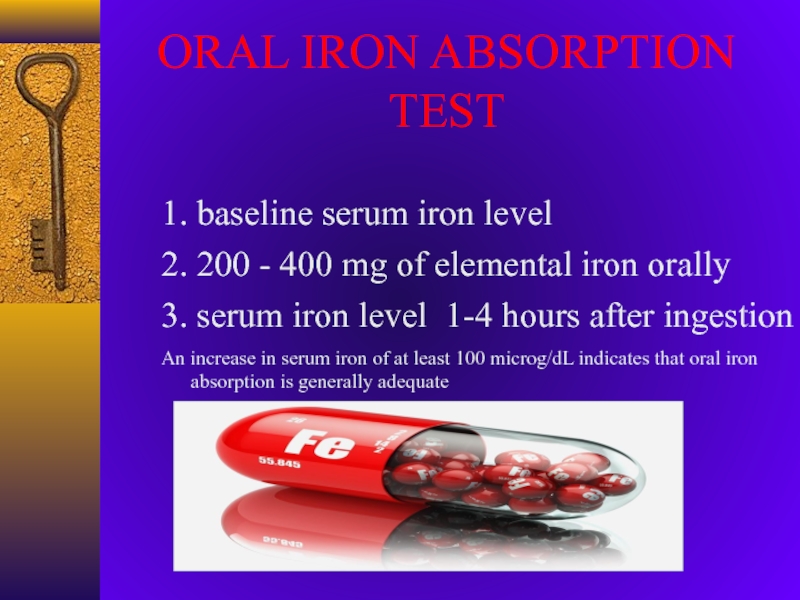
Слайд 24ORAL IRON ABSORPTION TEST
1. baseline serum iron level
2. 200 -
400 mg of elemental iron orally
3. serum iron level 1-4
hours after ingestionAn increase in serum iron of at least 100 microg/dL indicates that oral iron absorption is generally adequate
Слайд 25IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
CURE
ORAL
200 mg of iron daily 1 hour before
meal (e.g. 100 mg twice daily)
How long?
14 days + (Hg
required level – Hg current level) x 4half of the dose - 6 – 9 months to restore iron reserve
Слайд 27IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
CURE
PARENTERAL IRON SUBSTITUTION
Bad oral iron tolerance (nausea, diarrhoea)
Negative
oral iron absorption test
Necessity of quick management (CHD, CHF)
iron to
be injected (mg) = (15 - Hb/g%/) x body weight (kg) x 3IM or IV ? (risk of anaphilactic reactions)
Intramuscular iron — Mobilization of iron from intramuscular (IM) sites is slow and occasionally incomplete. As a result, the rise in the hemoglobin concentration is only slightly faster than that which occurs following the use of oral iron preparations.
Ferric carboxymaltose — is a novel stable iron complex for intravenous (IV) use which can be given at single doses of up to 1000 mg of elemental iron per week over a recommended infusion time of 15 minutes. A number of trials have shown efficacy and safety of this agent in iron deficient patients.
Слайд 28 "NPS News 70: Iron deficiency anaemia". NPS Medicines Wise. October
1, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
World Health Organization Fact Sheet No. 366,
Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections, updated June 2013"Iron deficiency anemia". Mayo Clinic. March 4, 2011. Retrieved December 11, 2012.
Decsi, T.; Lohner, S. (2014). "Gaps in meeting nutrient needs in healthy toddlers.". Ann Nutr Metab. 65 (1): 22–8. doi:10.1159/000365795. PMID 25227596.
Handout: Iron Deficiency Anemia – National Anemia Action Council
Norris, Jack. B12: Are You Getting It? Vegan Outreach. Available online: http://www.veganhealth.org/b12, Accessed October 26, 2009
References