Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
JSC Medical university Astana department of internal diseases No 1
Содержание
- 1. JSC Medical university Astana department of internal diseases No 1
- 2. PLANCHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS 1. Etiology and pathogenesis2. Classification3. Clinical picture4. Diagnosis5. Differential diagnosis6. Treatment
- 3. CHRONIC CHOLECYSTITISis chronic inflammation of gall-bladder.
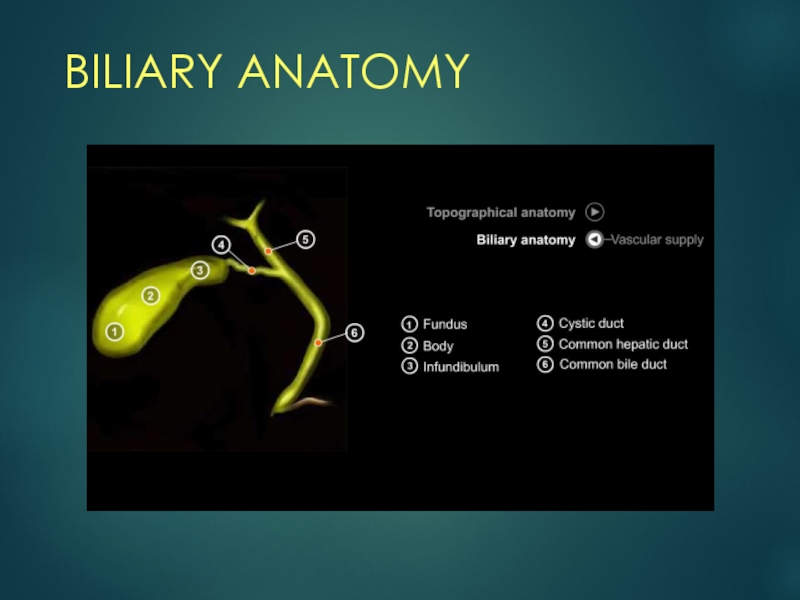
- 4. BILIARY ANATOMY
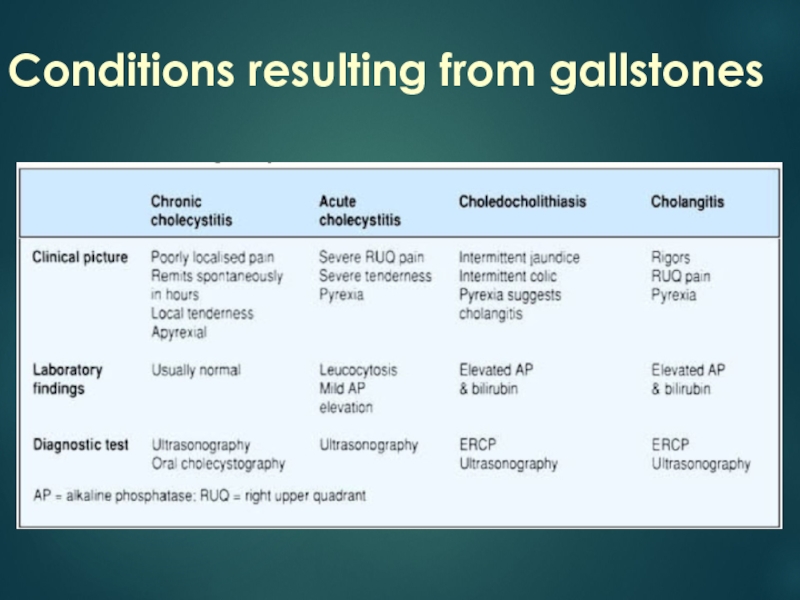
- 5. Conditions resulting from gallstones
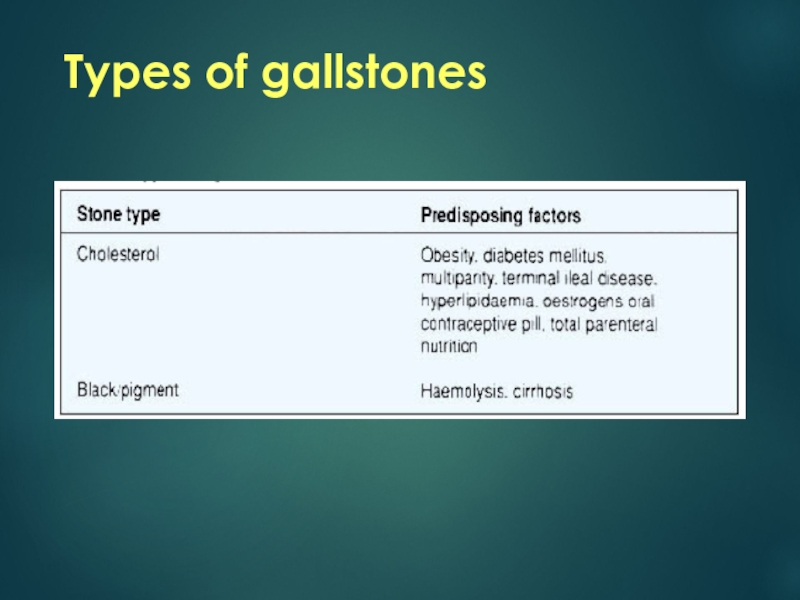
- 6. Types of gallstones
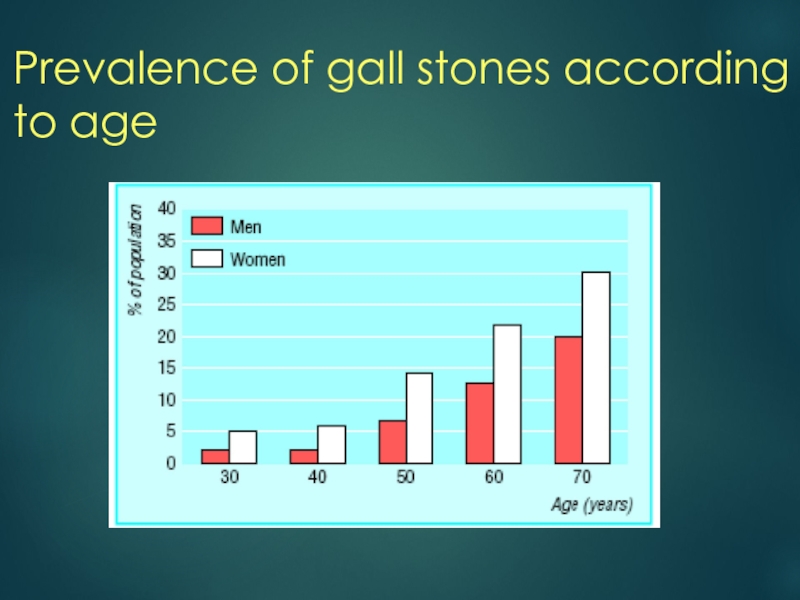
- 7. Prevalence of gall stones according to age
- 8. Gall stones vary from pure cholesterol (white), through mixed, to bile salt predominant (black).
- 9. Etiology and Risk Factors Acute or chronic
- 10. Etiology and Risk Factors Discoordination of bile
- 11. CLASSIFICATION - Chronic calculous cholecystitis - Chronic non-calculous cholecystitis
- 12. CLASSIFICATION I. Phase of disease:AcuteUncomplete remissionRemissionII. Severity
- 13. CLASSIFICATION V. Uncomplicated Complicated: -Pancreatitis,
- 14. -Hydropsy (mucocele) of gall-bladder is its aseptic
- 15. Example of diagnosis Chronic non-calculous recurrent cholecystitis, acute phase, moderate severity. Hypotonic biliary dyskinesia.
- 16. Symptoms and clinical signsPain syndrome. (-Pain in
- 17. Symptoms and clinical signsKehr's symptomMurphy's symptomOrtner's symptom
- 18. DIAGNOSTIC PROGRAMTotal blood countBiochemical analysis (Glucose, Bilirubin,
- 19. Ultrasound showing normal gallbladder Ultrasonography is the
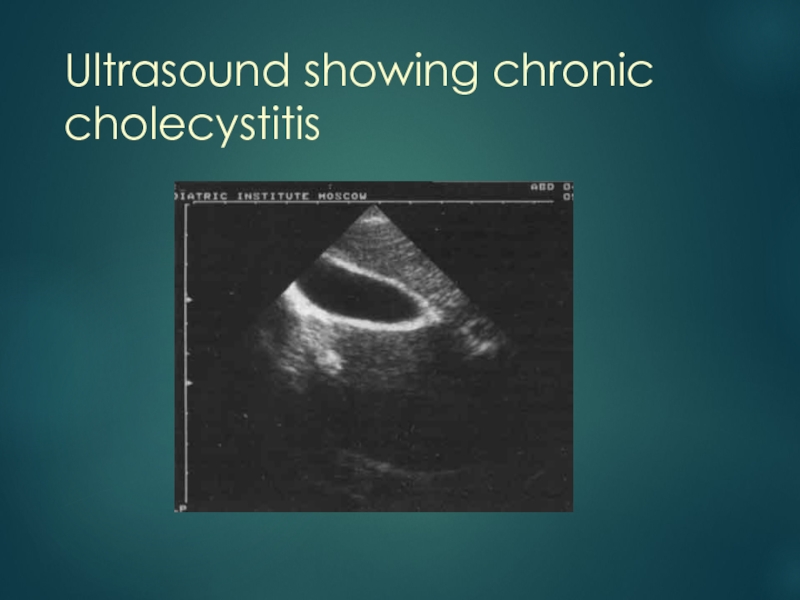
- 20. Ultrasound showing chronic cholecystitis
- 21. Stone in the gallbladder Ultrasound of the
- 22. Ultrasound image of gall bladder with dark
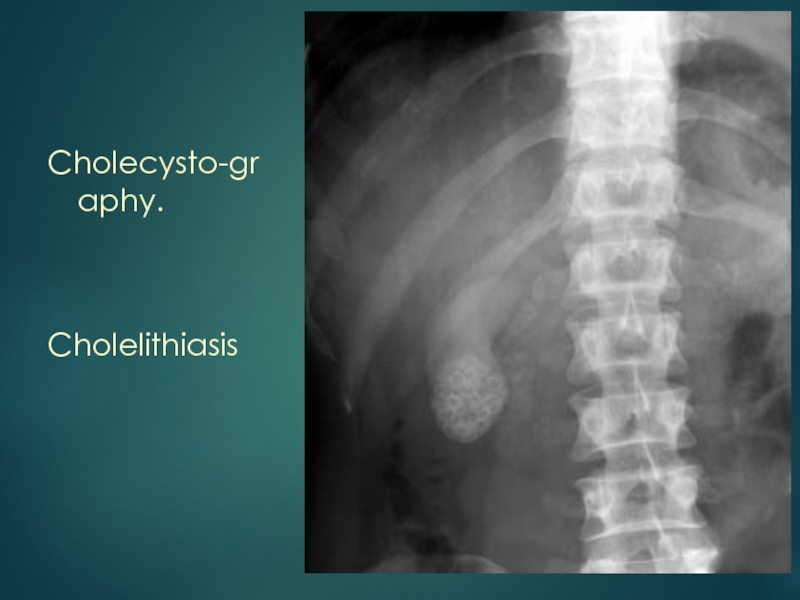
- 23. Cholecysto-graphy.Cholelithiasis
- 24. This magnetic resonance cholangiopancreato-gram shows multiple gallstones (arrows) in the common bile duct (choledocholithiasis)
- 25. Differential diagnosisPeptic ulcer diseaseChronic pancreatitisChronic hepatitisTumors (liver, gall bladder)Pleurisy (right-sided)Subdiaphragmatic abscess
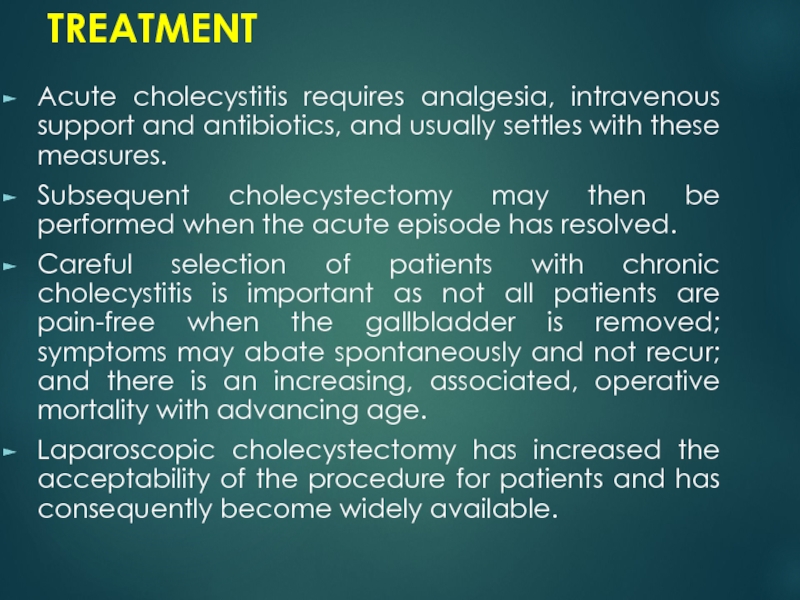
- 26. TREATMENTAcute cholecystitis requires analgesia, intravenous support and
- 27. TREATMENT1. Bed rest. 2. Hunger (1–3 days),
- 28. CHOLANGITISAcute cholangitis is a serious infection which
- 29. Medical management of gallbladder stonesDissolution therapy can
- 30. Indications for Surgical TreatmentAll forms of acute
- 31. Скачать презентанцию
PLANCHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS 1. Etiology and pathogenesis2. Classification3. Clinical picture4. Diagnosis5. Differential diagnosis6. Treatment
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2PLAN
CHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS
1. Etiology and pathogenesis
2. Classification
3. Clinical picture
4. Diagnosis
5.
Differential diagnosis
6. Treatment
Слайд 8Gall stones vary from pure cholesterol (white), through mixed, to
bile salt predominant (black).
Слайд 9Etiology
and Risk Factors
Acute or chronic infection
-Esherichia coli (35-40%),
-Staphylococus (15%),
-Enterococus
(15 %),
-Streptococus (10%)
Mixed microflora – 30%
- hematogenic way
- lymphogenic
way- contact way
Слайд 10Etiology
and Risk Factors
Discoordination of bile passage (hypotonic biliary dyskinesia), bile
congestion
Congenital defect of gall-bladder
Metabolic disturbance
Discoordination of neurohumoral regulation of biliary
system, stressAllergy
↓ Immune reactivity
Alimentary disorders
Слайд 12CLASSIFICATION
I. Phase of disease:
Acute
Uncomplete remission
Remission
II. Severity of disease: mild, moderate,
severe.
III. Course of disease: recurrent, permanent.
IV. Type of
dyskinesia: hypertonic, hypotonic.Слайд 13CLASSIFICATION
V. Uncomplicated
Complicated:
-Pancreatitis,
-Nonspecific Reactive Hepatitis,
-Pericholecystitis,
-Cholangitis
(Patients present with biliary pain, jaundice, fever and often rigors.
The septicaemia is usually due to Gram-negative organisms, is frequently severe and may be lifethreatening).Слайд 14 -Hydropsy (mucocele) of gall-bladder is its aseptic inflammation, that arises
up as a result of blockade of cystic duct by
concrement or mucus. During palpation increased and unpainfully gall-bladder is marked in patients. -Empyema of gall-bladder is unliquidated in time hydropsy, that at repeated infection is transformed in a new form. Gall-bladder in such patients is palpated as a dense, moderately painful formation, however, the symptoms of irritation of peritoneum, as a rule, are absent. The high temperature of body is periodically observed. In blood high leucocytosis with the shift of formula of blood to the left is present.Слайд 15Example of diagnosis
Chronic non-calculous recurrent cholecystitis,
acute phase,
moderate severity.
Hypotonic
biliary dyskinesia.
Слайд 16Symptoms and clinical signs
Pain syndrome.
(-Pain in right hypochondrium and
epigastric area with an irradiation in right supraclavicular area and
right shoulder.-If pain syndrome has the strongly expressed character, it is called hepatic colic).
Dyspepsic syndrome.
Asthenic syndrome.
Intoxication syndrome.
Слайд 18DIAGNOSTIC PROGRAM
Total blood count
Biochemical analysis (Glucose, Bilirubin, ALT, AST, GGT,
Alkaline phosphatase, Proteins, Amylase, Lipids, Cholesterol, Liver tests, Sodium, Potassium,
Urea, Creatinine)Urinanalysis, Diastase of urine
Coagulogram
Duodenal tubage and Examination of bile (chemical, bacteriological)
Examination of feces, Coprogram
ECG
Endoscopy
USD
Cholecystography
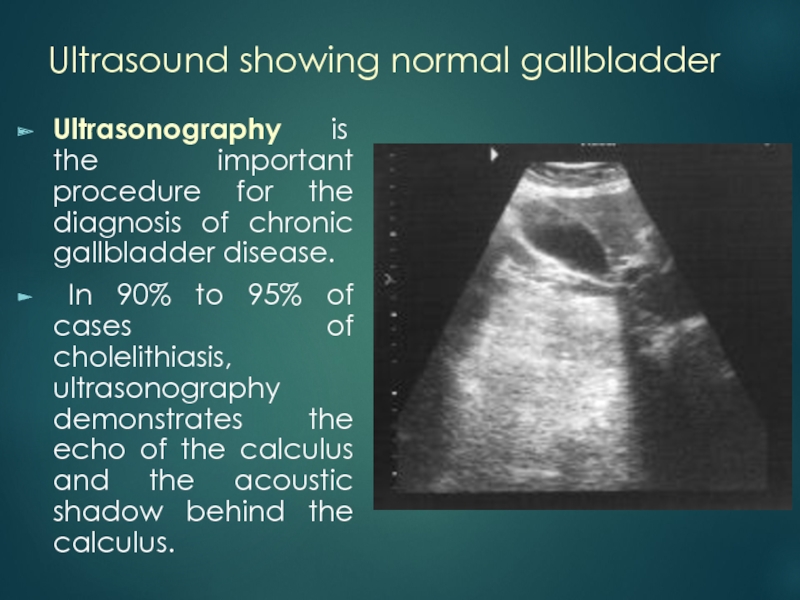
Слайд 19Ultrasound showing normal gallbladder
Ultrasonography is the important procedure for
the diagnosis of chronic gallbladder disease.
In 90% to 95%
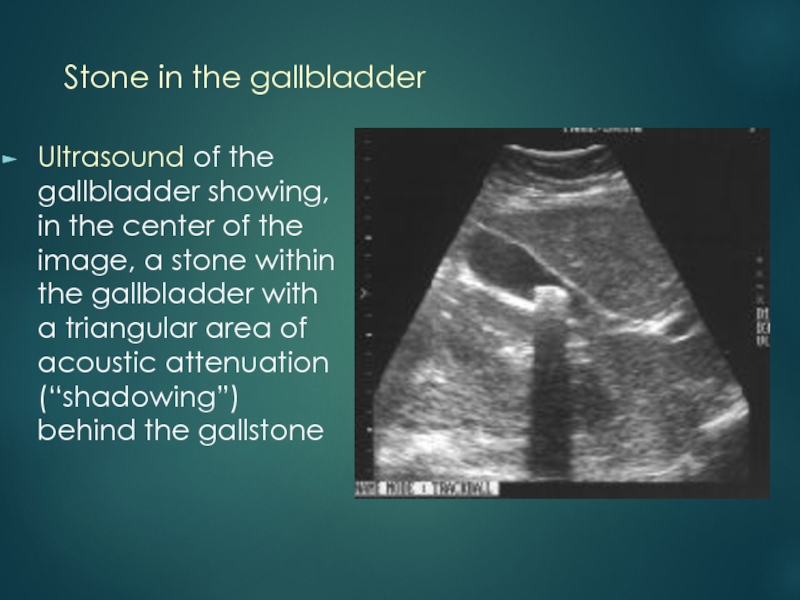
of cases of cholelithiasis, ultrasonography demonstrates the echo of the calculus and the acoustic shadow behind the calculus.Слайд 21Stone in the gallbladder
Ultrasound of the gallbladder showing, in
the center of the image, a stone within the gallbladder
with a triangular area of acoustic attenuation (“shadowing”) behind the gallstoneСлайд 22Ultrasound image of gall bladder with dark area (a) representing
gall bladder and multiple white echoes (b) representing stones.
Bottom:
The gall bladder after cholecystectomy with multiple small stones Слайд 24This magnetic resonance cholangiopancreato-gram shows multiple gallstones (arrows) in the
common bile duct (choledocholithiasis)
Слайд 25Differential diagnosis
Peptic ulcer disease
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic hepatitis
Tumors (liver, gall bladder)
Pleurisy (right-sided)
Subdiaphragmatic
abscess
Слайд 26TREATMENT
Acute cholecystitis requires analgesia, intravenous support and antibiotics, and usually
settles with these measures.
Subsequent cholecystectomy may then be performed
when the acute episode has resolved. Careful selection of patients with chronic cholecystitis is important as not all patients are pain-free when the gallbladder is removed; symptoms may abate spontaneously and not recur; and there is an increasing, associated, operative mortality with advancing age.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has increased the acceptability of the procedure for patients and has consequently become widely available.
Слайд 27TREATMENT
1. Bed rest.
2. Hunger (1–3 days), then diet №
5.
3. Desintoxication therapy.
4. Spasmolytics, Analgetics (Spasmalgon 5 ml,
No-shpa 2% 2 ml, Papaverin 2% 2 ml, Platyphyllin 0,1% 1 ml, Baralgin 5 ml, Analgin 50% 2 ml).5. Antibacterial therapy (Ampiox, Ofloxacin, Cephalosporines, Furasolidon)
Слайд 28CHOLANGITIS
Acute cholangitis is a serious infection which may be life-threatening.
Antibiotics such as third generation cephalosporins or amino-quinolones should be
used. Careful attention should be paid to fluid balance, urine output and renal function.
Слайд 29Medical management of gallbladder stones
Dissolution therapy can be considered in
patients with uncomplicated gallstone disease who are unwilling or unfit
for surgery.The prerequisites for treatment are that the stones should be non-calcified, the gallbladder should be functioning and the cystic duct not obstructed.
The bile acids, chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid are available and need to be given for long periods to be successful.
They have no effect on pigment stones.