Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
L. 3 DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGATION
Содержание
- 1. L. 3 DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGATION
- 2. Cell are disrupted in a homogenizer and
- 3. The centrifuge is primarily used to separated
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. The centrifugal force exerted on a particle
- 9. Слайд 9
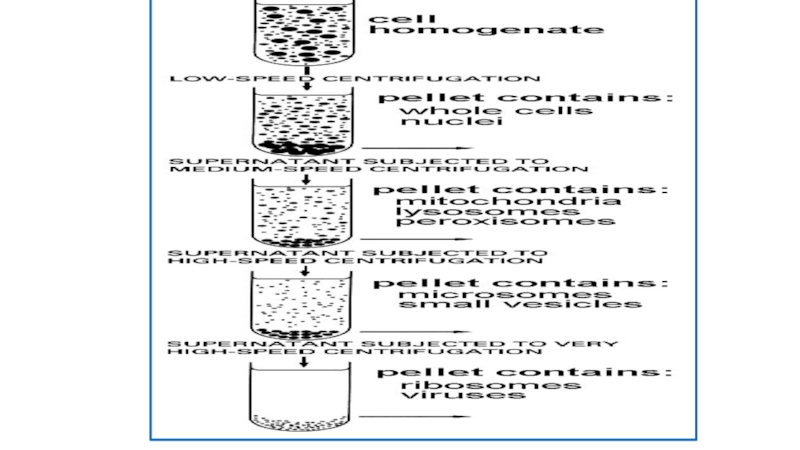
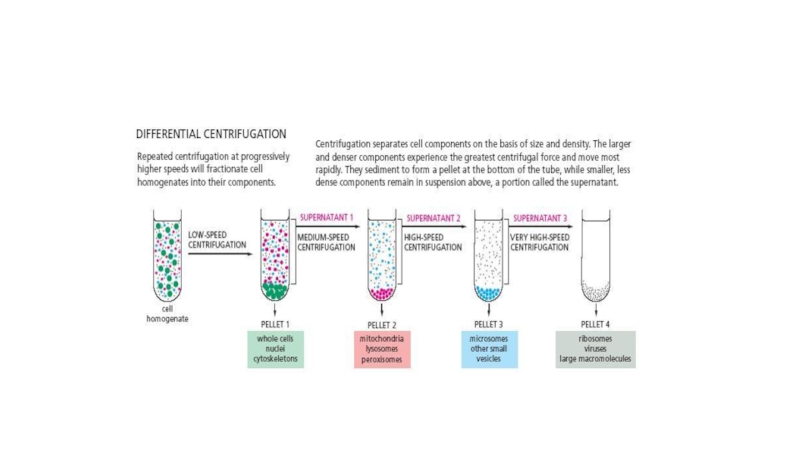
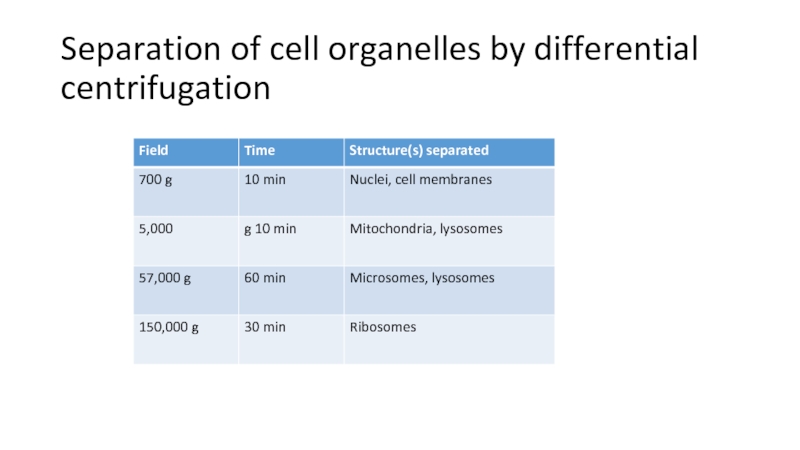
- 10. Separation of cell organelles by differential centrifugation
- 11. A Summary of Centrifuge Techniques and ApplicationsPreparativeVelocity
- 12. Centrifugation Through Density GradientsFast sedimenting particles will
- 13. Several different media are commonly used in
- 14. Types of density gradient centrifugationThe two types
- 15. Density gradient centrifugation Zonal Gradient is present
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Density gradients can be preformed or formed
- 18. Subcellular Fractionation and Marker Enzyme plasma
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Скачать презентанцию
Cell are disrupted in a homogenizer and the resulting mixture, called the homogenate. The broken cell preparation is referred to as cell-free preparation or ‘homogenate’. Properly prepared, a homogenate is the
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1L. 3 DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGATION
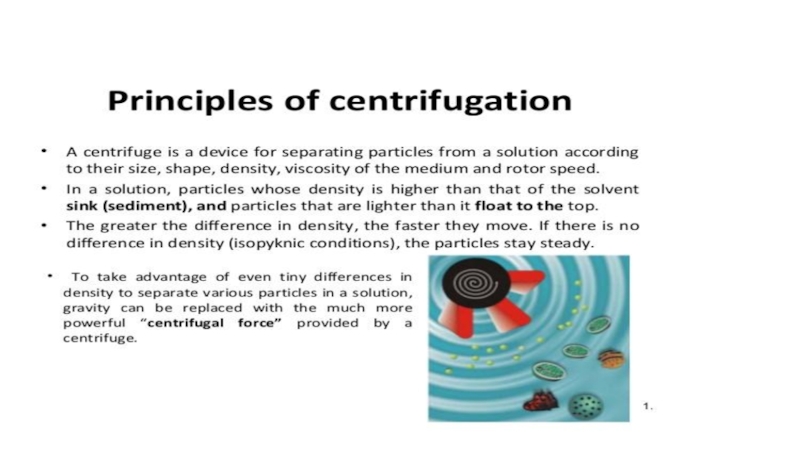
Principles of centrifugation
Centrifugation Through Density Gradients
Subcellular Fractionation
and Marker Enzymes
Слайд 2Cell are disrupted in a homogenizer and the resulting mixture,
called the homogenate. The broken cell preparation is referred to
as cell-free preparation or ‘homogenate’.Properly prepared, a homogenate is the sum of all the cel components obtained by rupturing the cell membrane.
Organelles and other subcellular components can be isolated
by differential centrifugation.
Differential centrifugation is carried out by centrifuging a sample at low speed and separating the supernatant and pellet. The supernatant is then recentrifuged at higher speed and the supernatant and pellet separated again
The denser (более плотный) material forms a pellet at lower centrifugal force than will the less-denser material. The isolated fractions is used for further purification.
Слайд 3The centrifuge is primarily used to separated biological
components based upon
differential sedimentation properties.
Many types of centrifuges are available for various
applications.All centrifuges basically consist of a motor which spins a
rotor containing the experimental sample.
The differences between centrifuges are in the speeds at which the samples are centrifuged and the volumes of samples.
Слайд 8The centrifugal force exerted on a particle in the solution
is expressed in multiples of the force exerted by gravity.
The centrifugal force is proportional to the radius of the centrifugal head and to the square of angular velocity.
Hence, it is more convenient to use relatively small heads rotating at high speeds. Thus, a head of approximately 10 cm diameter rotating at about 40,000 rpm will produce nearly 100,000 g.
At such high speeds, the head is run in a vacuum to prevent the heat produced by air friction.
The tube containing the homogenate is usually held at an angle to the axis of rotating to keep the path of particles through the solution as short as possible
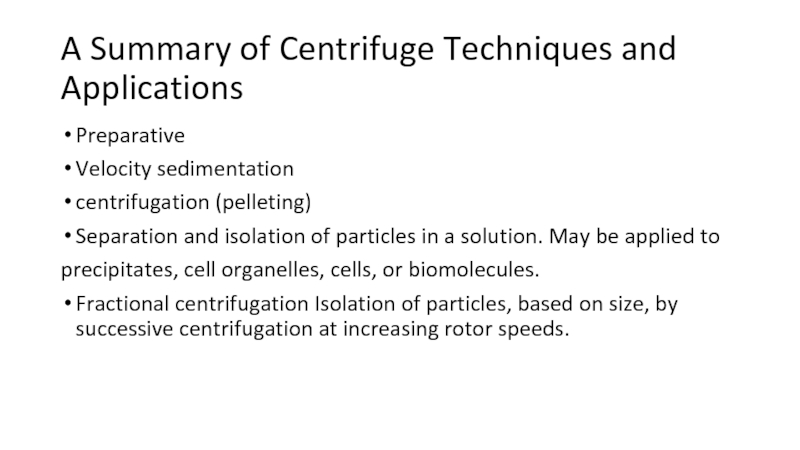
Слайд 11A Summary of Centrifuge Techniques and Applications
Preparative
Velocity sedimentation
centrifugation (pelleting)
Separation and
isolation of particles in a solution. May be applied to
precipitates,
cell organelles, cells, or biomolecules.Fractional centrifugation Isolation of particles, based on size, by successive centrifugation at increasing rotor speeds.
Слайд 12Centrifugation Through Density Gradients
Fast sedimenting particles will be contaminated with
slow sedimenting particles. The reason for this is that by
the time large particles near the top of the tube are pelleted, some of the small particles near the bottom of the tube have also pelleted.In addition, mechanical vibrations, thermal gradients and convection currents (конвекционные потоки) can also affect the sedimentation properties.
Centrifugation through a dense medium, or density gradient centrifugation, can alleviate these problems.
In addition, density gradient centrifugation allow for better separation of particles with similar properties.
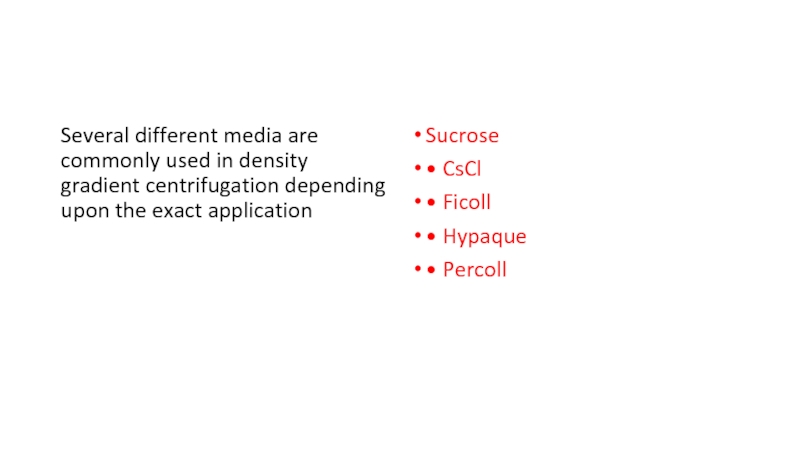
Слайд 13Several different media are commonly used in density gradient centrifugation
depending upon the exact application
Sucrose
• CsCl
• Ficoll
• Hypaque
• Percoll
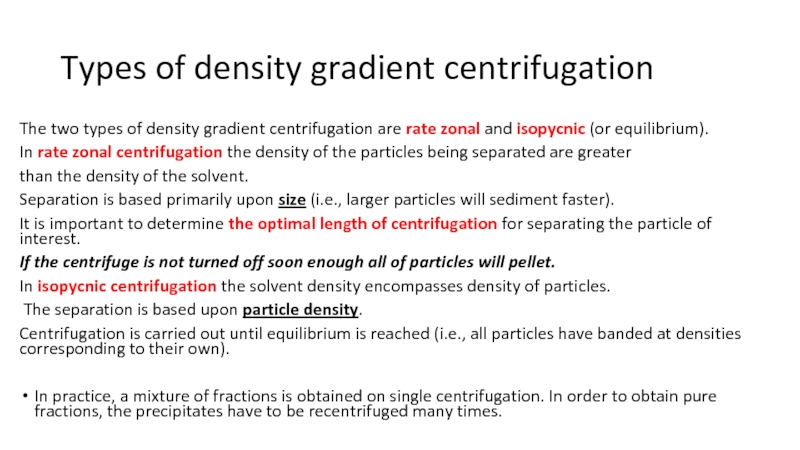
Слайд 14Types of density gradient centrifugation
The two types of density gradient
centrifugation are rate zonal and isopycnic (or equilibrium).
In rate
zonal centrifugation the density of the particles being separated are greaterthan the density of the solvent.
Separation is based primarily upon size (i.e., larger particles will sediment faster).
It is important to determine the optimal length of centrifugation for separating the particle of interest.
If the centrifuge is not turned off soon enough all of particles will pellet.
In isopycnic centrifugation the solvent density encompasses density of particles.
The separation is based upon particle density.
Centrifugation is carried out until equilibrium is reached (i.e., all particles have banded at densities corresponding to their own).
In practice, a mixture of fractions is obtained on single centrifugation. In order to obtain pure fractions, the precipitates have to be recentrifuged many times.
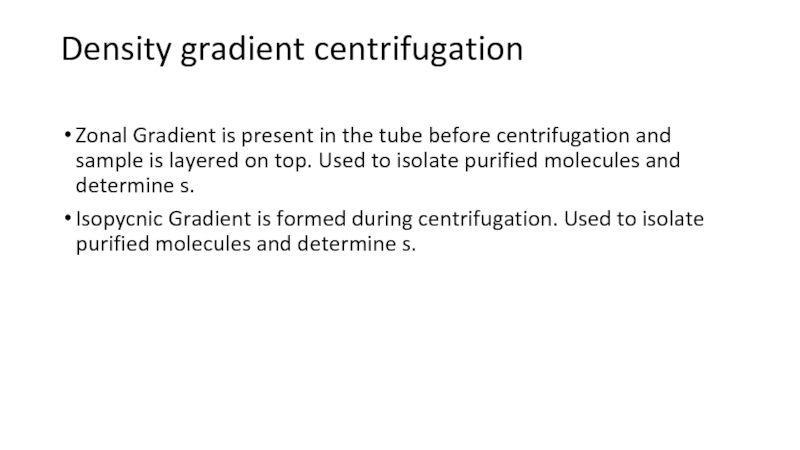
Слайд 15Density gradient centrifugation
Zonal Gradient is present in the tube before
centrifugation and sample is layered on top. Used to isolate
purified molecules and determine s.Isopycnic Gradient is formed during centrifugation. Used to isolate purified molecules and determine s.
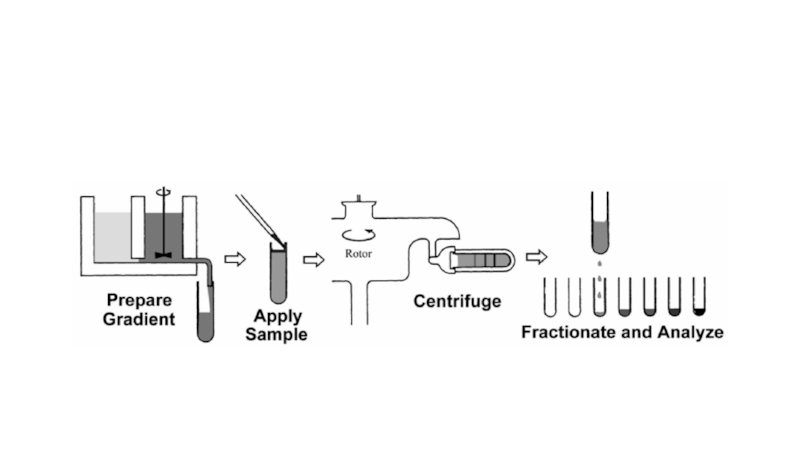
Слайд 17Density gradients can be preformed or formed during centrifugation.
In
the case of isopycnic density gradients it is possible to
mix the sample with the desity gradient medium and carry out the centrifugation until the density gradient forms.The various components in the sample will then be found at a position which corresponds to their density.
This is especially useful in the case of Percoll which rapidly forms density gradients when subjected to centrifugation.
Another common example in which self-forming gradients are commonly used is the separation of nucleic acids on CsCl gradients (Nucleic Acid Isolation).
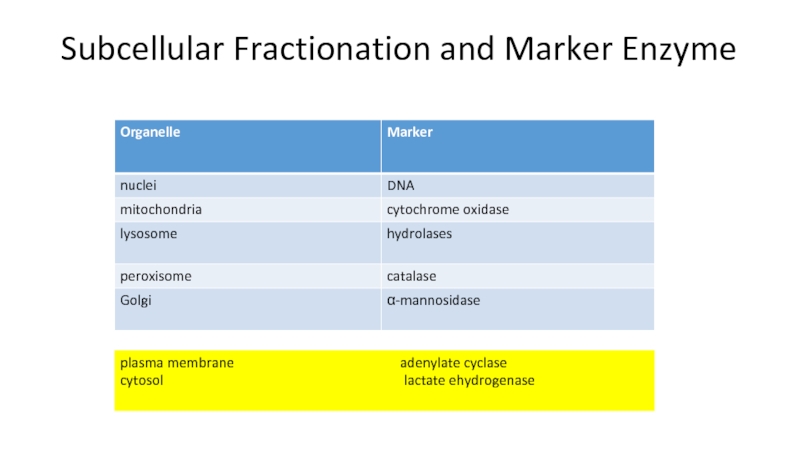
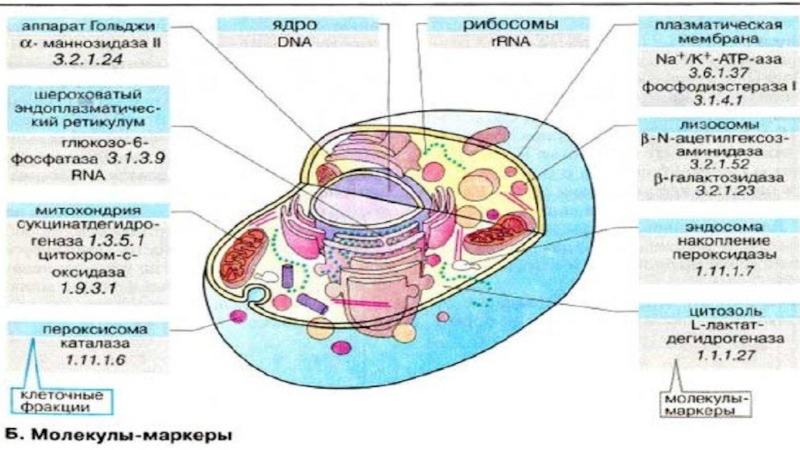
Слайд 18Subcellular Fractionation and Marker Enzyme
plasma membrane
adenylate cyclase
cytosol lactate ehydrogenase