Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture 8 Managing Human Resources. Creating and Managing Teams
Содержание
- 1. Lecture 8 Managing Human Resources. Creating and Managing Teams
- 2. Managing Human Resources
- 3. Learning ObjectivesExplain the importance of the human
- 4. Why Is HRM Important?As a significant source
- 5. Why Is HRM Important? (cont.)High – performance
- 6. Exhibit 12-1 High-Performance Work PracticesCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
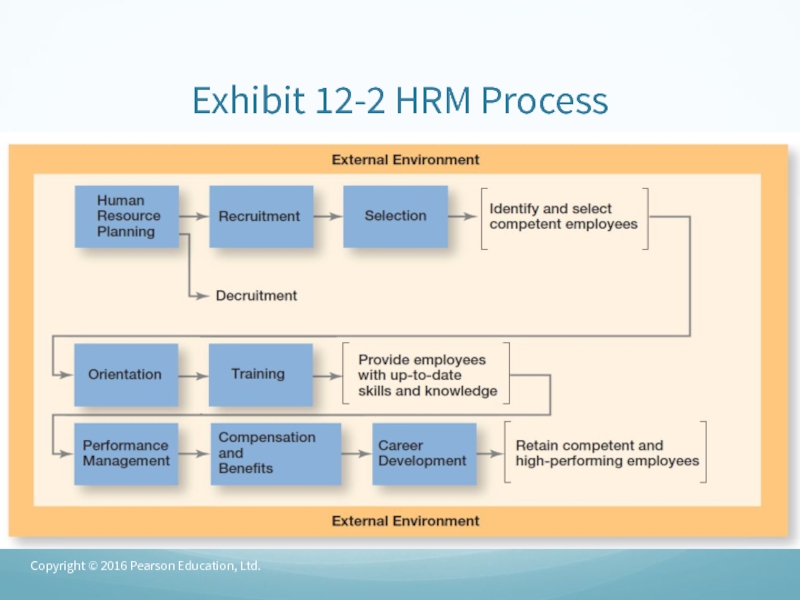
- 7. Exhibit 12-2 HRM ProcessCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 8. External Factors That Affect the HRM ProcessThe
- 9. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process
- 10. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process
- 11. Exhibit 12-3 Major HRM LawsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 12. Exhibit 12-3 Major HRM Laws (cont.)Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 13. Exhibit 12-3 Major HRM Laws (cont.)Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 14. Global HRM LawsWork councils – groups of
- 15. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process
- 16. Human Resource PlanningHuman resource planning
- 17. Human Resource Planning (cont.)Job description – a
- 18. Recruitment and DecruitmentRecruitment – locating, identifying, and
- 19. Exhibit 12-4 Recruiting SourcesCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 20. Exhibit 12-5 Decruitment OptionsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 21. SelectionSelection
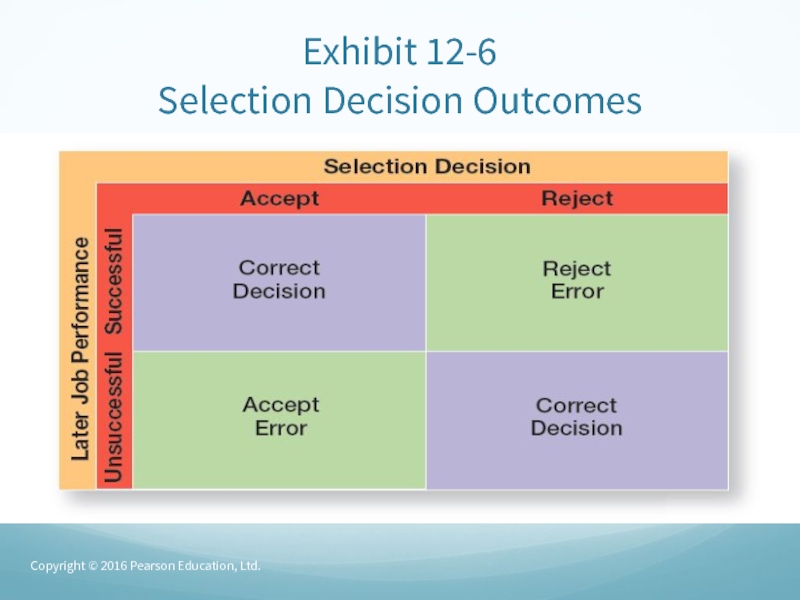
- 22. Exhibit 12-6 Selection Decision OutcomesCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 23. Exhibit 12-7 Selection ToolsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 24. Exhibit 12-7 Selection Tools (cont.)Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 25. Exhibit 12-7 Selection Tools (cont.)Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 26. Selection (cont.)Realistic
- 27. Providing Employees with Needed Skills and KnowledgeOrientation
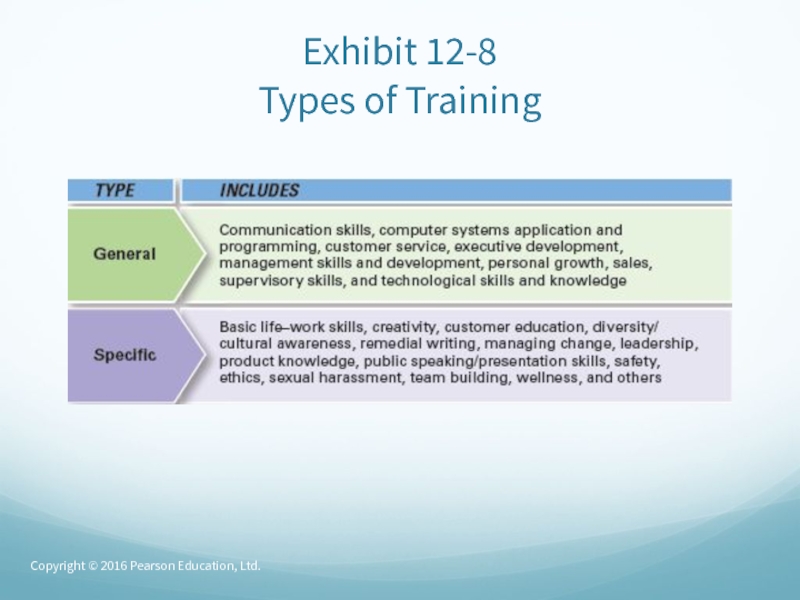
- 28. Exhibit 12-8 Types of TrainingCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 29. Exhibit 12-9 Traditional Training MethodsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 30. Exhibit 12-9 Traditional Training Methods (cont.)Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 31. Retaining Competent, High Performing EmployeesPerformance management
- 32. Exhibit 12-10 Performance Appraisal MethodsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 33. Exhibit 12-10: Performance Appraisal Methods (cont.)Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 34. Exhibit 12-11 What Determines Pay and BenefitsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 35. Contemporary Issues in Managing Human ResourcesDownsizing –
- 36. Exhibit 12-12 Tips for Managing DownsizingCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 37. Contemporary Issues in Managing Human Resources (cont.)Family
- 38. Contemporary Issues in Managing Human Resources (cont.)Employee
- 39. Creating and Managing Teams
- 40. Learning ObjectivesDefine groups and the stages of
- 41. What Is a Group?Group
- 42. Exhibit 13-1 Examples of Formal Work GroupsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 43. Stages of Group DevelopmentForming stage – the
- 44. Stages of Group Development (cont.)Performing stage –
- 45. Exhibit 13-2 Stages of Group DevelopmentCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 46. Work Group Performance and Satisfaction Why are
- 47. Exhibit 13-3 Group Performance/Satisfaction ModelCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 48. External Conditions Imposed on the GroupWork groups
- 49. Group Member ResourcesA group’s
- 50. Group StructureRole – behavior patterns expected of
- 51. Group Structure (cont.)Status – a prestige grading,
- 52. Exhibit 13-5 Group Cohesiveness and ProductivityCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 53. Group Structure (cont.)Group SizeSmall groups are faster
- 54. Group Structure (cont.)Group Processes
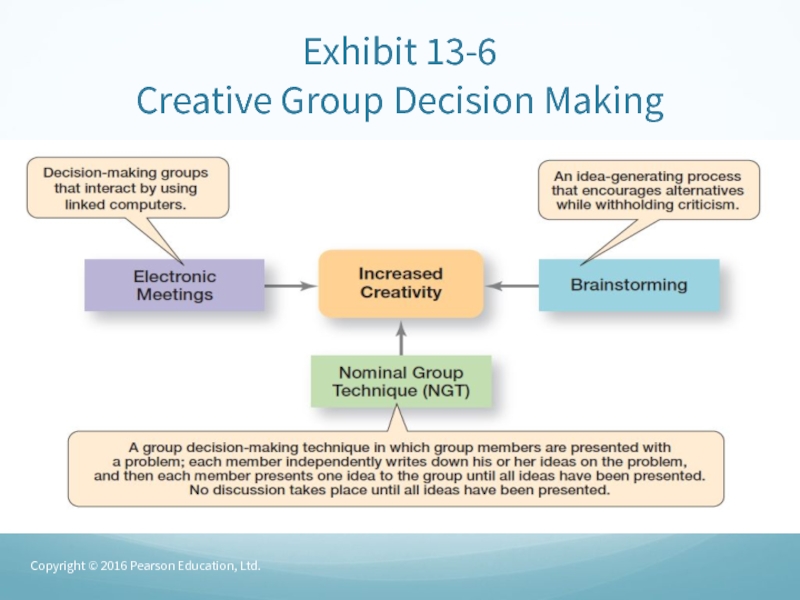
- 55. Group Structure (cont.)Group Decision-making – most organizations
- 56. Exhibit 13-6 Creative Group Decision MakingCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
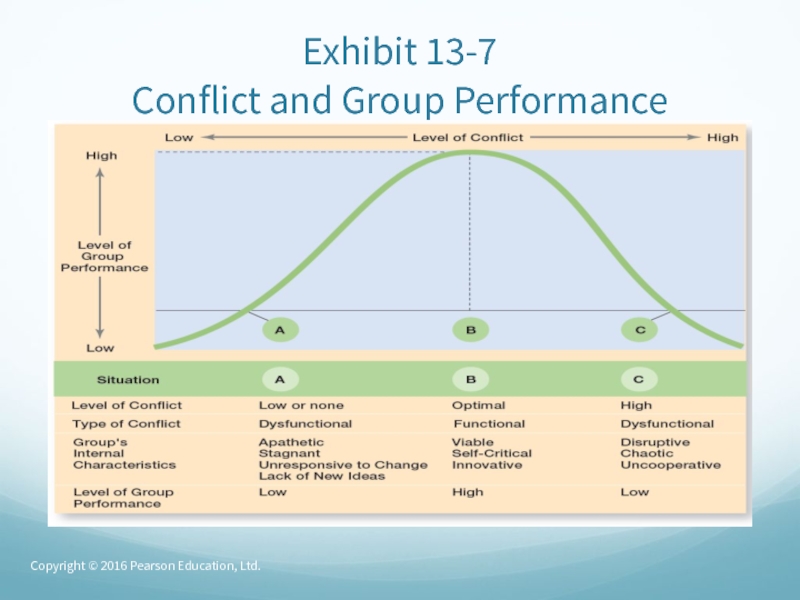
- 57. Conflict ManagementConflict
- 58. Conflict Management (cont.)Interactionist
- 59. Conflict Management (cont.)Task conflict – conflicts over
- 60. Exhibit 13-7 Conflict and Group PerformanceCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
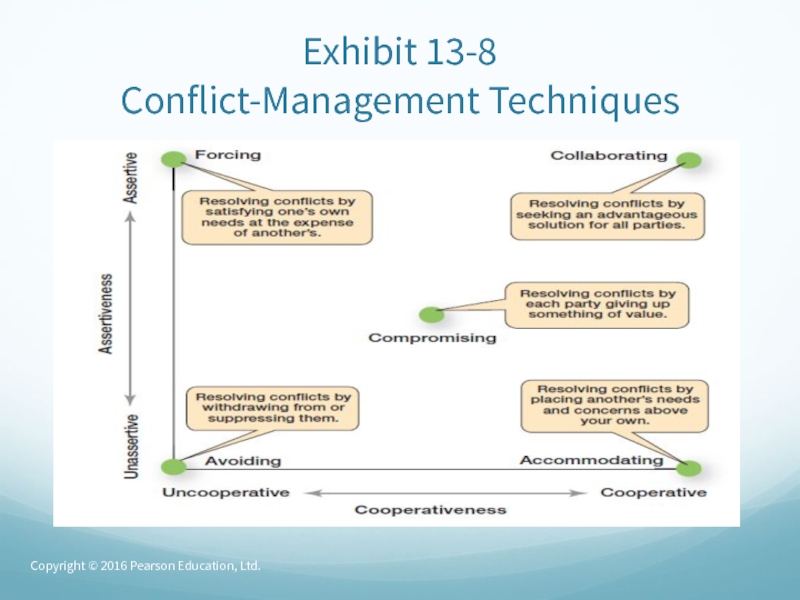
- 61. Exhibit 13-8 Conflict-Management TechniquesCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 62. Turning Groups into Effective TeamsWork teams
- 63. Exhibit 13-9 Groups Versus TeamsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 64. Types of Work TeamsProblem-solving team – a
- 65. Types of Work Teams (cont.)Cross-functional team –
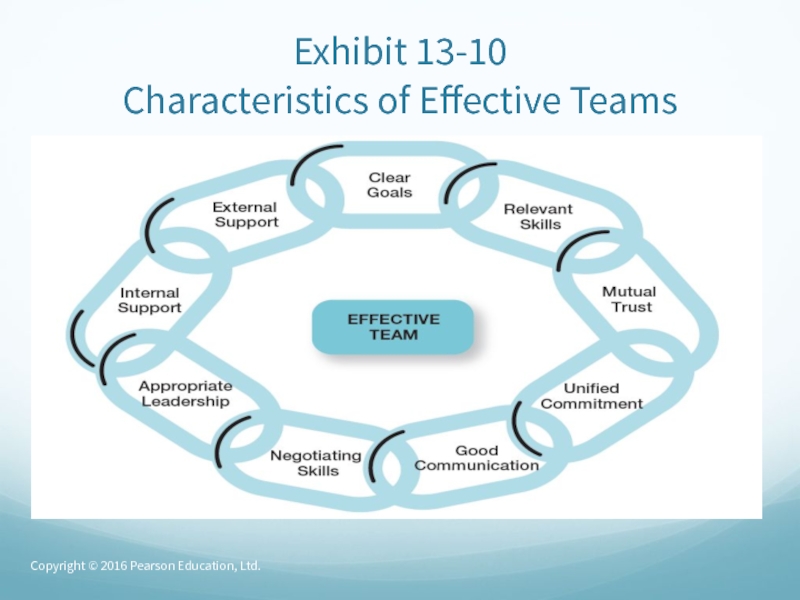
- 66. Creating Effective Work TeamsClear Goals – high-performance
- 67. Creating Effective Work Teams (cont.)Good Communication –
- 68. Exhibit 13-10 Characteristics of Effective TeamsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 69. Current Challenges in Managing TeamsGroup Member
- 70. Exhibit 13-11 Global TeamsCopyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 71. Understanding Social NetworksSocial NetworkThe patterns of informal
- 72. ThanksQuestions
- 73. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1
Lecture 8
Managing Human Resources. Creating and Managing Teams
Course Instructor: Diana
Amirbekova
Слайд 3Learning Objectives
Explain the importance of the human resource management process
and the external influences that might affect that process.
Discuss the
tasks associated with identifying and selecting competent employees.Know how to be a good interviewee.
Develop your skill at being a good interviewer.
Explain the different types of orientation and training.
Describe strategies for retaining competent, high-performing employees.
Discuss contemporary issues in managing human resources.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 4Why Is HRM Important?
As a significant source of competitive advantage:
People-oriented
HR creates superior shareholder value
As an important strategic tool
Achieve competitive
success through people by treating employees as partnersTo improve organizational performance
High performance work practices lead to both high individual and high organizational performance
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 5Why Is HRM Important? (cont.)
High – performance work practices –
work practices that lead to both high individual and high
organizational performance.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 8External Factors That Affect the HRM Process
The Economy's Effect on
HRM
The global economic downturn has left, what many experts believe
to be, an enduring mark on HRM practices worldwide.U.S. workers have dramatically lowered their career and retirement expectations for the foreseeable future.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 9External Factors That Affect the HRM Process (cont.)
Employee Labor Unions
Labor
union – an organization that represents workers and seeks to
protect their interests through collective bargaining.Work stops, labor disputes, and negotiations between management and labor are just a few of the challenges organizations and managers face when their workforce is unionized
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 10External Factors That Affect the HRM Process (cont.)
Legal Environment of
HRM
Affirmative action – organizational programs that enhance the status of
members of protected groups.Two current U.S. laws that each have the potential to affect future HRM practices:
Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA; commonly called the Health Care Reform Act)
Social Networking Online Protection Act (SNOPA)
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 14Global HRM Laws
Work councils – groups of nominated or elected
employees who must be consulted when management makes decisions involving
personnel.Board representatives – employees who sit on a company’s board of directors and represent the interests of the firm’s employees.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 15External Factors That Affect the HRM Process (cont.)
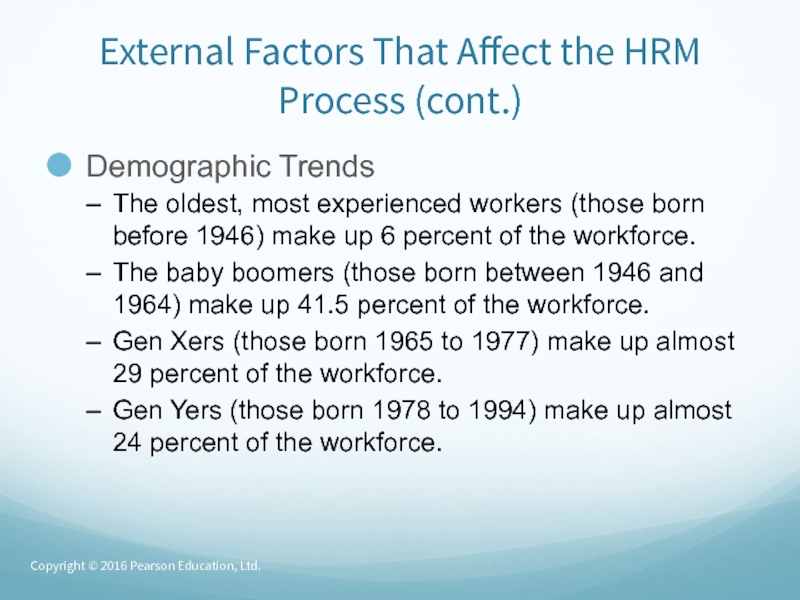
Demographic Trends
The oldest,
most experienced workers (those born before 1946) make up 6
percent of the workforce.The baby boomers (those born between 1946 and 1964) make up 41.5 percent of the workforce.
Gen Xers (those born 1965 to 1977) make up almost 29 percent of the workforce.
Gen Yers (those born 1978 to 1994) make up almost 24 percent of the workforce.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 16Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning
– ensuring that the organization has the right number and kinds of capable people in the right places and at the right times.
Job analysis – an assessment that defines jobs and the behaviors necessary to perform them.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 17Human Resource Planning (cont.)
Job description – a written statement that
describes a job.
Job specification – a written statement of the
minimum qualifications a person must possess to perform a given job successfully.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 18Recruitment and Decruitment
Recruitment – locating, identifying, and attracting capable applicants.
Decruitment
– reducing an organization’s workforce.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 21Selection
Selection
– screening job applicants to ensure that the most
appropriate candidates are hired.A valid selection device is characterized by a proven relationship between the selection device and some relevant criterion.
A reliable selection device indicates that it measures the same thing consistently.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 26Selection (cont.)
Realistic
Job Preview (RJP) – a preview of a
job that provides both positive and negative information about the job and the company.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 27Providing Employees with Needed
Skills and Knowledge
Orientation
– introducing
a new employee to his or her job and the organization.Employee Training is an important HRM activity.
In 2011, U.S. business firms spent more than $59 billion on formal employee training.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 31Retaining Competent,
High Performing Employees
Performance management system
– establishes performance standards used to evaluate employee performance.
Skill-based pay – a pay system that rewards employees for the job skills they can demonstrate.
Variable pay – a pay system in which an individual’s compensation is contingent on performance.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 33Exhibit 12-10:
Performance Appraisal Methods (cont.)
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 35Contemporary Issues in Managing
Human Resources
Downsizing – the planned elimination of
jobs in an organization.
Sexual harassment – any unwanted action or
activity of a sexual nature that explicitly or implicitly affects an individual’s employment, performance, or work environment.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 37Contemporary Issues in Managing
Human Resources (cont.)
Family
-friendly benefits – benefits that accommodate
employees’ needs for work–life balance.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 38Contemporary Issues in Managing
Human Resources (cont.)
Employee Health Care Costs –
since 2002, health care costs have risen an average of
15 percent a year and are expected to double by the year 2016 from the $2.2 trillion spent in 2007.Employee Pension Plan Costs – pension commitments have become such an enormous burden that companies can no longer afford them. In fact, the corporate pension system has been described as “fundamentally broken.”
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 40Learning Objectives
Define groups and the stages of group development.
Describe the
major components that determine group performance and satisfaction.
Define teams and
best practices influencing team performance.Know how to maximize outcomes through effective negotiating.
Develop your skill at coaching team members.
Discuss contemporary issues in managing teams.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 41What Is a Group?
Group
– two or more interacting and interdependent individuals
who come together to achieve specific goals.Formal groups
Work groups defined by the organization’s structure that have designated work assignments and tasks.
Informal groups
Groups that are independently formed to meet the social needs of their members.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
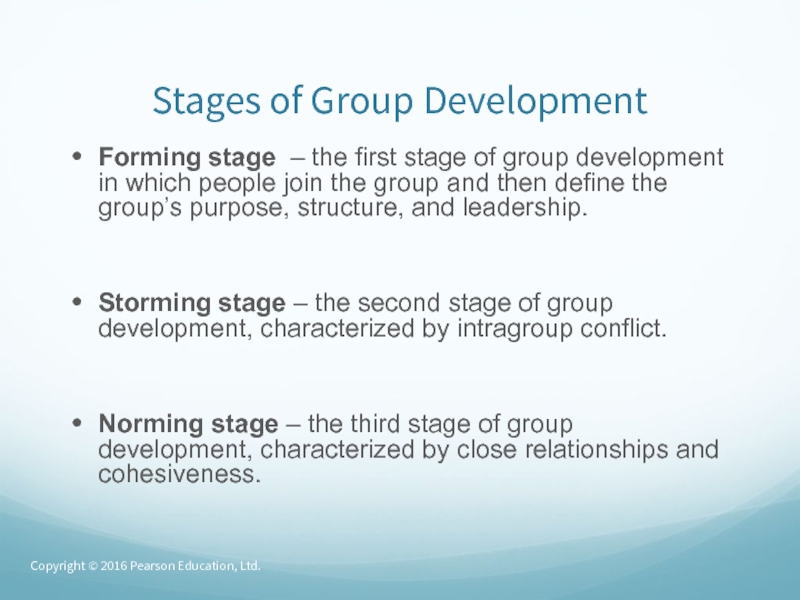
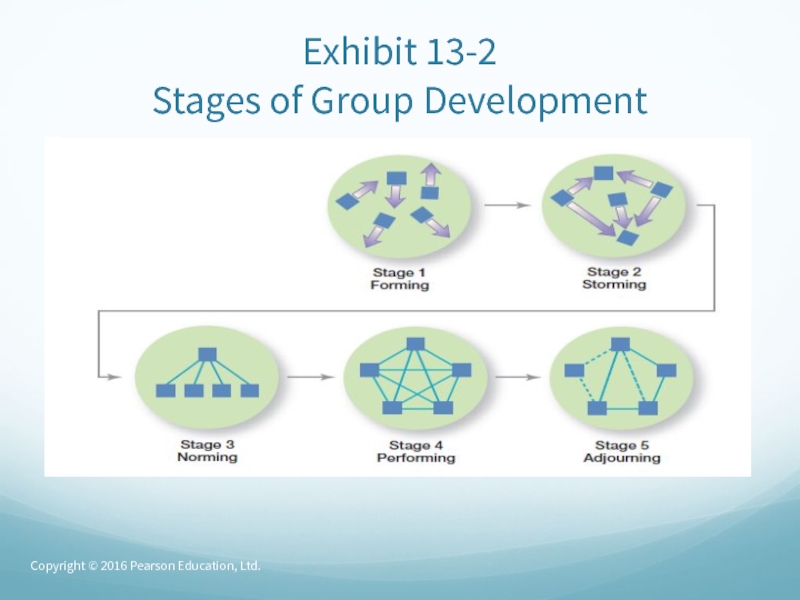
Слайд 43Stages of Group Development
Forming stage – the first stage of
group development in which people join the group and then
define the group’s purpose, structure, and leadership.Storming stage – the second stage of group development, characterized by intragroup conflict.
Norming stage – the third stage of group development, characterized by close relationships and cohesiveness.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 44Stages of Group Development (cont.)
Performing stage – the fourth stage
of group development when the group is fully functional and
works on group task.Adjourning – the final stage of group development for temporary groups during which group members are concerned with wrapping up activities rather than task performance.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 46Work Group Performance and Satisfaction
Why are some groups more
successful than others?
The abilities of the group’s members
The size of
the groupThe level of conflict
The internal pressures on members to conform to the group’s norms
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
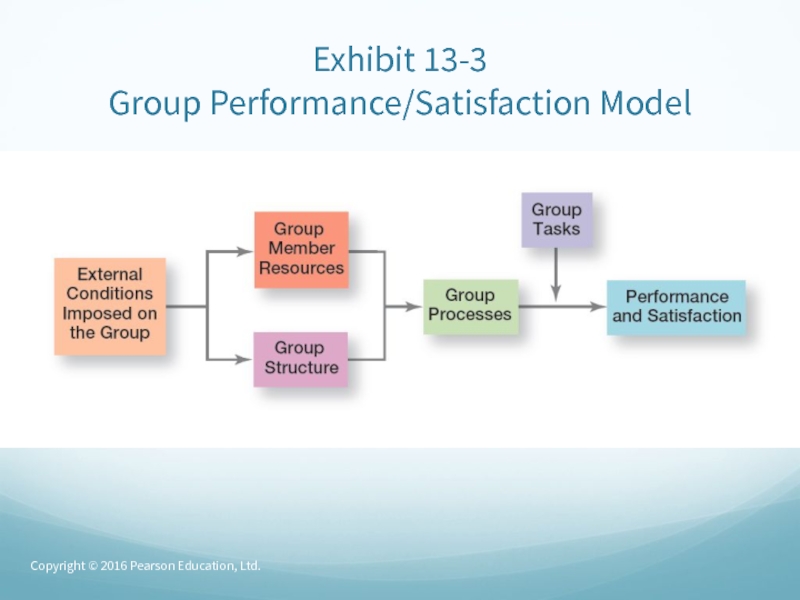
Слайд 48External Conditions Imposed on the Group
Work groups
are
affected by the external conditions imposed on it:The organization’s strategy
Authority relationships
Formal rules and regulations
Availability of resources
Employee selection criteria
The performance management system and culture
The general physical layout of the group’s work space
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 49Group Member Resources
A group’s
performance potential depends to a large extent
on the resources each individual brings to the group. These include:Knowledge
Abilities
Skills
Personality traits
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 50Group Structure
Role – behavior patterns expected of someone occupying a
given position in a social unit.
Norms – standards or expectations
that are accepted and shared by a group’s members.Groupthink – when a group exerts extensive pressure on an individual to align his or her opinion with that of others.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 51Group Structure (cont.)
Status – a prestige grading, position, or rank
within a group.
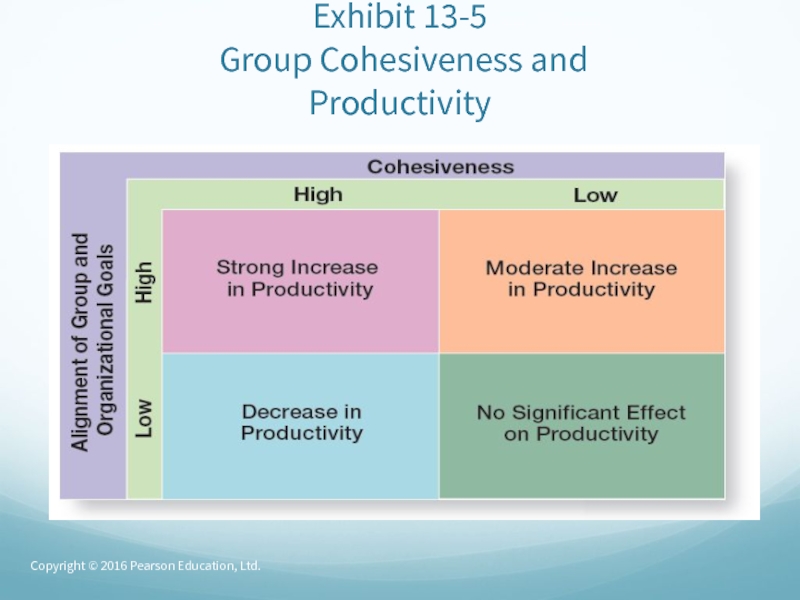
Social loafing – the tendency for individuals to
expend less effort when working collectively than when working individually.Group cohesiveness – the degree to which group members are attracted to one another and share the group’s goals.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 53Group Structure (cont.)
Group Size
Small groups are faster than larger ones
at completing tasks
Large groups consistently get better problem solving results
than smaller onesAmazon founder and CEO Jeff Bezos uses a “two-pizza” philosophy; that is, a team should be small enough that it can be fed with two pizzas.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 54Group Structure (cont.)
Group Processes
– processes that go on within a work group determines group performance and satisfaction. These include:
Communication
Decision-making
Conflict management
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 55Group Structure (cont.)
Group Decision-making – most organizations use groups to
make decisions.
Advantages of group decision-making
More complete information and knowledge
A
diversity of experience and perspectivesIncreased acceptance of a solution
Disadvantages of group decision-making
Groups almost always take more time to reach a solution
Dominant and vocal minority can influence the decision
Groupthink
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 57Conflict Management
Conflict
– perceived incompatible differences that result in interference or
opposition.Traditional view of conflict – the view that all conflict is bad and must be avoided.
Human relations view of conflict – the view that conflict is a natural and inevitable outcome in any group.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 58Conflict Management (cont.)
Interactionist
view of conflict –
the view that some conflict is necessary for a group to perform effectively.Functional conflicts – conflicts that support a group’s goals and improve its performance.
Dysfunctional conflicts – conflicts that prevent a group from achieving its goals.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 59Conflict Management (cont.)
Task conflict – conflicts over content and goals
of the work.
Relationship conflict – conflict based on interpersonal relationships.
Process
conflict – conflict over how work gets done.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 62Turning Groups into
Effective Teams
Work teams
– groups
whose members work intensely on a specific, common goal using their positive synergy, individual and mutual accountability, and complementary skills.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 64Types of Work Teams
Problem-solving team – a team from the
same department or functional area that’s involved in efforts to
improve work activities or to solve specific problems.Self-managed work team – a type of work team that operates without a manager and is responsible for a complete work process or segment.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 65Types of Work Teams (cont.)
Cross-functional team – a work team
composed of individuals from various functional specialties.
Virtual team – a
type of work team that uses technology to link physically dispersed members in order to achieve a common goal.Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 66Creating Effective Work Teams
Clear Goals – high-performance teams have a
clear understanding of the goal to be achieved.
Relevant Skills –
team members have the necessary technical and interpersonal skills.Mutual Trust – effective teams are characterized by high mutual trust among members.
Unified Commitment – members are dedicated to team goals.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 67Creating Effective Work Teams (cont.)
Good Communication – messages are clearly
understood.
Negotiating Skills – members need to be able to confront
and reconcile differences.Appropriate Leadership – leaders motivate a team to follow through difficult situations.
Internal and External Support – proper training, incentives, and resources.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 69Current Challenges in
Managing Teams
Group Member Resources in Global Teams
– managers need to clearly understand the cultural characteristics of
group members.Group Structure – issues include conformity, status, social loafing, and cohesiveness.
Group Processes – multicultural global team is better able to capitalize on the diversity of ideas.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
Слайд 71Understanding Social Networks
Social Network
The patterns of informal connections among individuals
within groups.
The Importance of Social Networks
Relationships can help or hinder
team effectiveness.Relationships improve team goal attainment and increase member commitment to the team.
Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.