Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
LECTURE № 14 METALS 18.04.2016
Содержание
- 1. LECTURE № 14 METALS 18.04.2016
- 2. Lecture Plan:Metal definitionCategories of various metalsThe structure
- 3. OBJECTIVES:Understand the physical properties of metals.Explains the
- 4. A metal (from Greek μέταλλον métallon, "mine,
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Metallic Elements: Alkali metals (group IA): Li,
- 7. Metallic Elements:4) Post-transition metals: Al, In, Ga,
- 8. The metallic bond causes many of the
- 9. In a piece of metal, all the
- 10. REASONS:Give 3 reasons Why tungsten is used
- 11. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF METALSGood electrical and heat conductors.Malleable
- 12. Density of MetalsLight metals
- 13. Melting point metalsRefractory metalsFusible metals
- 14. Metals have luster. This means they are
- 15. A chemical property of metal is its
- 16. These properties make metals most useful in daily life.
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF METALSUsually have 1-3 electrons
- 19. Reactivity series of metals The arranging of metals
- 20. Use the reactivity series to predict if
- 21. Reaction with oxygen : Metals react with oxygen
- 22. Reaction of metals with water Those metals staying
- 23. K, Na, Li and Ca react violently
- 24. Reaction with Concentrated Acids: HNO3 and H2SO4 Hydrogen
- 25. Reaction with HNO3Concentrated acid does not affect
- 26. Explaining displacement reactions The reactivity series can be
- 27. Reaction of metals with metal salt solutions
- 28. Displacement reaction Zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate
- 29. The more reactive aluminium takes the oxygen
- 30. Occurrence of metals
- 31. Occurrence of metals in nature High active
- 32. Extraction of metals from their ores : The
- 33. Ways of Metal ExtractionPotassium KSodium NaCalcium CaMagnesium Mg Aluminium AlZinc Zn Iron FeTin SnLead PbCopper CuMercury HgSilver AgGold AuPlatinum PtExtraction by electrolysis of
- 34. Steps involved in the extraction of metals
- 35. Using of Metals Metal used in manufacturing are
- 36. Ferrous Metals (black):Ferrous metals are based on
- 37. METALS ALLOYS An alloy is a homogeneous mixture
- 38. Слайд 38
- 39. Слайд 39
- 40. Слайд 40
- 41. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
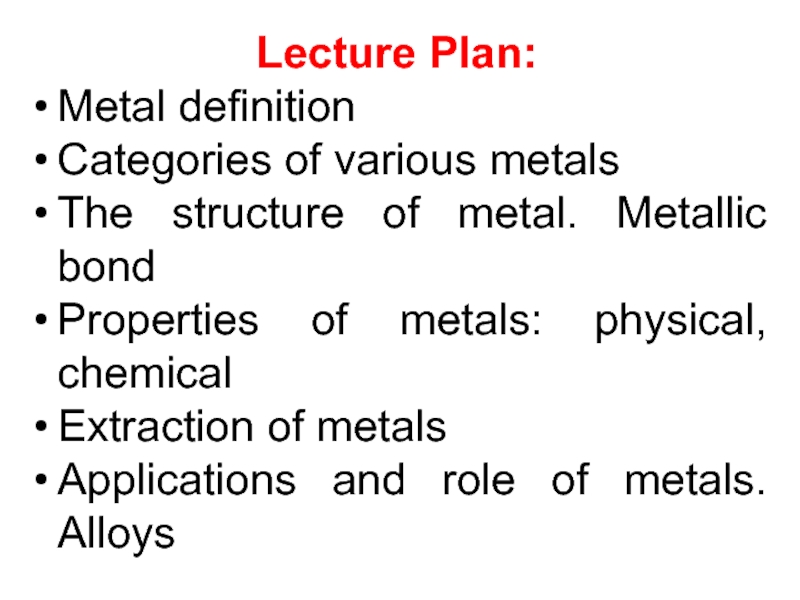
Слайд 2Lecture Plan:
Metal definition
Categories of various metals
The structure of metal. Metallic
bond
metals. AlloysСлайд 3OBJECTIVES:
Understand the physical properties of metals.
Explains the chemical properties of
metals.
Explain how the reactivity of metals changes across the periodic
table.List out the uses of metals and alloys.
Слайд 4 A metal (from Greek μέταλλον métallon, "mine, quarry, metal") is
a material (an element, compound, or alloy) that is typically
hard, opaque, shiny, and has good electrical and thermal conductivity.In chemical reaction: "Metals are the elements which form positive ions by losing electrons.“ They are also known as electropositive elements.
Metals are generally malleable — that is, they can be hammered or pressed permanently out of shape without breaking or cracking — as well as fusible (able to be fused or melted) and ductile (able to be drawn out into a thin wire).
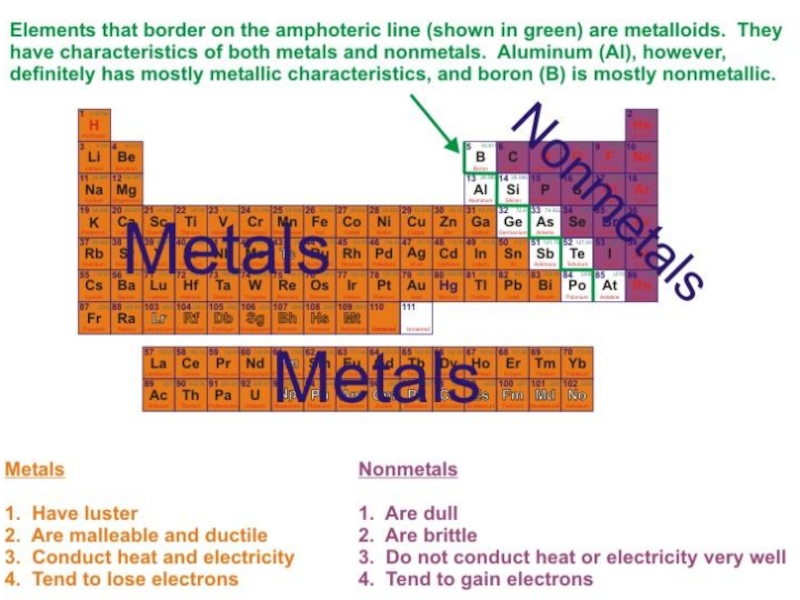
About 91 of the 118 elements in the periodic table are metals (some elements appear in both metallic and non-metallic forms).
Слайд 6Metallic Elements:
Alkali metals (group IA): Li, Na, K, Rb,
Cs, Fr
Alkali earth metals (group IIA): Be, Mg, Ca,
Sr, Ba, RaTransition metals (Group 3 – 12, d-elements): Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Cd, Os, Hg, Pt, Au, W
Iron Triad (Group 8, 9,10): Fe, Co & Ni = They create the magnetic field
Coinage Metals (Group 11): Cu, Ag, Au = They are used to make coins.
copper
silver
gold
Слайд 7Metallic Elements:
4) Post-transition metals: Al, In, Ga, Sn, Tl, Pb,
Bi, Po
5) Lanthanides
6) Actinides
7) Elements which are possibly metals: meitnerium,
darmstadtium, roentgenium, ununtrium, ununpentium, livermorium, ununseptium8) Elements which are sometimes considered metals: Ge, As, At, Sb
Слайд 8 The metallic bond causes many of the traits of metals,
such as strength, malleability, ductility, luster, conduction of heat and
electricity. Metallic bonding is the force of attraction between valence electrons and the metal positive ions.
Metallic Bonding
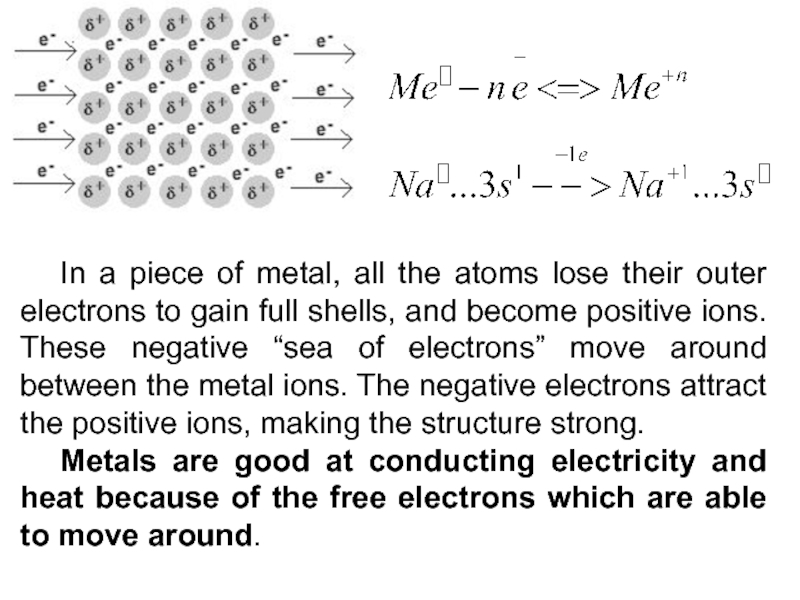
Слайд 9 In a piece of metal, all the atoms lose their
outer electrons to gain full shells, and become positive ions.
These negative “sea of electrons” move around between the metal ions. The negative electrons attract the positive ions, making the structure strong.Metals are good at conducting electricity and heat because of the free electrons which are able to move around.
Слайд 10REASONS:
Give 3 reasons Why tungsten is used to make the
filament inside an electric bulb?
1) Tungsten can be drawn into
very thin metal wires.2) Tungsten has the highest melting point (3422°C).
3) Tungsten has strong resistance to high temperature.
Слайд 11PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS
Good electrical and heat conductors.
Malleable - can be
beaten into thin sheets.
Ductile - can be stretched into wire.
Metals
have a high melting point. They are also very dense.Possess metallic luster.
Opaque as thin sheet.
Solid at room temperature (except Hg).
Слайд 12Density of Metals
Light metals
Heavy metals
Magnesium
1,74 g/cm3
Lead
11,3 g/cm3
Gold
19,3 g/cm3
Osmium
22,5 g/cm3
Lithium
0,53 g/cm3
Light metals have
density less than 5 g/cm3Heavy metals have density greater than 5 g/cm3
Слайд 14Metals have luster. This means they are shiny.
Ductile metals can
be drawn into wire.
Malleable metals can be hammered into
sheetsСлайд 15A chemical property of metal is its reaction with water
and oxygen. This results in corrosion and rust:
Me +
O2 = MexOy Me + [O] + H2O = Me(OH)n
The ability of metals to produce a particular sound when it is tapped on a hard surface is termed sonority.
Слайд 18CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS
Usually have 1-3 electrons in their outer
shell.
Lose their valence electrons easily.
Form oxides that are basic.
Are good reducing agents
Have
lower (EN<1,5) electronegativities.Слайд 19Reactivity series of metals
The arranging of metals in the decreasing
order of their reactivity is called reactivity series of metals:
K - PotassiumNa - Sodium Most
Ca - Calcium reactive
Mg - Magnesium
Al - Aluminium
Zn - Zinc Reactivity
Fe - Iron decreases
Pb - Lead
H - Hydrogen
Cu - Copper
Hg - Mercury Least
Ag - Silver reactive
Au - Gold
The activity series of metals is an empirical tool used to predict products in displacement reactions and reactivity of metals with water and acids in replacement reactions and ore extraction.
Слайд 20 Use the reactivity series to predict if a reaction will
take place and how intense the reaction will be:
acid
gold
metal
reacts with
calcium
sodium
oxygen
oxygen
oxygen
silver
prediction
zinc
water
no
reactionfizzing
burns vigorously
very slow reaction
burns moderately
Слайд 21Reaction with oxygen :
Metals react with oxygen to form metal
oxides:
2Cu + O2 = 2CuO – Q
4Al + 3O2 =
2Al2O3 – Q4Na + O2 = 2Na2O + Q
The most reactive metals as K, Na, Li, Ca and Mg react with oxygen and burn in air.
Metals from Al to Cu in the activity series of metals, react slowly when heated in air to form the metal oxides. Aluminium is the fastest and copper is the slowest of them.
Iron metal does not burn in dry air even on strong heating. In moist air, iron is oxidized to give rust:
Gold and platinum do not react with oxygen in air.
Слайд 22Reaction of metals with water
Those metals staying above hydrogen in
electrochemical series react with cold water or steam to produce
hydrogen:Active metals at room temperature are formed hydroxides:
Medium active metals at high temperature with steam are formed oxides:
Sn, Pb, Cu, Ag, Au and Pt do not react with water or steam.
Слайд 23 K, Na, Li and Ca react violently with dilute H2SO4 and
dilute HCl, forming the metal salt (either sulfate or chloride)
and hydrogen gas:Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid is often used for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen. The reaction is slow at room temperature, but its rate can be increased by the addition of a little copper (II) sulphate. Zinc displaces copper metal, which acts as a catalyst.
Metals below hydrogen (Cu, Ag, Au, Pt), will not react with dilute acids. They cannot displace hydrogen from the non-metal anion.
REACTION WITH ACIDS
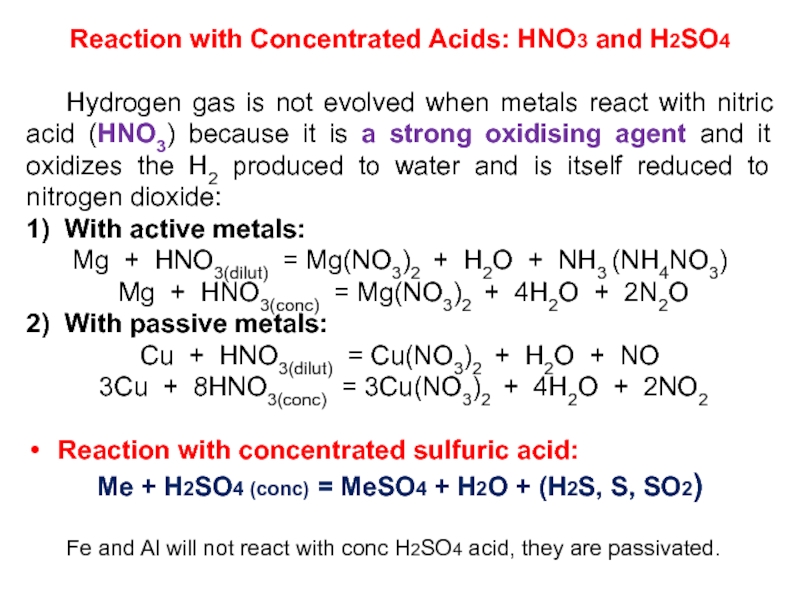
Слайд 24Reaction with Concentrated Acids: HNO3 and H2SO4
Hydrogen gas is not
evolved when metals react with nitric acid (HNO3) because it
is a strong oxidising agent and it oxidizes the H2 produced to water and is itself reduced to nitrogen dioxide:1) With active metals:
Mg + HNO3(dilut) = Mg(NO3)2 + H2O + NH3 (NH4NO3)
Mg + HNO3(conc) = Mg(NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2N2O
2) With passive metals:
Cu + HNO3(dilut) = Cu(NO3)2 + H2O + NO
3Cu + 8HNO3(conc) = 3Cu(NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2NO2
Reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid:
Me + H2SO4 (conc) = MeSO4 + H2O + (H2S, S, SO2)
Fe and Al will not react with conc H2SO4 acid, they are passivated.
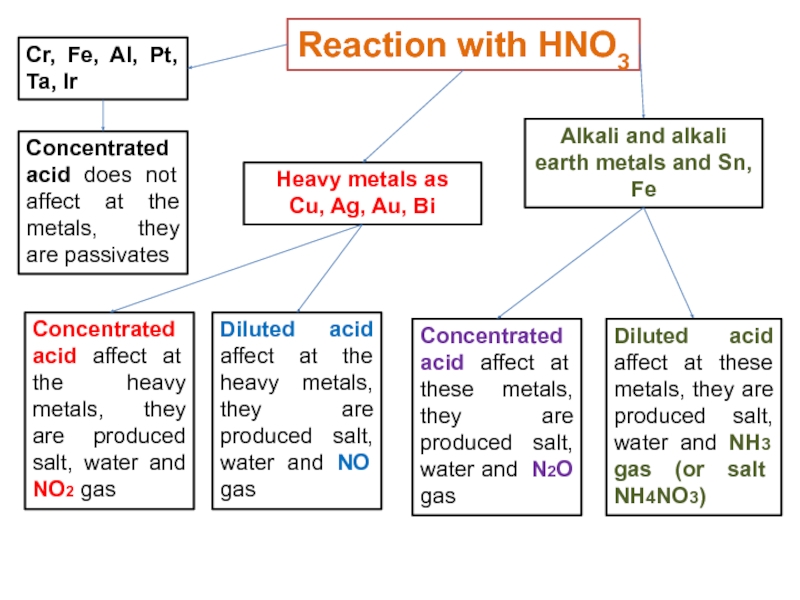
Слайд 25Reaction with HNO3
Concentrated acid does not affect at the metals,
they are passivates
Cr, Fe, Al, Pt, Ta, Ir
Concentrated acid
affect at the heavy metals, they are produced salt, water and NO2 gasHeavy metals as
Cu, Ag, Au, Bi
Diluted acid affect at the heavy metals, they are produced salt, water and NO gas
Alkali and alkali earth metals and Sn, Fe
Concentrated acid affect at these metals, they are produced salt, water and N2O gas
Diluted acid affect at these metals, they are produced salt, water and NH3 gas (or salt NH4NO3)
Слайд 26Explaining displacement reactions
The reactivity series can be used to predict
if a metal will react with a metal compound. If
the metal is more reactive than the metal in the compound, it pushes out, or displaces, the less reactive metal from its compound. If the metal is less reactive than the metal in the compound, it will not compete and so there is no reaction.
more reactive metal
less
reactive metal compound
more
reactive metal compound
less reactive metal
+
+
less reactive metal
more reactive metal compound
no reaction
+
Слайд 27Reaction of metals with metal salt solutions and oxides
A displacement
reaction is one where a more reactive metal will displace
a cation of less reactive metal from a compound (salt, oxide:-2,37 V
active
metal
+0,34 V
passive
metal
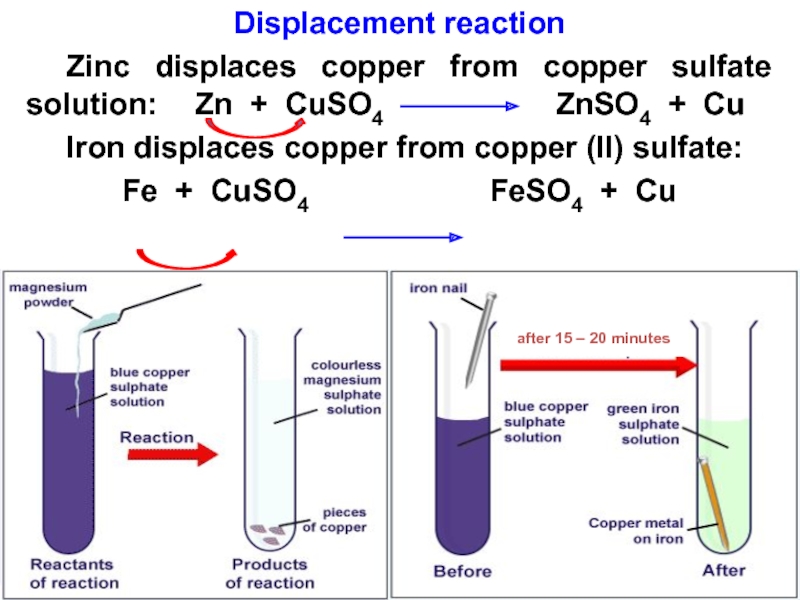
Слайд 28Displacement reaction
Zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate solution: Zn +
CuSO4
ZnSO4 + CuIron displaces copper from copper (II) sulfate:
Fe + CuSO4 FeSO4 + Cu
after 15 – 20 minutes
Слайд 29 The more reactive aluminium takes the oxygen from the less
reactive iron.
The reaction gets so hot that the iron
melts! It is used to weld railway tracks.Aluminium + Iron oxide => Aluminium oxide + Iron
In this reaction, aluminium reacts with iron oxide to make aluminium oxide and iron:
Слайд 30 Occurrence of metals :
Some metals like
gold, silver, platinum etc are found in the free state
(nugget) in the earth’s crust because they are least reactive. Most metals are found as oxides, carbonates, sulfides, halides etc.Minerals: are elements or compounds which occur naturally inside the earth’s crust.
Ore: is a mineral from which metals can be extracted profitably.
Gangue: is the impurities present in the ore like rock particles, sand particles, clay particles etc.
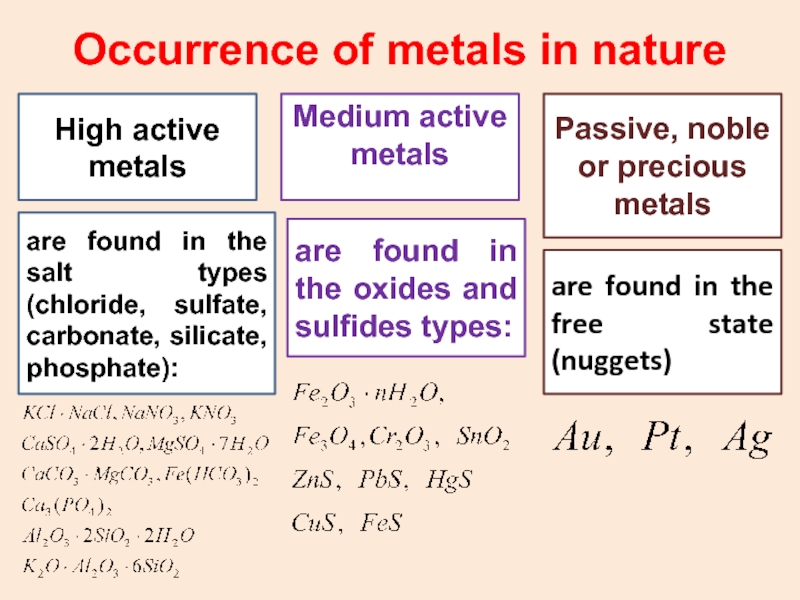
Слайд 31Occurrence of metals in nature
High active metals
Medium active
metals
Passive, noble or precious metals
High active metals
are found in
the salt types (chloride, sulfate, carbonate, silicate, phosphate): are found in the oxides and sulfides types:
are found in the free state (nuggets)
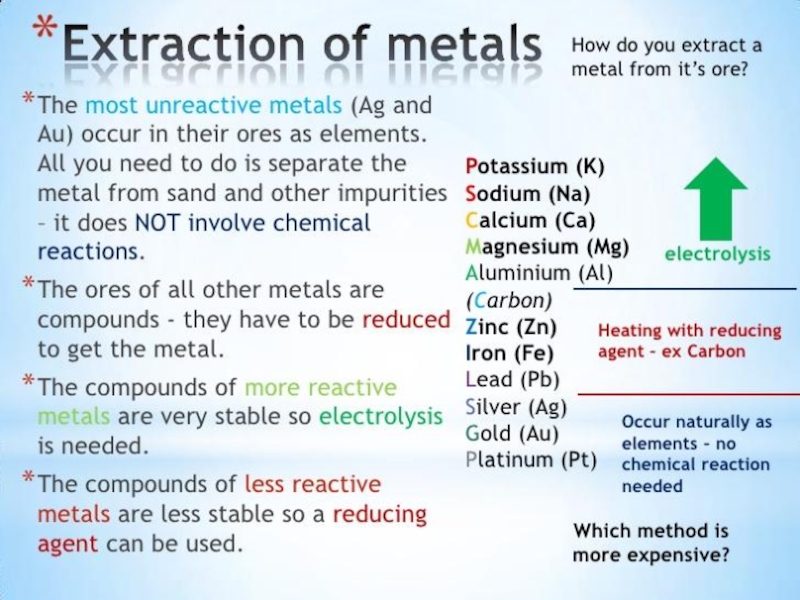
Слайд 32Extraction of metals from their ores :
The various processes involved
in the extraction of metals from their ores and refining
them are known as metallurgy.Metals are extracted from their ores in three main steps. They are :
Concentration of the ore (Enrichment of the ore).
Reducing the metal compound to the metal (by O2, H2, C, CO, Al and electrolysis)
Refining (Purification of the metal by electrolysis).
Слайд 33Ways of Metal Extraction
Potassium K
Sodium Na
Calcium Ca
Magnesium Mg
Aluminium Al
Zinc Zn
Iron Fe
Tin Sn
Lead Pb
Copper Cu
Mercury Hg
Silver Ag
Gold Au
Platinum Pt
Extraction by electrolysis of molten Al2O3 dissolved
in cryolite
Extracted by electrolysis of molten chlorides
Extraction by reduction of
oxides using carbonRoasting ore by heating alone
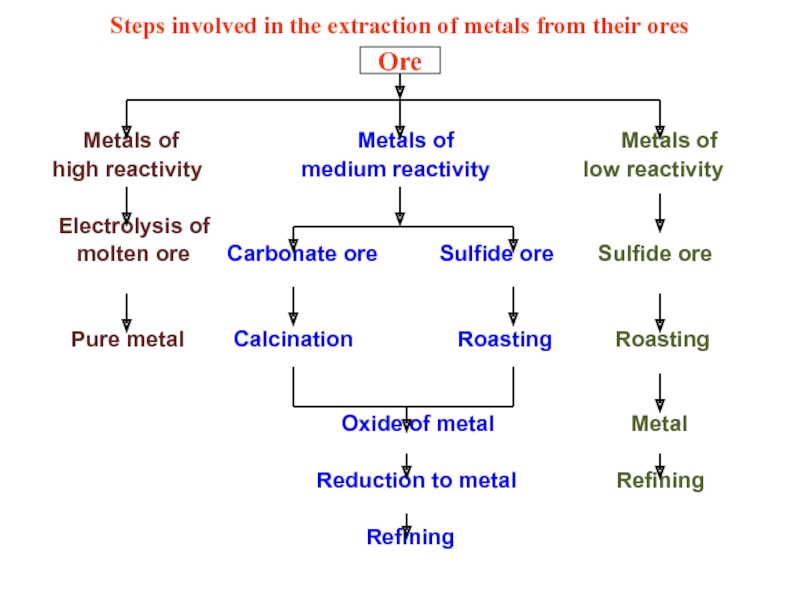
Слайд 34Steps involved in the extraction of metals from their ores
high reactivity medium reactivity low reactivity
Electrolysis of
molten ore Carbonate ore Sulfide ore Sulfide ore
Pure metal Calcination Roasting Roasting
Oxide of metal Metal
Reduction to metal Refining
Refining
Ore
Слайд 35Using of Metals
Metal used in manufacturing are usually alloys, which
are composed of two or more elements, with at least
one being metallic element.Metals can be divided into two basic categories:
Ferrous
Non ferrous
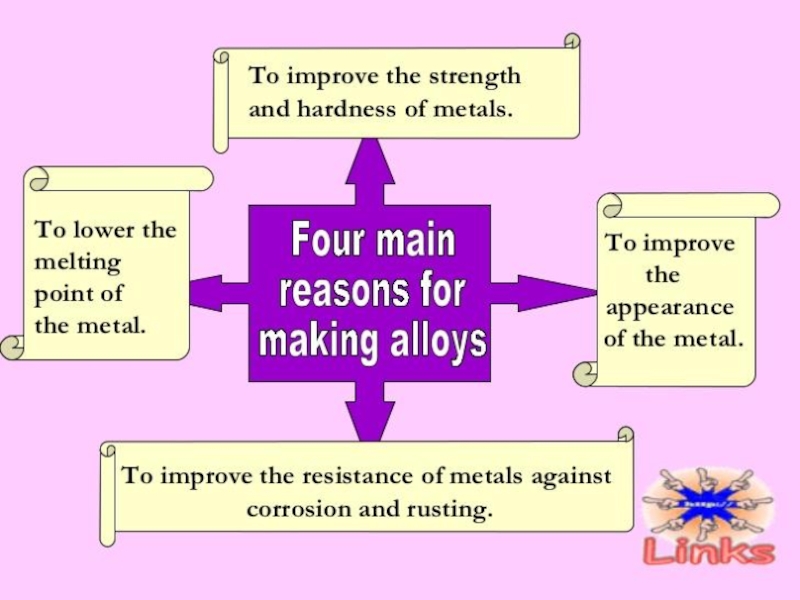
Alloys are stronger and harder than pure metals and they also can with stand corrosion better. Pure metals are relatively a little softer (but they are still hard) and they have a low resistance to corrosion as they are affected by air and water easily. Hence alloys are used more often instead of pure metals. Nowadays, complex alloys have been made with specific desired properties. Usually, transition metals are used in the production of alloys.
Слайд 36Ferrous Metals (black):
Ferrous metals are based on iron: the group
includes steel and cast iron. Pure iron has limited commercial
use, but when alloyed with carbon. Iron has more uses and greater commercial value than any other metal.Non ferrous (colored):
They include the other metallic elements and their alloys. They include metals and alloys of aluminum, copper, gold, silver and other metals.
Слайд 37METALS ALLOYS
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of a metal
with other metals or non metal:
Steel and cast iron –
iron, carbonStainless steel – iron, carbon, cobalt, nickel
Brass – copper, zinc
Bronze – copper, tin
Solder – Lead, tin (used for welding electrical wires together)
If one of the metals in an alloy is mercury, it is called an amalgam.