Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
lnternational Marketing Chapter 7 Global competitive strategy
Содержание
- 1. lnternational Marketing Chapter 7 Global competitive strategy
- 2. Industry analysis (Five Forces Model)Competitive advantage and strategyGlobal competition
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. A. .Industry analysisFive Forces model Michael
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. The five forces are environmental
- 7. Q1: For what reasons.the rivalry among the
- 8. 1. Rivalry Among Existing CompetitorsWhat cause the
- 9. Low swithing cost Low level of product differentiation Strategic stakes are high High exit barriers
- 10. In pursuring anadvantage over its rivals.A firm
- 11. 2.Threat of New Entrants Profitable markets that
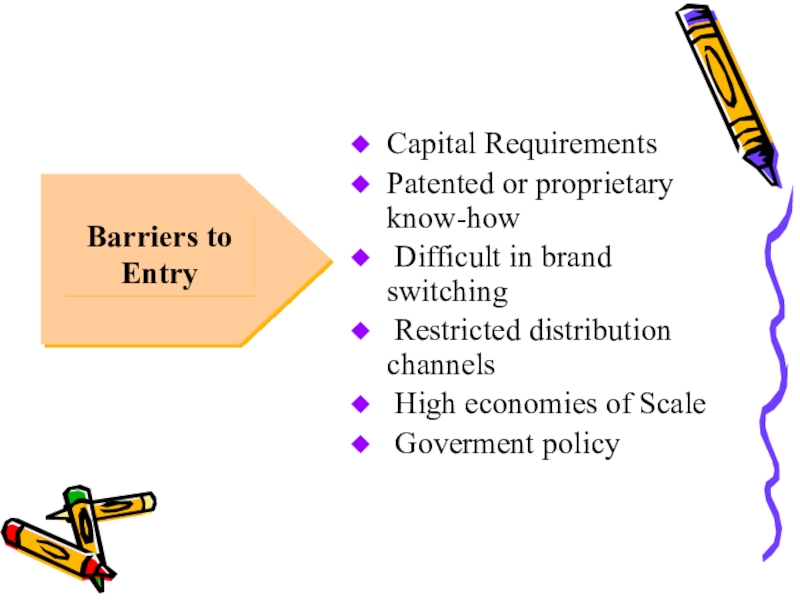
- 12. Capital RequirementsPatented or proprietary know-how Difficult in
- 13. 3. Bargaining Power of SuppliersSuppliers are likely
- 14. 4. Bargaining Power of BuyersBuyer groups are
- 15. 5.Threat of Substitute ProductsProducts with improving price/performance
- 16. Factors that determine the threat of substitute
- 17. Number of substitute products available in the
- 18. B. Competitive advantage An advantage that
- 19. CASE
- 20. 1. Cost advantage strategy It is
- 21. CASE
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. CASE 2
- 24. Any benefit? Higher profit margin.achieve more earnings from its products Increased market shareSustainabilityCapital for grwoth
- 25. Risky?Focusing on price can make the company
- 26. 2. Differential advantage strategy A differential
- 27. A product or service that differs from
- 28. CASE 1
- 29. The key to differential advantage is that
- 30. CASE 2
- 31. Differential advantage= High cost?
- 32. C. Global competition Strategic initiatives should address
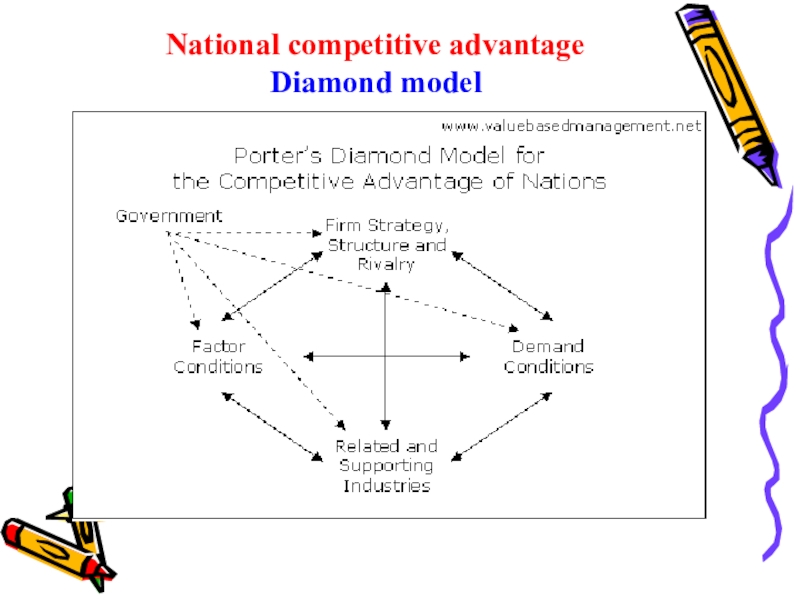
- 33. National competitive advantage Diamond model
- 34. It analyzing why some nations are more
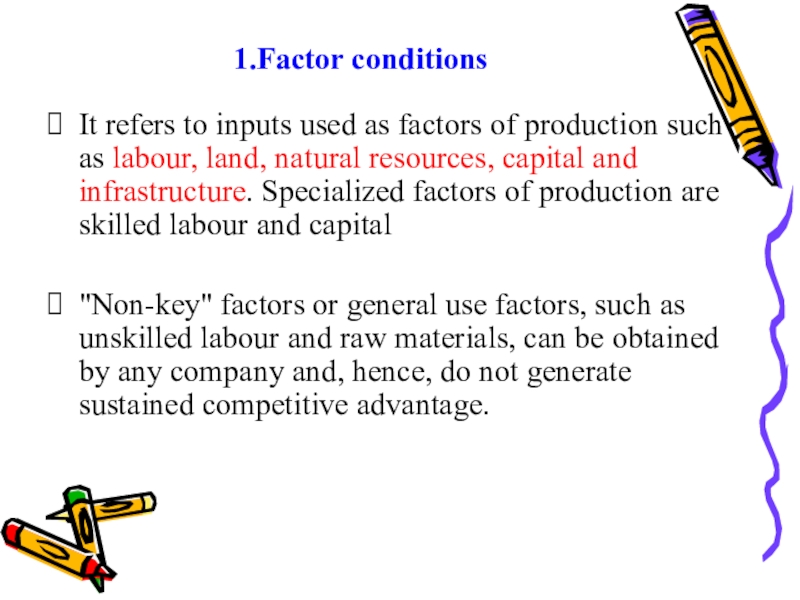
- 35. 1.Factor conditionsIt refers to inputs used as
- 36. 2. Demand Conditions Demand conditions in the
- 37. CASE 1 The French are sophisticated
- 38. CASE 2
- 39. CASE 3
- 40. CASE 4
- 41. 3. Related and Supporting Industries a set
- 42. CASE 1 The shoe and leather
- 43. CASE 2
- 44. 4. Firm Strategy, Structure and RivalryNational performance
- 45. CASE It provide intense competition in
- 46. ALSO.Cultural aspects play an important role. In
- 47. CASE Germany tends to have hierarchical
- 48. 5. Government The government plays an
- 49. Governments can influence all four
- 50. SummaryFive Forces Model: Rivalry Among Existing Competitors.
- 51. Reference竞争战略 迈克尔·波特 华夏出版社 竞争优势 迈克尔·波特 华夏出版社 国家竞争优势 迈克尔·波特 华夏出版社 竞争的资本 Stuart Crainer,中国青年出版社 海尔中国造之竞争战略与核心能力 胡泳 海南出版社http://www.ceconlinebbs.com/(世界经理人互动社区 国家竞争优势案例分析)
- 52. Слайд 52
- 53. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 6 The five forces are environmental forces that impact
on a company’s ability to compete in a given market.
The purpose of five-forces analysis is to diagnose the principal competitive pressures in a market and assess how strong and important each one is.Слайд 7Q1: For what reasons.the rivalry among the
industry will be increased?
Q2: How to set barriers to new
entrants?Q3: In which situation. buyers have strong
bargaining power?
Q4: In which situation. suppliers have strong
bargaining power?
Q5: What determine the threat of Substitute
Products?
Слайд 81. Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
What cause the increase of rivalry
among the industry?
A larger number of firms
Slow market
growthHigh fixed cost
High storage cost
Слайд 9 Low swithing cost
Low level of product differentiation
Strategic
stakes are high
High exit barriers
Слайд 10In pursuring anadvantage over its rivals.
A firm can choose from
several competitive moves:
Changing prices
Improving product differentiation
Creatively using
channels of distributionExploiting relationships with suppliers
Слайд 112.Threat of New Entrants
Profitable markets that yield high returns will
attract new firms. This results in many new entrants, which
eventually will decrease profitability for all firms in the industry.Inductries possess characteristics that protect the high profit levels for firms in the market.There are barriers to entry.
Слайд 12
Capital Requirements
Patented or proprietary know-how
Difficult in brand switching
Restricted
distribution channels
High economies of Scale
Goverment policy
Слайд 133. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Suppliers are likely to be powerful
if :
High cost to switch suppliers
Supplier industry is dominated
by a few firmsSuppliers’ products have few substitutes
Buyer is not an important customer to supplier
Suppliers’ product is an important input to
buyers’ product
Suppliers’ products are differentiated
Слайд 144. Bargaining Power of Buyers
Buyer groups are likely to be
powerful if :
Buyers are concentrated or purchases are large relative
to seller’s salesPurchase accounts for a significant fraction of supplier’s sales
Products are undifferentiated
Buyers face few switching costs
Buyers’ industry earns low profits
Слайд 155.Threat of Substitute Products
Products with improving price/performance tradeoffs relative to
present industry products
A threat of substitutes exists when a product’s
demand is affected by the price change of a substitute product.Слайд 16Factors that determine the threat of substitute
products?
Buyer propensity to
substitute
Relative price performance of substitute
Buyer switching costs
Perceived
level of product differentiation Слайд 17Number of substitute products available in the market
Ease of substitution.
Information-based products are more prone to substitution, as online product
can easily replace material product.Substandard product
Quality depreciation
Слайд 18B. Competitive advantage
An advantage that a firm has over
its competitors, allowing it to generate greater sales or margins and/or retain
more customers than its competition.There can be many types of competitive advantages including the firm's cost structure, product offerings, distribution network and customer support.
Слайд 201. Cost advantage strategy
It is a firm's ability to
produce a good or service at a lower cost than its
competitors, which gives the firm the ability sell its goods or services at a lower price than its competition or to generate a larger margin on sales.Слайд 24Any benefit?
Higher profit margin.achieve more earnings from its products
Increased market share
Sustainability
Capital for grwoth
Слайд 25Risky?
Focusing on price can make the company lose sight of
evolving customer tastes and preferences.
Once a company introduces a process
that saves the business money, other companies can quickly copy that technique and lower their prices. The cost leadership strategy does not work in every industry . For instance, consumers purchasing luxury goods do not care about price as much as someone looking to purchase food staples.
Слайд 262. Differential advantage strategy
A differential advantage is created
when a firm's products or services differ from its competitors
and are seen as better than a competitor's products by customers.Слайд 27A product or service that differs from
its rivals:
Differences
in quality which are usually accompanied by differences in price
Differences in functional features or design
Sales promotion activities of sellers and, in particular, advertising
Differences in availability (e.g. timing and location).
Слайд 29The key to differential advantage is that the customer should
not only appreciate the benefit it brings, but be prepared
to pay a premium price for it.Economic models usually assume the customer makes rational decisions. By this logic, a customer will therefore only see a differential advantage if she believes she couldn't get the same benefit from another company.
Слайд 32C. Global competition
Strategic initiatives should address
competitiveness issues
not only at the level of the
individual product and
service sector but at the national level as well.
Слайд 34It analyzing why some nations are more competitive than others
are, and why some industries within nations are more competitive
than others are .It suggests that the national home base of an organization plays an important role in shaping the extent to which it is likely to achieve advantage on a global scale. This home base provides basic factors, which support or hinder organizations from building advantages in global competition.
Слайд 351.Factor conditions
It refers to inputs used as factors of production
such as labour, land, natural resources, capital and infrastructure. Specialized
factors of production are skilled labour and capital"Non-key" factors or general use factors, such as unskilled labour and raw materials, can be obtained by any company and, hence, do not generate sustained competitive advantage.
Слайд 362. Demand Conditions
Demand conditions in the domestic market provide
the primary driver of growth, innovation and quality improvement
Firms
that face a sophisticated domestic market are likely to sell superior products because the market demands high quality and a close proximity to such consumers enables the firm to better understand the needs and desires of the customersСлайд 37CASE 1
The French are sophisticated wine consumers.
These consumers force and help French wineries
to produce high quality wines.Слайд 413. Related and Supporting Industries
a set of strong related
and supporting industries is important to the competitiveness of firms.
This includes suppliers and related industries. This usually occurs at a regional level as opposed to a national level.
Слайд 42CASE 1
The shoe and leather industry in Italy.
Italy is not
only successful with shoes and
leather, but with related products and services such as leather working machinery, design, etc.
Слайд 444. Firm Strategy, Structure and Rivalry
National performance in particular sectors
is inevitably related to the strategies and the structure of
the firms in that sector. Competition plays a big role in driving innovation and the subsequent upgradation of competitive advantage.Since domestic competition is more direct and impacts earlier than steps taken by foreign competitors, the stimulus provided by them is higher in terms of innovation and efficiency.
Слайд 45CASE
It provide intense competition in the domestic market,
as well as the foreign markets in which they compete.
Слайд 46ALSO.Cultural aspects play an important role. In different nations, factors
like management structures, working morale between companies are shaped differently.
Some countries may be oriented toward a particular style of management. Those countries will tend to be more competitive in industries for which that style of management is suited.
Слайд 47CASE
Germany tends to have hierarchical management structures composed
of managers with strong technical backgrounds and Italy has smaller,
family-run firms.Слайд 485. Government
The government plays an important role in
diamond model. "Government’s proper role is as a catalyst and
challenger; it is to encourage - or even push - companies to raise their aspirations and move to higher levels of competitive performance "Слайд 49 Governments can influence all four of determinants through
a variety of actions:
Subsidies to firms
Tax codes applicable to corporation
Educational
policies that affect the skill level of workers. They should enforce tough standards.
Слайд 50Summary
Five Forces Model: Rivalry Among Existing Competitors. Threat of New
Entrants. Bargaining Power of Suppliers. Bargaining Power of buyers. Threat
of Substitute ProductsCompetitive advantage and strategy: Cost advantage strategy. Differential advantage strategy
Diamond model: Factor conditions. Demand
Conditions.Related and Supporting Industries.Firm Strategy, Structure and Rivalry. Government