Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Managing Entrepreneurial Ventures
Содержание
- 1. Managing Entrepreneurial Ventures
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice HallA–Exhibit A–1 Evaluating Potential Ideas
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice HallA–Exhibit A–4 Legal Forms of Business Organization
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice HallA–Leading Issues (cont’d)Empowering EmployeesParticipative decision makingDelegationRedesigning jobs
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 32. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 33. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 34. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Managing
Entrepreneurial Ventures
Слайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.A1. The Context of Entrepreneurship
Differentiate between entrepreneurial ventures and small businesses.
Explain why entrepreneurship is important in the United States and globally.
Describe the four key steps in the entrepreneurial process.
Explain what entrepreneurs do.
Discuss why social responsibility and ethics are important considerations for entrepreneurs.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Learning
Outcomes
A2. Start-Up and Planning Issues
Discuss how opportunities are important to
entrepreneurial ventures.Describe each of the seven sources of potential opportunity.
Explain why it’s important for entrepreneurs to understand competitive advantage.
List possible financing options for entrepreneurs.
Describe the six major sections of a business plan.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Learning
Outcomes
A3. Organizing Issues
Contrast the six different forms of legal organization.
Describe
the organizational design issues that entrepreneurs face.Discuss the unique human resource management issues entrepreneurs face.
Describe what an innovation-supportive culture looks like.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Learning
Outcomes
A4. Leading Issues
Explain what personality research shows about entrepreneurs.
Discuss how
entrepreneurs can empower employees.Explain how entrepreneurs can be effective at leading employee work teams.
A5. Controlling Issues
Describe how entrepreneurs should plan, organize, and control growth.
Describe the boiled frog phenomenon and why it’s useful for entrepreneurs.
Discuss the issues an entrepreneur needs to consider when deciding whether to exit the entrepreneurial venture.
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
The
Context of Entrepreneurship
What Is Entrepreneurship?
Entrepreneurship is the process of starting
new businesses, generally in response to opportunities.Entrepreneurial Ventures
Organizations that pursue opportunities, are characterized by innovative practices, and have growth and profitability as their main goals.
Small Business
A firm that is independently owned, operated, and financed; has fewer than 100 employees; doesn’t necessarily engage in new or innovative practices, and has relatively little impact on its industry.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Why
Is Entrepreneurship Important?
Innovation
Engage in the creative destruction process
Act as agents
of changeNumber of New Startups
Increasing numbers of new firms
Job Creation
New ventures create 60-80% of net new jobs
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
The
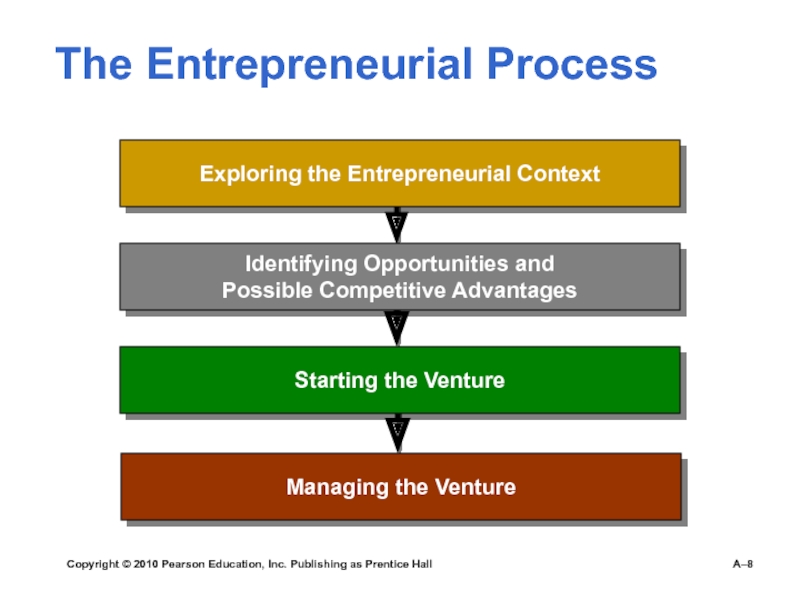
Entrepreneurial Process
Exploring the Entrepreneurial Context
Identifying Opportunities and
Possible Competitive Advantages
Starting
the VentureManaging the Venture
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
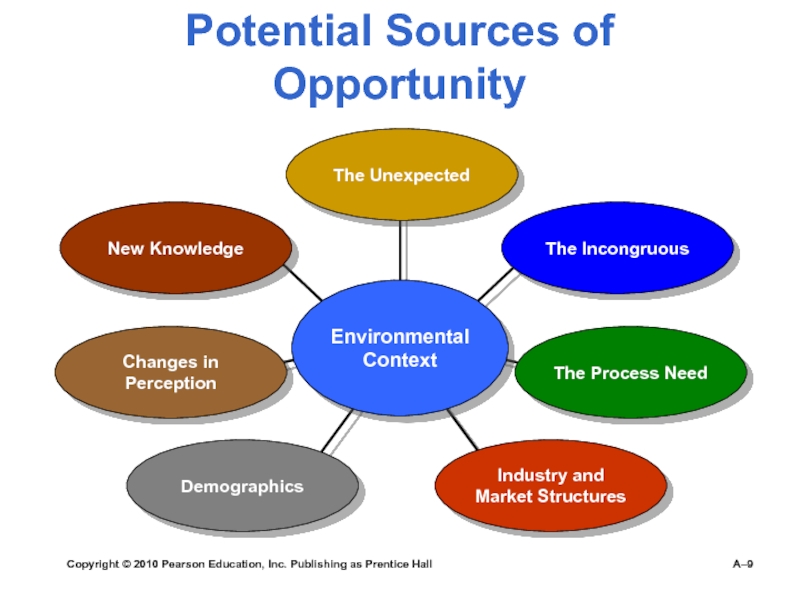
A–
Potential
Sources of Opportunity
Environmental Context
The Incongruous
The Process Need
Industry and Market Structures
Demographics
Changes
in PerceptionNew Knowledge
The Unexpected
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
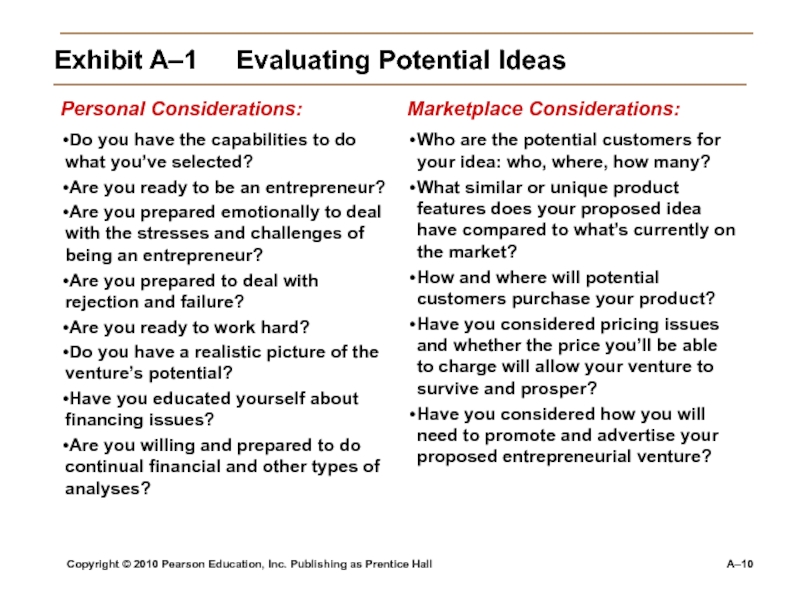
Exhibit
A–1 Evaluating Potential Ideas
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–2 Feasibility Study
A. Introduction, historical background, description of product or service:
Brief
description of proposed entrepreneurial ventureBrief history of the industry
Information about the economy and important trends
Current status of the product or service
How you intend to produce the product or service
Complete list of goods or services to be provided
Strengths and weaknesses of the business
Ease of entry into the industry, including competitor analysis
B. Accounting considerations:
1. Proforma balance sheet
2. Proforma profit and loss statement
3. Projected cash flow analysis
Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
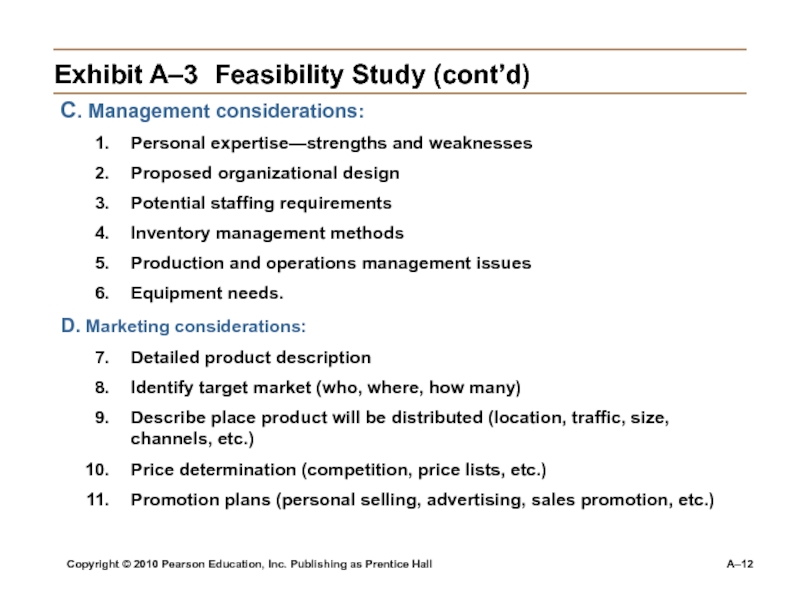
A–3 Feasibility Study (cont’d)
C. Management considerations:
Personal expertise—strengths and weaknesses
Proposed organizational design
Potential
staffing requirementsInventory management methods
Production and operations management issues
Equipment needs.
D. Marketing considerations:
Detailed product description
Identify target market (who, where, how many)
Describe place product will be distributed (location, traffic, size, channels, etc.)
Price determination (competition, price lists, etc.)
Promotion plans (personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, etc.)
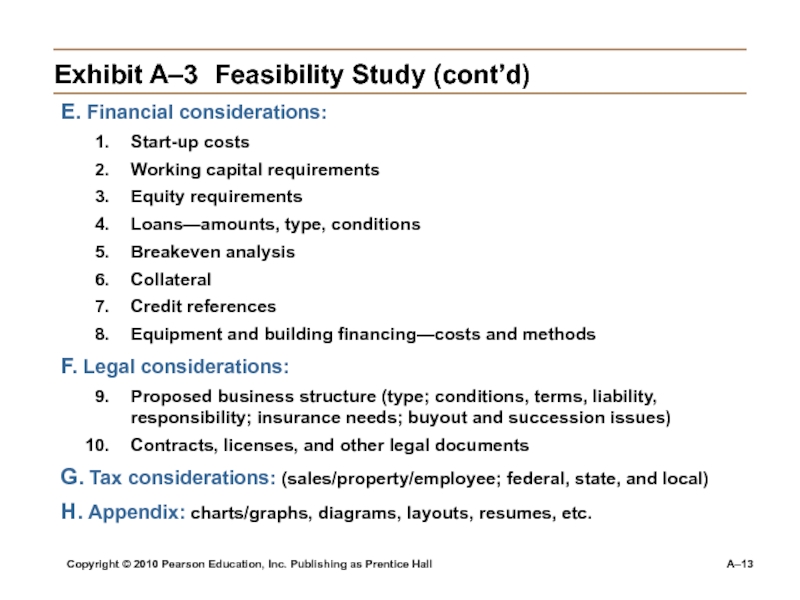
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–3 Feasibility Study (cont’d)
E. Financial considerations:
Start-up costs
Working capital requirements
Equity requirements
Loans—amounts, type,
conditionsBreakeven analysis
Collateral
Credit references
Equipment and building financing—costs and methods
F. Legal considerations:
Proposed business structure (type; conditions, terms, liability, responsibility; insurance needs; buyout and succession issues)
Contracts, licenses, and other legal documents
G. Tax considerations: (sales/property/employee; federal, state, and local)
H. Appendix: charts/graphs, diagrams, layouts, resumes, etc.
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Researching
Competitors
Competitor Intelligence:
What types of products or services are competitors offering?
What
are the major characteristics of these products or services?What are their products’ strengths and weaknesses?
How do they handle marketing, pricing, and distributing?
What do they attempt to do differently from other competitors?
Do they appear to be successful at it? Why or why not?
What are they good at?
What competitive advantage(s) do they appear to have?
What are they not so good at?
What competitive disadvantage(s) do they appear to have?
How large and profitable are these competitors?
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–3 Possible Financing Options
Entrepreneur’s personal resources (personal savings, home equity, personal
loans, credit cards, etc.)Financial institutions (banks, savings and loan institutions, government-guaranteed loan, credit unions, etc.)
Venture capitalists—external equity financing provided by professionally-managed pools of investor money
Angel investors—a private investor (or group of private investors) who offers financial backing to an entrepreneurial venture in return for equity in the venture
Initial public offering (IPO)—the first public registration and sale of a company’s stock
National, state, and local governmental business development programs
Unusual sources (television shows, judged competitions, etc.)
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Investing
in Entrepreneurial Ventures
Venture Capitalists
External equity financing provided by professionally-managed
pools of investor money.Angel Investors
A private investor (or group of private investors) who offers financial backing to an entrepreneurial venture in return for equity in the venture.
Initial public offering (IPO)
The first public registration and sale of a company’s stock.
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Developing
a Business Plan
Business Plan
A written document that summarizes a business
opportunity and defines and articulates how the identified opportunity is to be seized and exploited.Elements of a Business Plan
Executive summary
Analysis of opportunity
Analysis of context
Description of the business
Financial data and projections
Supporting documentation
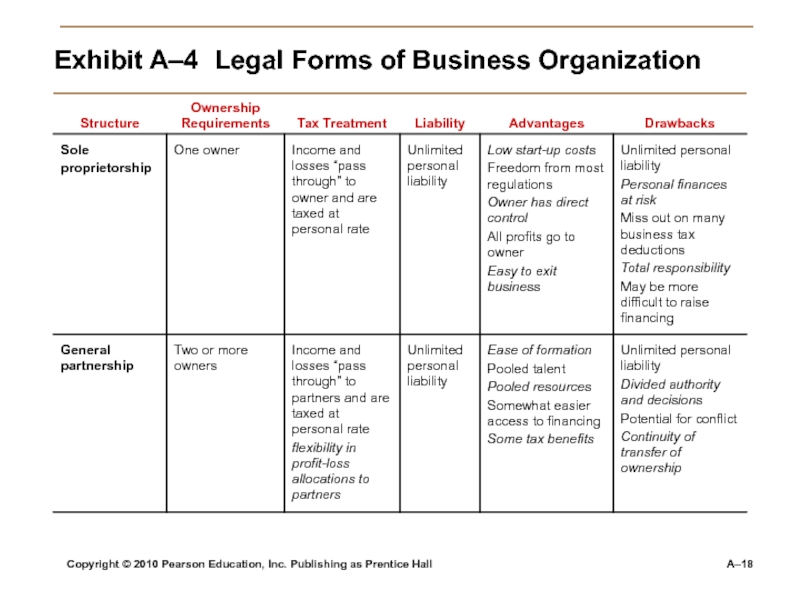
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–4 Legal Forms of Business Organization
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–4 Legal Forms of Business Organization
(cont’d)
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–5 Legal Forms of Business Organization
(cont’d)
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Human
Resource Management Issues In Entrepreneurial Ventures
Employee Recruitment Concerns
Locating high potential
employees who:can perform multiple roles
are willing to “buy-in” (commitment)
Filling critical skill gaps
Employee Retention Issues
Potential for damage to client/customer relationships due to loss of employees
Need to offer desirable benefits
Compensation: base pay and incentives
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exhibit
A–5 Suggestions for Achieving a Supportive
Growth-Oriented Culture
Keep
the lines of communication open—inform employees about major issues.Establish trust by being honest, open, and forthright about the challenges and rewards of being a growing organization.
Be a good listener—find out what employees are thinking and facing.
Be willing to delegate duties.
Be flexible—be willing to change your plans if necessary.
Provide consistent and regular feedback by letting employees know the outcomes—good and bad.
Reinforce the contributions of each person by recognizing employees’ efforts.
Continually train employees to enhance their capabilities and skills.
Maintain the focus on the venture’s mission even as it grows.
Establish and reinforce a “we” spirit since a successful growing venture takes the coordinated efforts of all the employees.
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Leading
Issues
Personality Characteristics of Entrepreneurs
High level of motivation, abundance of self-confidence,
ability to be involved for the long term, high energy level, persistent problem solver, high degree of initiative, ability to set goals, and moderate risk-taker.Proactive personality
Individuals who are more prone to take actions to influence their environment—that is, they’re more proactive.
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Leading
Issues (cont’d)
Motivating Employees Through Empowerment
Empowerment
Giving employees the power to make
decisions and take actions on their own to solve problemsBenefits of Empowerment
Improved flexibility and speed
Stronger work motivation
Higher morale
Better work quality
Higher job satisfaction
Lower turnover
Higher productivity
Improved quality
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Leading
Issues (cont’d)
Empowering Employees
Participative decision making
Delegation
Redesigning jobs
Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
The
Entrepreneur as Leader
Leading Employee Work Teams
Empowered teams
Have the authority to
plan and implement process improvementsSelf-directed teams
Are nearly autonomous and responsible for many managerial activities
Cross-functional teams
Are composed of individuals from various specialties who work together on various tasks
Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Controlling
Issues
Managing Growth
Managing Downturns
Exiting the Venture
Managing personal life
choices and challenges
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Controlling
Issues (cont’d)
Managing Growth
Planning for growth
Organizing for growth
Financing growth
Finding people
Creating a
growth-oriented cultureControlling for growth
Managing Downturns
Recognizing crisis situations—avoiding the boiled frog phenomenon
Dealing with downturns, declines, and crises
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Exiting
the Venture
Why Leave?
Desiring to harvest the value of the venture
Facing
serious organizational performance problemsDesiring to pursue other interests/opportunities
Business Valuation Methods
Asset valuations
Earnings valuations
Cash flow valuations
Слайд 30Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Managing
Personal Life Choices and Challenges
Balancing Work and Personal Life
Become a
good time managerSeek professional business advice when needed
Deal with conflicts as they arise
Developing a network of trusted friends and peers
Recognize when personal stress levels are too high
Слайд 31Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Terms
to Know
entrepreneurship
entrepreneurial ventures
small business
feasibility study
venture capitalists
angel investors
initial public offering (IPO)
business plan
sole proprietorship
general partnership
Слайд 32Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
A–
Terms
to Know, cont.
limited liability partnership (LLP)
corporation
closely held corporation
S corporation
limited liability company (LLC)
operating agreement
proactive personality
“boiled frog” phenomenon
harvesting