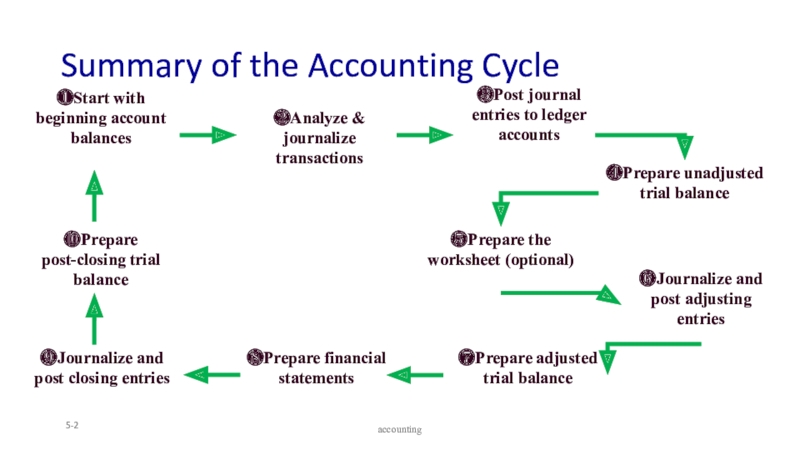
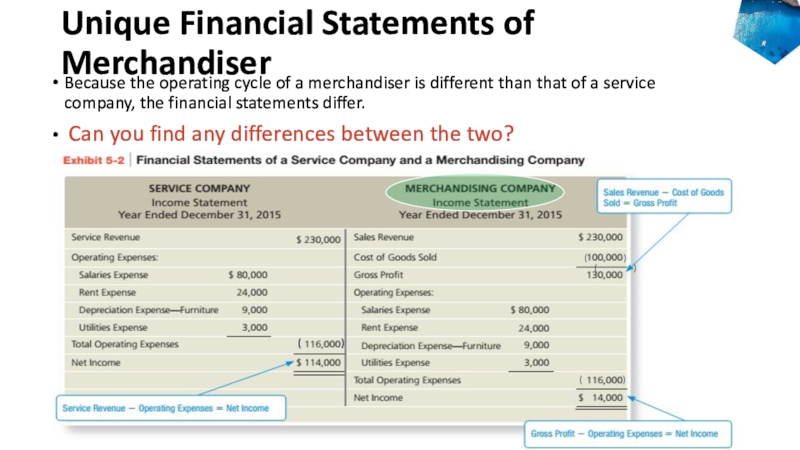
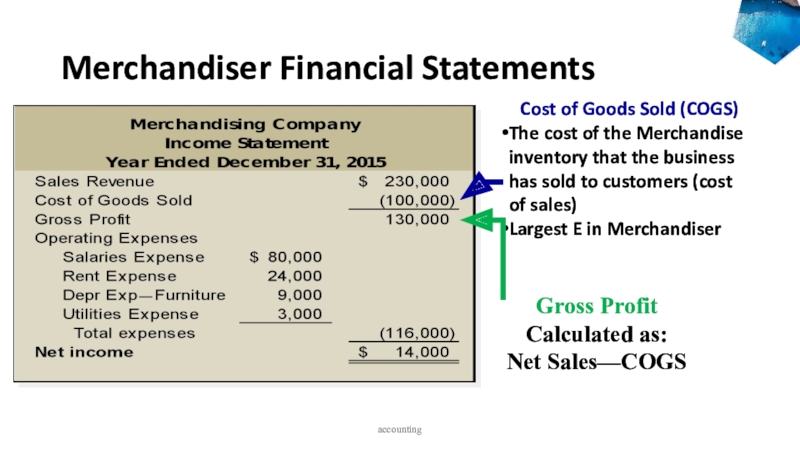
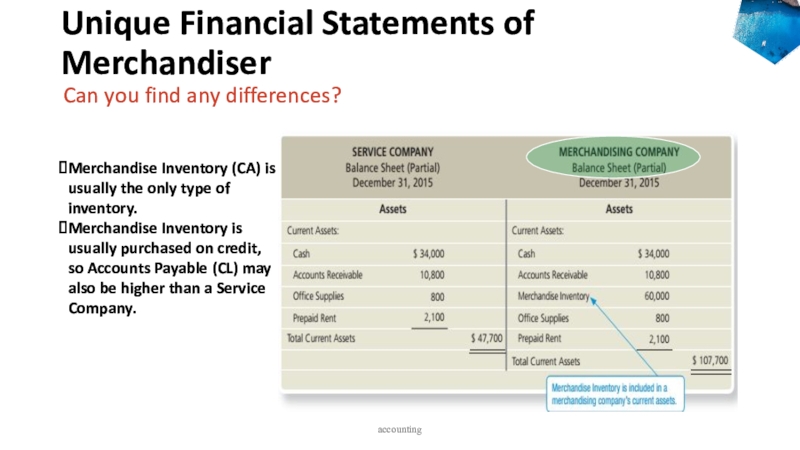
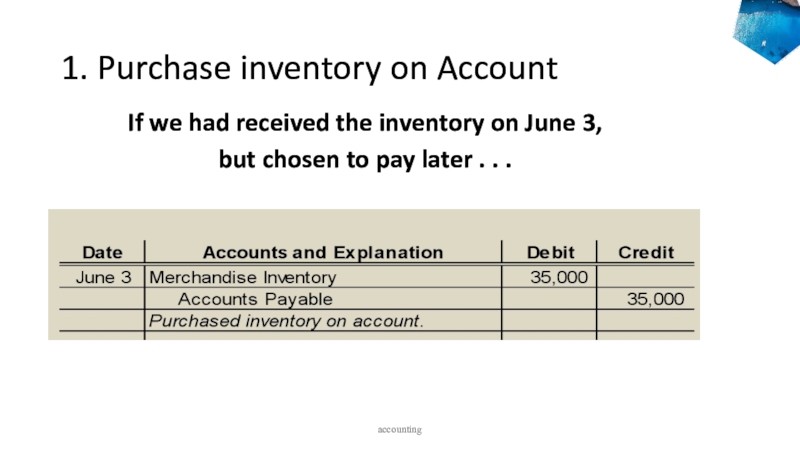
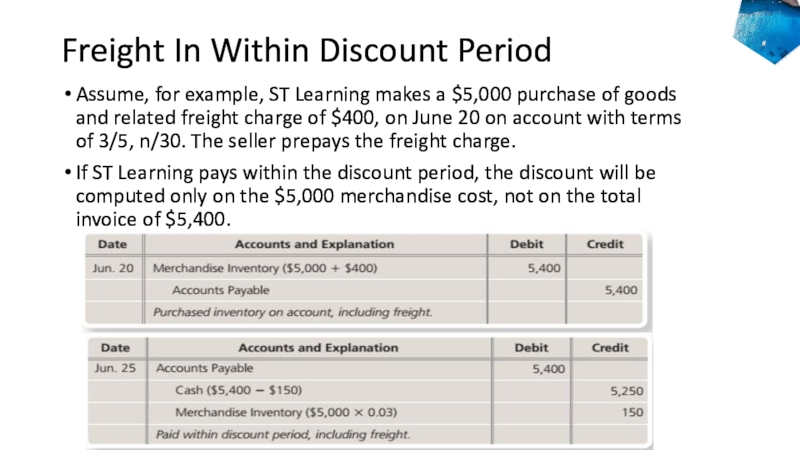
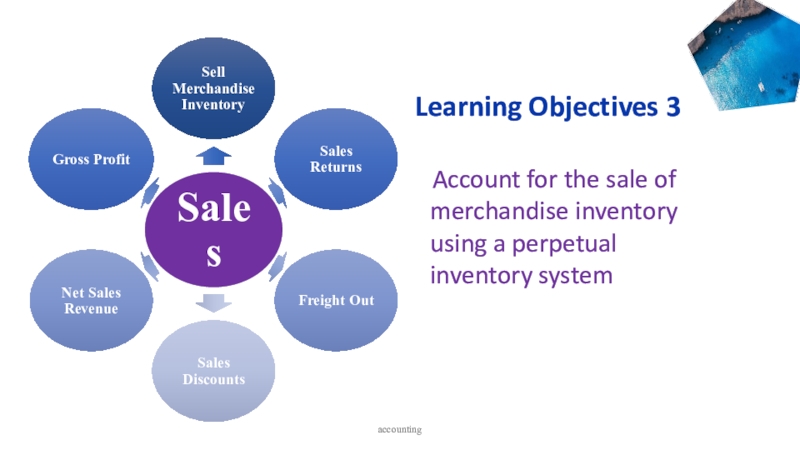
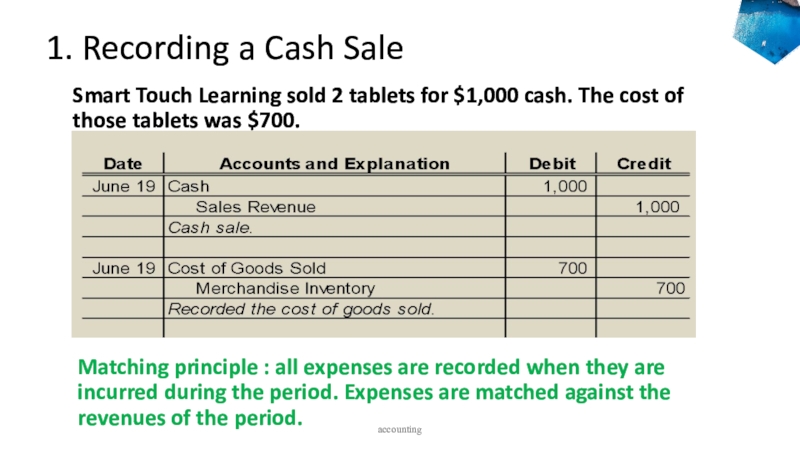
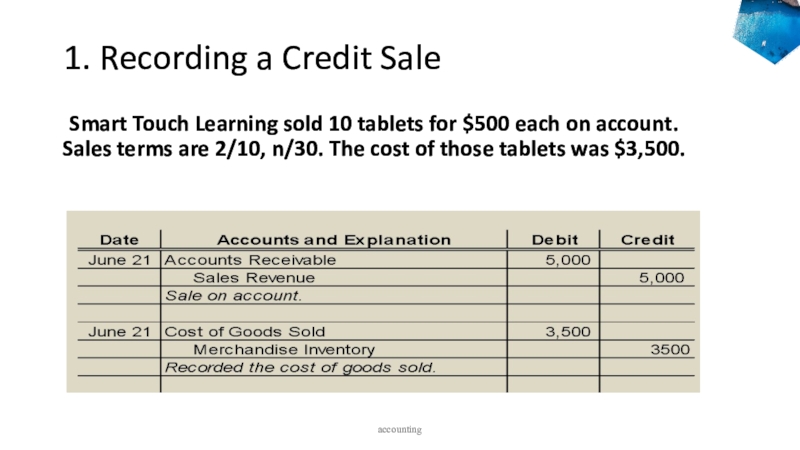
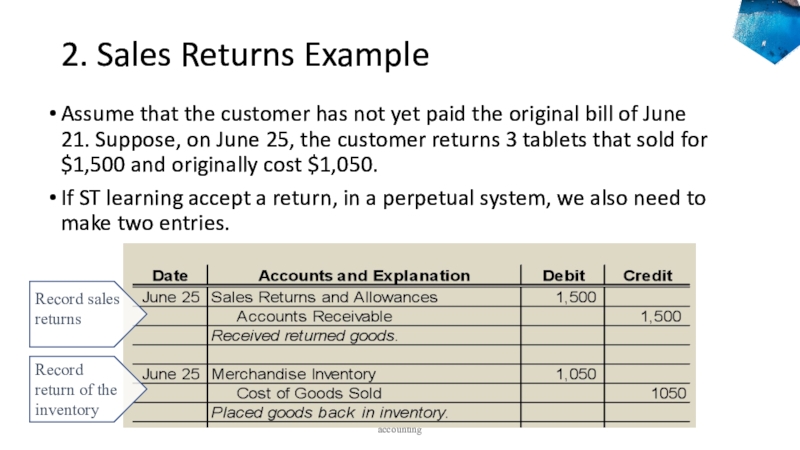
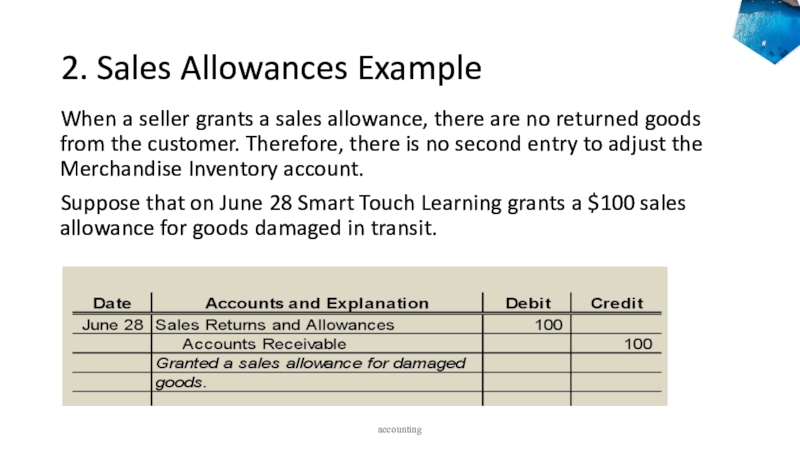
to ledger accounts
Prepare unadjusted trial balance
Journalize and post adjusting entries
Prepare
adjusted trial balancePrepare financial statements
Prepare post-closing trial balance
Journalize and post closing entries
Start with beginning account balances
Prepare the worksheet (optional)
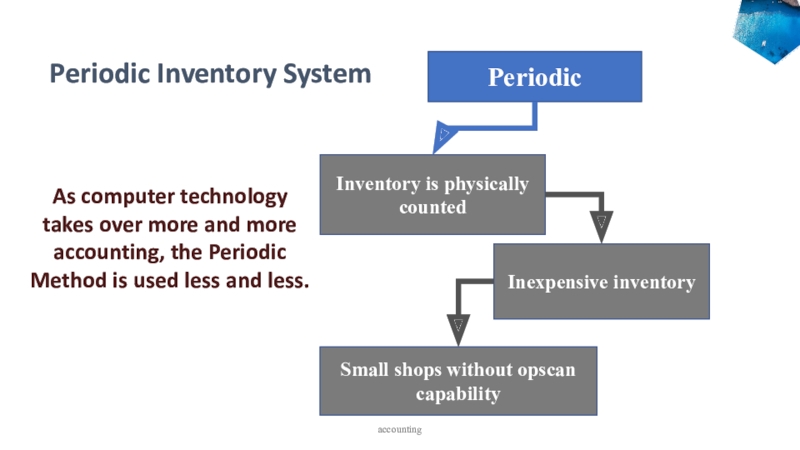
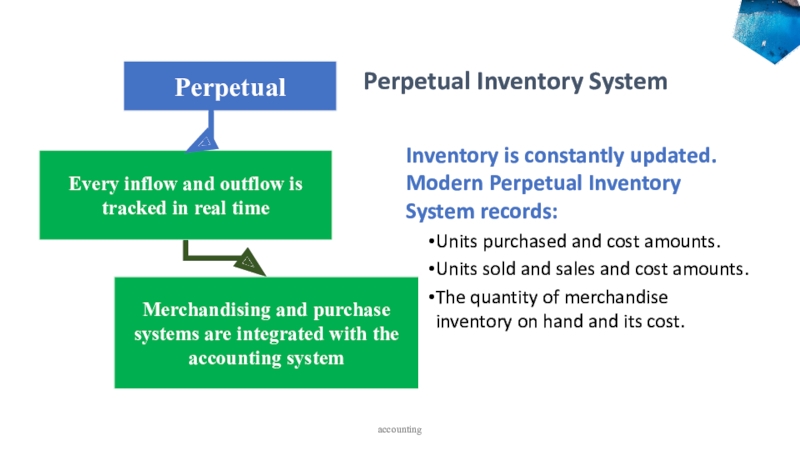
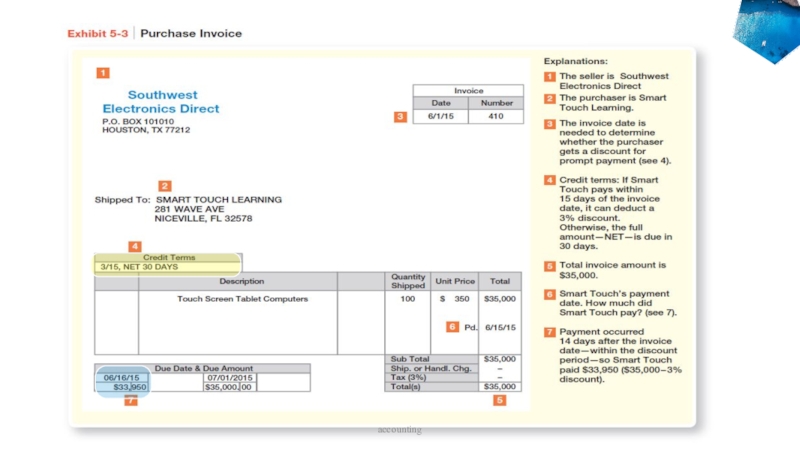
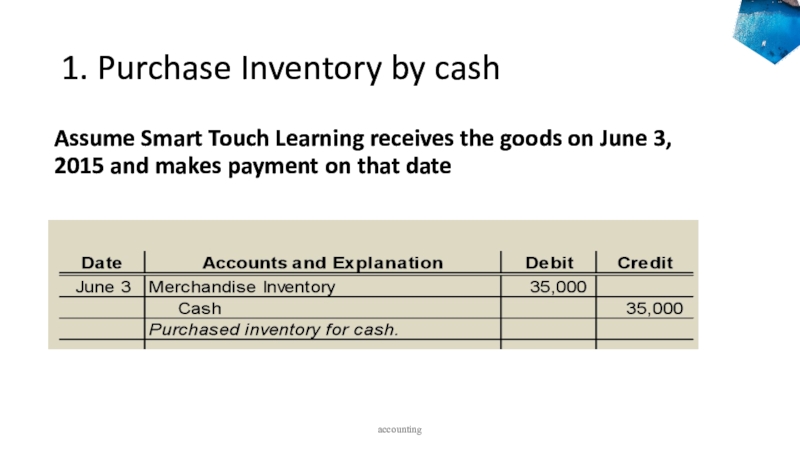
accounting