Слайд 1Ministry education and Science of Republic of Kazakhstan
Karaganda State University
named after academician Ye.A. Buketov
Biological and geographical faculty
Botany Department
Course – Botany
Specialty - 5В011300 – «Biology»
Lecture № 28
Bases of plants ecology
(2 hours)
Lecturer: candidate of biological science, associated professor
Ishmuratova Margarita Yulaevna
Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 Ecological factors for plants.
2 Ecological groups of
plants.
3 Life forms of plants.
Слайд 3Basic literatures:
1 Еленевский А.Г., Соловьев М.П., Тихомиров В.Н. Ботаника:
систематика высших, или наземных, растений. 2 изд. - М.: Academіa,
2001. - 429 с.
2 Нестерова С.Г. Лабораторный практикум по систематике растений. - Алматы: Қазақ ун-ті, 2011. - 220 с.
3 Родман А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Additional literatures:
1 Билич Г.Л., Крыжановский В.А. Биология. Т. 2: Ботаника. - М.: Оникс 21 век, 2002. - 543 с.
2 Ишмуратова М.Ю. Систематика и интродукция растений (курс лекций). - Караганда: РИО Болашак-Баспа, 2015. - 100 с.
3 Тусупбекова Г.Т. Основы естествознания. Ч. 1. Ботаника. – Астана: Фолиант, 2013. – 321 с.
Слайд 4Plant ecology- is a science about communication between plants and
elements of environment.
All elements of environment are separated into
3 groups:
Need for plants;
dangerous;
Indifferent .
Need and dangerous element in general are called ecological factors.
Слайд 5Classification of ecological factor:
1. Abiotical factors – are factors of
non-living nature:
а) climate - light, worm, humidity, composition and moving
of air;
б) edaphic (soil) – is different chemical and physical peculiarities of soils;
в) topographic – are factor of relief.
2. Biotic factors – are influences of living together organisms to each others.
а) influence one plant into neighbor plants;
б) influence animals into plants;
в) influence micro organisms into plants.
3. Anthropogenic factors – are different influence of human into plants.
Слайд 6Plasticity of plants species is vary in wide conditions. So,
all plants can be ranged into 3 groups:
Stenotope –
with a small ecological diapasons. For example, trees of tropical forest.
2) Everytope – with a wide ecological diapasons. For examples, Pinus sylvestris.
3) Average plasticity – are the most species. They lie between stenotope and everytope species.
Слайд 7To influence of humidity it is determined the following groups
of plants.
1. Xerophytes – are plants growing in arid conditions
with deficit of water in soil or air.
2. Mesophytes – are plants growing in conditions with enough amount of water.
3. Hygrophytes – are plants growing in the conditions with high level of humidity of soil or air.
4. Hydrophytes – are species growing in water conditions.
Слайд 8By influence to sun light it is usually separated the
following groups:
1) Heliophytes;
2) Scioheliophytes;
3) Sciophytes.
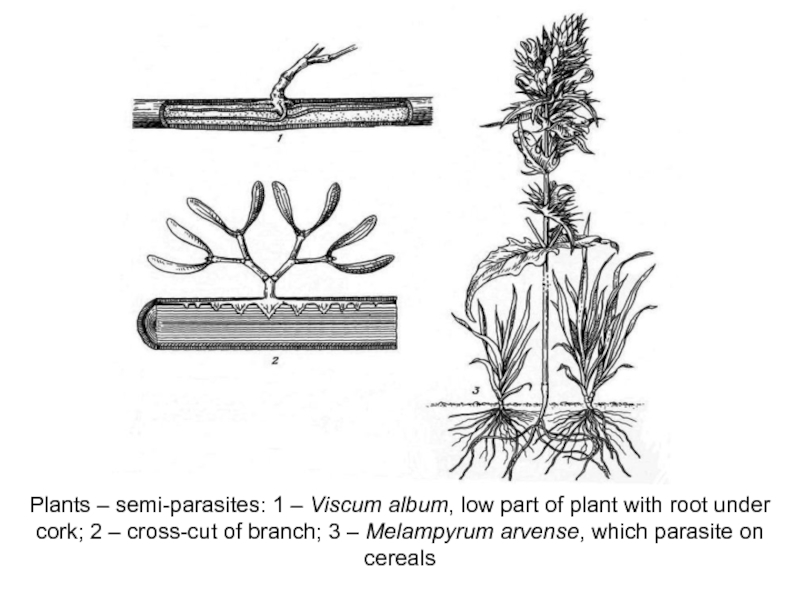
Слайд 10Plants – semi-parasites: 1 – Viscum album, low part of
plant with root under cork; 2 – cross-cut of branch;
3 – Melampyrum arvense, which parasite on cereals
Слайд 11To depending from temperature it is separated 4 ecological groups:
Megaterm
– hot-resistant plants;
Mesoterm – lnot hot resistant;
Microterm – growing
in cold climate;
Gecistoterm – cold resistant plants.
Слайд 12Depending of soil chemical conditions are separated the following ecological
groups of plants:
Acidophytes;
Basiophytes;
Neutrophytes.
Слайд 13Types of communication between plants:
1. Mutualism.
2. Commensalism.
3. Parasitism.
4. Concurention.
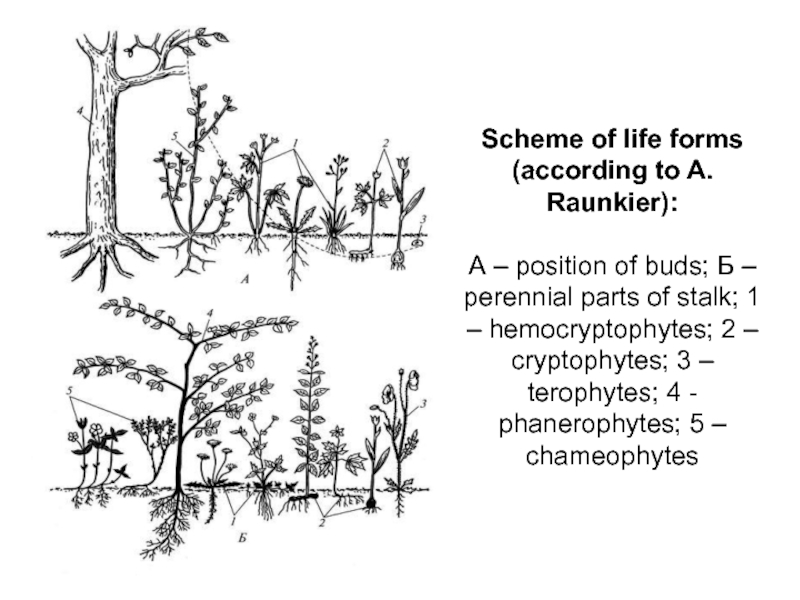
Слайд 14Scheme of life forms (according to A. Raunkier):
А –
position of buds; Б – perennial parts of stalk; 1
– hemocryptophytes; 2 – cryptophytes; 3 – terophytes; 4 - phanerophytes; 5 – chameophytes
Слайд 16Test question:
Groups of plants to soil conditions:
A) mesophytes
B) heliophytes
C) xerophytes
D)
acidophytes
E) galophytes
F) Succulent
G) petrophytes