Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
N a m e : A v a n i Rathod G r p. N o. : 1 9 5 - B T o p i c : G e n e t i c L
Содержание
- 1. N a m e : A v a n i Rathod G r p. N o. : 1 9 5 - B T o p i c : G e n e t i c L
- 2. Genetic load Genetic load: the extent to
- 3. Genetic load: the difference between the average
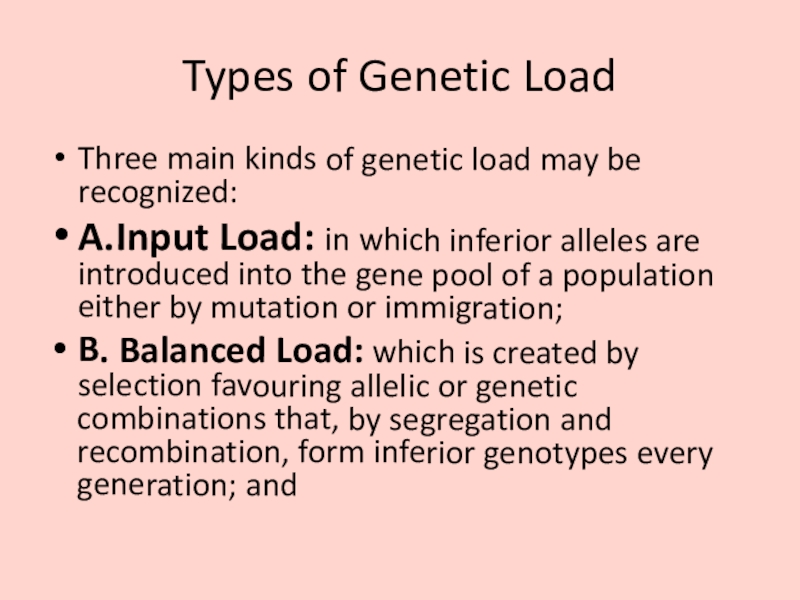
- 4. Types of Genetic LoadThree main kinds of
- 5. C. Substitutional Load: Which is generated by
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Genetic load an Example… Selective death
- 8. Causes of Genetic Load1.Deleterious mutation2.Beneficial mutation3.Inbreeding4.Recombination/segregation load
- 9. DELETERIOUS MUTATIONSDeleterious mutation load is the main
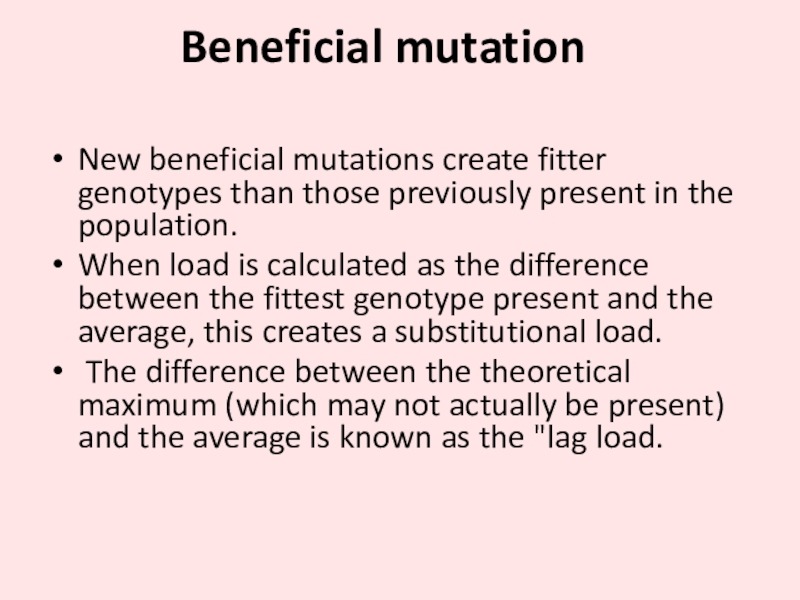
- 10. Beneficial mutation New beneficial mutations create fitter
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. InbreedingInbreeding increases homozygosity. In the short run,
- 13. Recombination/segregation loadCombinations of alleles that have evolved
- 14. Recombination load arises through unfavorable combinations across
- 15. Genetic load : Mutation
- 16. Genetic load: segregational Segregational load is a
- 17. There is a cost to selection, in genetic death, during this time period
- 18. Migration loadMigration load is the result of
- 19. “It is altogether unlikely that two genes
- 20. Defining Directional SectionDirectional selection: selection that favours
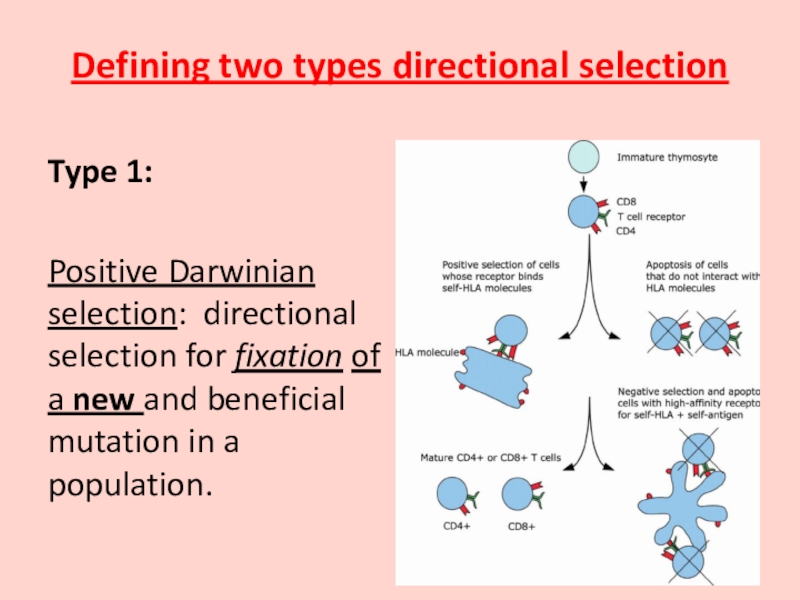
- 21. Defining two types directional selection
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. THANK YOU
- 25. Скачать презентанцию
Genetic load Genetic load: the extent to which the fitness of an individual is below the optimum for the population as a whole due to the deleterious alleles that the individual
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Genetic load
Genetic load: the extent to which the fitness
of an individual is below the optimum for the population
as a whole due to the deleterious alleles that the individual carries in its genome.Genetic load : The average number of lethal mutations per individual in a population. Such mutations result in the premature death of the organisms carrying them.
Слайд 3Genetic load: the difference between the average fitness of the
population and the fitness of the best genotype. It measures
the probability of selective death of an individual in a population.W = average fitness
Genetic load (L) = 1 - W
Слайд 4Types of Genetic Load
Three main kinds of genetic load may
be recognized:
A.Input Load: in which inferior alleles are introduced into
the gene pool of a population either by mutation or immigration;B. Balanced Load: which is created by selection favouring allelic or genetic combinations that, by segregation and recombination, form inferior genotypes every generation; and
Слайд 5C. Substitutional Load: Which is generated by selection favouring the
replacement of an existing allele by a new allele.
Originally called
the ‘cost of natural selection’ by the geneticist J. B. S. Haldane, substitutional load is the genetic load associated with transient polymorphism. The term ‘genetic load’ was originally coined by H. J. Muller in 1950
Слайд 7Genetic load an Example… Selective death (or genetic death): the chance
that an individual will die without reproducing as a consequence
of natural selection. [e.g.,15% of offspring in above]Слайд 8Causes of Genetic Load
1.Deleterious mutation
2.Beneficial mutation
3.Inbreeding
4.Recombination/segregation load
Слайд 9DELETERIOUS MUTATIONS
Deleterious mutation load is the main contributing factor to
genetic load overall.
Most mutations are neutral or slightly deleterious,
and occur at a constant rate. The Haldane-Muller theorem of mutation–selection balance says that the load depends only on the deleterious mutation rate and not on the selection coefficient.
High load can lead to a small population size, which in turn increases the accumulation of mutation load, culminating in extinction via mutational meltdown.
Слайд 10Beneficial mutation
New beneficial mutations create fitter genotypes than those previously
present in the population.
When load is calculated as the difference
between the fittest genotype present and the average, this creates a substitutional load.The difference between the theoretical maximum (which may not actually be present) and the average is known as the "lag load.
Слайд 12Inbreeding
Inbreeding increases homozygosity.
In the short run, an increase in
inbreeding increases the probability with which offspring get two copies
of a recessive deleterious alleles, lowering fitnesses via inbreeding depression.In a species that habitually inbreeds, e.g. through self-fertilization, recessive deleterious alleles are purged.
Слайд 13Recombination/segregation load
Combinations of alleles that have evolved to work well
together may not work when recombined with a different suite
of coevolved alleles, leading to outbreeding depression.Segregation load is the presence of underdominant heterozygotes (i.e. heterozygotes that are less fit than either homozygote).
Слайд 14Recombination load arises through unfavorable combinations across multiple loci that
appear when favorable linkage disequilibria are broken down.
Recombination load can
also arise by combining deleterious alleles subject to synergistic epistasis, i.e. whose damage in combination is greater than that predicted from considering them in isolation.Слайд 16Genetic load: segregational
Segregational load is a big problem for the
balance school:
Well known examples exist; Haemoglobin, MHC locus, etc.
Слайд 18 Migration load
Migration load is the result of nonnative organisms that
aren’t adapted to a particular environment coming into that environment.
If they breed with individuals who are adapted to that environment, their offspring will not be as fit as they would have been if both of their parents had been adapted to that particular environment.
Слайд 19“It is altogether unlikely that two genes would have identical
selective values under all the conditions under which they may
coexist in a population. … cases of neutral polymorphism do not exist … it appears probable that random fixation is of negligible evolutionary importance”-------Ernst Mayr
Слайд 20Defining Directional Section
Directional selection: selection that favours the phenotype at
an extreme of the range of phenotypes
Directional selection: can be
subdivided into two broad categories.1.Positive Darwinian selection
2.Negative Darwinian selection
Слайд 21Defining two types directional selection
Type 1:
Positive Darwinian selection: directional selection for fixation of a new and beneficial mutation in a population.
Слайд 22
Type 2:
Negative Darwinian selection: directional selection for removal of a new and deleterious mutation from a population.
Negative selection: same as “negative Darwinian selection”.
Purifying election: same as negative selection.